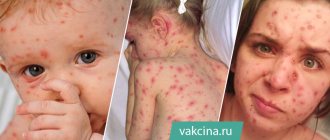
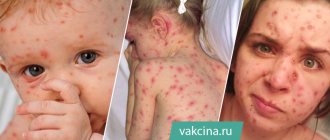
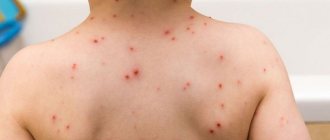
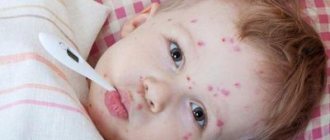
Chickenpox in adults - incubation period, first signs and main symptoms (photo)
Chicken pox or “chickenpox” is an acute viral disease that is transmitted by airborne droplets and has pronounced external manifestations. This disease is suffered only once, usually in childhood, however, many avoid this fate.
Even though this fact seems pleasant, you will most likely still get chickenpox. And it is worth saying that in adulthood this disease is more difficult to bear and brings more inconvenience both because of its appearance and because you have to get sick at home, since the disease is contagious.
All these factors knock an adult out of his usual working rhythm for some time, which is undoubtedly very unpleasant.
How can you get infected?
Chickenpox is caused by infection with the Varicella Zoster virus (HSV-3, or herpes simplex virus type 3). During the incubation period, which lasts 2 weeks, an adult may not experience chickenpox symptoms.
Doctors have noticed that the older the patient, the more time passes before pronounced signs of pathology appear. For example, the body temperature of an infected person may rise after 3 weeks of contact with a carrier of the virus.
How is the chickenpox virus Varicella Zoster transmitted? Doctors identify three routes of transmission:
- Airborne (through saliva, during sneezing).
- Tactile (close communication, kissing).
- Close contact with a person with herpes zoster.
The pathogen enters a healthy body through the epithelial tissues of the respiratory tract, then moves to regional lymph nodes. The virus enters the bloodstream along with lymph and causes intoxication syndrome. Externally, the disease manifests itself on the skin and mucous membranes in the form of blistering rashes.
Re-infection with chickenpox is possible with HIV, after chemotherapy and organ transplantation. The state of the immune system in such patients is unsatisfactory, which is why relapses of many diseases occur.
Relapses
Once contracted, the disease provides lifelong immunity. Chickenpox scars, like in the photo, are a kind of payback for this. At the same time, relapses are not excluded. So, in the future, chickenpox may return in the form of shingles, photographs of which you can see on a separate page.
WE RECOMMEND YOU TO WATCH:
Chickenpox incubation period in adults
This period of time is characterized by the absence of any symptoms and lasts from the moment of infection until the first signs of intoxication appear.
The classic development of the clinical picture suggests that the incubation period lasts approximately 2 weeks, however, the older a person becomes, the longer it takes from infection to the first symptoms. In an adult, it is considered normal if the temperature rises three weeks after contact with an infected person.
Epidemiology of chickenpox
- Chickenpox is an extremely common disease. Susceptibility to it reaches 100%. Chickenpox patients are the only sources of infection.
- Patients become infectious from the end of the incubation period until the rash appears and until the end of the next 5 days after the last element rashes.
- Viruses are released in large quantities during coughing, sneezing and talking. Chickenpox is dangerous for the fetus if a pregnant woman has it.
- Children 1 to 10 years old are especially susceptible to infection. The maximum number of cases occurs between the ages of 3 and 4 years.
Rice. 3. Chickenpox is a highly contagious disease, the susceptibility to which reaches 100%.
Symptoms and first signs
According to statistics, in adults over 18 years of age, the severity of the disease and the frequency of complications after chickenpox are the same as in a 20-year-old person as in a 50-year-old person. However, in the older population, due to possible immunity disorders and existing chronic diseases, a greater number of cases of complications of this disease are recorded.
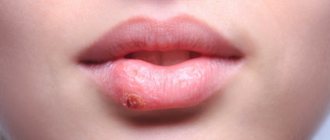
What are the symptoms and first signs of chickenpox in adults? Chickenpox begins (see photo) like a cold, flu, with general intoxication:
- Pain in muscles, joints
- A slight increase in temperature to subfebrile levels of 37.3-37.5C
- General weakness
- Headache
As soon as pink spots appear on the scalp and face, the period of rashes begins:
- Signs of intoxication of the body increase, high temperature up to 40C, chills, weakness, etc.
- A profuse rash throughout the body creates severe itching of the skin, even on the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract and in the mouth enanthems form. People after 20 years old always develop rashes on the genitals, which is accompanied by severe pain when urinating. First a spot appears, then a bubble with liquid and a depressed center. If the crust is burned with alcohol dye or torn off, a scar will remain. The bubbles then burst, releasing liquid and subsequently forming a dried crust, which, with regular processing, leaves no trace in the future. When a secondary infection penetrates the wound, the course of the disease becomes more complicated, weeping pustules appear, which after healing leave scars on the body.
- The patient's lymph nodes are enlarged - behind the ear, inguinal, submandibular and axillary, they become painful on palpation.
- An undulating course of rashes that lasts about 10 days.
- If the patient has a very weakened immune system, the rash can provoke the development of fasciitis, abscesses and even sepsis.
Sometimes in adults, chickenpox begins with signs of cerebral edema, nervous system disorders, and also as primary chickenpox pneumonia or encephalitis, with the following symptoms added:
- Nausea, vomiting
- Irritation from sharp sounds and bright lights - sound sensitivity, photophobia
- Coordination of movement, convulsions, and general muscle weakness are impaired.
Possible consequences and complications
The negative consequences of chickenpox in children are rarely diagnosed; most often, dermatological purulent complications occur - abscess, phlegmon, boils, which leave scars. If the disease is severe, the virus affects internal organs and dangerous concomitant diseases develop.
Possible consequences of chickenpox:
- Encephalitis - pathology manifests itself 7–12 days after the onset of the disease, characterized by frequent convulsions, severe headache, and impaired consciousness. In rare cases, idiocy develops.
- Myocarditis - the virus provokes the development of an inflammatory process in the heart muscle, shortness of breath occurs, the pulse rate is disturbed, and the child may complain of chest pain.
- Pneumonia – occurs in infants with neonatal chickenpox; the condition is dangerous and can be fatal.
- Nephritis is an inflammation of the kidneys that develops 10 days after the first signs of pathology appear; the disease goes away on its own and no specific treatment is required.
Since the virus can penetrate all tissues and mucous membranes, the consequences of chickenpox can be blurred vision, damage to the mucous membranes of the eyes, hepatitis, problems with the pancreas and spleen.
Forms and stages of the disease
The disease occurs with or without obvious symptoms. Dermatologists identify several characteristic forms of chickenpox:
| Light | the rash is not abundant, the condition is satisfactory, there are no secondary rashes, there are no enanthems. |
| Medium-heavy | Intoxication, weakness, and headaches were noted. Repeated rashes are observed, the period is up to five days. A specific rash is noticeable, enanthems are detected. The temperature reaches 39 degrees. |
| Heavy | pronounced intoxication, high temperature (up to 40 degrees). Numerous blisters cover the entire body, including the scalp and genitals. There is a high risk of damage to internal organs. Often the picture is complicated by a pyogenic infection. |
The hidden or atypical form has several varieties. All of them are dangerous with serious complications:
| Generalized | noted in patients receiving chemotherapy and people with reduced immunity. Internal organs, the nervous system, are affected, the brain is affected, and chickenpox pneumonia develops; |
| Hemorrhagic | difficult to treat, the prognosis for a weakened immune system is extremely unfavorable; |
| Gangrenous | the variety is characterized by the addition of pathogenic microflora, severe poisoning of the body, necrosis of certain areas of the skin, and poor health. |
Diagnostics
It is not difficult to recognize typical chickenpox after a thorough physical examination, since the disease has a classic clinical picture. The atypical form can be confused with herpes simplex, bullous dermatosis, eczema, congenital syphilis, pyoderma; laboratory tests will help differentiate chickenpox from other infections.
What tests need to be taken:
- clinical blood test to determine the level of ESR;
- microscopic examination of fluid from vesicles;
- blood chemistry;
- serological tests - RSK, RTGA.
In severe cases of the disease, a general urine test, ultrasound of the abdominal organs, CT scan of the brain, and electrocardiogram are additionally prescribed to identify which organs have been affected by the virus.
Chickenpox during pregnancy
If a woman does not have immunity to the chickenpox pathogen at the time of conscious planning of pregnancy, she will be recommended to undergo appropriate vaccination. Infection during pregnancy is dangerous for the fetus until about 20 weeks. At this stage, the virus causes intrauterine death of the fetus, which ends in miscarriage or stillbirth. It is also possible to develop severe defects that lead to disability of the born child.
At later stages, the effect of the virus on the body of both mother and fetus weakens, reaching a second peak immediately before childbirth. Infection with chickenpox in the later stages is fraught with the development of pneumonia, which can also lead to the death of the child. In such cases, special therapy with immunoglobulins and specific antibodies is carried out.
Lack of immunity to chickenpox in general is not an indication for termination of pregnancy.
How to treat chickenpox in an adult?
Comprehensive treatment of chickenpox in adults includes antiviral therapy and symptomatic measures; in complex cases, placement in an infectious diseases hospital is indicated. To avoid negative consequences, you must strictly follow medical recommendations on how to treat chickenpox in adults at home:
- Limit any types of loads. High fever and the appearance of neurological symptoms necessarily require bed rest.
- Isolate the patient for the entire “infectious” period, since susceptibility to chickenpox in people without specific immunity is 100%.
- Follow a low-carbohydrate diet with normal protein content: unsweetened dairy products, vegetables, fruits.
- Keep skin clean. It is recommended to take a daily shower at a comfortable temperature, without a washcloth, steaming or rubbing. Gently dry the wet body with a soft towel so as not to damage the crusts.
- Increase fluid intake, priority is berry fruit drinks.
- Carry out antiviral therapy. The drugs Acyclovir, Virolex, Panciclovir and others block the reproduction of the virus, stop the growth of rashes, and prevent the generalization of infection and complications.
- Reduce the temperature if it rises to 38 degrees. Paracetamol and ibuprofen can be used as an antipyretic. Taking aspirin for chickenpox is strictly prohibited!
- Treat rashes with alcohol- and water-based antiseptics to relieve itching and drying. Apply the solution, gel, ointment after bathing pointwise, 1 – 2 times a day.
- Take antihistamines (Suprastin, Diazolin, Tavegil). They reduce the itching of chickenpox in adults and promote faster drying of the elements.
- Include antibiotic ointments in treatment if a bacterial infection is identified.
- If papules appear in the oral cavity or on the genitals, rinse with antiseptic solutions (furacilin, weak potassium permanganate, boric acid).
- Place a person in a hospital for any manifestations of severe or atypical chickenpox.
How long chickenpox lasts in adults depends on the severity of the condition and the intensity of the rash. In mild cases, about 2 weeks pass from infection to complete recovery, in more complex cases it takes a month or more: up to 21 days – latent period, up to 10 days – wave-like addition, up to 20 days – cleansing of the skin.
Treatment with brilliant green
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
Contrary to popular belief, chickenpox is not treated with brilliant green. Zelenka in the treatment of a disease is nothing more than a marking method necessary to track new rashes and the course of the disease. It is much more problematic to trace the stage when the chickenpox depicted in the photo ceases to be dangerous to others without brilliant green.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is not officially recognized by medicine, but has the right to exist.
- Immunity can be supported with a tincture of chamomile flowers, calendula, basil leaves and lemon balm. For the same purpose, you can use a mixture of lemon juice and honey, which should be taken three times a day, 1 tsp.
- To reduce pain and itching on the skin, use a soda solution (1 glass of warm water, 1 teaspoon of soda), which is used to dip the affected areas.
- Baths with chamomile or calendula, celandine remove the manifestations of chickenpox.
- At elevated temperatures and if you have a headache, viburnum drink, sea buckthorn tea, rosehip infusion and cranberry juice help well.
- At home, you can brew chopped parsley leaves and drink 1-4 glasses several times a day.
- Those who do not tolerate the acute period of intoxication well can try fresh celery juice.
- Skin itching and pain disappear perfectly under the influence of tea tree oil, applied directly to the elements of the rash.
- Blueberries have an excellent antiviral effect in any form.
Traditional methods do not replace qualified medical care and taking medications prescribed by a doctor.
Prevention
Usually people get chickenpox in early childhood, since the pathogen is extremely easily transmitted from person to person. However, some people reach adulthood without having immunity to the Varicella Zoster virus.
To avoid getting sick, it is recommended to undergo a special vaccination, after which lifelong immunity will be developed, as if the patient had chickenpox. You can get vaccinated even if you had contact with a sick person and no more than 72 hours have passed since that contact.
Varicella zoster virus
The chickenpox virus is quite large. It is a member of the family Herpetosviridae (Varicella Zoster). In addition to chickenpox, which mainly affects children, the virus is the cause of herpes zoster, which most often affects older people.
Rice. 4. The photo shows the chickenpox viruses Varicella zoster.
The life and reproduction of viruses occurs only in the human body. In the external environment, viruses are weakly resistant, they die quickly, being in the external environment, they persist in droplets of saliva for no more than 15 minutes. Viruses quickly die when heated and exposed to ultraviolet radiation. With chickenpox, viruses are contained in large quantities in the vesicles during the first 4 days of the disease. Then their number sharply decreases and by the 8th day they disappear completely. With repeated rashes, the patient again becomes highly contagious.
Chickenpox vaccine for adults
The chickenpox vaccine is not included in the mandatory vaccination schedule and is used only at the request of the person. Vaccination against chickenpox among adults can be used at any time, especially if the person has not previously suffered from this pathology in an active clinical form. In most situations, persons whose work involves daily contact with children are interested in vaccination against chickenpox, since chickenpox is a fairly common infectious pathology among organized children's groups.
Currently, vaccines such as Okavax and Varilrix, which exhibit identical effectiveness, are used to vaccinate against chickenpox in adults.
- Vaccination using the Varilrix vaccine is used in most situations as an emergency preventive measure, and its effectiveness directly depends on the time of use. Thus, in a situation where more than 72 hours have passed since a healthy person came into contact with a chickenpox-infected patient, vaccination is considered irrational. Vaccination against chickenpox using the Varilrix vaccine should be carried out twice at intervals of three months. Among the contraindications to the use of the Varilrix vaccine, it should be noted that the patient has signs of immunodeficiency or any acute infectious pathology.
- The Okavax vaccine is a live chickenpox vaccine and is approved for use in both children and adults. Vaccination using Okavax is a subcutaneous injection of one dose of the drug in the projection of the outer surface of the shoulder. In most situations, vaccination against chickenpox in adults proceeds without complications, however, in some situations, the patient may experience a short-term local reaction in the form of slight swelling, thickening or hyperemia in the projection of the direct injection. An absolute contraindication for vaccination against chickenpox using a live vaccine is any trimester of pregnancy and severe somatic pathology accompanied by immunodeficiency.
In a situation where vaccination against is carried out routinely in relation to a woman of reproductive age, it should be carried out no later than three months before the expected pregnancy. Active synthesis of specific antibodies against the chickenpox virus in adults, which is observed after vaccination with a live vaccine, may be accompanied by the appearance of a low-intensity rash on the skin, the pathomorphological elements of which are similar to those of chickenpox. This condition is considered by infectious disease specialists as reactive and does not require drug correction. The effectiveness of chickenpox vaccination has a limited duration of thirty years.
What to do if scars appear after chickenpox?
There are various options to solve this problem:
- Ointments and gels for the treatment of scars. A small amount of gel is rubbed into the scar 2-3 times a day. For old scars, apply the gel under the bandage at night. The course of treatment can take from 1 month to a year. For treatment the following are used: Contractubex; Aldara; Dermatix; Kelofibrase; Skarguard.
- Chemical peeling using phenol. Under the influence of aggressive chemicals, the keratinized layer of the epidermis and dermis is removed. After the epidermis is restored (takes up to 2 weeks), the skin becomes smooth.
- Injection of collagen under the skin. The substance fills the skin defect and stimulates the formation of connective fibers.
- Microdermabrasion is the mechanical polishing of the skin with particles of a solid substance (diamond). As a result of microtraumas, collagen production is activated. The procedure allows you to even out the skin texture and make scars less noticeable.
- Laser skin resurfacing. A focused laser beam penetrates the superficial layers of the dermis and heats them, evaporating the water. After the regeneration of skin cells, its surface is leveled. Caution: Carbon dioxide laser treatment may cause the appearance of a hypertrophic keloid scar that rises above the skin. Therefore, an erbium or carbon dioxide laser is used.
Before use, you should consult a specialist.