Seborrheic dermatitis on the face photo
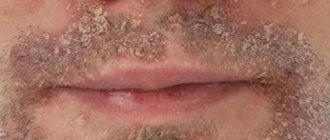
Photo 1. Seborrheic dermatitis on the face of an adult
Photo 2. Seborrheic dermatitis on the face of an adult
Photo 3. Seborrheic dermatitis
Photo 4. Seborrheic dermatitis on a child’s face
Causes of diathesis
If in childhood the occurrence of diathesis is associated with incompletely formed organ systems, then in adults the causes are several factors combined with each other. This can be nervous overload, depression, chronic fatigue, etc. They provoke the release of certain substances into the blood that cause immune reactions.
There are a huge number of risk factors. What causes diathesis on the face in adults:
- due to systemic diseases of internal organs;
- poor nutrition;
- alcohol abuse and smoking;
- diseases of the endocrine system;
- allergies to sweets;
- exposure to low temperatures.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis on the face
The main cause of seborrheic dermatitis is the increased functioning of the sebaceous glands and a change in the composition of the fat they produce. A similar situation develops when the Malassezia fungus multiplies excessively (normally it is part of the skin microflora). In this case, it penetrates the sebaceous glands and produces a special secretion that forces subcutaneous fat to break down, forming fatty acids that irritate the skin and contribute to the occurrence of rashes.
Dermatitis affects men more often than women, which is explained by the action of androgen, a male hormone. This hormone stimulates the synthesis of subcutaneous sebum. In women, the disease usually manifests itself when estrogen levels decrease and androgen concentrations increase.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the forehead is especially often diagnosed in people whose close relatives have a similar problem, which is associated with a hereditary predisposition.
Other factors can also provoke the development of the disease:
- hormonal imbalances;
- disruption of the endocrine system (especially the thyroid gland);
- weakened immunity;
- hypovitaminosis;
- unfavorable environmental situation;
- improper facial skin care;
- excessive sweating;
- poor nutrition;
- lack of sleep;
- uncontrolled use of medications, especially hormonal ones;
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- presence of infection in the body;
- dysfunction of the nervous system, manifested in the form of epilepsy or schizophrenia;
- diabetes;
- pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract;
- frequent stressful situations;
- overwork;
- malignant tumors in the adrenal glands or genitals.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face
18.02.2021
Dermatitis of various origins and types occupy one of the leading places among chronic skin diseases. This pathological condition can occur at almost any age, but most often appears during puberty due to an increase in the secretion of the sebaceous glands, which is caused by hormonal changes in the body. The disease does not in any way affect the general state of health, but it causes significant discomfort to patients, both psychological and mental.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face , the treatment of which requires long-term treatment, can be prevented in the early stages of development if the facts contributing to its development, the main causes, symptoms and signs are well studied.
The causative agent of this disease can be called fungi belonging to the genus Malassezia furfur. They are a component of the normal microflora of human skin in more than ninety percent of the population of the entire planet. Fungi are located in close proximity to the sebaceous glands and break down sebum into free fatty acids, then use them for their development and growth.
Under the influence of certain factors, this pathogenic microflora becomes hyperactivated. These include:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- weakening immunity ;
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system , stress;
- excessive sweating, pathological increase in sebum production;
- poor nutrition;
- use of alkaline-based detergents.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face most often occurs in men, since the activity of the sebaceous glands is regulated by their hormones .
With the development of seborrheic dermatitis on the face , in most cases, the so-called T-zone is affected - areas with a large number of sebaceous glands and their increased activity. The main clinical symptoms of this disease are:
- inflammation and peeling of the skin;
- the appearance of rash elements - dry scaly or yellowish-red spots and papules with clearly defined contours near the eyelashes, eyebrows, on the wings of the nose , cheekbones, and behind the ears;
- intense itching, burning sensation in the affected areas of the skin.
If treatment for dermatitis on the face is not carried out or it is untimely or illiterate, peeling becomes pronounced, the scales become greasy, thick, and turn a specific yellowish color. Pathological rashes take the form of continuous inflamed foci, and characteristic papules form on the skin.
The main methods of conservative treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the face are based on data that prove the fungal origin of this disease. Therefore, the most effective are drugs from the group of glucocorticosteroids (hydrocortisone ointment). However, these drugs have disadvantages in the form of undesirable side effects: erythema, skin atrophy, exacerbation or development of oral dermatitis , transillumination of blood vessels , and the appearance of rosacea .
Various physiotherapy procedures are also used to treat this disease. These include ultraviolet radiation, cryomassage , darsonvalization (the action of high-frequency currents). These procedures have virtually no side effects. Thanks to them, the condition of patients improves, their appearance, the symptom of skin itching and the severity of the inflammatory process disappear, local immunity blood microcirculation , and the degree of resistance of the epidermis to mechanical damage increases. These techniques have a beneficial effect on the state of the nervous system , which increases the concentration of adrenaline and testosterone in the blood , which leads to improved functioning of the sebaceous glands.
Seborrheic dermatitis on the face is also treated with drugs from the group of antibiotics, antiallergens, and vitamins.
Among the folk remedies, the most common are masks made from cucumber pulp, decoctions of chamomile flowers, St. John's wort, calendula, and plantain leaves for treating affected areas. They help relieve symptoms of itching, inflammation, and improve the overall condition of the skin.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis on the face
With seborrheic dermatitis on the face, symptoms appear:
- the appearance of pink, red or burgundy spots on the skin;
- the formation of white or yellowish scales and hemorrhagic crusts;
- peeling of the skin;
- irritation and increased sensitivity of the skin;
- itching and burning of varying intensity.
The course of the disease worsens in the autumn. In summer, unpleasant symptoms usually disappear.
If the ducts of the sebaceous glands become clogged, acne appears.
The disease is especially severe in men who grow beards and mustaches. Large plaques form under the hairline, which eventually transform into papules. If an infection occurs, then erythroderma is also detected. When papules coalesce, swollen areas colored red form.
The symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis are similar to those of other dermatological diseases. Therefore, only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis after a thorough examination of the patient.
Types of diathesis
Depending on the cause, the following types of diathesis may occur in adults:
- Allergic. The most common form, the nature of the course resembles a common allergy. Also called exudative diathesis, which manifests itself as intolerance to certain allergens: food, pollen, medications, household chemicals, etc.
- Neuro-arthritic. The main reason for the appearance of rashes on the body is increased nervous excitability in combination with disorders of protein metabolism.
- Lymphatic-hypoplastic. It is not the skin that is affected, but the mucous membranes. The reason is infectious diseases.
- Gastrointestinal. Associated with diseases of internal organs and poor nutrition. Manifests itself in the form of intestinal colic, digestive problems and dysbiosis.
- Uric acid. Develops against the background of metabolic disorders.
- Hemorrhagic. A rare form of the disease, which is associated with the body’s tendency to hemorrhage. The most characteristic symptom is hemorrhages in the form of small rashes or large hematomas on the body.
How to treat seborrheic dermatitis on the face?
If symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis appear on the face, treatment should be carried out by a specialist. Self-medication can only worsen the condition.
The dermatologist will examine the patient’s skin and refer it for laboratory testing. If necessary, he will advise you to consult a neurologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, andrologist or gynecologist. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor will select the optimal treatment, which should be comprehensive. First, the dermatologist prescribes weak drugs. If they do not produce the desired result, then he moves on to potent ones.
To effectively cope with the disease, it is imperative to identify and eliminate the cause of the disease. If dermatological problems are caused by disturbances in the digestive system, the patient is referred to a gastroenterologist. After the examination, he will prescribe suitable medications, most often enzymes, sorbents and choleretic agents. Enzymes and choleretic drugs will restore the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, and sorbents will remove toxic substances from the body.
Typically, treatment for nasal dermatitis includes:
- compliance with the diet prescribed by a specialist;
- drug therapy;
- physiotherapy;
- maintaining personal hygiene using gentle products.
Drug therapy involves taking:
- antihistamines - relieve itching;
- probiotics – restore intestinal microflora and normalize the functioning of the digestive tract;
- vitamin complexes – strengthen the immune system and increase the body’s resistance.
In addition to medications intended for oral use, external agents that have a moisturizing, anti-inflammatory and antifungal effect are recommended.
Both glucocorticosteroid hormonal ointments and non-hormonal drugs can be used. But you need to know that glucocorticosteroids, although they have an effective effect (relieve inflammation, swelling and redness), but they are addictive and, with prolonged use, provoke side effects (vasodilatation, the formation of rosacea and telangiectasia, the development of erythema).
Therefore, it is better to give preference to non-hormonal drugs, among which the products of the “Losterin” series (cream, ointment, gel, shampoo) have shown particular effectiveness. They are characterized by a neutral composition, do not contain hormones, do not irritate the skin and are not addictive. The drugs included in the “Losterin” line can be used not only by adults, but also by newborn babies. They are recommended for daily use both during remission and during acute inflammation. Active substances (naphthalan, salicylic acid, natural oils, medicinal plant extracts) are included in the composition of “Losterin” products in optimal proportions, which determines the most effective therapeutic effect. Even if seborrheic dermatitis has passed, Losterin should continue to be used to prevent a relapse.
Physiotherapeutic procedures can effectively complement drug treatment. Small doses of ultraviolet light will ease the course of the disease, restore the functioning of the sebaceous glands, and relieve redness, swelling and itching.
Prevention of seborrheic dermatitis on the face
To prevent dermatitis on the forehead from causing a relapse, it is recommended to follow several rules:
- strengthen the immune system;
- cleanse the body of waste and toxins;
- exclude from the diet salty and spicy foods, fatty and smoked foods, marinades, spices and condiments, sweets, chips and crackers, products containing preservatives, flavor enhancers and dyes;
- introduce fermented milk products into the menu, which include lacto- and bifidobacteria, animal proteins, bran, buckwheat, oatmeal;
- cook food with vegetable oil;
- restore the functioning of the digestive system.