Flawless nail shape and smooth skin complete the look and make it flawless. Psychologists say that the hands reveal a lot about a person. For example, about his age, social status, habits and level of culture.
Women go to beauty salons to get a beautiful manicure. When trusting the hands of a master, few people think about their health. Unfortunately, the usual procedure can lead to dire consequences if the manicure tools are not properly sterilized.
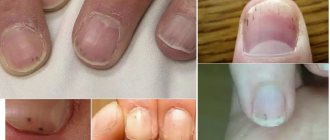
Types of abscesses on fingers or toes
Paronychia
A mild form of finger ulcer, or paronychia, occurs when pathogens enter the skin. During the course of the disease, infiltrative and purulent stages .
Paronychia begins with redness and swelling of the skin around the nail. Then a pain syndrome occurs, the appearance of intercellular fluid containing microbes. As the infiltrate accumulates, a vesicle is formed, the contents of which become purulent. The following types of paronychia are distinguished: 1 . Paronychia of acute and chronic nature - depending on the duration.
Subepidermal paronychia
Acute paronychia occurs suddenly and is characterized by severe pain in the area of suppuration. Typically, this type of paronychia is caused by a bacterial infection - Staphylococcus aureus after injury to the upper phalanx (damage to the cuticle).
The chronic form manifests itself gradually : first, the skin around the nail turns red, the finger swells, and pain in this area occurs. 2. Paronychia is superficial (subepidermal) and deep , affecting the thickness of the nail fold near the base of the nail.
These varieties differ in localization and clinical course. With subepidermal paronychia, pus accumulates under the epidermis near the edge of the nail fold. Panaritium occurs when paronychia is treated incorrectly.
The following varieties are distinguished:
| Type of panaritium | description |
| Cutaneous panaritium | Occurs on the back of the finger. With this disease, pus accumulates under the epidermis, resulting in the formation of a vesicle with a cloudy liquid, often mixed with blood. The skin turns red, the pain syndrome is mild, and sometimes a burning sensation is felt. An enlarged vesicle indicates that the inflammatory process is developing in deeper tissues and the disease is progressing. |
| Periungual felon (paronychia). | described above |
| Subungual panaritium | Inflammatory process in the tissues under the nail plate. It develops when pus penetrates under the nail. The cause of the development of such a disease may be a splinter getting under the nail plate or an injection. |
| Localization of subcutaneous panaritium | Palmar surface of the finger. Inflammation occurs under the skin. The pus formed there cannot break through the thick enough skin in this part of the finger and come out, so the inflammatory process goes deeper - tendons, joints and bone tissue are affected. |
| Bone panaritium occurs when the bone of the finger is affected. | This occurs when the infection directly penetrates into the bone tissue (open fractures with infection) or when the purulent process spreads to the bone from the tissues surrounding it. |
| Articular felon is called purulent arthritis of the interphalangeal joint | This disease occurs due to the direct penetration of infectious agents into the joint cavity, as well as due to the prolonged course of subcutaneous panaritium. This type of panaritium is manifested by a sharp limitation of the motor functions of the joint, pain during palpation and movement of the finger. |
| Tendon panaritium is also called tenosynovitis. | This is a rather serious disease that leads to long-term limitation of the functioning of the hand. With such panaritium, swelling occurs, the finger takes a bent position, and movements are limited. Tendon panaritium differs from its other varieties in its severe pain syndrome. |
Kinds
According to the nature of the course, paronychia can be:
- Spicy. It occurs quite often and is bacterial in nature. Lasts less than 6 weeks. Accompanied by severe pain, formation of pus;
- Chronic. If the inflammation continues for more than 6 weeks, then it is chronic paronychia. It is caused by mechanical, chemical factors, contact dermatitis, onychomycosis, eczema, psoriasis.
Depending on the nature and severity of the inflammatory process, the following types of paronychia are distinguished:
- Simple. Characterized by slight swelling, redness, moderate pain in the nail fold area;
- Purulent. Its symptoms include severe throbbing pain, a feeling of squeezing, and severe swelling in the area of the affected nail fold. In places where pus accumulates, the skin acquires a yellow tint, and pain is felt when pressed;
- Ulcerative. Painful ulcerations form on the surface of the nail folds, from which pus is periodically released;
- Fungal (candidal paronychia). Caused by fungi of the genus Candida. Symptoms are mild. There is slight redness of the skin, disappearance or reduction of the cuticle, and nail changes specific to onychomycosis;
- Paronychia with eczema or psoriasis. It is characterized by moderate inflammation, peeling, and the appearance of blisters on the skin, which form crusts as they dry.
Due to the occurrence of the inflammatory process, paronychia occurs:
- Bacterial. Acute forms in most cases are caused by Staphylococcus aureus, chronic forms - by streptococci and pseudomonads. In children, acute forms resulting from the habit of biting nails or sucking fingers are associated with infection of the nail tissues by aerobic and anaerobic bacteria of the oral cavity;
- Viral. It is caused by the herpes simplex virus;
- Fungal. Develops against the background of infection of the tissues of the nail folds by yeast-like fungi of the genus Candida;
- Non-infectious. It is caused by contact irritants, excessive humidity, side effects of certain medications, and chronic skin diseases.
The most common are bacterial and fungal paronychia.
Causes of a sore finger near a toenail or hand nail
Improper manicure as a cause of paronychia
One of the most common causes of inflammation of the finger in the nail area is incorrect performance of pedicure and manicure.
Careless actions can damage the cuticle and provoke an inflammatory process with further accumulation of pus around the nail. Typically, such inflammation is caused by streptococcal and staphylococcal microorganisms that live on the skin of every person.
The development of the inflammatory process is influenced by certain conditions, such as:
- decrease in the body's immune forces
- presence of severe concomitant blood diseases
- metabolic disorders.
- fungus on the feet or nails.
Most cases of felon development occur after injury to the skin on the fingers. Moreover, the inflammatory process can occur even due to minor injuries - abrasions, scratches or splinters, cracks due to the skin being too dry and flaking. An infection penetrates the skin, which gives rise to purulent inflammation. For this reason, even minor wounds should be immediately treated with alcohol-containing solutions or iodine. Hangnails can also cause inflammation and the formation of pus in the tissues of the finger near the nail.
Prevention of nail diseases
Everyone knows that it is easier to prevent a disease than to treat it. But in everyday life people are too careless. They easily trust their health to professionals from a beauty bar or the nearest beauty salon, without checking the sterility of the instruments. Because of this, a situation arises when a finger suddenly becomes inflamed after a manicure. Everyone probably knows what to do to protect themselves. Unfortunately, this knowledge is rarely used in real life.
To avoid troubles and preserve your health, you should strictly monitor the master’s compliance with the following rules:
- The manicure table must be perfectly clean. Before starting to serve a new client, the technician must wash and disinfect his hands. The client should do the same.
- The manicure bath should be wrapped in a clean plastic bag. It is changed before each client.
- Tools must be packaged in a kraft paper bag, in which they are processed in a dry-heat oven. They should only be opened in front of the client.
- Files must be kept in an ultraviolet sterilizer. They should be taken out in front of the client.
- You can protect yourself from all risks if you bring your own set of instruments to the procedure.
Inflammation of the toe from an ingrown toenail
An ingrown toenail is also often the cause of inflammation and suppuration of the area around the nail plate.
Inflammation from an ingrown toenail
There are people prone to this problem. The most susceptible to ingrown toenails is the big toe. This is influenced by the special location and size of the periungual fold, as well as the growth of the nail itself. Also, an incorrectly done pedicure on the feet can contribute to ingrowth: if the corners of the nail plate on both sides are prevented from growing by the periungual ridge, they grow into the soft tissue. Therefore, it is necessary to properly treat the nail plates during a pedicure:
- control the length of your nails and do not grow them;
- do not give your nails a square shape or file off the corners;
- regularly carry out foot baths to soften the skin and nails;
- remove dead skin particles in areas of possible ingrown nails.
The first sign of an ingrown nail is pain in the periungual fold near the edge of the nail plate . Then the pain spreads to the entire phalanx. Due to the fact that such sensations are tolerable, most people do not pay much attention to this problem. But then they notice that the skin around the nail is inflamed. If measures are not taken, the situation will become more serious and suppuration will begin around the nail plate. If an abscess forms, it is better to consult a doctor to avoid complications.
Fungus treatment
Nail fungus cannot go away on its own. He needs to be treated. To choose the most effective drug, it is recommended to consult a dermatologist. The following products have proven themselves to be effective:
- "Exoderil";
- "Fluconazole";
- "Lamisil";
- "Mikozan";
- "Loceryl";
- "Clotrimazole";
- "Batrafen".
In the treatment of fungus, it is recommended to combine drug treatment and traditional medicine methods. Baths made from a decoction of medicinal herbs or sea salt help well. Additionally, the following treatment methods can be used:
- Apply a mixture of sea salt and grated mint to your nails twice a day.
- Treat the affected plates with rich sour cream mixed with vinegar.
- Apply iodine or tea tree oil to the affected areas daily.
- Mix crushed garlic cloves with vegetable oil and treat the nail plate.
- Once a day, apply 20% alcohol tincture of propolis to the affected area.
Splinter as a cause of nail abscess
A splinter is the cause of inflammation of the fingernail.
A splinter can cause an abscess under the nail if it gets into this area.
In this area, small splinters are difficult to notice. They are not exposed to mechanical stress, so in such situations a strong inflammatory process develops. If it is possible to remove the splinter on your own, after removing it, you should use means to relieve inflammation. This way the situation will quickly return to normal. In some cases, removing a splinter may require the help of a doctor.
Disease prevention: what to do?
The main cause of skin abscesses around the finger is various skin injuries. To protect yourself from this unpleasant problem, you need to follow simple preventive steps.
- Immediately treat all wounds with antiseptics (brilliant, iodine, alcohol).
- After any “dirty” work, wash your hands thoroughly.
- Do not allow wounds to become contaminated.
- Trim your nails carefully so as not to damage the cuticles.
- Immediately remove splinters and then disinfect wounds.
- Be sure to treat fungal infections.
- Get manicures and pedicures done by professionals, and monitor the sterility of instruments.
- Do not wear tight and uncomfortable shoes.
Signs of a nail abscess
In most cases, the big toe is affected by paronychia and panaritium; any finger on the hands can become inflamed.
By the damage to several nails at the same time, one can judge the work of the body’s immune forces - its decrease. Also, an inflammatory process on more than two toes may indicate the presence of foot or nail fungus. But no matter what causes felon, the characteristic symptoms will be:
|
If you find these signs in yourself, it is better to contact a surgeon to prescribe the correct treatment and avoid complications.
What causes inflammation around the nail?
To understand where exactly inflammation occurs during paronychia, let’s look at how the nail and the soft tissue around it are structured. The nail apparatus has a complex structure. It consists of five main structures: the nail plate, matrix, nail bed, cuticle and nail folds.
The cuticle is an important protective element; it connects the skin of the finger and the nail plate together. Mechanically protects against irritants, allergens, and pathogenic microorganisms getting under the nail from the side ridges and the growth zone. Another feature of this skin over the nail is that it has no blood vessels or nerve endings. That's why we don't feel pain or see blood when a manicurist trims the cuticle. But, on the other hand, the lack of blood supply means the lack of local protection from external foreign bodies, irritants, and pathogenic agents. This function is performed by leukocytes - white blood cells. Therefore, in case of injury to the cuticle, negative factors do not encounter obstacles and immediately pass deeper.
The main factor that causes acute paronychia is infection. Even with minor trauma to the cuticle or destruction of the integrity of the skin on the nail folds, pathogenic microorganisms penetrate deep into the tissues of the nail apparatus. In 60% of cases, inflammation develops due to strains of Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus aureus). Infection with mixed pathogenic microflora and streptococcus is possible.
More often paronychia occurs on the hands. The fingers, unlike the toes, come into more contact with the environment, are exposed to mechanical injuries, contact with water, aggressive substances, and potential sources of infection. Cracks that are invisible to the eye, the presence of which you may not even suspect, become gateways for the penetration of pathogenic bacteria and fungi and provoke inflammation.
The most common causes of paronychia include:
- poor disinfection of hands or instruments during manicure or pedicure;
- splinters, abrasions, cuts, scratches in the area around the nail;
- torn or bitten off burrs;
- habit of biting nails;
- tight, uncomfortable shoes (causes paronychia on the toes)
- ingrown nails;
- wearing artificial nails;
- fungal infection of the skin or nails (onychomycosis);
- careless or improper trimming of nails at home.
The habit of sucking fingers can cause inflammation of the nail folds in young children.
Chronic paronychia is an inflammatory reaction that occurs in response to irritants or allergens. If in the acute form, as a rule, only one nail is affected, then in the chronic form, several are affected at the same time. Usually these are the thumb, index and middle fingers of the working hand.
Chronic paronychia develops as a consequence of irritant contact dermatitis or fungal infection.
It often occurs among housewives and people of certain professions who come into contact with irritating substances and high humidity. Such professions include cleaners and laundry workers who are constantly in contact with water, powders, weak alkalis, acids, detergents and household cleaning products.
Also at risk are professions related to the kitchen, cooks, bartenders, and dishwashers. Fungal paronychia, caused by a fungus of the genus Candida, is commonly called bakers' or confectioners' disease. Constant contact with moisture, dough, and sugars creates favorable conditions for the development of such a fungal infection.
A chronic form of inflammation of the skin around the nail is often found among employees of chemical laboratories and people working with fuels and lubricants. At risk are professional swimmers whose hands and feet are constantly in contact with water and pool disinfectants.
With constant exposure to aggressive substances, the protective barrier of the nail is gradually destroyed, which leads to inflammation.
Chronic paronychia often occurs in people with diabetes and chronic skin diseases such as eczema and psoriasis. It can also be caused by long-term use of certain medications. For example, drugs from the group of retinoids and protease inhibitors.
Complications of finger inflammation
An abscess in an advanced form is very dangerous : the purulent inflammatory process can spread deeper: to the tendons, bone tissue, and finger joint. The finger may partially or completely lose its function. Moreover, inflammation can affect the hand and forearm. A severe form of panaritium with concomitant diseases, such as diabetes, can lead to the following complications:
more complicated than nail inflammation
- sepsis (blood poisoning) - a rather dangerous condition that can lead to death without qualified help;
- phlegmon of the hand - acute purulent inflammation of the cellular tissue of the hand;
- tenosynovitis - a purulent inflammatory process in the tendon sheaths, the most severe condition in which there is a long-term loss of mobility of the affected finger;
- osteomyelitis - a severe purulent process of bone tissue that requires immediate surgical intervention, sometimes complete amputation of the finger.
Possible complications
If the big toe abscesses for a long time, and there is no appropriate therapy, the pathological process spreads to the muscles, tendons, and bones.
The condition is complicated by the addition of secondary pathologies, which lead to dysfunction not only of the big toe, but of the entire foot, and sometimes of the lower limb.
In addition, a severe form of the pathology may be caused by elevated levels of glucose in the blood.
Particular complications from an abscess on the toe include:
- general blood infection - sepsis when the pathogen enters the bloodstream;
- phlegmon of the foot - spread of the purulent process to adjacent tissues with the formation of an unlimited abscess;
- tenosynovitis - inflammation in the tendon sheath, which, as it progresses, can lead to contracture (limited mobility) or ankylosis (immobilization) of the finger;
- osteomyelitis is a purulent-necrotic lesion of the bone structures of the foot.
Abscesses on the fingers that seem harmless at first glance, if performed incorrectly during self-medication and in the absence of diagnosis, often become the cause of disability for the patient. Therefore, having noticed the first symptoms, if your toe is festering, you should not postpone a visit to the doctor for an accurate diagnosis and emergency treatment.
First aid for a nail abscess
In order to normalize the situation when the first symptoms of an abscess appear on a toe or hand, you should know the rules of first aid, as well as warnings. What you should not do under any circumstances is to pierce a bubble with pus in order to get rid of it, because in a greater degree of probability, it will not be possible to completely remove all the purulent fluid, and such an effect will not have any effect.
This is quite dangerous - if you insert the needle too deeply, you can provoke blood poisoning and the infection will spread throughout the body, and this is fraught with serious consequences.
What you can do: a warm bath with substances that have anti-inflammatory properties: salt, soap or chamomile decoction. The foot should be immersed in this liquid several times a day, which will significantly reduce the occurrence of unpleasant symptoms. After the procedure, you should blot the limb with a towel, then you are allowed to make an onion compress or use aloe leaves instead.
Treating an abscess with surgery and medication
Many parents are thrown into a state of panic by pus on the child’s toe near the nail. What to do in such a situation? At the first signs of inflammation under the nail plate, you should consult a specialist. Based on a visual examination and some tests, the doctor will be able to prescribe treatment. If you have been treating an abscess at home, but there is no improvement, and the condition is only getting worse (fever, fever), then you should immediately go to the hospital.
Treating an abscess with medications involves taking strong antibiotics. If felon has a chronic form, then you can regularly use antifungal ointments. In advanced cases, doctors prescribe pills.
If the pus on the toe near the nail has developed into an acute abscess and the infection has spread beyond the affected area, surgery may be required. The doctor will hide the boils and clean out the pus that has accumulated in them. After this, the affected area is disinfected. An antiseptic bandage is applied to the sore spot.
Laser therapy is gaining popularity every year. This is a modern and highly effective method that helps minimize pain during surgery. In addition, after such an intervention there are no noticeable scars or cicatrices. Laser can be used to treat suppuration on the nail without deforming the plate. The rehabilitation period is also reduced to a minimum. The patient does not require any additional treatment. Due to the fact that the edges of the wound are welded, the risk of repeated suppuration is minimal.
Another innovative method of surgical intervention is cryotherapy. It is based on the use of cold. The abscess is removed using liquid nitrogen. Low temperatures reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings, so the procedure is almost painless.
Treatment of paronychia and panaritium
For abscesses on the toe and hand, medications are more effective than traditional methods of treatment.
- One such medicine is Dimexide . It is prescribed when the patient cannot use warm baths. This drug has powerful antiseptic properties and good penetration through the skin. Dimexide is often used by doctors for purulent dressings.
The solution is applied to a cotton swab and applied to the inflamed area of the finger. If adverse reactions occur, the drug is discontinued.
- For moderately severe inflammation, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics taken by mouth .
- If pus accumulates near the nail plate, the surgeon will numb the area and remove the fluid.
- For chronic paronychia caused by a fungal infection, the doctor will prescribe topical medications against this type of fungus. These drugs include Clotrimazole, Ketonazole and others.
Treatment can be quite long - from several weeks to several months. In complicated cases, oral antifungal drugs or steroids will be required.
| If treatment for a chronic abscess on the finger is ineffective, it is necessary to exclude various neoplasms, since the signs of these conditions may be similar. |
How to treat?
It is better to entrust the treatment of paronychia on the hands or feet to a doctor, especially if it is a purulent inflammation. Contact a podiatrist, surgeon or dermatologist with this problem. He will examine the affected area, assess the severity of the infection, clean the pus, and select medications for further home use. If necessary, he will refer you for additional examinations and analysis of purulent contents to identify a specific pathogen.
Attempts to treat paronychia at home, and especially squeezing out pus, are dangerous due to the spread of infection to neighboring tissues and the addition of new pathogenic pathogens.
The indication for surgical intervention is inflammation of any form if it is accompanied by an accumulation of pus.
Therefore, consult a doctor if the following symptoms appear:
- redness, swelling and tenderness of the skin at the base of the nail plate or in the area of the lateral nail folds;
- suppuration, causing detachment of the skin and nail plate, discharge of pus;
- a sharp increase in pain when pressing on the nail and fingertip.
Treatment of acute form
Treatment of acute paronychia is based on the severity of inflammation and the presence of an abscess. If there is an abscess, it should be opened to remove the pus. Without this procedure, the condition will only get worse.
Inflammation with accumulation of pus in the nail fold is treated with minor surgery. Removal of paronychia and cleansing of pus is performed through small incisions using local anesthesia or needle puncture without anesthesia. This procedure is necessary to remove pus that has accumulated under the skin. In severe cases, where the abscess extends to the nail bed or is associated with an ingrown nail, it may be necessary to remove part of the nail plate.
Local medications for the treatment of paronychia include ointments aimed at combating bacterial infection. Broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory and antibacterial agents are used, which must be effective against Staphylococcus aureus. After removing the pus, the doctor applies a sterile gauze bandage with medicinal ointment to the resulting wound. As soon as the pus begins to come out, the person immediately feels relief. Throbbing pain and tension goes away.
For severe forms of inflammation, antibiotics may be prescribed orally. This is necessary in cases of severe infections, immunodeficiency conditions, or if adequate drainage cannot be provided for the outflow of pus.
After drainage, it is important to follow all recommendations of the doctor who performed the procedure to prevent secondary infection. After a few days, the patient should again see a specialist to assess the condition of the periungual tissues. With proper care after draining the abscess, the affected finger heals quickly without any complications.
If the opening of the paronychia occurs on its own, treat the wound with an antiseptic. Use a solution of chlorhexidine, hydrogen peroxide, furatsilin for this. Wrap with a sterile bandage and consult a doctor for further care advice.
Is it possible to cure paronychia on your own at home?
It is possible, but only in the initial stages, when there is no formation of pus yet. For inflammation without an obvious abscess, warm baths with antiseptic solutions (chlorhexidine, povidone-iodine), and salt baths help. They need to be done 4–5 times a day for 10–15 minutes. If your condition does not improve within two days, see a doctor. It is not recommended to use anti-inflammatory and antibacterial ointments on your own. Such drugs must be prescribed by a doctor.
If you consult a specialist in a timely manner, treatment of acute inflammation has a favorable prognosis. The condition improves within a few days. If acute paronychia is constantly repeated, then it develops into chronic. Therefore, patients should take steps to avoid future nail fold injuries.
Treatment of paronychia with concomitant skin diseases
If the cause of acute paronychia is associated with psoriasis or eczema, then treatment in these cases should be aimed at the underlying cause. Contact your dermatologist and tell him about your nail problem.
Eczema and psoriasis are not contagious chronic skin diseases; their course consists of alternating periods of exacerbations and remission. Unfortunately, it is not yet possible to completely get rid of them. The main goal of treating these diseases is to relieve symptoms and achieve stable remission.
Oral medications, local ointments and creams, and physical therapy help. Giving up bad habits, strictly following a diet and avoiding nervous stress is of great importance. Since often these factors become the trigger for the onset of exacerbation. Foods that cause allergies, alcohol, sweets, as well as fatty, spicy, and smoked foods that are difficult to digest should be excluded.
During exacerbations, the skin turns red, becomes inflamed, begins to peel, and itch. Ulcers and rashes may appear on it. It is important to prevent complications in the form of a secondary bacterial or fungal infection, as this leads to paronychia and slower skin recovery.
Treatment of the chronic form
Treatment of chronic paronychia is aimed at identifying and eliminating the source of irritation. You need to prepare for the fact that it will be long, it will take from several weeks to several months, depending on the severity of the condition. The fact is that chronic paronychia responds slowly to treatment.
In case of a chronic inflammatory process, if possible, they try to avoid contact with the irritant, and prescribe local anti-inflammatory agents that restore the protective functions of the skin.
If paronychia occurs as a result of taking certain medications, then the doctor and patient must decide together whether the adverse effects of such treatment are acceptable for the therapeutic effect of the drug. Or you should think about choosing another drug. Stopping taking the medication that provokes inflammation will allow you to quickly restore the periungual tissues, remove irritation and discomfort.
If the cause is a fungal infection, local antifungal agents are prescribed in the form of ointments, gels, and solutions. If necessary, clean the area damaged by the fungus with a hardware medical manicure or pedicure.
The success of treatment of chronic paronychia largely depends on following the doctor’s instructions and prevention, which the patient will carry out independently.
Antibiotics for the treatment of abscess on the finger
When treating suppuration caused by streptococci or staphylococci, antibacterial drugs are always prescribed.
- With subcutaneous panaritium, antibiotics are used when the inflammatory process moves deeper, but in the absence of purulent tissue decomposition.
The greatest effect is observed from drugs of the cephalosporin or penicillin series.
- At the beginning of the development of articular panaritium, intra-articular injections with broad-spectrum antibacterial drugs are used. But in severe cases of this disease and in the absence of effect from injections, the only treatment method will be surgery, which also uses antibiotics.
This group of drugs is also prescribed for phlegmon of the hand or finger, if after surgery there are foci of inflammation and pus. In such cases, antibiotics are used to prevent infection of adjacent tissues. Broad-spectrum drugs for this condition are prescribed in fairly high doses.
inflammation surgery
These are antibiotics such as Ampicillin, Oxacillin, Cloxacillin, Erythromycin, Methicillin, Chloramphenicol . For local exposure, the affected area is pierced with a penicillin solution containing novocaine. The dosage is determined by the doctor individually.
Preventive measures
To avoid a similar illness in the future, you must follow safety precautions:
- It is advisable to disinfect manicure instruments.
- If during a manicure the cuticle area is accidentally damaged, it should be immediately treated with an antiseptic solution.
- You should always have nourishing and softening products for the cuticle on hand.
- It is useful to do vitamin baths for your hands from time to time.
- When contacting household chemicals, use gloves.
Surgery to treat nail inflammation
If conservative treatment was started late and did not bring results, complications arise that can only be eliminated through surgery. To do this, drainage of purulent fluid is performed under local anesthesia . If the skin in the area of the abscess has acquired a white or yellow color, local anesthesia is not performed, since this sign indicates damage to the nerve fibers. Surgical options:
| 1. Surgical intervention for superficial paronychia is carried out by cutting without the use of local anesthesia of the exfoliated skin, followed by its excision and removal of the purulent mass. Then an antiseptic bandage is applied for 5 days. This time is necessary for epithelization of the wound area. |
| 2. In case of deep paronychia, a 10 mm incision is made in the direction of the palm at the marginal part of the base of the nail. The skin covering the base of the nail plate is not cut, but is pushed back, cleaned and turned away from the damaged side. If the nail plate at the base peels off due to a purulent mass, it is carefully excised. If this area is accidentally damaged, the growing nail will become deformed. |
| 3. If the entire nail bed or its middle part is damaged Two 10-15 mm incisions are made. A trapezoid-shaped area of skin is turned away from the base. The part of the nail that is peeled off due to pus is removed and the pus is eliminated. A special rubber strip is placed under the skin flap, onto which Vaseline is applied, and the skin returns to its place. An antiseptic bandage is applied to the finger. After a day after the operation, the finger is dipped in a warm solution with the addition of potassium permanganate, the rubber gasket is changed and left for another day. If the purulent inflammatory process ceases, the rubber strip is no longer used, and a bandage with ointment is applied to the wound surface. |
For faster healing of incisions and to prevent secondary infection, a course of antibiotics and antiseptics is prescribed.
First aid
Conservative treatment of panaritium is possible only in the initial stages of the disease. Any wound after a manicure should be immediately treated with an antiseptic. At home, you need to additionally lubricate it with iodine or brilliant green.
If the actions taken do not bring the desired result and the finger becomes inflamed, you should prepare a hand bath. The water should be hot, but comfortable for a person. The following bath compositions are good for relieving inflammation:
- Hypertonic solution. To prepare it, pour a tablespoon of salt into a glass of boiling water. When the water has cooled a little, immerse the affected finger in it for 30 minutes.
- Potassium permanganate. Several crystals of potassium permanganate are dissolved in warm water. The color of the solution should be light pink. The finger is lowered into it for no more than 10 minutes.
- Soda solution. Two tablespoons of powder are poured into a glass of boiling water. When the water reaches a comfortable temperature, the affected finger is immersed in it for 30 minutes.
- Copper sulfate. A pinch of powder is required for 50 ml of hot water. The duration of the procedure is 15 minutes.
- Healing herbs. Take a tablespoon of calendula, chamomile and celandine. Pour two cups of boiling water over the herbs. After the infusion has cooled, use it for baths.
- Calendula. Pour three tablespoons of herbs into a glass of boiling water. Put your finger down for 15 minutes.
- Garlic baths. Pass a few cloves through a press and pour a glass of boiling water. When the liquid has cooled, use it for baths.
The methods listed should relieve discomfort if your finger hurts after a manicure. A compress with Dimexide helps complete the treatment. The drug is diluted with water in a ratio of one to four. Gauze or a cotton pad is soaked in the solution, then applied to the finger. Wrap cling film on top and leave it in place for 40 minutes.
Home treatment for nail abscess
Treatment of nail and subcutaneous panaritium at home is possible only at the onset of the disease and under the close supervision of a doctor. If there is no effect from ointments, baths and the signs of the disease intensify, the only way to get rid of purulent inflammation will be surgery. Treatment in the clinic can be carried out for such types of panaritium as subcutaneous, cutaneous and nail. When purulent inflammation spreads to the joints, tendons and bone tissue, the patient is referred
Herpes infection on toe
to the surgical department of the hospital.
Drug treatment
What to do if your toe has become infected is determined by a medical specialist after examining and identifying the cause of the disease. The most effective way to pull pus out of your finger is to use local medications:
- The use of Dimexide solution is prescribed from the first days of treatment. To remove an abscess, a cotton swab made of sterile material is soaked in the medicine and placed on the hyperemic part of the finger. For convenience, the cotton wool can be secured with a bandage or medical adhesive plaster.
- If there is a superficial accumulation of exudate, the doctor cuts the skin with anesthesia, as for local surgery, to remove pus from the finger.
- The abscess cavity is washed with an antiseptic solution, after which a sterile bandage is applied to the wound surface.
Taking into account concomitant pathologies, specific therapy is prescribed. If the patient has a fungal infection, he will need local treatment with creams or ointments for mycosis (Clotrimazole, Exoderil).
In case of long-term persistent felon of fungal etiology, local treatment is supplemented with systemic treatment using tableted antifungal drugs (Ketoconazole, Nizoral).
Following medical recommendations on how to cure an abscess on the toe, the following drugs are used:
- Iodine preparations to remove pus - Yodovidone, Sulyodopirone.
- Furagin is an antimicrobial drug for the destruction of staphylococcal infections.
- Miramistin is an antiseptic, effective if your finger breaks, which can be done with irrigation or rinsing.
Antibiotic therapy
If the finger has become infected, local antibacterial treatment is carried out, which is necessary to cleanse the site of infectious inflammation from pathogenic microflora. The main indication for prescribing antibiotics is the penetration of bacteria into the deep layers of tissue.
Antibacterial drugs prescribed for felon:
- Ointment for pus on the finger with an antibiotic has an antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effect. Most often, ointment with Tetracycline, Erythromycin or Syntomycin liniment is prescribed. In addition to ointment bases, a solution of penicillin with procaine is used for lotions and rinsing.
- In case of extensive suppuration or the development of phlegmon, Azithromycin and Cefatoxime are used for a general effect on the body.
Pyogenic microbes (staphylococci, streptococci) often contribute to an abscess on a child’s finger. Antibacterial drugs in this case are used according to an individual scheme according to age limits. If a child’s finger breaks out after all the therapeutic measures taken, the purulent formation is opened surgically.
Abscess removal surgery
Your doctor will tell you what to do if your toe festers and conservative methods do not bring the desired result.
Surgical treatment is carried out with local anesthesia or without anesthesia for the superficial form of panaritium.
A small incision is made on the finger and the purulent contents are removed. After which the wound is treated and drainage is installed to evacuate exudate when it forms.
A sterile bandage is applied on top for 5 days, during which active tissue epithelization occurs. If pus does not form again, the drainage is removed during the next dressing.
Recovery of the operated area occurs within several days. As a rule, relapses occur in rare cases.
Laser therapy
Treatment of purulent inflammation on the toes is effective using a surgical laser. The advantage of this method is minimal trauma and absence of scars after removal of the abscess. The therapeutic effect of a laser beam achieves the following effect:
- no bleeding;
- minimal recovery period;
- sterility of the area after removal of the abscess;
- if the purulent process has spread into the subungual space, it is gently removed without subsequent deformation;
- no relapses.
During laser exposure, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort.
Cryotherapy
One of the best methods of auxiliary treatment is cold procedures. When using liquid nitrogen, the patient does not feel pain, only a slight numbness. The manipulation is repeated in a course of 5 sessions after cleansing the abscess. After cryotherapy there are no unpleasant sensations, after loss of sensitivity a pleasant warmth appears.
Herpes infection of sore finger
If there are blisters on the inflamed finger or toe , filled with clear liquid or mixed with pus and blood, the cause of panaritium is most likely caused by herpes pathogens. Most often, herpes infection on the fingers occurs in children , but such blisters are also present on other parts of the body - in the mouth, on the lips.
| The difference between herpes inflammation on the fingers and others is that it does not respond to treatment with antibacterial drugs. For abscesses caused by these pathogens, surgical intervention is not performed, as there is a risk of infection spreading throughout the body and causing serious complications. |
If you suspect herpes inflammation of the finger, treatment should be carried out as follows: 1. Apply Acyclovir ointment to the inflamed area for a week. After this treatment, the skin will return to normal in 1 or 2 weeks. 2. A bandage can be applied to the site of inflammation in order to reduce the risk of the herpes infection spreading to healthy parts of the body, especially the mucous membranes. If the use of the ointment does not bring results and the inflammatory process only intensifies, you need to make an appointment with a doctor to choose further treatment tactics.
Causes of the disease process
Cuticle inflammation can be caused by a variety of things. Most often, an abscess on a finger appears after an unsuccessful manicure, but this is far from the only reason. Having determined what caused the irritation, it is much easier to decide what further treatment will be.
- Incorrect treatment of the cuticle during manicure. After this procedure, hangnails may appear around the nail. They cannot be torn off; there is a risk of getting a purulent abscess. Poorly trimmed, unsoftened cuticles or the use of unsterile equipment may also be the cause.
- Ungroomed hands. If you do not systematically treat the skin around your fingers, there is a chance of getting into trouble. For example, a cuticle that is too large is susceptible to minor injury and is much more likely to become inflamed around the nail. In addition, if the cuticle is very dry, there is a possibility that your fingers have a fungal infection.
- Harmful microorganisms. Very often, after minor injuries, the periungual tissues of the hands can become infected. Quite often it is a fungus. It is accompanied by peeling and severe irritation.
- Allergic reaction. Swelling and redness are the main symptoms of allergies. After your fingers come into contact with an irritant, they may swell. If this is the reason, swelling will appear in other parts of the hands.
- Injuries and other external influences. Impacts, cuts, pressure or wearing ill-fitting shoes can cause swelling, inflammation and irritation.
Folk remedies for the treatment of felon on the arm or leg
Traditional methods are effective only at the initial stage of inflammation and abscess on the toes and hands.
- For this, lotions with an infusion of herbs that have antiseptic properties are used: chamomile, calendula.
To obtain the product you will need 200 ml of boiling water and 1 spoon of dry raw materials. The grass is poured into a container with liquid and left for a while. A cotton swab is soaked in the cooled infusion and applied to the affected area and fixed.
- potassium permanganate or soda and salt are no less effective . Bath with potassium permanganate
The amount of potassium permanganate should be such that the liquid acquires a pale pink color. The finger with the abscess is dipped into this solution, after a while it is removed, blotted with a towel and ointment is applied to the affected area, followed by a bandage.
- To obtain a salt-soda bath, you need to dissolve a spoonful of soda and salt in 200 ml of water. Such baths are allowed to be performed alternately.
- Onion compress
A compress with onions is a fairly effective remedy in the treatment of panaritium. In order to prepare it, you need to take ¼ of the onion, grate it on a coarse grater and place it on gauze to form a layer 1 cm thick. The compress is applied to the finger, covered with film, and then secured with a bandage. You should keep such a compress on the affected area for 2 hours, then take a bath with soda and salt and replace the onion mass with fresh one. This alternation should be carried out 2 times a day. If there is no effect within 3 days, consult a doctor.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine recipes can effectively fight diseases. These methods have absorbed the experience and wisdom of several generations of people. Many recipes have been collected over centuries. At the same time, several treatment options are offered for each disease.
Traditional medicine knows well how to treat an abscess on a finger. She has several dozen different recipes in store for this. The most effective are the following:
- Compress with baked onions. Accelerates the maturation of the purulent capsule and accelerates the release of its contents to the outside. The onion is cut into two parts. The halves are baked in the oven. When the onion has cooled, apply it to the affected area, fix it and leave it for several hours.
- Aloe. Peel the pulp from the leaf and apply it to the inflammation.
- Castor oil. Heat the substance to a temperature of 40 degrees in a water bath. Soak gauze in oil and place it on your finger.
- Flax seeds. An excellent remedy not only for felon, but also for furunculosis. Add a tablespoon of flax seeds crushed in a coffee grinder to 250 ml of boiling milk. In addition, you can add a few dried chamomile flowers. Boil the mixture for two to three minutes and strain. Apply the resulting mass to the inflammation and secure with a bandage. Leave for three hours.
- Milk foam. If your finger becomes infected after a manicure, you need to help ensure that the infection goes away as soon as possible. To do this you will need the fattest milk you can find. The liquid should be poured into a clay pot and placed in the oven. When brown foam forms on the surface of the milk, it must be removed and applied to the affected area. Apply a bandage on top and leave it overnight. Repeat the steps in the morning. The result will not take long to arrive. By the end of the second day, the pus will come out.
- Potatoes or beets. Vegetables help prevent the development of a pus sac. A paste of fresh beets or potatoes should be applied to the inflammation after baths with a hypertonic solution or potassium permanganate.
- Honey compress. For treatment you will also need a baking onion and flour. All ingredients, mixed in equal quantities, are thoroughly ground. The resulting paste is applied to the inflamed area, covered with gauze and secured with a bandage.
Panaritium in a child
Finger abscess in a child
You need to watch your child’s fingers especially carefully, since children, more often than adults, have the habit of biting their nails and tearing off hangnails, which can lead to an inflammatory process on the hands. If a red spot appears near a child’s fingernail, you should immediately smear it with iodine solution . You can also apply a cotton pad soaked in calendula tincture. Lotions will also help. This is necessary to stop the inflammatory process at the very beginning of its development. If an abscess appears, you should never try to treat it yourself or pierce it with a needle. The best solution would be to consult a doctor, he will carry out the necessary manipulations. Since in children the inflammatory process and the formation of pus occurs very quickly , surgical treatment is usually used.
In order to prevent the development of felon in a child, you need to:
|
Finger felon, symptoms
Acute inflammation of the finger near the nail
The infection, penetrating under the skin near the nail, into the upper layer of the epidermis, begins its development. Swelling, redness, and itching appear on the skin. The area near the nail begins to hurt. The inflammatory process, penetrating deeper into the skin tissue, forms stripes of purulent blisters in it. When affected, the joint becomes hot, hard, inflamed, and the finger hurts and cannot bend. If the tendons and fatty tissue have festered, then the temperature may rise and your health may deteriorate.
For all types of felon there are several common symptoms.
In adults and children, the disease develops in the same way; its main symptoms are:
- pulsation, pain and discomfort in the affected area
- increased pulsation and pain when lowering the patient
- limbs and relief of its condition when lifted
- tumor, edema
- redness of the skin around the site of infection
- restriction of movement of the injured finger
Swelling, redness and formation of pus - symptoms of panaritium
What to do and how to effectively resist the sore is described below.
When an abscess occurs, the finger swells and produces pus.
Prevention of paronychia and panaritium
The main preventive measure for such conditions is to avoid damage and injury to the skin on the fingers: bruises, cuts. It is also important to maintain daily foot hygiene . More information about paronychia can be found in the video.
Using the services of a professional pedicurist will protect you from improper treatment of the nail plates and its consequences: damage to the skin, ingrown nails and inflammation.
Wearing comfortable shoes will also eliminate these unpleasant situations. Treatment of chronic diseases that can cause inflammation of the toes is also important. Diabetes requires constant monitoring of blood sugar levels. Increasing immunity will strengthen the body and activate forces to fight infections.
How to prevent paronychia?
To prevent inflammation around the nail, carefully observe personal hygiene rules. Proper nail care will significantly reduce the risk of infection and keep your nails, nail folds and nail beds healthy. If accidental injury or irritation occurs, immediately treat the skin around the nail with an antiseptic. Carry an antiseptic spray in your purse. After all, trouble in the form of a splinter, cut, scratch, or abrasion can happen anywhere, and disinfection of the injured area will prevent infection.
To prevent paronychia, follow these recommendations for caring for your nails and skin of your hands and feet:
- keep your hands and feet dry and clean;
- Apply moisturizer after swimming or every time after washing your hands if you have dry skin, this will help prevent cracking;
- avoid prolonged contact with potential irritants (chemicals, household chemicals, varnishes, paints), use protective gloves;
- do not bite your nails or pick the skin around them;
- do not cut the cuticle, especially on the toenails, destruction of the nail or cuticle will lead to the entry of bacteria and fungi;
- do not bite off or tear off hangnails, carefully trim them with nail clippers;
- do not grow your nails too long, trim them regularly and smooth out sharp edges with a nail file;
- keep your hands away from constant exposure to water, avoid contact of irritants or allergens with your skin;
- disinfect manicure instruments before the procedure;
- keep your blood sugar levels normal if you suffer from diabetes;
- Keeping your shoes and socks always dry will help prevent the development of fungal paronychia.
If you cannot avoid paronychia, do not be afraid and seek medical help. We will always be happy to help you at the Eva Korneeva Podology Center. With us you can quickly, safely and painlessly cure inflammation around the nail. All manipulations are performed under 100% sterility conditions without the risk of complications. Quick rehabilitation after the procedure will allow you to return to your business, but without pain and discomfort in your fingers.
To make an appointment, call +7 (985) 489-45-86.
5 5
Localization of abscesses in the finger area and signs
A common variant of inflammation in the area of a toenail or finger is when it breaks out cutaneously or subcutaneously. Causes redness, pain when pressing on the formation, swelling of the tissue in the nail growth area.
If it breaks out under the toenail, the existence of an abscess is accompanied by a feeling of pulsation, pain, and swelling of the finger. Pus collects under the plate, preventing its free outflow; treatment is necessary.
If suppuration on the toe has affected the nail fold (the skin around the nail breaks), it is localized on the free edge of the big toe, causing pain, a feeling of tightness, and suppuration. A plate that is trimmed or sawed improperly begins to change its growth trajectory over time, growing into the side edge of the roller.
When an abscess or abscess is localized between the toes, if there is no pus, but there is itching, redness, skin separation, unpleasant odor and weeping, it is more advisable to suspect a mycotic infection rather than felon. Treatment is carried out by a dermatologist, mycologist.