Urticaria is an allergic disease. Most often it is diagnosed in children under 3 years of age. There are several forms of the disease. The mildest cases occur without complications and are quickly treatable. But a severe form can lead to dangerous consequences. That is why the diagnosis and treatment of the disease must be taken with full responsibility. Treatment of urticaria in children at home is permissible only in the initial stages of the disease. In other cases, doctors recommend resorting to drug treatment.
Causes
Flowers are one of the possible causes of the disease
Urticaria is a common disease, but in half of the cases it is impossible to determine the exact cause of its occurrence. Once symptoms occur, a laboratory test must be taken to identify the allergen. Not all parents have this opportunity, so it is enough to know the list of foods and things that can contribute to the occurrence of hives:
- fluff, dust, pollen;
- food: brightly colored vegetables, apples, lemons, oranges, tangerines, dairy products, eggs, nuts, smoked meat and fish, seafood, honey, strawberries, chocolate;
- antibiotics and other drugs: non-steroids, analgesics, etc.
- perfumed cosmetics;
- household chemicals;
- insect bites;
- sweating;
- metal;
- Sun;
- frost, low air temperature.
The appearance of urticaria can be caused by a stressful condition, a weakening of the body's protective properties.
Symptoms
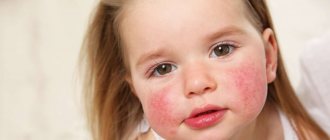
What urticaria looks like in children is of interest to any parent. The main signs will help you quickly recognize the disease and prevent it from developing into a complex or chronic form.
- papules and blisters of various shapes and sizes. They can be located separately or merge with each other;
- the color of the rash ranges from light pink to deep red;
- if you put a little pressure on the rash, a white spot will appear in the center;
- temperature increase. This symptom indicates that an inflammatory process has begun in the body;
- swelling;
- localization of rashes. As a rule, they appear in one place - not the cheeks, arms, legs, stomach, knee bends, etc.
- itching;
- upset stomach, swelling of the face, nausea and vomiting, fever. These are signs of a severe course of the disease.
Photo of hives on a child's legs
The manifestations are similar to other skin rashes - roseola in children, acne, prickly heat, etc. The more detailed you study them, the faster you will decide on the correct diagnosis and further treatment. How quickly does hives go away? In mild cases, within a few hours or days. If there is no treatment, the rash takes longer to resolve. Severe forms of urticaria are more difficult to treat and take longer to treat, since it is necessary to relieve a number of symptoms. Treatment for severe cases may take several weeks.
Hives
The article was checked by physician-therapist L.N. Staurina. , is for general informational purposes only and does not replace specialist advice. For recommendations on diagnosis and treatment, consultation with a doctor is necessary.
The treatment of urticaria is based on an integrated approach, which involves identifying the allergen and correcting the allergic reaction. Doctors at the Yauza Clinical Hospital have accumulated extensive experience in the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria and have all the capabilities to identify the causes of the disease - they conduct allergy tests, extensive laboratory and, if necessary, instrumental examinations to exclude diseases that provoke urticaria, and consultations with any specialists. Along with drug therapy in the case of chronic urticaria, which is difficult to treat, we use extracorporeal hemocorrection methods.
Urticaria (urticaria) is a common allergic disease, which, according to some data, occurs at least once in approximately 30% of the world's population. Despite its widespread prevalence, urticaria is not easy to treat as there are many causes that can cause it. That is why the doctor who is involved in diagnosis and treatment must conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and correctly select therapy.
Symptoms of urticaria
The disease got its name because with hives, red spots appear on the skin, which are similar to those left after a nettle burn. These may be individual small spots, or there may be quite large areas of damage. Hives are accompanied by itching and burning in the area of redness.
There are acute and chronic forms of urticaria:
- acute urticaria usually occurs a short time after contact with the allergen; Blisters and redness appear on the skin. The rashes can be profuse, but after a few days everything goes away. There are no traces left after acute urticaria
- chronic urticaria is a form of the disease that lasts more than 6 weeks. Rashes can appear spontaneously, without any obvious reason. Often the cause of chronic urticaria remains unclear, but it is known that it can be triggered by climate change, various diseases (including acute respiratory infections), menstruation in women, etc.
Urticaria can lead to a dangerous condition - Quincke's edema. In this case, swelling of the face, mucous membranes, and larynx begins, which threatens suffocation. In this condition, the patient must be hospitalized as quickly as possible.
Causes and pathogenesis of urticaria
As with many other allergic diseases, there can be many reasons that cause unpleasant manifestations on the skin. For example, urticaria can be caused by contact with plant pollen, animal fur, food, medication, cold, exposure to the sun, etc.
Urticaria can be associated with various diseases: viral and bacterial infections, parasitic infections, and the presence of chronic inflammation. Chronic urticaria is thought to be autoimmune in nature.
There are a number of diseases that can provoke urticaria (chronic form): diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine (including diabetes), chronic foci of infection, fungal diseases, the presence of parasites and helminths, tumors, systemic connective tissue diseases and others.
Diagnosis and treatment of urticaria at the Yauza Clinical Hospital
As we have already mentioned, the main difficulty that a doctor faces with urticaria is to establish its cause. This is especially difficult to do in the case of a chronic disease. That is why patients with symptoms of urticaria undergo a comprehensive diagnosis, which includes:
- blood, urine, stool tests
- blood test for immunoglobulins
- examination of the immune system
- endocrine system examination
- gastrointestinal examination
Treatment consists mainly of avoiding contact with allergens and relieving the unpleasant symptoms of hives on the skin. The doctor develops individual recommendations that help avoid relapses of the disease. We prescribe drug therapy using hyposensitizing, antihistamine, hormonal and other drugs. In difficult cases, we use hemocorrection methods.
Treatment of urticaria using hemocorrection methods
The treatment of urticaria is based on an integrated approach, which involves not only identifying the allergen, but also correcting the allergic reaction. To do this, specialists at the Clinical Hospital on Yauza use extracorporeal hemocorrection methods that make it possible to cleanse the blood of antibodies and substances that provoke the development of the disease, namely:
- combination of cryoapheresis and cell mass incubation;
- cascade plasma filtration.
Extracorporeal hemocorrection methods provide:
- normalization or improvement of blood test results;
- improvement of the patient’s well-being, reduction or disappearance of skin rashes and itching, due to the attenuation of autoimmune inflammation;
- an increase in the duration of remission, a significant decrease in the intensity of possible subsequent exacerbations of the disease.
rapid remission of the disease due to the removal of harmful substances from the blood;
Cost of services
You can see prices for services
Treatment
The success of treating urticaria in children depends on accurate identification of the allergen. Therefore, the first thing doctors recommend is to get tested. After laboratory testing, medications are prescribed. External processing agents:
- "Fenistil";
- "Advantin";
- "Gistan";
- "Elidel"
Doctors do not recommend wiping the rash with products containing alcohol, as they can burn the skin. In difficult cases, injections and oral medications are prescribed. All medications are selected individually by the doctor, depending on the characteristics of the child’s body. In the simplest cases, they resort to folk remedies. Medicinal herbs help relieve itching, improve skin condition, and dry out pustules and blisters.
Recipes for medicinal infusions:
- Pour a handful of dried nettle flowers with 1 tbsp. boiling water, leave for 30 minutes. The infusion should be given to a child with hives in small portions throughout the day.
- Take equal quantities of dried nettle, chamomile, licorice and valerian roots. Grind the herbal mixture, measure out a large spoon, pour 1 tbsp. boiled water, leave for 45 minutes. Let your child drink the infusion in small portions throughout the day.
It is useful to wash the affected areas of the body with an infusion of medicinal herbs: chamomile, calendula, string. The infusion should be at a pleasant room temperature. What should you not do if you have hives? You should not sunbathe or swim in open reservoirs and pools. After the first symptoms appear, give your baby as much water as possible. If you are sure that the rash is a sign of hives, give your child activated charcoal. To prevent your baby from scratching the blisters, trim his nails. In most cases, the cause of itchy rashes is the foods that the baby consumed the day before. Therefore, the children's menu must be carefully analyzed and the necessary adjustments made.
Komarovsky's technique
The basis of Komarovsky’s technique is data from authoritative scientific journals and recommendations of the World Health Organization. The doctor has a negative attitude towards treatment with homeopathy, drugs with unproven effectiveness, and he is skeptical about traditional medicine.
Urticaria, according to Dr. Komarovsky’s definition, is a rash that manifests itself in the form of blisters on the skin, which have a clear localization and are accompanied by itching.
In some cases, it can appear on the mucous membranes, causing severe swelling. As a rule, the symptoms of urticaria disappear within a few hours after starting treatment.
As a result of certain processes, in particular changes in the capillaries of the skin, a number of substances are released, one of which is histamine. It causes certain reactions, which manifest themselves in the form of urticaria.
What could be the causes of the disease?
If attacks of the disease are single, then most likely they are caused by:
- Food.
- Medicines.
- Viral infection.
This type of urticaria is called acute and its course usually does not last long; most often it goes away without treatment, provided that the provoking factors are eliminated.
As a rule, hives are most often caused by food allergens.
These could be products such as:
- Strawberry.
- Citrus.
- Eggs.
- Seafood.
- Nuts.
- Some types of fish.
To reduce the likelihood of illness, you must first exclude these foods from the child’s diet. Allergic urticaria appears for some time after ingestion of a food product.
This takes from several minutes to hours. It depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. But besides this, medications can also cause such a symptom. For example, such drugs could be:
- Medicines to relieve pain, such as codeine or aspirin.
- Antibiotics of the penicillin or sulfonamide group.
But any drug comes under suspicion, even if it has been used for a long time before and there have been no reactions to it.
Few people know, but physical factors can cause symptoms of urticaria, as well as aggravate its chronic course. These include:
- Sunlight.
- Sweat.
- Cold.
- Pressure.
Why a rash may appear in a child, watch this video:
As a rule, the patient is aware of such factors, since he often notices certain reactions.
Frequent appearance
If the disease occurs almost every day and does not go away for more than 2 months, its chronic course is diagnosed. For most people, the cause of this disease cannot be determined. Physical factors can be aggravating.
The cause of chronic urticaria is rarely found in food, but despite this, foods have the ability to aggravate the disease. One of the main causes of a disease that does not go away for a long time is infection.
This could be, for example, candidiasis. It can also often be caused by emotional stress. In approximately 50% of cases, it resolves spontaneously after six months.
Dr. Komarovsky about urticaria
In one of his speeches about rashes, Komarovsky told how to treat urticaria in children. In his opinion, this disease does not pose any danger to the baby. But only if it manifests itself as a rash and itching. If swelling occurs on the face (swollen lips and eyelids), you should immediately consult a doctor. This is a common disease, which, as already mentioned, does not pose a threat to children's health, but at the same time causes severe discomfort in the baby. Therefore, it is important to diagnose the disease in time and take corrective measures.
Watch the video and leave comments
By
Causes of giardiasis
The mechanism of transmission of Giardia is fecal-oral. That is, Giardia is excreted from the body along with feces, and enters through the mouth - along with food or water.
Giardia exists in two forms - vegetative (in which Giardia feeds and grows) and in the form of a cyst (when the body of the microorganism is covered with a protective shell). Outside the human body, vegetative forms die, but cysts remain viable.
For Giardia infection to occur, it is enough for 10 to 100 cysts to enter the body. Giardia cysts can be present in the ground, in water, including running water and even spring water, and carried on the legs of flies. Only cooling below 13°C or boiling kills cysts.
A cyst that enters the human body reaches the duodenum, where it dissolves under the influence of intestinal juice. From one cyst, two vegetative forms of Giardia are formed. Giardia attaches to the villi of the intestinal mucosa and is believed to feed on products of parietal digestion. Giardia reproduces by division. Every 9-12 hours the number of Giardia doubles.
When it enters the colon, Giardia changes shape, turning into a cyst. Cysts leave the body with feces.