The rectum worries children mainly due to pinworms and constipation. If bowel movements are painful, it can lead to constipation, as well as an anal fissure, a painful injury to the lining of the rectum, which in turn often makes constipation worse.
For many children, itching in the rectum is caused by pinworms. The itching in such cases intensifies at night; it bothers the child no less than pain associated with constipation or anal fissure. Scratching further traumatizes the skin and increases the likelihood of infection.
A streptococcal infection can also cause inflammation of the skin around the anus. Serious causes of rectal itching in children, such as hemorrhoids, are rare. It is more common in adults, but in children it can indicate a serious illness.
Any injury in a child in the anus for no apparent reason should alert parents and suspect sexual abuse of the child, especially if he refuses to explain its origin. In such cases, the child may need the help of a child psychologist.
THE DOCTOR'S CONSULTATION
Contact your doctor if your child:
- itching or bleeding from the rectum
- severe constipation
- haemorrhoids
- itching that gets worse at night
- painful red rash in the anus
- trauma to the anus
ATTENTION!
An anal fissure cannot be cured without the use of products that help soften stool. As a result of treatment, the child ceases to be afraid of pain during bowel movements.
| ASK YOURSELF A QUESTION | POSSIBLE REASON | WHAT TO DO |
| Is your child irritated and scratching his anus? Does itching get worse at night? In feces you can sometimes see small, mobile white worms, less than a centimeter long? | Pinworms | Contact a pediatrician who will examine the child and prescribe the necessary tests. All family members should be treated (see “Treatment of pinworms” at the end of this article). |
| Does the child experience pain during bowel movements and for several minutes after it? Is there fresh blood on toilet paper or in stool? | Anal fissure | Bring your child to see a pediatrician , who will examine the child and confirm the diagnosis. As a rule, an anal fissure appears if the stool is too dense. Treatment includes agents that help soften stool. As a result, the child ceases to be afraid of pain during bowel movements, which aggravates stool retention |
| A child has a painful red rash in the anus | Inflammation of the skin around the anus caused by streptococcal infection (perianal dermatitis) | Make an appointment with a pediatrician who will examine the child and, if necessary, prescribe treatment (possibly prescribing antibiotics). After defecation, rinse the anus with clean water and apply zinc ointment or a doctor-prescribed ointment. |
| Is your child bleeding from the rectum or in pain? The general condition is not impaired, is it active? | Intestinal polyps; Meckel's diverticulum; Saccular process of the ileum | Contact a pediatrician who will examine the child and, if necessary, refer to another specialist |
| Does the rectum protrude from the anus after defecation? Do you strain a lot when defecating? Does your child have a chronic, serious illness, such as cystic fibrosis? | Rectal prolapse | If your child is not in pain, gently try to push the bowel back into place with a sterile gloved finger or by wrapping it in toilet paper. Then contact your pediatrician. If your attempt causes pain or there is bleeding, contact your pediatrician . |
| Does your child have a strange gait or pain in the rectal area? Is he refusing to go potty? | Foreign body in the rectum (the child, out of curiosity, can insert it himself) | Bring your child to see a pediatrician , who will examine the child and identify a foreign body. If it is large, with sharp edges, the pediatrician will refer the child to another specialist |
| Does your child have pain, swelling, or redness in the anus? | Perianal abscess/fistula; Crohn's disease | Consult a pediatrician who will examine the child and decide what treatment is needed |
FOR INFORMATION
Treatment of pinworms
Pinworms can appear in a person of any age, level of education and wealth. They are especially common in children and are easily transmitted from child to child in kindergartens and schools. Pinworms are very annoying, but cannot cause serious harm to health, although they sometimes transfer bacteria from the rectum to the girl’s genital tract, causing vulvovaginitis. Pinworm eggs, which can be found under nails, on clothes and linen, in house dust, enter the mouth, then the stomach. There they open, and the larvae move into the small intestine, where they mature into small, mobile white worms less than a centimeter long. At night, females lay eggs on the skin in the anus. This causes itching, the child scratches the skin, the eggs get under his nails - this is how the infection cycle repeats.
When a child has itching, he is irritable and has difficulty sleeping. To diagnose, a doctor may apply adhesive tape to the anus and look for worm eggs on it.
A short course of treatment is required to cure pinworms. Because re-infection is not uncommon, treatment sometimes needs to be repeated. To disinfect clothes and linen, washing, boiling and ironing are necessary.
Description of the disease
Anal fissure develops less frequently in children compared to adult patients.
This is due to a small number of provoking factors and rapid restoration of the mucous membrane with proper treatment. The disease affects boys and girls equally often. Anal fissure is rarely encountered by children under the age of 3-5 years, whose stool is extremely rarely thick. An exception may be cases of congenital malformations of the rectum.
Depending on the nature of development, an anal fissure can be:
- acute;
- chronic.
The latter option most often occurs in adolescents in the absence of proper treatment for the disease at the earliest stages of its development.
In such cases, sometimes it is even necessary to surgically remove the affected tissue, and only then carry out conservative therapy. Depending on the location, anal fissures are divided into 3 types:
- rear;
- front;
- lateral.
The pathological process can occur with or without spasm of the anal sphincter. Prolonged tonic contraction of the annular muscles of the anus aggravates the course of the disease. Against the background of spasm, the child has bowel movements less often. This leads to hardening of the stool, which subsequently further injures the rectal mucosa. The child has a fear of going to the toilet. This closes a vicious circle, causing a deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
Symptoms of anal fissure in children
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the stage of development, the individual characteristics of the child and the size of the mucosal defect. Classic symptoms of anal fissure:
- Pain in the anal area during bowel movements. This is one of the most common signs of the disease, which is caused by mechanical damage to the inner surface of the intestine. Between bowel movements, the baby can behave absolutely normally and not show any complaints.
- Blood in the stool. This is the most common reason for parents to turn to a pediatric proctologist, who notice streaks of scarlet blood during the next diaper change or while cleaning the potty. Its appearance is due to the presence of a defect in the mucosa and injury to small vessels.
- Abnormal bowel movements such as constipation. Due to pain in the anorectal area, the child tries to suppress the defecation reflex. There is a fear of bowel movements.
- Anxiety, sleep disturbance, moodiness. All these symptoms are caused by the child’s irritation, which develops against the background of pain in the anus and bowel dysfunction.
If the above symptoms occur, you should seek help from a pediatrician, proctologist or pediatric surgeon. This will allow you to identify the problem in the early stages of its development and begin adequate treatment without delay.
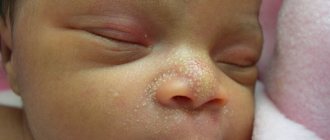
Red bottom in a newborn, one-month-old baby, infant: reasons, what to do?
There are many reasons for redness of the skin on the buttocks in infants:
- Diaper rash. They appear as a result of improper care of the child's skin. Change the brand of diapers, you can buy a special skin care cream. Change diapers frequently and use wet wipes to remove excess urine from your skin.
- Disturbances in the intestines. If the child is breastfed, then the mother should change her diet, eliminating milk, fresh vegetables and fruits. They are the cause of allergies and dysbacteriosis in the baby.
- Dysbacteriosis, taking antibiotics. In this case, gastrointestinal ailments are treated and probiotics are taken.
Red bottom in a newborn, one-month-old baby, infant: reasons, what to do?
Causes of anal fissure
The pathogenetic basis for the development of anal fissure in children is a violation of the integrity of the anal mucosa. The cause of such a defect may be:
- Tear of tissue due to the passage of too thick stool.
- Incorrect placement of cleansing enemas or gas exhaust tubes when the mucous membrane is injured by hard elements of medical products.
- Incorrectly performed surgical interventions in the anorectal area.
It is important to understand that a violation of the integrity of the mucous membrane in the described situations does not always occur. The risk of developing the problem is increased by provoking factors:
- Genetic predisposition or the presence of congenital malformations of the anorectal region or the entire gastrointestinal tract (GIT).
- Chronic intestinal infections accompanied by diarrhea. In such cases, the mucous membrane becomes thinner and becomes more vulnerable to the mechanical impact of thick feces.
The situation is further aggravated by the presence of a local inflammatory process.
- Proctitis and other diseases of the rectum, which directly reduce tissue resistance.
- Metabolic disorders. Diabetes mellitus and pathology of absorption of individual food components create conditions for defecation disorders and changes in the normal architecture of tissues.
- Traumatic injuries to the anorectal area - falls, blows, scratching of the anal area against the background of helminthic infestation.
Why does a one-year-old child have a red bottom and how to treat it?
Causes of redness of the buttocks in a child and methods of treatment:
- Teething. Give the child “biters”, use an antipyretic in case of fever, apply gel to the gums.
- Diarrhea. In this case, you should consult a doctor, as the cause of diarrhea may be an intestinal infection.
- Allergy. In this case, all possible allergens are eliminated. This applies to food and household chemicals.
- Using rich cream . Parents often purchase very rich cream for diapers. This is what can cause redness. It is worth changing the cream and bathing the child more often, using emollients (Lipikar, Physiogel).
Why does a one-year-old child have a red bottom and how to treat it?
Expert opinion
Anorectal fissure in a child is a relatively favorable condition compared to adults. If you seek specialized help in a timely manner, the problem can be eliminated conservatively in a short time. Due to the good ability to restore the mucous membrane in children, therapy can take only 4-5 days. The main thing is not to ignore the first signs of the disease. Otherwise, an acute crack becomes chronic, becomes a cause of daily discomfort for the patient, and requires surgical intervention.
A child has irritation on his bottom, a red rough spot: causes, photos
There are many reasons for peeling skin on the buttocks. These may be ailments of internal organs or external causes.
Causes of redness and peeling of the buttocks in a child:
- Failure to comply with hygiene rules
- Contact or diaper dermatitis
- Worms
- Dysbacteriosis
- Candidiasis
- Allergy
- Overheat
A child has irritation on his butt, a red rough spot: causes, photo A child has irritation on his butt, a red rough spot: causes, photo
Diagnosis of anal fissure
Anal fissure is diagnosed by a pediatric proctologist or surgeon.
Even when parents first contact a doctor, a specialist may suspect the presence of this disease. The doctor pays attention to the child’s characteristic complaints, the influence of provoking factors, and the history of the development of the pathological process. A digital rectal examination is required to make a definitive diagnosis. However, in order not to cause psycho-emotional discomfort in the presence of severe pain, the doctor may first limit himself to a simple examination of the anal area. Sometimes the defect can be identified immediately.
If a rectal examination is not performed immediately, it will be postponed to the next visit. The fact is that anal fissures are often a consequence of other proctological diseases, which may not be diagnosed without a full examination. This means that the pathology of the rectum will steadily progress.
To comprehensively assess the patient’s condition, the following tests are performed:
- General blood and urine analysis. Allows you to identify concomitant diseases, primarily anemia, inflammation.
- Coprogram is a microscopic analysis of feces, which is especially important if dysfunction of other parts of the gastrointestinal tract is suspected.
- Blood chemistry. Detects metabolic changes in the body.
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs. Detects abnormalities in the development of internal organs.
If a concomitant pathology is identified, its treatment is carried out in parallel, which helps to avoid recurrence of the anal fissure.
Treatment of anal fissure
Anal fissure in children is a disease that in the early stages of its development responds well to conservative treatment. Surgery may be indicated only if drug therapy is ineffective or the process is long-term and chronic, when a ridge of dense scar tissue forms around the crack, interfering with healing.
Conservative treatment
A key aspect of effective treatment of anal fissure in children at an early stage of the disease is the correction of diet and water balance.
This allows you to soften the stool and prevent re-traumatization of the mucous membrane. It is recommended to temporarily exclude fatty and fried foods from the diet and reduce the amount of meat consumed. It is worth increasing the amount of fruits and vegetables that are rich in fiber. Coarse fiber attracts liquid, increases the volume of stool and thereby helps normalize stool. In addition to diet correction, the proctologist prescribes the following groups of medications:
- Mild laxatives (if constipated).
- Healing ointments and creams, suppositories.
- Anti-inflammatory suppositories.
To cleanse the intestines and eliminate the local inflammatory process, it is recommended that the child take baths with chamomile decoction for 2-5 days. The water temperature is about 37°C. If a child has anemia due to minor bleeding, the doctor prescribes iron supplements, vitamin B 12, and folic acid.
Surgery
Surgical excision of anal fissure in children is performed when conservative treatment methods are ineffective.
It is indicated for the chronic form of the disease and is practiced mainly in adolescence, when the process has turned from acute to chronic. The essence of the operation is the excision of pathological scar tissue and the crack itself with further suturing of the defect. After this, the patient receives standard conservative therapy aimed at stabilizing the stool and healing the postoperative wound.
Red butt in a child after antibiotics: how to treat it?
After taking antibiotics, the normal microflora in the intestines is disrupted. Moreover, even if you took lactobacilli, you should drink them after completing the course of antibiotics for another 2 weeks. At the same time, prepare special decoctions for the bath. To do this, take a handful of chamomile flowers and a tablespoon of string in a saucepan of water. Boil the mixture for 2-3 minutes. Wash your baby's bottom and genitals with the resulting broth or pour it into the baby's bath, adding water.
Red butt in a child after antibiotics: how to treat it?
Questions
- Which doctor treats anal fissure in children?
A pediatric proctologist or surgeon is involved in identifying and treating anal fissure. - Is it possible to cure anal fissure with folk remedies?
Conservative treatment of anal fissure in children is aimed at stabilizing stool and rapid healing of damaged tissue. In some cases, this effect was achieved using traditional medicine - chamomile baths, sea buckthorn suppositories and other local remedies in combination with diet. However, in any case, you must first consult with a specialist. Anal fissures are often a consequence of other proctological diseases, which can progress without adequate treatment. - Does my child need surgery for anal fissure?
In 90% of cases, if the patient seeks help in a timely manner, surgical intervention is not required. Timely initiation of conservative therapy promotes complete healing of the mucosal defect without subsequent relapses. The exception is advanced cases when dense scar tissue forms along the edges of the crack, which interferes with healing. As part of the surgical intervention, it is excised and the defect is sutured, after which standard medications are prescribed to speed up healing. - How to independently identify an anal fissure in a child?
Pain during bowel movements and red blood in the stool are sure signs of a problem. You can also examine your child's anal area yourself. In 50-60% of cases, the mucosal defect is visible without the use of additional instruments. However, such a self-diagnosis complex does not replace consultation with a specialist. Only a comprehensive examination and personalized treatment can radically solve the problem of anal fissure in childhood.