What to do and how to treat an abscess on the lip inside and outside?
First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the sore on the lip.
Based on the primary source, etiotropic treatment is prescribed. Symptomatic remedies that accelerate the maturation of the tumor and help remove pus without spreading the infection will help eliminate external manifestations. Local therapy involves the use of gels, solutions and ointments:
Why do sores form?
An ugly and painful abscess that appears suddenly and seemingly out of nowhere is a fairly common occurrence. Any neoplasm on the body, mucous membranes or inside the body requires a medical examination so as not to aggravate the malaise with further complications.
Only a doctor can reliably determine the reason for the ulcers. They can be located in any part of the oral cavity; white, bloody bumps in the lip area are often observed.
Research has shown the following reasons for their occurrence:
- the mucous membrane is damaged with the formation of microcracks, a favorable place for the development of microbes that cause inflammatory processes
- a consequence of colds, weakening of the immune system, leaving viruses in the form of herpes
- trauma to the mouth from thermal and chemical substances
- from being in the wind, drafts
- allergy or trigger of another disease
- insufficient hygiene care
Each unfavorable manifestation is different in its appearance, has a certain classification of infectious origin, but these inflamed skin, abscessing mucous membranes are united - treatment by its identity. The effectiveness of the procedures performed depends on the severity of the infection.
- if an ulcer has just begun to form, it cannot be stopped, you need to wait until the root of the formation appears
- Special ointments in the form of ichthyol will help as a good pathogen to help in the maturation of the sore, but you should wait for a doctor’s prescription so that he can determine the clinical picture. With the help of medications, pus randomly comes out; they need to be applied carefully, only if the wound is on top, they need to be lubricated around the formation
- An effective remedy is the medicinal plant aloe; ordinary, peeled potatoes will help against purulent inflammations
- antiviral oxolinic ointments are used for cold ulcers; there is no need to be alarmed when such a substance changes color in the air
What is stomatitis?
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa. According to statistics, about 20% of the population of our planet faces it. In adults and children, it can take the form of an independent disease or act as a symptom indicating pathologies of the body. In both cases, treatment is carried out comprehensively and under the supervision of a doctor.
What does the disease look like?
Stomatitis is not difficult to recognize. The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the appearance of mild swelling of the oral mucosa. It becomes redder, drier and shiny. A plaque may appear on its surface, and at the site of future lesions the patient feels an unpleasant itching or burning sensation.
As the disease develops, small ulcers and wounds appear on the mucous membrane - painful oval or round lesions. Their location may be the inside of the lips, cheeks, palate, tonsils, or mucous membrane under the tongue. Their appearance can be seen in the photo at the end of our article.
Types of ulcers that may appear on the lip
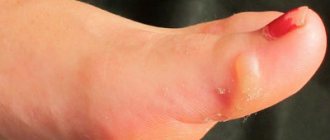
The formation of a boil on the upper or lower lip is usually preceded by swelling and moderate pain. In the first couple of days, swelling and redness occur. Following them, a bubble with an abscess appears. Typically, patients complain of pain when trying to touch the tumor. If you do not respond to the symptom in time and do not start treatment, the boil will begin to fester. Sometimes, along with other symptoms, the patient’s health noticeably worsens and the temperature rises.
When herpes occurs, swelling appears
If this is a manifestation of herpes, then a blister with a clear liquid usually appears on the lip, which becomes covered with a crust after 3-4 days. This also causes itching, a feeling of tightness and pain. It is easier to stop an exacerbation of a viral infection if you start treatment at the reddening stage.
“Oh, I’m already tormented with this herpes. As soon as you get into a draft, it immediately pops up on your lip. All my life I have been saving myself with Acyclovir, as for me, they haven’t come up with anything better. By the way, regular toothpaste dries well, a proven old-fashioned method.”
Lenka1989, from correspondence on the woman.ru forum
Aphtha is an abscess inside the lip. Such rashes usually appear on the mucous membrane, and can be recognized by their white heads. As a rule, this is a sign of aphthous stomatitis, which can develop in both adults and children. In this case, neoplasms can be localized not only on the lips, but also on the inside of the cheeks and even on the tongue.
This is what aftas look like
Sometimes a lipoma is mistaken for a boil, but this is a pathological phenomenon of a completely different nature. This is a benign neoplasm, which is a dense node that forms inside the soft tissue. Essentially, this is a cavity filled with dead epithelial cells and fatty contents. Its removal is carried out surgically.
Causes of stomatitis
The mechanism of stomatitis is not yet fully understood. But scientists are inclined to believe that the root cause of its development is the reaction of the human immune system to various irritants. At some point, the immune system ceases to recognize the potential threat of internal and external factors, which causes its atypical reaction, as a result of which “aggressive behavior” of lymphocytes is observed. The attack of lymphocytes against irritant molecules leads to lesions of the oral mucosa.
A variety of factors can provoke an atypical reaction of the immune system. The most likely of them are the following irritants:
- Pathogenic microorganisms that live in the mouth.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Various damage to the mucous membrane, for example, burns from eating too hot food or mechanical injuries from seeds, nuts, crackers and other hard foods.
- General dehydration due to high fever, blood loss, vomiting, diarrhea, or thirst.
- Poor quality treatment of teeth and gums.
- An allergic reaction to dental structures in the mouth - braces, implants, crowns, bridges, etc.
- Long-term use of medications.
- A diet depleted of beneficial vitamins and elements.
- Smoking.
- Malignant formations of the oral cavity, respiratory organs or undergoing a course of chemotherapy.
- Hormonal imbalances in the body, for example in pregnant women or children during puberty.
- The presence of chronic diseases or allergies.
- Severe stress.
Interesting to know! Frequent stomatitis in adults can be caused by the use of toothpaste containing sodium lauryl sulfate, a substance added to oral care products to form a thick foam. According to recent studies, it dehydrates the oral mucosa and makes it vulnerable to various types of irritants. Patient observation data confirms the fact that avoiding the use of sodium lauryl sulfate paste can reduce the risk of developing stomatitis in adults by 81%.
What to do if pimples appear on your lips?
If you have pimples on your lips, you shouldn’t immediately run to the pharmacy for saving ointment. Despite popular misconception, the term “acne” does not refer to any specific disease. The rash can be a manifestation of many dermatoses. Only a specialist, having studied her character and collected anamnesis, will be able to prescribe adequate treatment.
With acne, inflammation around the lips is usually rare, but if the rash around the lips turns out to be acne, the doctor may prescribe topical antibiotics18. These include Clindovit® gel. Its main active ingredient is clindamycin phosphate, which upon contact with the skin is hydrolyzed to form clindamycin6. The drug is active against propionibacteria and helps reduce the level of free fatty acids6. To reduce the risk of developing antibiotic resistance, it is recommended to combine the use of Clindovit® with azelaic acid preparations (Azelik® gel) or benzoyl peroxide28.
Symptoms of the disease
Stomatitis can occur at any age. In the early stages, its course is accompanied by swelling, redness and dryness of the oral mucosa. The main sign of the disease is the presence of one or multiple ulcers and their appearance.
- Oval or round ulcer shape.
- Small sizes.
- Smooth edges.
- The presence of a thin grayish or white film in the central part of the ulcer.
- The ulcer is surrounded by a slightly reddish halo.
- The mucosal tissue around the lesion has a normal, healthy appearance.
The slight itching or burning sensation that the patient experienced at the beginning of the disease is replaced by pain. The ulcers hurt when eating, talking and smiling broadly. Any touch to them causes pain, which complicates hygiene measures and leads to bad breath.
On average, the disease lasts from 4 to 14 days. Its clinical picture depends on the individual characteristics of the organism, the form and type of the disease. During this period, in addition to the main signs of pathology, other symptoms of the disease may be observed.
- Increase in temperature - during the first days, until characteristic ulcers appear (in severe forms of stomatitis, the elevated temperature persists throughout the entire illness).
- General malaise and fatigue.
- Chills.
- Headache.
- Lack of appetite (especially in children).
- Enlarged lymph nodes (in rare cases).
Important to remember! Severe inflammation, toothache or high temperature for a long time indicate a severe form of stomatitis or the development of its complications. In this case, immediate medical attention is required, and if necessary, hospitalization of the patient is possible.
Treatment options
The appearance of a boil on the lip usually requires complex treatment, but the cause of its occurrence must first be determined. As part of maintenance therapy, vitamin therapy is recommended to improve immunity. The doctor chooses a specific treatment vector based on the prerequisites for the appearance of the tumor:
- herpes - Acyclovir, Penciclovir or Docosanol ointments are prescribed. All of these drugs are most effective if therapy is started at the redness stage,
- aphthae - first you need to determine the type of stomatitis, and then, based on an accurate diagnosis, you can begin adequate treatment. Antiseptics Inhalipt, Actovegin or Stomatidin are usually prescribed. If it is a fungal form of the pathology, “Mikozon” or “Levorin” is prescribed; if it is an allergic form, “Suprastin” is prescribed.
- boils - local therapy is carried out using antiseptic solutions twice a day until the abscess ruptures. Compresses with Ichthyol ointment are also recommended. In some cases, the formation has to be opened in a hospital setting. Next, the wound is treated with antiseptics and ointment, for example, “Vishnevsky” is applied. Be sure to prescribe multivitamin complexes to strengthen the immune system.
For each specific case, you need to select the appropriate treatment. You
should consult a doctor if the boil has become of an impressive size, if there is a sharp deterioration in the condition, or an increase in temperature. The most important thing is not to try to open it yourself. Only a specialist can do this correctly and without the risk of undesirable consequences.
Can stomatitis go away on its own?
As a rule, mild forms of the disease caused by trauma to the mucous membrane, poor oral hygiene or an allergic reaction of the body can go away on their own. Severe stomatitis caused by infection requires qualified treatment. In both cases, it is better not to wait and not to self-medicate. Because the disease not only causes pain and discomfort, but can also lead to generalization of infection and serious complications.
Consequences and complications of the disease
Possible complications arise when the patient ignores treatment for stomatitis. As a result, mild and severe forms of the disease become chronic. The neglected process turns into an ulcerative-necrotic and then gangrenous form of the disease, as a result of which not only the mucous membrane is damaged, but also the soft tissues of the mouth and jaw bones.
Other serious consequences of untreated stomatitis include the following complications.
- Bleeding gums.
- Scarring of the oral mucosa, disruption of its elasticity and mobility.
- Attachment of a secondary infection.
- Tooth loss.
- Voice changes – hoarseness, hoarseness.
Important to remember! A small ulcer on the oral mucosa is a potential threat to the entire body. Infection from it can spread to other organs and systems, which will disrupt the functions of the heart, liver, kidneys, gastrointestinal tract and respiratory organs.
Folk remedies
For treatment, you can use traditional medicine. The following juices, decoctions, oils and infusions have proven themselves well.
You can gently lubricate the affected areas of the mucous membrane with juices and oils. Solutions and decoctions of herbs are used for regular rinsing of the mouth.
Important! Before using traditional medicine, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist can determine the advisability of their use without harm to health. The use of folk remedies does not cancel the main therapy, but only complements its effect.
How many days does treatment last?
Correct, competent treatment of stomatitis significantly speeds up the healing process. Depending on the type of disease, it lasts for 3 to 7 days. If after 1 week of treatment the signs of the disease have not disappeared or worsening is observed, then the patient most likely has complications. The following factors may be the probable reasons for its development.
- The patient self-medicated or did not follow the doctor's instructions.
- Decreased immunity.
- The presence of chronic diseases of the body.
- Regular injury or infection of the oral mucosa.
- Undiagnosed allergy.
- Having bad habits - smoking, chewing, etc.
- Depression or frequent stress.
- Improper oral hygiene.
- Uncontrolled use of medications.
- The use of oral hygiene products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
Returning to the question - can stomatitis go away on its own - it should be noted that a seemingly harmless disease can turn into serious problems for the patient. Therefore, you should remember three “don’ts” - don’t
engage in self-medication,
do not
put off visiting a specialist and
do not
ignore the recommendations of your doctor.
How to understand that stomatitis has passed?
Very simple! A complete cure is indicated by the absence of lesions in the oral mucosa. There are no small ulcers, wounds or plaque on the cheek, palate, lip, tongue or tonsil area. The mucous membrane looks healthy, is well moisturized, does not cause pain and does not create discomfort during eating, talking, smiling and performing hygiene procedures.
What can cause an abscess on the lip? Possible causes and treatments
The appearance of a neoplasm in the form of a boil on the lip should at least alert you. Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out such pustules yourself or pierce them. Otherwise, this may lead to the spread of purulent exudate throughout the adjacent soft tissues and, accordingly, to the development of complications. To understand how to get rid of such an unpleasant phenomenon, you first need to establish the cause of its occurrence. And for this it is better to contact a specialist. Read further in this article about why an abscess may appear on the inside or outside of the lip and what to do about it.
Types of stomatitis in adults
The clinical picture of the disease indicates that stomatitis can be mild or severe, have an acute or chronic course. To facilitate the diagnosis and treatment process, experts have developed the following classification of the disease.
- Allergy is usually a chronic disease that occurs as a result of an allergic reaction of the body to an irritant. In addition to the characteristic ulcers, it may be accompanied by the appearance of white spots, blisters and small hemorrhages on the mucous membrane.
- Herpetic or herpes - the disease occurs due to the entry of the causative agent of the herpes virus into the human body. Stomatitis of this type is characterized by an acute course. Bubbles appear on the surface of the mucous membrane, which open to form erosions and crusts.
- Traumatic (bacterial) – a consequence of mechanical trauma to the oral mucosa and infection entering the wound. As a rule, the disease is mild, with symptoms characteristic of stomatitis.
- Catarrhal and catarrhal-hemorrhagic stomatitis is a mild form of stomatitis, the causes of which are poor oral hygiene, the development of candidiasis, decreased immunity or gastrointestinal pathologies. The disease is accompanied by a typical clinical picture for the disease.
- Candidal (fungal) stomatitis is an acute form of the disease, the so-called thrush, caused by the activity of bacteria of the genus Candida. It is most common in young children, the elderly, and patients who overuse antibiotics. Accompanied by the appearance of a white coating on the mucous membrane, a burning sensation and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
- Ulcerative is a severe form of the disease that occurs independently or as a result of a complication of the catarrhal course of stomatitis. It occurs acutely, with increased body temperature and enlarged lymph nodes. The resulting ulcers are very painful and can unite and form extensive lesions of the mucous membrane.
- Aphthous stomatitis is a severe form of the disease, occurring acutely or chronically. Accompanied by the appearance of single or multiple gray-white ulcers. The ulcers are surrounded by a red halo and are very painful.
It is important to know! By analyzing the condition of the oral mucosa, the nature of the ulcers and the patient’s complaints, specialists accurately determine the type of stomatitis and make an accurate diagnosis. Thanks to this, treatment of the disease occurs quickly and without complications.
Why do sores form?
An ugly and painful abscess that appears suddenly and seemingly out of nowhere is a fairly common occurrence. Any neoplasm on the body, mucous membranes or inside the body requires a medical examination so as not to aggravate the malaise with further complications.
Only a doctor can reliably determine the reason for the ulcers. They can be located in any part of the oral cavity; white, bloody bumps in the lip area are often observed.
Research has shown the following reasons for their occurrence:
- the mucous membrane is damaged with the formation of microcracks, a favorable place for the development of microbes that cause inflammatory processes
- a consequence of colds, weakening of the immune system, leaving viruses in the form of herpes
- trauma to the mouth from thermal and chemical substances
- from being in the wind, drafts
- allergy or trigger of another disease
- insufficient hygiene care
Each unfavorable manifestation is different in its appearance, has a certain classification of infectious origin, but these inflamed skin, abscessing mucous membranes are united - the treatment has its own identity. The effectiveness of the procedures performed depends on the severity of the infection.
Which doctor should I contact for stomatitis?
If you notice the first signs of damage to the oral mucosa, you should immediately consult a dentist. After differential diagnosis of the disease and an accurate diagnosis, it is possible to observe it with a general practitioner or other specialized specialist, for example, an allergist.
Do not ignore preventive visits to the dentist.
It is enough to visit a specialist 1 – 2 times a year, which will allow you to promptly identify any dental problem at an early stage of development. This means that its elimination will be quick, easy and without complications.
By clicking the “request a call” button you agree to the personal data processing policy.
What to do and how to treat an abscess on the lip inside and outside?
First of all, it is necessary to determine the cause of the sore on the lip. Based on the primary source, etiotropic treatment is prescribed. Symptomatic remedies that accelerate the maturation of the tumor and help remove pus without spreading the infection will help eliminate external manifestations.
Medicines
If signs of an inflammatory process occur, the use of antiviral and anti-inflammatory drugs is prescribed. To improve the immune system, immunostimulants are taken, especially if pustules have formed on the child’s lips. If you have pain symptoms, you are allowed to take a painkiller.
Local therapy involves the use of gels, solutions and ointments:
- antiseptics for rinsing the mouth (if the abscess occurs not only on the lip, but also in the mouth);
- enzymatic local wound treatment products;
- vitamin preparations for applying compresses to the affected area (for example, B12);
- antiseptics for applying compresses to the abscess (Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, hydrogen peroxide).
To accelerate the maturation of the abscess, Salicylic ointment or Baziron ointment is prescribed. When a viral infection activates in the body, Zovirax or Acyclovir ointment will be effective. Antibiotics are prescribed Cefixime and Amoxiclav.
READ ALSO: Forms of ear eczema. Diagnosis of ear eczema
If the lip inside is festering from a blow, in combination with drug treatment, the doctor may prescribe physiotherapeutic procedures, for example, UHF and electrophoresis.
After the abscess breaks through, novocaine and an antibiotic are applied to the affected area. Such remedies help eliminate pain and prevent the generalization of infection.
Traditional methods
Many folk remedies are no less effective than ready-made medications, for example, antibacterial ones. Brewer's yeast, onions, and honey help speed up the ripening of the abscess and draw out the purulent exudate. However, their use in the treatment of skin diseases is prohibited in case of hypersensitivity to the substances included in the composition.
Since abscesses and boils often occur against the background of metabolic disorders in the body and weakening of the protective function, increased immunity is required. Brewer's yeast contains useful components (zinc, magnesium, calcium, iron, etc.) that help quickly cure an abscess and prevent its recurrence.
Take yeast 2 times a day before meals, about an hour before, 1 tbsp. l. Contraindications include hypersensitivity to components and the development of kidney disease.
No less effective is honey, from which a medicinal cake is prepared: the beekeeping product is mixed with flour and grated laundry soap in equal proportions. The result should be a product that resembles plasticine in consistency. The cake is applied as a compress to the boil, fixed with a band-aid and left in place for 3 hours.
You can speed up the opening of an abscess using baked onions. One head is baked, cut into pieces, and after cooling, applied to the affected area, secured on top with a band-aid. Carry out the procedure before bedtime, keeping the compress on until the morning.
How to distinguish stomatitis from other diseases?
The main sign of stomatitis is the presence of characteristic ulcers, the tissue around which looks healthy. The disease is rarely accompanied by systemic symptoms and, as a rule, recurs from time to time. For a competent specialist, it is not difficult to distinguish stomatitis from other ailments.
For a sore throat
When you have a sore throat, your body temperature always rises. In this case, it is not the ulcers themselves that hurt, but the throat area. Upon visual examination, the tonsils appear swollen, inflamed and red.
For herpes
The problem is that herpetic stomatitis is one of the manifestations of herpes. A viral disease is accompanied by the formation of characteristic blisters that burst and dry out. In the presence of other types of stomatitis, the nature of the ulcers is completely different.
For cancer
Ulcers due to cancer of the oral mucosa do not go away on their own even after treatment. Over time, they increase in size and may bleed and become painful.
From thrush
Candidal stomatitis is thrush caused by the activity of bacteria of the genus Candida. In all other cases, the nature of the disease will be different and can be easily distinguished from thrush by the presence of characteristic ulcers.
For syphilis
When infected with syphilis, a red spot appears on the surface of the mucous membrane. Gradually it thickens, takes the form of a dense nodule and ulcerates - a typical hard chancre is formed, which is completely different from ulcers with stomatitis.
Stomatitis varieties
There is probably no person who has not experienced the appearance of disgusting sores, be it an abscess on the lip inside or in another place.
All of them have been studied, and doctors have divided them into the following types:
- Herpes blisters appear inside the mouth filled with a white substance. They bother you with their itching and burning sensation in the lips.
- Candidiasis plaques are formed from a yeast fungus. Usually it is peacefully located in the human microflora. When a favorable provocation is applied, the fungus begins to multiply intensively, covering the mucous membrane inside the mouth and on the lips with a white coating.
- The internal membranes are also captured by the aphthae. These bacteria are more serious, and if at first a small abscess appears in the form of a bubble, then after it deforms, a circle with a white dot in the middle forms, with bloody borders. A person feels weak from elevated temperature, blood is released from the gums, swelling appears with increased sensitivity in the mouth.
- The following sores speak for themselves by their name; these are allergic rashes. They can be caused by any product or medicinal substance that has come into contact with the oral cavity. But the sensations are deplorable from swelling, red mucous membranes, and inflammation. Round formations rupture and erosion appears.
- Traumatic ulcers can be characterized by the following type of abscesses in the mouth from burns, injuries, and poor-quality dentures.
- Bacterial stomatitis affects people from infection with infectious diseases through wounds, cracks, and microorganisms multiply in them.
To avoid infection of the lips and mucous areas, careful hygiene is necessary, it is important to monitor the condition of the teeth and carry out special rinses.
Recommendations during treatment
Treatment of stomatitis should be carried out comprehensively - local therapy, taking medications appropriate to the type of disease, and strengthening the immune system. During the treatment period, you must adhere to the following recommendations.
- Compliance with the diet - you need to exclude from the diet spicy, salty, sour, too sweet, smoked, hot, cold and any dishes that are traumatic to the mucous membranes.
- Maintaining oral hygiene . To maintain it, it is necessary to use antiseptic agents that you regularly rinse your mouth with.
- Taking vitamin-mineral complexes that strengthen the body's protective functions.
If the doctor has diagnosed the presence of candidal stomatitis, then you should not drink milk or consume fermented milk products, which activate the activity of pathogenic fungi.
Any medications should be used only as prescribed by a doctor. Especially antibiotics.
It is important to know! It is not recommended to cauterize emerging ulcers with pure alcohol solutions. The only thing that is allowed is treating the lesions with a weak solution of iodine or potassium permanganate.
Prevention
To avoid the occurrence of stomatitis and its relapses, you should adhere to the following recommendations.
- Maintain oral hygiene.
- Avoid using products containing sodium lauryl sulfate.
- Protect the oral mucosa from injury.
- To treat teeth and gums, contact experienced, qualified specialists.
- Balance your diet with healthy foods.
- Strengthen immunity.
- Be attentive to your physical health and psycho-emotional state - if necessary, seek help from specialized specialists.
And do not forget that herpes stomatitis can be transmitted from person to person - follow the rules of hygiene.
Photo of stomatitis
Author: Elena Grunina Dentist-therapist, endodontist. Work experience more than 9 years. The information is for reference only. Before treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.