December 07, 2020
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus (the third group of the herpes family). This disease is treated in children by a pediatrician, in adults by a therapist; the infection is characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes.
Chickenpox is an infectious disease caused by the Varicella-Zoster virus (the third group of the herpes family). This disease is treated in children by a pediatrician, in adults by a general practitioner; the infection is characterized by a profuse itchy rash on the skin and surface of the mucous membranes. The incubation period for chickenpox can range from 10 days to 3 weeks. Chickenpox is highly contagious and the virus is transmitted through direct contact with a carrier.
Children often get sick in entire groups (groups in kindergarten or classes at school). When the virus first enters the human body, it provokes chickenpox, most often this occurs at the age of 3-6 years. Having chickenpox forms a stable immune response of the body to repeated infection; after 6 years of age, 70% of children already have stable immunity to this disease.
Once infected, the virus remains latent in nerve cells and can regenerate, causing a secondary infection called herpes zoster, also called “shingles.” It usually occurs in adults aged >50 years or in frail and immunocompromised individuals. Accompanied by a painful rash that can lead to permanent nerve damage.
Chickenpox symptoms
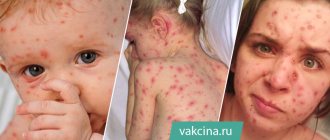
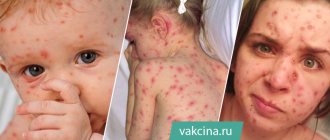
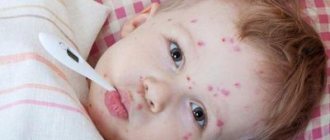
On the first day of the rash, the temperature rises; the higher its numbers, the more intense the appearance of a new rash and a more severe course are predicted. This temperature reaction lasts from 2-7 days to two weeks or more. The rashes are blisters with transparent contents, which can fester (then the contents turn white or yellow) or dry out (this is how crusts appear).
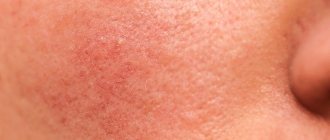
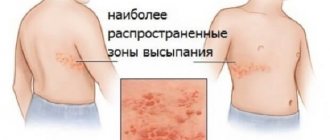
The process of rash with chickenpox is cyclical: spot - blister - crust. The appearance of the rash is accompanied by severe itching. The spread of the rash also has characteristic features: first it appears on the torso, then on the arms and legs, then on the face and under the hair. The disease is accompanied by body aches, weakness, lethargy, headache, fatigue, drowsiness, and lack of appetite.
In adults, chickenpox is accompanied by symptoms of intoxication of the body. Atypical clinical forms are also possible: rudimentary, the rash is either absent or does not develop beyond the spot stage. With hemorrhagic, a bloody mixture appears in the blisters, small hemorrhages appear on the affected areas of the skin, with bullous, along with ordinary chickenpox, other blisters appear, filled with a cloudy yellowish liquid, which take a long time to dry out. If such blisters burst prematurely, the area of skin underneath them becomes wet for a long time and does not heal. When the tissue inside the blisters becomes gangrenous, they die, ulcers form underneath them, and purification of pus is often required.
The generalized form of chickenpox is considered separately. It is characterized by damage to internal organs. It is difficult to tolerate and there are deaths. At risk are patients taking steroid hormones and the elderly. The most dangerous complications of chickenpox are damage to internal organs and the brain. The most common are pneumonia, meningitis, encephalitis, and myocarditis.
Chickenpox in adults: features of the course
According to the observations of domestic infectious disease specialists, in the structure of the incidence of chickenpox in adults, moderate forms are recorded in 85% of cases, severe forms are recorded in about 8%, and only in 7% of cases a mild course is observed, as in children.
The incubation period for chickenpox in adults usually lasts up to 21 days. Next comes a pronounced prodromal period, which lasts about 2 days. This stage is characterized by general malaise, a rise in temperature from 37 to 39 degrees Celsius, decreased appetite, lethargy, and drowsiness. Usually on the 3rd–4th day the manifest period of chickenpox begins: a rash appears on the skin, accompanied by itching.
The elements of the rash look like small nodules on a red background. Very quickly, in place of the nodules - papules - single vesicles with a thin covering and transparent contents - vesicles - form. Sometimes the contents of the vesicles are red-brown (hemorrhagic). Within a few days, the vesicles become covered with brown crusts. Sometimes their contents fester, become opaque, and a pustule forms. The rash in adults is very profuse. In approximately 50% of adults with chickenpox, the rash festeres, which is accompanied by a repeated rise in temperature to 39–40 degrees Celsius.
The eruptions occur over several days, so all the elements of a chickenpox rash can be observed on the skin at the same time: papules, vesicles, pustules and crusts.
Rashes are also observed on the mucous membranes of the mouth and eyes, on the genitals, which leads to pain when urinating and defecating.
A feature of the course of chickenpox in adults is the severity of intoxication and a long febrile period of 7–9 days or more. In adults, enlarged lymph nodes are often observed - lymphadenopathy.
Diagnostics
Typically, the diagnosis of chickenpox is made after examining the patient and determining the nature of the rash. In this case, the period that elapses from contact with an infected person until the appearance of rashes is of great importance. In addition, a scraping (smear) from the affected area, culture to detect the virus, and laboratory blood tests can be performed. Using special staining of the smear, you can determine the presence of giant multinucleated cells characteristic of this infection.
PCR analysis can detect even a small number of pathogens in the blood. Detection of immunoglobulin M antibodies may indicate ongoing infection with varicella-zoster virus. Antibodies of this class appear on the fourth day from the onset of the rash and sometimes persist for up to several months.
An increase in the level of leukocytes and ESR in a general blood test may also indicate an analysis. The level of hepatic protein ALT is most often significantly increased in patients with chickenpox. A chest x-ray is performed if a complication of chickenpox such as pneumonia is suspected.
Chicken pox in adults: what it means and how to treat it
Chickenpox in adults: what it threatens and how to treat
From a “trifling” childhood infection, chickenpox can turn into a life-threatening disease. This happens in adults who did not have the chance to encounter chickenpox in time.
chicken pox
Chickenpox is an acute viral disease that is accompanied by the appearance of a characteristic rash on the body and is transmitted by airborne droplets.
The causative agent of chickenpox is the varicella-zoster virus. This representative of herpes viruses is so widespread and contagious (infectious) that in most cases people get chickenpox at the first contact, that is, in childhood. Therefore, chickenpox is traditionally considered a childhood infection. However, 2% of people suffer from this disease into adulthood. In adults, chickenpox is more severe and is often accompanied by complications.
The source of chickenpox is always human. A person is contagious throughout the entire period of illness and for 5 days after the last element of the rash appears.
Chicken pox: the dangers of a “childhood” disease
This winter in the Novosibirsk region, experts noted an increased number of complicated forms of chickenpox. The media started talking about a mutant virus. How justified is such information and why is it really dangerous?
“
chickenpox
”
, the Sibmeda portal found out from Tatyana Ivleva, a doctor at the city vaccination office.
“Two-faced” Varicella Zoster
– Tatyana Yuryevna, what is chickenpox or, in popular parlance, “chickenpox”?
– Chickenpox is an infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets.
The causative agent is the Varicella Zoster virus (from Latin the first part is translated as “chickenpox”, and the second as “herpes zoster” or “shingles”). The complex name suggests that this virus can cause two manifestations of the disease. During primary infection, the disease occurs in the form of chickenpox, familiar to many from childhood. After the first period, the virus remains in the ganglia of the nervous system and, when conditions favorable for it arise, it can be activated, and then the second period occurs - herpes zoster or herpes zoster. The disease manifests itself as herpetic eruptions along the nerve endings, most often intercostal. In this case, severe pain may occur, which causes much more suffering than with primary chickenpox. In some people, unfortunately, the pain syndrome remains even after the herpetic elements go away, so it is not at all necessary to say that chicken pox is a “harmless childhood disease”. – What can cause the reactivation of the virus?
– First of all, age-related changes in immunity, which are often observed in older people.
Immune problems can provoke the manifestation of the virus at a younger age. Often, activation of herpes zoster is observed after viral infections, including influenza. Another category is children and adolescents aged 7-14 years who had chickenpox in very early childhood - up to two years. – What are the symptoms of primary chickenpox?
– Classic childhood chickenpox is most often manifested by a rise in temperature and the appearance on the body of characteristic rashes in the form of blisters with a depressed center and a red rim around the edge. Over time, the bubbles burst and become crusty. Parents should be aware that from the moment of the last rash, the child remains contagious for another five days. You need to understand that chicken pox is a very contagious disease due to the airborne transmission method, susceptibility to it is 100%!
The infection is also insidious in that an infected person begins to release the virus into the environment a day before the first chickenpox elements appear, thereby infecting people in contact with him. You should know that people with shingles are also contagious.
Complications of chickenpox
- What complications can occur with chickenpox?
– Fortunately, most children easily tolerate this disease, but complications also occur. Most often they are local - when the blisters become infected and secondary purulent infection occurs. The bubbles can form into huge drainage pockets, and then chickenpox becomes very severe. This virus often provokes pneumonia and meningitis - almost every year our children with such complications are admitted to the hospital and require increased attention from doctors.
Children with genetic characteristics associated with immune defects are susceptible to severe complications. Patients with blood diseases and low coagulability may experience bleeding. The virus is capable of activating a predisposition to chronic infections; a number of pathological conditions can be triggered that work in a vicious circle, from which it is very difficult to escape and this can lead to the death of the child. – This happened in January 2016 in Iskitim, when a three-year-old girl died from chickenpox?
– Chickenpox has a very low mortality rate (0.1%), however, like any disease, it exists. Unfortunately, in some years in the Novosibirsk region there are one or two cases of children dying from this “mild infection”. This, unfortunately, happened in Iskitim.
The whole difficulty lies in the fact that it is never possible to predict how a child will survive a particular disease. Of course, we can assume that children with chronic diseases and children with allergies, who already have problems with their skin, will get sick more severely, but, as practice shows, it happens that completely healthy children have a very difficult time with chickenpox and may die. Therefore, it is very important here to take the child to the hospital in case of any complication - if this is done on time, then doctors, as a rule, will be able to help even children with severe forms of chickenpox.
– After the incident in Iskitim, information appeared in the media that the virus had mutated and could cause severe complications. Should doctors sound the alarm?
– The chickenpox virus, fortunately, is not a variable virus; it is stable.
To date, there is no scientific data that would confirm its mutations. On the other hand, we can say that the population itself has become more susceptible to viral diseases. This is largely due to the active development of medicine - for example, today we are caring for children who would not have been viable a few decades ago. They often have problems with the immune system and are very vulnerable to any infections. Today, people with chronic diseases not only live full lives, but also have children themselves, passing on immune system defects. Such people are more defenseless against infectious diseases, especially in an urban environment, where everything is very crowded and cramped. – Can we say that in recent years chicken pox has become more severe?
– There are no exact statistics on this topic. Although, for example, several years ago, infectious disease specialists from St. Petersburg said that they were noticing a more severe course of the disease, since such a number of chickenpox meningoencephalitis had not been recorded before. One thing we can say absolutely for sure is that the number of complications from chickenpox is not decreasing.
Risk factors
– What factors can complicate the course of chickenpox?
– First of all, these are genetic predispositions to certain types of infections.
The second point is the presence of chronic diseases. Third are unfavorable social factors: poor nutrition, poor living conditions, poor quality child care. Lack of body weight also does not contribute to strong immunity. There is a group of patients in whom the severe course of chickenpox can be reliably predicted - these are children with oncohematological diseases. By the way, initially the chickenpox vaccine was created specifically for them, in order to “cover” these children from chickenpox infection, which can be fatal, during the period of heavy chemotherapy. – Can improper care of chickenpox elements cause complications?
– Let’s start with the fact that the treatment tactics for these elements should always be coordinated with the attending physician, who sees what is happening to the child.
Often parents believe that rashes must be lubricated with “green paint” or fucorcin, but in fact, these lubricants have only one meaning - to understand whether the child is developing new elements. There is no evidence that these solutions have any therapeutic effect for chickenpox. If we talk about local treatment with antibacterial drugs, it can be prescribed by a doctor if, for example, a child has allergic diseases. In such children, as a rule, staphylococcus lives on the skin, which can complicate the course of the infection, so the doctor will try to prevent this. – How is chickenpox treated today?
– Treatment of uncomplicated forms of chickenpox is primarily symptomatic. This is a decrease in temperature, and, if necessary, treatment of rashes on the skin and mucous membranes. In some cases, antiviral drugs may be prescribed. If chickenpox is severe, then, as a rule, treatment in a hospital is indicated.
Re-infection: is it possible?
– On forums on the Internet you can find information that there are people who had chickenpox and then became infected with it again.
What can official medicine say about this? – Experts in the field of infectious diseases say that chickenpox happens to a person once in a lifetime. But we all know and see patients who get chickenpox twice; most pediatricians have such stories. For example, there are cases when a child may have chickenpox rashes twice in one year, usually in a mild form. This can be explained by the fact that after the first episode, immunity to the disease has not formed and re-infection occurs. It is also possible that the re-infection is not classic chickenpox, but a variant of another herpetic disease with similar symptoms. There are situations when there are several children in a family, including a baby under one year old. The older child “brings” chickenpox, the little one may develop small rashes, but since he is under the protection of his mother’s antibodies, he will not develop complete immunity to chickenpox. And then such a child may get sick again in the future. As for adults, there is most likely inaccurate information about the illness suffered in childhood. In any case, if a controversial situation arises, you can donate blood and look at the level of antibodies, which will show whether the person had chickenpox or not.
– It is believed that it is better to get chickenpox in childhood, since in adults it is much more severe. Is this really true?
– If you put the question this way, then yes, indeed, it is better to get over this infection in childhood, since in adults the percentage of complications from chickenpox is 30 times higher than in children. Adults more often exhibit high temperature reactions, they have more chickenpox elements themselves, and their general well-being suffers more. Their complications are the same: purulent local reactions, pneumonia and meningitis. Here we need to pose the question differently: why get sick at all if there is an opportunity to avoid it? You can get a vaccination, which will minimize the risk of “catching” chickenpox, and even if a person gets sick, it will be in a mild form, without complications and, especially, deaths.
Protection – in vaccination
– What is the chickenpox vaccine?
– Today, only one vaccine against this infection is used in Russia – Varilrix. It belongs to the live preparations, as it contains a greatly weakened live chickenpox virus. Approved for use from 12 months of age, there is no upper vaccination threshold. Both children and adults are given 2 doses of the vaccine with a minimum interval of 2 months. Double immunization provides lifelong lasting immunity in 97-98% of those vaccinated. Most often, the vaccine is well tolerated; the most common reaction we observe is pain at the injection site for one to two days.
The chickenpox vaccine has another very big advantage - it can be vaccinated within 72 hours after contact with a patient with chickenpox. This will reduce the likelihood of getting sick by up to 80%, since the vaccine has time to develop protection faster than the virus develops in the body.
If we talk about contraindications to vaccination, they are classic - a period of acute diseases and exacerbation of chronic ones, as well as situations that are accompanied by a strong decrease in immunity. This vaccine is also contraindicated for pregnant and breastfeeding women.
– If an adult does not know whether he had chickenpox as a child, but wants to get vaccinated, can he do so?
- Yes, maybe nothing bad will happen.
But if you want to know one hundred percent, then you can donate blood to check the level of antibodies to chickenpox and, depending on the result, make a decision whether you need to be vaccinated or not. – Today, vaccination against chickenpox is paid (the price of the vaccine varies from 3 thousand to 4 thousand rubles per dose).
Is there a chance that someday this vaccine will appear in the National Vaccination Calendar and be available to all children for free? – The chickenpox vaccine is one of the candidates for inclusion in the National Calendar, and we really hope that it will appear there soon. Moreover, there are countries that have long included this vaccination in their calendars. A striking example of this is Germany. The Germans use a four-component vaccine against measles, mumps, rubella and chickenpox, because the advantage of the chickenpox vaccine is that it combines well with other vaccinations.
Parents can consult with their doctor and include it in their vaccination schedule along with other important vaccines to protect their child from chickenpox infection.
Read on the topic: Sibmeda consultation. Is it dangerous to get chickenpox during pregnancy?
If a child or adult shows signs of chickenpox, it is recommended to contact the nearest branch of the Mama Papa Ya network of family clinics.
Unlike a regular local doctor, such a specialist will arrive to the patient faster.
- The doctor has much more time to examine the patient and prescribe treatment.
- Observation over time will help to detect early signs of complications in time and begin their treatment.
- The doctor will give recommendations to all family members on how to avoid infection, paying special attention to elderly and weakened patients.
The Mama Papa Ya clinic offers chickenpox vaccination services for children and adults. To do this, you need to make an appointment with a pediatrician or therapist, who, after an examination, will give a referral to a treatment room. An examination by a doctor and the vaccination itself take little time and are available in numerous branches of a network of clinics located in Moscow and other cities. Medical services are provided at affordable prices.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
Treatment of chickenpox in adults
In most cases, treatment of chickenpox is symptomatic. To reduce body temperature, antipyretics based on paracetamol and ibuprofen are prescribed. To reduce itching and inflammation, antihistamines are used. In some cases, antiviral drugs and interferons are prescribed. Antibiotics are indicated for the abundant appearance of pustules, as well as for the development of other bacterial complications of chickenpox, strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
For the entire febrile period, bed and semi-bed rest, good nutrition, and plenty of warm drinks are recommended.
Hygiene of the skin and mucous membranes is of great importance. Rashes are treated with a solution of brilliant green, fucorcin (Castellani liquid) and other drugs with antimicrobial and antipruritic effects. While taking water procedures, you should not use a washcloth or rub with a towel.
Features of chickenpox in adults:
- high body temperature;
- severe intoxication;
- an abundance of rashes and suppuration of elements;
- lymphadenopathy;
- frequent complications such as pneumonia and encephalomyelitis.