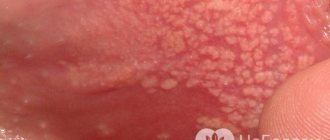
Human papillomavirus is one of the most common sexually transmitted infectious diseases. A certain percentage of people live with a virus that does not manifest itself in any way in a latent state, without even knowing about its presence in the body. But in some cases, HPV causes inconvenience. For example, the manifestation of a virus in the form of warts or genital warts on the genitals is perceived as an aesthetic defect. But this is not even the true threat of the disease. At first glance, a harmless papilloma on the genitals can degenerate and take on a malignant form. In this case, the diagnosis is oncology. Is it possible to prevent such risks?
Important: The International Agency for Research on Cancer identifies 1.5 dozen strains of papillomavirus that lead to the development of cancer. The most dangerous (up to 90% of cancer cases) are the 16th and 18th types of the virus.
Specialists at the Lasersvit Mole Diagnostic Center talk about the causes of papillomas on the genitals, the threats and effective methods of combating them. The leading specialized clinic in Kharkov offers services for the diagnosis and treatment of HPV on the genitals. You can make an appointment and consultation with a dermatologist by phone. In the meantime, doctors at the medical institution are answering the most frequently asked questions related to genital HPV.
How does HPV manifest itself on the genitals?
Genital papilloma may look like a small bump, a hair from the epidermis, or a ball on a stalk. This can be a single growth or a group of formations in the intimate area, a flat wart or a large growth similar in shape to cauliflower. What unites them is their location - neoplasms appear in the anorectal area, in the perineum, on the scrotum and directly on the penis in men, on the labia and in the vagina in women.
Important: HPV strains that cause papillomas of the vagina, labia, scrotum and head of the penis rarely provoke the appearance of growths on the oral mucosa. These are papilloma viruses 6, 11, 16, 18, 33, 35 and some other types. Laboratory tests can determine the exact strain of the virus. Well, such a symptom as growths on the inside of the lips and cheeks should be a reason to consult a doctor.
Causes of papillomas in the intimate area
Papillomas, or genital warts, in intimate places in women have a viral etiology. HPV is transmitted exclusively from person to person and leads to changes in the pattern of tissue growth. There are many types, or strains, of the virus that cause the growth of benign warts in women and provoke cancer of the vagina, cervix, and anus.
All strains of the virus are divided into groups according to their ability to induce malignant transformation of tissues.
| Degree of oncogenic risk | Type of human papillomavirus |
| Low | 3, 6, 11, 13, 32, 34, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 51, 61, 72, 73 |
| Average | 30, 35, 45, 52, 53, 56, 58 |
| High | 16, 18, 31, 33, 39, 50, 59, 64, 68, 70 |
The growth of genital warts in most cases is provoked by HPV strains 6 and 11.
Diagnosis and clinical manifestations
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out through visual examination and laboratory tests of blood, skin, and mucosal tissue samples. As a rule, it is enough for a gynecologist, dermatologist, urologist or other medical specialist to examine the genital area to suspect an infection. After all, as mentioned above, the human papillomavirus on the genitals manifests itself as unsightly growths.
Important: HPV enters the body through microtraumas of the skin and mucous membrane. He can “sleep” for several months and even years. In people with strong immunity, doctors often record self-healing. Well, when the body’s protective functions are weak or under the influence of unfavorable factors, the virus is activated. Genital papillomas appear in men and women.
Clinical manifestations of the pathology are chaotic division of epithelial cells. Many patients complain of discharge and itching. But the main symptom of the disease remains condylomas that grow at the entrance or even inside the vagina in women, in the labia minora, near or inside the anus, around the genitals in men.
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe cytology of cervical tissue samples, PCR testing, and smears for concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
Diagnosis of papillomas in intimate places in women
When genital warts appear in the genital area, patients usually turn to a dermatologist and gynecologist. When conducting diagnostics, the doctor:
- interviews the patient;
- studies the history of the development of the disease;
- examines the external genitalia;
- takes a cytological smear (scraping of cells from the cervical canal and vaginal part of the cervix for evaluation under a microscope);
- conducts a gynecological examination;
- performs a colposcopy (examination of the vagina, cervix and the initial part of the cervical canal using an optical device - a colposcope);
- takes material for histological examination if he suspects the malignant nature of the formation;
- recommends taking blood to determine HPV type using polymerase chain reaction (PCR);
- screens for sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
If genital papillomas located in the urethra are detected, an examination by a urologist and urethroscopy may be necessary. It is mandatory to screen your sexual partner for the presence of HPV and STIs.
Papillomas on the genitals: causes of pathology development
The most common route of infection is direct contact, in which the skin and mucous membranes of the virus carrier and a healthy person come into contact. As a rule, this is sexual contact. Although there is a risk of infection of the child from the mother, the household method is through personal hygiene items. You can also become infected with HPV in common areas – swimming pools, showers.
Important: With each new sexual partner, the risk of infection for a healthy person increases by 20%. Unfortunately, standard protective equipment used during sexual intercourse does not protect against HPV, since latex products do not protect all parts of the genital organs from contact.
The causes of infection are not as important as methods of combating it. After all, the risk of direct or household infection is very high. The main thing is to start treatment on time to avoid complications. It is noteworthy that Western scientists understand the importance of the problem. Up to 6 billion dollars a year are allocated for HPV research and the development of new treatment protocols in the USA alone. But a medicine that will cure the virus once and for all has not been found. However, today’s methods of combating pathology are quite effective with timely access to a specialized medical institution.
Probability of infection
HPV infection of the genitals and perineum is highly contagious, or contagious. Infection during a single sexual contact with a partner who has the virus occurs in six out of ten cases. The possibility of genital warts increases even more in the presence of a number of conditions.
| Predisposing factor | Characteristic |
| Young age | Most often, clinical signs of HPV infection appear in patients aged 20 to 24 years. In general, the age range from 17 to 33 years is the most likely for women in terms of the growth of papillomas in intimate areas. |
| Early sexual debut | Early onset of sexual activity, when the processes of hormonal changes have not yet been completed, is a factor that increases the risk of genital papillomatous formations. |
| Frequent change of sexual partners | A large number of sexual partners, frequent and promiscuous sexual contacts significantly increase the chances of contracting human papillomavirus infection. |
| Unprotected sexual contacts | Barrier contraception - the use of a condom - still remains the only easily accessible and relatively inexpensive means of possible, but not absolute, protection against HPV. It is impossible to completely get rid of the likelihood of infection with its help, since a condom may not isolate all contacting areas of damaged skin. But unprotected sexual intercourse is an almost guaranteed infection. Unprotected anal sex is an even greater risk factor, as it is often accompanied by microtrauma to the mucous membrane and skin. |
A combination of factors greatly facilitates the possibility of infection.
Why are papillomas on the genitals dangerous?
The disease must be treated. This is a strong recommendation from both specialists from the World Health Organization and leading dermatologists-oncologists of Ukraine. In addition to the fact that papilloma on the labia or papilloma on the penis looks extremely unattractive, the disease, as mentioned above, is also dangerous.
Let's start small. When wearing tight underwear, during hygiene procedures, or during intimate caresses, the growth can be injured. And this is fraught with bleeding and secondary infection.
Important: The intimate area takes on an ugly appearance. This may cause disgust on the part of the sexual partner. Without treatment of the pathology, the area where the growths are located may increase. New areas of skin are gradually involved. The formations grow, over time they can interfere with urination and defecation.
If the outcome is unfavorable, HPV in the vagina and on the penis can take on a malignant form. A benign condyloma yesterday can become an oncological tumor with metastasis to the pelvic organs tomorrow. That is why you should not ignore the problem.
Important: Aggressive types of HPV cause cervical cancer, cancer of the small lips, vagina, penis and anus.
Traditional methods
There are many folk recipes that allow you to get rid of papillomatous formations at home (which in no case should be torn off). For removal use: celandine, garlic, lemon juice, hydrogen peroxide. All of these products are dangerous for use in the intimate area. You should also remember that you cannot cure an infection simply by getting rid of visible growths. To combat the virus, systemic therapy is necessary, so it is better not to self-medicate, but to contact specialists immediately.
How to get rid of genital papillomas?
Despite the scale of research and understanding of the problem by the medical scientific community, it has not been possible to develop specific drugs for the treatment of HPV, as already mentioned. Some countries offer vaccination against the virus at an early age. However, high positive results cannot be achieved with this measure. After all, the vaccine is effective for a fairly short time, but the risk of infection is present throughout life.
Important: The HPV vaccine can only protect up to a certain point. For example, young people who have not reached puberty and have no history of sexual contact are offered to use this type of protection against the virus. After all, it is during adolescence, when the first sexual experience is acquired, that the greatest change of sexual partners is noted, weakened immunity is diagnosed, and infection most often occurs.
But if you couldn’t protect yourself from the virus, you can fight it. An integrated approach to treatment includes:
- measures to strengthen the immune system, because the body’s internal defenses can suppress the activity of the virus;
- taking antiviral drugs that chemically inhibit the spread of the virus;
- removal of papillomas on the genitals, oral cavity and other parts of the body.
Important: If HPV is detected in one partner in a couple, treatment is carried out on both of them, because the risk that both are infected is more than 80%. An adequate, gentle treatment program is developed for an individual patient or couple, taking into account the manifestations of the disease and the type of virus identified through laboratory tests.
There is a chance of self-healing, but it is quite low. And not in a couple where there will be constant relapses. At the same time, a well-chosen treatment tactic by a doctor allows you to get rid of the pathology quite quickly.
Important: It is strictly not recommended to remove papillomas at home, since the use of aggressive media based on vinegar and iodine is dangerous to health. An extensive tissue burn may form at the site of exposure. In this case, self-medication will not bring the desired result. After all, the skin tumor must be removed completely “at the root.” Only in this case it will not grow again.
Do not try to remove warts at home or in a beauty salon. Such treatment does not provide a complete picture of a person’s health status. The type of virus is not determined, and antiviral therapy is not carried out. This means that the symptoms are only muted, and the problem gets worse.
Medical methods for treating genital and other types of papillomas are:
- Radio wave method.
- Laser method.
- Use of liquid nitrogen.
The best of them today is burning out tumors with a laser. A safe, bloodless and painless method has virtually no contraindications. One or two warts are removed in 5 minutes. Hospitalization of the patient is not required, as the procedure is performed on an outpatient basis. Immediately after micro-surgery, a person can return to his usual lifestyle.
The laser burns out pathological tissue completely and without a trace. There are no scars or scars left on the skin. Papilloma on the genitals or in the perineum is removed forever. It is enough to look at the photos of the skin before and after the procedure to be convinced of this.
You can learn more about laser removal of warts at the Lasersvit clinic at your appointment. You can sign up for a consultation right now at a time convenient for you.
How are papillomas on the genitals in men removed?
Many men are embarrassed by warts on the penis and try to remove them at home using various aggressive media. This is a harmful practice that carries a high risk of complications. A secondary infection may be added to a skin burn. In this case, the treatment will be long. At the same time, it is not difficult to get rid of penile HPV if you go to a specialized medical institution.
Our clinic employs qualified dermatologists who clearly know how to treat papillomavirus on the penis. Rest assured, in a fairly short period of time there will be no trace of the pathology left.
We use a laser method that allows us to target the overgrown tissue of the epidermis. Adjacent tissues are not damaged. And since the capillaries are immediately cauterized, no bleeding occurs.
How are papillomas on the genitals of women removed?
Due to the structural features of the female genital organs, removal of papillomas in women is somewhat more difficult. The papillomavirus on the genitals of women often spreads not only to the external genitalia, but also to the vagina and cervix. Therefore, the removal of warts after a thorough examination, taking tissue samples, in case of external manifestations is carried out by a dermatologist, and in case of internal manifestations, it is carried out by a gynecologist. Any independent attempts to get rid of papillomas are unacceptable and dangerous.
Reviews of methods of treating papillomas
Patient reviews about the treatment of papillomas:
- Drug treatment. After using ointments for papillomas (Viferon, Oxolinic ointment), patients note a quick and guaranteed effect after 1-1.5 months. Many patients choose this method of therapy because it has proven to be a gentle and at the same time effective method.
- Laser removal. After laser removal of tumors, patients were satisfied that they were performed quickly and painlessly. The effect is observed immediately after the procedure, but in some cases it is necessary to resort to laser removal again, since papillomas form again.
- Cryodestruction. Patients were satisfied with the effectiveness of this method and the speed of implementation. Few people have reported slight pain during the procedure. The disadvantages include high cost and long healing time with the need for a repeat procedure.
- Diathermocoagulation. Among the advantages, patients note painlessness, speed and absence of traces after the procedure. The disadvantages include an unpleasant odor during the destruction of pathological formations and a long healing process. In addition, the treatment site should not be wetted for several days.
- Folk remedies. When using folk remedies, many people highlighted advantages such as painlessness, but among the disadvantages, patients noted a long course of treatment and ineffectiveness in some cases.