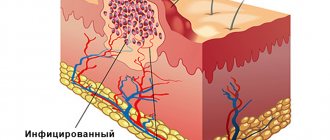
Papilloma is a formation that can appear on the skin or mucous membranes of a person and, without appropriate intervention, lead to serious consequences, including the development of cancer. Papillomas on the human body signal the presence of HPV (human papillomavirus) in the body. At the moment, a fairly large number of varieties of this virus have been identified. It has also been proven that about 70% of the sexually active population are its carriers.
Medical is a clinic that provides a wide range of medical services, including in the field of urology. The clinic’s specialists approach the treatment of each patient individually: this applies to both the timing of treatment and the treatment measures themselves, which most often allows for very effective results.
Papillomas in men: causes of occurrence
The cause of the appearance of papillomas on the body in men and women is a virus that can enter the body in various ways:
- Due to unprotected sexual contact: the most common type of infection, including because a person can be a carrier of the virus for a long time, without even knowing it, since the virus has the ability to manifest itself only under the influence of external factors. Transmission is also possible through direct contact of mucous membranes. In this case, the risk of infection increases if the skin or mucous membranes are damaged (there are cracks, scratches, cuts, etc.). Due to the prevalence of this cause of infection, it is understandable that quite often papillomas (condylomas) in men and women appear in the intimate area, at points of contact, from which the risk of infection in men is usually higher, due to their greater sexual activity, but the mucous membranes of women are less protected .
- Through household contact: it has now been proven that the HPV virus can enter the human body through ordinary contact (even a handshake), especially in public places (baths, swimming pools, gyms, etc.).
It is also necessary to remember that infection with the specified virus does not mean its manifestation.
Most often, the disease becomes more active and makes itself felt if:
- the patient's immunity is weakened;
- there were great physical or mental stress, stress, exhaustion;
- There are various types of sexually transmitted diseases.
HPV in men: consequences
The virus can cause condylomas, or genital warts, which, as the name suggests, are located in the groin, as well as on the head of the penis and foreskin. This kind of condylomas has very dangerous consequences for men and requires treatment.
Condylomas on the penis can lead to a narrowing of the foreskin, which can make it difficult to expose the head of the penis and lead to problems in your personal life.
It must also be remembered that in some cases such formations are not an indicator of HPV, but of other sexually transmitted diseases that have not yet manifested themselves (for example, syphilis).
Another danger of HPV is that a carrier of the virus can transmit it to their partner, also putting them at risk of developing cancer. Transmission of the virus is also possible to the fetus from an infected mother, so couples wishing to have children should pay special attention to HPV and other diseases of this kind.
Symptoms of virus infection
At the clinical stage, visible signs of infection appear. The symptom complex depends on the strain of the virus and the location of the affected area. Possible symptoms include:
- the appearance of warts and papillomas on various parts of the body;
- in women: a feeling of discomfort in the vagina, painful sexual intercourse, bleeding from the cervix outside the menstrual cycle;
- copious discharge with an uncharacteristic odor;
- the formation of benign tumors on the genitals, in the anus, in the urethra;
- associated diseases: inflammation of the cervix (cervicitis), bacterial vaginosis, dysplasia of the cervical epithelium.
Indirect symptoms of the disease are chronic fatigue, problems with concentration, physical weakness, and enlarged lymph nodes.
HPV in men: symptoms
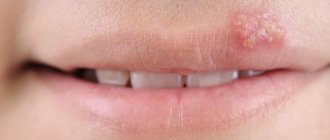
Most often, HPV can be present in the human body for a long time without manifesting itself. However, the most important sign (symptom) of the possible presence of HPV in men and women is the appearance on the skin and mucous membranes, including in the groin or pubic area, of condylomas and papillomas - warts, lumps and irregularities of the skin, the color of which does not differ from the main one skin.
Condyloma is a genital type of papilloma, which looks like a small growth attached to the mucous membrane with a kind of “leg”. The size of condyloma can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters - in the latter case we are talking about an accumulation of condylomas.
Such papillomas can appear on the head of the penis, on the foreskin, and also around the anus (then there is a high probability that condylomas may also be in the rectum). Most often they are painless, but in some cases men may experience additional symptoms of the human papillomavirus if the disease manifests itself as:
- pain when urinating, defecating, or having sex;
- bleeding of condylomas: sometimes ulcers that do not heal for a long time may form in their place;
- also sometimes condylomas can itch.
The listed symptoms usually indicate damage to the condyloma.
The appearance of papillomas, in addition to the presence of HPV in the human body, also indicates a depleted immune system and the possible presence of other sexually transmitted diseases. In addition, some types of papillomas, in particular condylomas on the head of the penis, have a high oncological potential, so when signs of the disease are first detected, you should consult a specialist. The sooner you start treating the human papillomavirus, the more chances a man has to avoid serious health consequences of condylomas. (All of the above applies to women as well.)
Initial appointment
An initial appointment with a specialist involves a thorough visual examination of the patient’s mucous membranes and skin, as well as questioning him and prescribing tests.
Although most often papillomas have a characteristic appearance, additional tests and diagnostics make it possible to absolutely accurately determine the presence of HPV in the patient’s body.
If HPV infection is suspected in men, the following tests are usually prescribed:
- blood test (for condylomas, also analysis of urethral discharge): modern diagnostic methods make it possible to isolate the DNA of the virus from the available material and thereby confirm its presence in the patient’s body;
- biopsy of papillomas (condylomas): done in order to determine the presence or absence of cancer cells in neoplasms.
HPV type 68
Skrgej
3381 views
January 8, 2020
HPV type 68 was discovered 6 years ago. 3-4 warts appeared on the pubic area but then went away on their own, there was inflammation of the prostate and clear discharge for a long time (about a year), then everything gradually went away. Now PCR has shown again the presence of HPV 68 - Abs. Value -6, Dygen test is relative. — 11.1. At the moment, I am worried about the frequent exacerbation of prostatitis with decreased immunity. donated prostate secretions - leukocytes in 15 places to 30 The urologist says prostatitis is not associated with HPV, but is this so? Could it be that due to a constant inflammatory process, the urethra, bladder and prostate are damaged by this HPV? For a month, I studied everything there is on the Internet about this type of HPV on Russian and foreign sites and realized that no one really writes anything specific. Everyone says that with HPV, genital warts appear and they are removed, and if there is nothing, then there is no need to treat anything. I began to study it myself on the Internet on Russian and foreign sites. Here are the facts that I was able to find: 1) this type of HPV is poorly studied, is not very common in Europe and Russia, there are controversial facts about its oncogenicity (in various studies in Korea and Europe they write about isolated cases of HPV being found in the studies they conducted - within 1 -2% of all patients they studied). It is more common in Asia (Korea China) where it is detected in up to 5% of cases. In these study groups, HPV 68 was more often found in either patients with normal cytology or LSIL. There are isolated cases of carcinoma. 2) On the Russian Internet they write that, according to statistics, it is not as terrible as 18 and 16, which cause up to 70% of oncology. But this statistics is not informative - it simply says that these are the most common types of all oncogenic types, but this does not say anything about the degree of oncogenicity, but only about their prevalence among the population, right? On many Russian-language sites they write information that contradicts foreign sites - for example, by searching for HPV 68 in Yandex and studying the first 20 sites, I found out that 68 is very aggressive and very dangerous, and that there is a 70% chance of cervical cancer, which scared me so much that I can’t sleep peacefully for a month . It’s unclear who to trust! I am interested in the following: if the virus does not eliminate itself (they say that in 90% of cases it goes away on its own, but this is not a fact, most likely it just falls asleep, as I understand it), and if a woman after 30 has it in her body, WHAT IS THE PROBABILITY of abnormalities in the cervix in the future? That is, what is the chance that the virus will not cause problems? 50/50 or 70/30 or 90/10? Are there statistics on this topic? In just one place I found that with highly oncogenic HPV, the risk is 10% for dysplasia and within 1% for oncology, and even then it is not clear which gynecologist writes. It seems that in Russia they do not conduct full-fledged research, they do not study HPV as they do abroad. Does anyone have any statistics on this type? Are there any studies by Russian scientists on this topic and specifically on HPV types? (Naturally I am interested in HPV68). Are there specific symptoms for this type of HPV? I understand from reading Russian-language websites that it may not cause genital warts, but at the same time everything can be covered with flat, barely noticeable papillomas, and inside the urethra and bladder.. both in men and women. There is a risk of damage to the intestines and the entire genitourinary system. Who can say something more specific about the symptoms of type 68? Today I have been taking isoprinosine for a month after the removal of two papillomas on the scrotum to exclude a relapse as prescribed by an immunologist. Is it possible to immediately give injections of Allokin alfa after isoprinosine? Many doctors recommend and write that it has a great effect on oncogenic HPV. Panavir suppositories were also recommended. What do you advise? 5. When and what should I take after taking isoprinosine to see the dynamics?
Age:
38
Chronic diseases:
Prostatitis
The question is closed
Destructive and surgical treatment methods
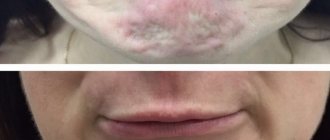
To quickly eliminate warts, condylomas, and papillomas, destructive techniques are used. Unlike conservative treatment, they do not allow you to wait until the tumor necrotizes and falls off on its own. In the office of a dermatovenerologist, skin defects can be eliminated in one visit. Removal of pathologies in hard-to-reach places is carried out only by surgical methods.
Electrocoagulation
During electrocoagulation, defects are removed with an electric knife. It generates electrical waves that cut off skin growths and destroy pathological tissues. Electric waves cauterize small vessels, there is no bleeding after surgery. Removing one defect takes from a few seconds to five minutes. Removal of small papillomas on the skin with an amount of more than 20 pcs. costs 200 rubles. for 1 unit. Large tumors are removed under local anesthesia at a cost of 1000–1500 rubles.
Cryodestruction
Liquid nitrogen is used for cryodestruction. The temperature of the substance is -190 degrees. When liquid nitrogen gets into the defects, necrosis occurs. Extremely low temperatures cause cell destruction, blockage of oxygen, and blockage of blood vessels. A thermal burn is formed and the tissues die. The operation is carried out under the supervision of an experienced doctor, who ensures that the substance does not come into contact with healthy skin. The effect of the procedure does not occur immediately, but after 5–10 days, when the necrotic papilloma tissue is completely rejected. The cost of cryodestruction usually ranges from 500 to 1500 rubles. per element.
Radio wave surgery
The operation uses a device that emits radio waves at high frequencies. Radio waves destroy skin defects using thermal energy. The device is operated by an experienced doctor. It directs radio waves, focusing the flow on the growth, avoiding touching healthy skin. This is the most effective and cost effective method for removing papillomavirus tumors on the skin and mucous membranes. The cost of the procedure is from 300 rubles. for the destruction of multiple small papillomas, up to 1500 -2000 rubles, for the removal of large tumors.
Laser defect removal
A directed beam of laser beams removes skin defects. Under the influence of the laser, the cells evaporate. A protective crust is formed at the site of the removed growth. Destruction of the defect takes from 5 seconds to two minutes. Healthy skin forms under the horny crust. About a week after the intervention, the crust disappears. The cost of laser removal of large papillomas is from 1000 rubles.
Removal of affected tissue
Invasive intervention techniques are used for deep tissue damage, when the process of malignant degeneration has already begun. Knife conization is used to remove pathological areas of the epithelium. When HPV is advanced and oncology begins to develop, they resort to removing the cervix with a scalpel.
Our doctors use an integrated approach to the treatment of HPV, which provides close to 100% effect from the therapy. It includes a combination of injectable, tableted immune, antiviral and topical medications. Removal of tumors is carried out using the chosen method against the background of drug treatment, which allows you to completely get rid of papillomas and condylomas and other manifestations of HPV, and prevent recurrence of the infection.
HPV: can it be treated or not?
It happens that papillomavirus is cleared from the body within two years after infection. But this is typical mainly for children and young people. However, since the prevalence of the virus is high, there is a risk of re-infection (relapse). Immunity after an illness is not formed for life, but for 1–3 years. It is this fact that underlies the statement that HPV cannot be cured.
In most cases, in adults, the papillomavirus does not leave the body on its own, but is integrated into the genome, provoking the development of tumors, including cancer. We advise you not to rely on luck, but to start treatment at the first symptoms of the disease. Human papillomavirus infection is successfully treated with modern medicine. New growths on the skin are removed using destructive methods.
Effective treatment is possible only according to the regimen proposed by the attending physician. When prescribing therapy, the dermatovenerologist takes into account the HPV strain, the degree of oncogenicity, and the patient’s immune system. Self-selection of medications will most likely not give the desired result. After therapy, you need to get tested for HPV every 2 years to avoid relapse of the disease.