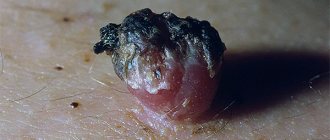
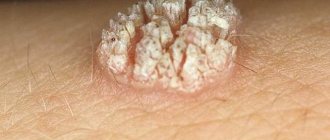
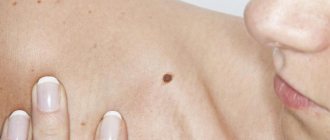
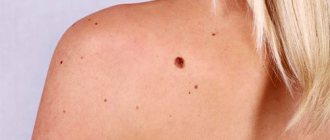
Anal warts are just one of the types of manifestations of HPV (human papillomavirus), which is very common these days. In this case, the disease manifests itself in the form of dry growths or genital warts, concentrated around the anus and in the adjacent area of the rectum.
Often, such neoplasms merge with each other, forming conglomerates, which in exceptional cases completely block the anus and complicate the process of defecation. As a rule, this happens if, in addition to HPV, the infected person suffers from diabetes mellitus or an immunodeficiency virus.
What types of condylomas, papillomas and warts are there?
Warts are growths on the skin or mucous membrane, have a pea shape and a rough surface, and can be localized in any part of the body (most often appear on the hands, face, feet). Papillomas are “pedunculated” growths that appear in folds of the skin where fluid can accumulate (knees, elbows, neck). Condylomas are a type of wart that affects the genital area (genitals, anus). Warts can disappear (shrink out) and appear again, unlike papillomas, which do not disappear on their own.
Based on their clinical appearance and location, the following types of warts are distinguished:
- common warts;
- filamentous warts;
- flat warts;
- palmar and plantar warts;
- mosaic warts;
- anogenital warts (genital warts).
How are anal warts treated?
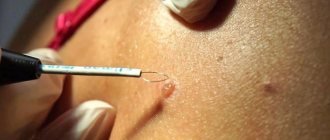
Laser therapy is a method of removing warts.
Comprehensive treatment of anal warts includes two main aspects: fighting the virus that became the root cause of the disease and getting rid of growths on the skin that interfere with normal life.
Today, there are a huge number of ways to safely remove papillomas. Here are just a few of them:
- Laser therapy. The essence of the method is a targeted thermal effect on the affected areas of the skin, which entails the “evaporation” of warts.
- Electrocoagulation. In this case, the destruction of wart cells and the formation of a scab in its place occurs due to exposure to electric current. This procedure is quite painful and, therefore, is performed exclusively under local anesthesia.
- Excision with a radio wave knife. During such an operation, the papilloma is cut off using special equipment, and the wound remaining in its place is immediately cauterized painlessly.
- Cryodestruction. Using this technology, the affected areas of the skin are filled with liquid nitrogen, which entails the death of the warts.
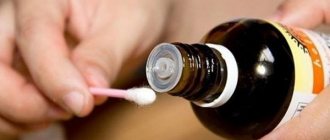
- Treatment with chemicals. The essence of the operation is to burn out (even to the point of necrosis) areas of skin affected by warts using products based on triacetic acid.
In order for the treatment of anal warts to be as successful as possible, doctors often ask their patients to follow some simple recommendations. So, in order not to provoke a relapse of the disease, you need to:
- completely quit smoking and alcohol;
- eat properly and balanced;
- to live an active lifestyle;
- be regularly checked by relevant specialists (proctologist, dermatovenerologist and gynecologist or urologist).
What causes anal condylomas, papillomas and warts?
Anal papillomas (genital warts) are growths in the form of warts on the skin around and inside the anus. The cause of anal papillomas is the human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is an infection that is transmitted from person to person through sexual contact (STI), through direct contact with the mucous membranes and skin of an HPV-infected person.
The infection can remain hidden for a long period. The virus actively manifests itself during a period of weakened immunity. Anal condylomas appear as small growths and in most cases do not cause pain or discomfort. A number of reasons provoke the growth and spread of anal warts to different parts of the genitals:
- chaotic sex life (unprotected sexual intercourse, sex life in early years);
- alcohol abuse, smoking;
- long-term treatment with antibiotics;
- chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and genitourinary system.
What types of anal warts are there?
Genital warts are a type of anal wart.
Depending on their appearance, manifestations of HPV in the form of anal warts can be divided into several large groups. Their classification will look like this:
- Genital warts. These formations look like elongated “papillae”. When several warts are concentrated in one place, they resemble a cockscomb in appearance.
- Papules. Such formations are characterized by small sizes and the absence of “finger-like” (in other words, elongated) elements. In small quantities, often almost invisible above the skin.
- Common warts. As a rule, these neoplasms look like flat spots and are distinguished by a wide variety of shapes, colors and sizes.
- Buschke-Lowenstein condylomas. These formations are quite rare in practice. They differ from ordinary condylomas by their unusually large, almost gigantic size.
- Bowen's disease. With this diagnosis, neoplasms affect the entire area of the mucous membrane in the anus. The second name for this disease is intraepithelial neoplasia.
Despite the fact that HPV (especially types 16 and 18) often provokes the development of malignant tumors and other serious diseases, the appearance of anal warts in itself is not a cause for alarm. Typically, such reactions are caused by the entry into the body of subtypes of the virus numbered 6 or 11, each of which is known for its low oncogenic activity.
Symptoms of anal condylomas, papillomas and warts
Anal warts are usually painless and begin as small bumps that are difficult to notice. Sometimes anal condylomas are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- itching in the anus;
- sensation of swelling in the anal canal;
- discharge of mucus from the anal canal;
- pain during bowel movements;
- burning and discomfort in the anal area;
- blood in the anus.
Diagnosis of condylomas occurs through a visual examination by a proctologist. The proctologist will examine the skin around the anus and examine the anal canal using an anoscope.
About the prevention of anal warts
It is important to understand that there is no 100% guarantee of avoiding infection with HPV (and, in particular, anal warts). However, certain measures can help minimize this risk. Doctors give the following recommendations on this matter:
- It is important to regularly undergo complete medical examinations, including examination by a proctologist, dermatovenerologist, as well as a gynecologist or urologist.
- Timely vaccination against HPV helps reduce the risk of contracting this disease several times.
- During each sexual intercourse (especially not with a regular sexual partner), you should use condoms.
Treatment methods for condylomas
Condylomas have the ability to grow rapidly, so their removal is necessary. In addition, condyloma is capable of degeneration into a malignant tumor. There are several ways to treat condylomas:
- drug treatment of condylomas;
- cryotherapy (freezing condylomas with liquid nitrogen);
- electrocautery (removal of condylomas using an electrocoagulator, which produces an electric current for cauterization);
- laser removal of condylomas;
- radio wave method for removing condylomas.
Treatment of condylomas with topical medications is possible if the condylomas are small in size and located only on the skin. In some cases (for larger condylomas), surgical excision of the condylomas may be required.
Condylomas may reappear after removal because HPV is a chronic infectious disease that cannot be treated. Therefore, it is important to follow preventive measures and carry out follow-up visits to the proctologist, especially in the first three months.
Often, genital warts appear in women during pregnancy, although there were no symptoms of HPV before. Increased growth of condylomas occurs due to changes in hormonal levels and the immune system. Genital warts do not pose a great risk to the woman and the unborn child. However, consultation with a gynecologist is required. Removal of condylomas during pregnancy is required as a last resort and is not carried out earlier than the 28th week, because by this time all the child’s organ systems have been formed and there is no threat of negative effects on him from medications.
Treatment of genital warts and other types of papillomas is carried out medically. Minimally invasive, painless removal of warts, papillomas, and condylomas is performed under local anesthesia; if the growths are extensively localized, the procedure can be carried out in stages. Along with the operation to excise warts, papillomas, and condylomas, therapy is carried out aimed at strengthening the protective function of the body.
How are anal warts diagnosed?
If you detect symptoms of HPV, you should contact a proctologist.
A doctor specializing in this problem can confirm or refute the diagnosis of anal warts.
Therefore, if you discover symptoms of one or another type of HPV, any health-conscious citizen is obliged to make an appointment with a proctologist and dermatovenerologist.
If warts are localized not only in the anus, but also on the external genitalia, it would also be a good idea to visit a gynecologist (for women) or a urologist (for men).
Prevention of condylomas, papillomas and warts
The appearance of papillomas, condylomas and warts can be prevented by observing the following preventive measures:
- get tested for STDs, including for your sexual partner (every six months, if there is more than one partner);
- timely treatment of STDs;
- use of contraception;
- vaccination against human papillomavirus.
Prevention of condylomas involves personal hygiene and STD prevention. An effective preventive measure is HPV vaccination. Vaccination is recommended to prevent HPV infections and HPV-related diseases, including some types of cancer. The Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) recommends HPV vaccination at the age of puberty and before sexual debut.
Where can you catch HPV?
HPV is rarely transmitted from mother to child.
The most common way of contracting HPV in general and anal warts in particular is considered to be sexual intercourse.
There is a particularly high likelihood of contracting the virus by having unprotected anal sex (perhaps this is why patients with this diagnosis are so often found among homosexuals).
As a rule, infection occurs as a result of microtrauma of papillomas and subsequent mild bleeding, which is almost inevitable during intimate intimacy with the carrier of the disease.
Once in the body, the virus is initially in a “dormant” state and is not characterized by any external manifestations. That is why it is often impossible to diagnose HPV at an early stage of the disease. It is worth considering, however, that if in a monogamous relationship one of the partners suffers from anal warts, the other most likely has a similar diagnosis.
Where do anal warts come from?
Who is at risk of developing condylomas on the anus? There will be an increased risk of infection and spread of warts around the anus and inside the anus if you:
- like to have unprotected sex;
- have several sexual partners;
- allow anal sex, incl. in hetero-homo- and bisexual relationships;
- being a virgin, you allow the penis to penetrate the rectum;
- practice surrogate types of intimacy with the entry of dildos through the anus;
- had anal sex or had other intimate contacts with a carrier of HPV or condylomatosis;
- you are sexually active from an early age, often change partners;
- you have reduced immunity or have chronic diseases of the genital area.
Diagnostics
1. Who would benefit from being checked for the possible presence of condylomas of the anus and anus? Firstly, for those who have complaints about the feeling of a foreign body in this area, have felt some kind of rash or have any other discomfort. Secondly, these are people who have the risk factors listed above.
2. What diagnostic methods are there and which doctor should I contact for condylomas and who in the clinic deals with this problem? A gynecologist can diagnose anal condylomas in women by visual examination in a chair. Some specialists use special solutions during the examination. This causes the bumps to appear white and more visible. As for anal condyloma, examination to identify it is best done in the knee-elbow position. Instrumental examination includes an internal examination of the rectal mucosa using a device called an anoscope or a special rectal speculum.
Of course, the presence of papillomatous formations in the anal area in a woman requires a thorough examination for the possibility of pathology in neighboring places (on the vulva, labia, urethra, etc.), including using colposcopy, and testing (Dig. test and smear for oncocytology). Those who want to see photos of anal condylomas can contact any well-known search engine, because For humanitarian reasons, we did not dare to publish such photographs on our website.
Symptoms of warts on the butt
Photo of warts on the buttocks
The development of warts on the butt in men and women is evidenced by small skin lumps, which over time grow into round-shaped formations with a diameter of up to 2 cm. In this case, the color of the structures practically does not differ from the color of the skin. In rare cases, if the problem is ignored, warts on the buttocks in women and men can grow up to 3 cm in diameter and acquire a rough structure.
Important! If you do not systematically palpate the soft tissues and do not detect compactions in time, not only the growths themselves increase, but also their number.
A wart on the buttock can also be located in the anus or fold. Such a place is subject to high humidity and frequent friction with the skin or underwear, which can provoke injuries to the formations, and it will not be possible to conduct an independent examination of this area of the body. In this case, the reason for a visit to the doctor may be pain when moving, bleeding after bowel movements, or a burning sensation.
It is possible to determine the presence of human papillomavirus in the body before the development of formations only with the help of specialized tests. Such tests can be carried out at the patient's initiative. In case of a positive result, it is recommended to use preventive measures to avoid the development of growths.
- See also what papillomas in the anus look like in women