Papilloma is a benign growth on the skin.
Its occurrence is a reason to contact a specialist, since it indicates the presence of HPV in the body.
Under the influence of a number of factors, papilloma can change and develop into a tumor. It is important to promptly pay attention to changes in the structure, shade of the tumor or the appearance of itching. Timely therapy will relieve unpleasant symptoms and prevent degeneration into a malignant tumor.
Why do papillomas appear?
The etiology of papillomas is most often viral. The causative agent is human papillomavirus (HPV) - family Papovaviridae (simian vacuolating virus). More than 130 strains are known, each of which has its own characteristics and manifests itself differently. The virus is not persistent in the external environment; infection occurs through direct contact. Predisposing factors to infection are smoking, vitamin deficiency, endometriosis, and immunodeficiencies.
When HPV enters the body, it first infects the basal (lying on the surface) epithelial cells. The penetration of the virus into the body is facilitated by microtraumas and cracks. The virus can multiply for a long time, but does not manifest itself clinically. If HPV multiplies in the stratum corneum of the skin, cell hyperplasia is observed over time.
What is human papillomavirus
HPV is a virus that causes a benign tumor in the form of papilloma. It is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD) along with syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis and chlamydia. However, it can also be contracted in everyday life - for example, through close contact with a carrier of the virus through touch or when visiting public places (it penetrates through scratches on the skin). There is another way of infection - self-infection during shaving or hair removal.
When the virus has already “taken root” in your body, an outbreak of papillomas is provoked by any, even the most insignificant, at first glance, factor - stress, exacerbation of gastrointestinal diseases, a recent cold. As a rule, papillomavirus occurs precisely against the background of weak immunity.
Why do papillomas itch?
The location, color, and shape of the neoplasm depend on its causative agent. And the causes of itching mainly depend on the characteristics of papillomas.
Plantar papillomas, the causative agent of which is HPV 1, 2, 4, are small in size and have a lump shape. They are characterized by severe itching and even pain, especially while walking. New growths are confused with calluses and attempts are made to cauterize, open, or use medications to eliminate them. Pressure injuries and exposure to chemicals contained in medications cause irritation and itching.
Thread-like papillomas, or acrochords, arise as a result of damage to the body by HPV 3, 5, 8. Neoplasms are localized in the groin area, armpits, neck, and skin around the eyes. Acrochords, located in places where trauma is possible, often become inflamed and cause discomfort. If the papilloma on the eyelid itches, but does not turn red or enlarge, most likely it was carelessly caught, for example, while washing. If the tumor becomes inflamed or larger, you should consult a doctor.
What to do if the papilloma turns red? — Clinic “Good Deed”
Patients diagnosed with HPV often face various problems. Most often they have complaints due to injuries to the growths. Against this background, inflammatory processes and other side effects occur.
Papillomas and warts in themselves are harmless and harmless phenomena. But what to do when the papilloma becomes inflamed and red? This manifestation is worth special attention, since most likely a more dangerous complication is occurring. Therefore, at the first changes, it is urgent to make an appointment with a venereologist.
The papilloma became inflamed and reddened
Among the main causes leading to inflammation are:
- Chronic diseases not directly related to the occurrence of formations. In this case, complex therapy is necessary to eliminate the initial disease, which led to the activation of HPV.
- Woman's pregnancy. With a decrease in immunity and changes in the body, the virus is sharply activated.
- The reason that the papilloma has turned red and swollen may be its damage due to friction, impact, tearing and other physical influences.
- Action of ultraviolet rays.
- Prolonged nervous condition, stress, severe emotional shock.
- Hormonal imbalances and the process of malignancy.
The papilloma has enlarged and turned red
Many people ask what to do if the papilloma on the leg turns red and enlarges? In this case, you should not hesitate to seek help from the clinic.
Any changes in the shape, structure and color of HPV formations may indicate the development of malignant manifestations.
Moreover, if the shape of the growth is mushroom-shaped and the stalk of the papilloma turns red, then it is susceptible to tearing off, which can lead to complications.
The papilloma has turned red and swollen, what should the patient do?
HPV tumors can be localized in various areas of the skin. Very often their swelling occurs due to careless handling, or due to wearing tight underwear.
Changes in color and shape can occur after taking hormonal medications. Hygiene procedures or simple scratching also have a mechanical effect on papillomas.
As a result of such actions, the wart may swell or turn red. In any case, if such changes are detected, the patient should consult a doctor for examination and recommendations.
A venereologist will conduct an examination and prescribe appropriate HPV treatment.
Why does papilloma hurt?
If the papilloma is red and painful, this indicates that the patient has a progressive papilloma viral infection. Painful sensations occur when the growths are subjected to physical impact.
Papilloma can be damaged very easily. As a result, the top layer through which the infection penetrates is disrupted. This is what causes inflammation and pain.
Pathogenic microorganisms cause suppuration, redness, an increase in the size of tumors and pain.
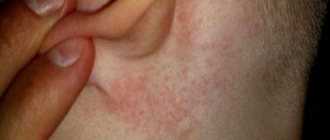
Inflamed papilloma on the neck
- burning;
- skin redness;
- itching;
- unpleasant odor;
- pain;
- change in the shape and size of the tumor.
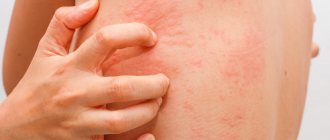
Papilloma itches and turns red
There are many factors that can complicate the course of the disease and cause itching from inflamed papilloma. These include:
- secondary infections, which manifests itself with additional symptoms;
- friction when using tight clothing, especially synthetic ones;
- failure to comply with hygiene procedures, which are especially necessary in the presence of formations in the groin, axillary areas, and anus;
Why does the skin around the papilloma turn red?
Since the infection enters the body through microcracks and scratches, the first sign of activation of the virus may be redness of the skin around the papilloma. This mainly happens if the crack is located directly next to the mole. To avoid further complications, you must urgently seek help from a doctor.
In modern medicine, there are several methods for treating HPV. Laser removal of papillomas is considered the most effective. This method has a number of advantages that help prevent relapse.
The private clinic “Blagoye Delo” is a multidisciplinary institution that has been providing high-quality medical services at affordable prices for many years. Our doctors are certified specialists with extensive experience. They have high-precision laboratory equipment and modern treatment methods in their arsenal.
Is it possible to scratch papillomas?
Papilloma is a small, dense or soft-to-touch formation on a long or short stalk. Neoplasia consists of connective tissue stroma and epithelium. The stroma is filled with small vessels, and if they are traumatized, bleeding is possible.
If the papillomas itch, then touching them is highly recommended. Any strain of the virus can infect a person. They are divided into three groups according to the degree of oncogenicity:
- Low risk. Single neoplasms, only on the surface of the skin, do not pose a threat to the body. They only cause a cosmetic defect.
- Moderate oncogenicity. Under the influence of certain factors, they can cause changes in the genome of cells.
- High oncogenic risk. Papillomas with this strain of the virus often degenerate into cancerous tumors.
Scratching the latter can lead to accelerated cell division. Papilloma, as a rule, increases in size and changes color (the stratum corneum changes to a new one). The tumor may not only itch, but also hurt, and your overall health may worsen. If you have such symptoms, you should see a dermatologist and oncologist.
How does HPV manifest?
There are different strains of the papilloma virus. For example, genital warts are papillary skin growths on the genitals and perineum. Depending on the intensity of the lesion, these formations can look different: either as single growths or as a whole cluster, visually similar to a head of cauliflower. The growths cause a lot of discomfort: they itch and even bleed.
It happens that patients come to medical clinics who have been unsuccessfully treated for years for “exacerbations of candidiasis” with “just one pill.” They are quite surprised by the fact that they do not have any thrush, the smear turns out to be “clean”, and itching and irritation are caused by condylomas.
Papillomas and condylomas, like herpes, periodically appear and disappear, since they are only consequences of the virus itself. An exacerbation of the disease occurs during a period of decreased defenses.
Factors influencing the occurrence of itching
Why do papillomas itch on the neck, eyelid or elsewhere? A virus is to blame for the appearance of tumors. Its presence is abnormal, the body tries to fight it, the immune system gradually weakens. And since the virus is localized in papillomas, they become more sensitive and react more sharply to various irritants.
The most common irritants that cause itching are:
- Uncomfortable clothing or jewelry. Tight underwear rubs against the papilloma, and the irritated skin begins to itch. Synthetic fabrics or clothing dyes can also be irritating. Papillomas in the neck area may itch from friction with the metal of jewelry.
- Allergy to soap, shower gel. Manifestations of allergies, such as redness, itching, usually occur in pathologically changed areas of the skin (scars, rashes, swelling, neoplasms).
- Poor hygiene. Rare trips to the shower, especially in hot weather or during physical activity, as well as in diseases accompanied by profuse sweating, contribute to the proliferation of pathogenic flora. Failure to comply with hygiene can threaten the introduction of another infection into the body. Reduced immunity contributes to the activation of HPV.
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation. As is known, prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays (sun, solarium) on the skin promotes malignancy even in cells not affected by the virus. If the cause of papillomas is a virus of high oncogenic risk, then ultraviolet light will accelerate the development of cancer. Itching may be a consequence of active cell division.
- Hormonal drugs. Incorrectly selected steroid medications or non-compliance with the rules for taking them can cause hormonal imbalances in the body. Against their background, HPV may become more active.
Is itchy papillomas dangerous?
To understand whether danger exists in each specific case, you should understand what factors provoked this sensation.
In the presence of external provoking factors, after they are eliminated, the feeling of discomfort disappears, and the condition of the growth returns to normal.
Papilloma can begin to itch if there are serious problems with the body or cause their formation.
When scratching, there is a risk of damaging the growth, and this can happen accidentally.
Then, in addition to itching, other symptoms will appear:
- the appearance of redness around the tumor.
- painful sensations.
- growth tear.
- discoloration, including black.
- increase in the size of papilloma, intensive growth.
- loss of shape.
- bleeding of the growth.
- the appearance of cracks on the surface of the neoplasm.
If the cause of the itching is not identified in time, the risk of developing negative consequences increases.
There is a risk of the following complications:
- infection by pathogenic microorganisms;
- development of papillomatosis;
- suppuration of the affected area;
- development of sepsis;
- tissue necrosis.
One of the most dangerous complications is the possibility of papilloma degenerating into melanoma.
Melanoma takes about two months to form, after which the person is diagnosed with cancer.
Melanoma is one of the most terrible complications, since the development of this form of cancer cannot be stopped.
She is not amenable to chemotherapy and other procedures.
Therefore, if discomfort appears in the area where skin tumors are localized, you should immediately seek advice from the appropriate medical institution.
Timely measures taken will save health, and in some cases, life.
Papilloma itches, what should I do?
Itching at the site of tumors is always caused by some reason. If papillomas on the body itch, there is no need to panic right away. First you need to evaluate their size and color. It is necessary to exclude as much as possible everything that can cause irritation of papilloma: uncomfortable clothes, low-quality jewelry, any substances that cause allergies, prolonged exposure to the sun.
If you observe visible changes in the tumor (enlargement, redness) and pain, you should visit a doctor. The greatest danger is the excessive activity of the virus. HPV is embedded in human DNA and spreads through the natural process of cell division. Under the influence of certain factors, the virus changes the genome of the cell, and it begins to divide randomly. Of course, not all hyperplasias develop into malignant tumors, but only a doctor can accurately determine the nature of the tumor.
Medicines that relieve itching and their use
The examination always takes some time. If the papillomas itch, and the itching is difficult to tolerate, you can use medications to alleviate the situation. Before using them, you should consult your doctor. Drugs that help relieve itching:
- Antihistamines. The products reduce hyperemia (redness occurs from scratching the skin with fingers), prevent the development of edema, and reduce capillary permeability. In addition, if the itching occurs due to allergies, then antihistamines will eliminate the cause itself. Medicines should be chosen with fewer side effects and greater and faster therapeutic effectiveness. These include: “Fenistil”, “Zodak”, “Zyrtec”.
- Local anti-inflammatory drugs, calcineurin inhibitors. The drugs act locally without causing skin atrophy or side effects. The most popular ointments are “Elidel”, “Protopic”, “Tacropic”.
- Antiseptics. The drugs have antimicrobial activity and prevent inflammatory processes. Unfortunately, they are not effective against viruses and are not suitable for preventing HPV. Miramistin and Chlorhexidine will help you quickly get rid of itching and inflammation.
Folk remedies to help relieve irritation
You can get rid of the unpleasant feeling of irritation not only with the help of medications; some folk remedies are no less effective:
- You can eliminate itching with a mixture of chopped garlic and butter in a 1:1 ratio. The pulp is placed in gauze and applied to the tumors for 30 minutes, then washed off with water.
- If papillomas on the neck itch, where the use of garlic is not advisable, you can use castor oil. New growths are also lubricated with it twice a day, but unlike garlic mass, oil can be used for no more than five days in a row.
- The feeling of irritation and inflammation is well relieved by cabbage leaves. They must be applied to the tumors for 40 minutes. You can apply it at any free time, the number of times has no restrictions. Some claim that using this method they got rid of papillomas altogether.
Is it possible to remove papillomas?
This is usually one of the first questions that arises when tumors appear. If the papillomas itch, it would be very logical to simply get rid of them - eliminating the object that causes itching will automatically relieve the discomfort.
It is strictly forbidden to remove them yourself. Many medical organizations offer papillomas removal services. Their cost depends on the method:
- cryodestruction – destruction of pathological epidermal growths by exposing them to liquid nitrogen;
- electrocoagulation – a procedure for removing low-frequency electric current;
- laser destruction – destruction of a tumor using a laser.
Only papillomas of low oncogenic risk can be removed. Before invasive manipulation, an examination is mandatory.
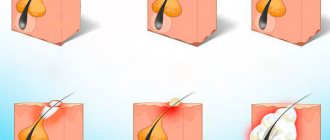
The mechanism of appearance of papillomas
The first stage is characterized by damage to epithelial cells by the human papillomavirus. A viral infection enters the body directly through small cracks in the skin, microtraumas and other damage. The pathology may not manifest itself for a long time, effectively making the infected person a chronic carrier.
The reproduction of HPV in the superficial layers of the skin leads to the appearance of growths that can cause visual and physical discomfort (itching).
HPV is transmitted both sexually and through household contact. Bad habits and reduced immunity are factors predisposing to infection.
Video
HPV infection
Causes of itching and discomfort
Papillomas can appear on any part of the body. The following areas are often affected:
- neck.
- Genital area.
- Armpits.
A benign neoplasm usually does not cause any discomfort and does not manifest itself in any way. If the papilloma itches and increases in size, this can be explained by many reasons.
Injury
One of the reasons why a tumor itches is because it is injured. Mechanical damage to papilloma occurs due to systematic friction of the growth on clothing, underwear or shoes. Even a scarf or headdress can contribute to injury to the tumor located in the corresponding area.
In addition, itching can be caused by unnatural fabrics from which clothing is made, or jewelry.
Occurrence of infection
Papilloma infection is a fairly common cause of itching and discomfort. Active reproduction of the virus is necessarily accompanied by swelling, slight tingling, and an increase in size of the growth. The clinical picture of the pathology suggests the appearance of new rashes.
The affected area should be kept clean. If papillomas itch, this may indicate a lack of proper care for the skin and mucous membranes. Particular attention should be paid to the groin area and anus, the appearance of growths in which is not a rare occurrence.
Excess ultraviolet radiation
Papillomas can itch from exposure to direct sunlight. Moreover, excessive passion for natural tanning can provoke not only itching, but also malignancy of papilloma.
To prevent the negative effects of ultraviolet radiation on existing growths, you should use special cosmetics before going out into the sun. It is better to choose the highest possible degree of protection.
Malignant degeneration
Another name for this process is malignancy. The definition implies the transition of a growth from a benign to a malignant tumor, which explains why papilloma itches. The appearance of a tumor is necessarily accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- severe itching, pain.
- Changing the shade of papilloma.
- Inflammation of the growth and nearby tissues, redness.
- The appearance of ulcers on the papilloma, which bleed when the thin film is removed from them.
Even if the growth has dried and fallen off without using any therapy for papillomatosis, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Treatment of itching and removal of growths
Visual changes and physical discomfort may well indicate negative processes occurring in the body. Since there is a risk of developing cancer, if the papilloma begins to itch, you should consult a doctor.
Therapy for itching involves an integrated approach, which is based on relief of symptoms and subsequent removal of papilloma. To stop the growth from itching, they take medication.
Please note: you cannot select medications yourself. Only a competent specialist can recommend a medicine.
Anti-itch medications
If suspicious symptoms occur, you should immediately visit a doctor. A qualified specialist will tell you what to do if papillomas itch.
Drug therapy for papillomatosis is aimed not only at relieving itching. The patient is additionally prescribed drugs that stimulate a weakened immune system. Taking them will suppress the human papilloma virus.
The following remedies will help stop itching and reduce the size of the wart:
- antihistamines. Typically, antiallergic drugs are taken orally.
- Antiviral. Reduce the rate of virus reproduction.
- Anti-inflammatory.
A specialist may recommend the following medications:
- Feresol. Disinfects the skin, relieves itching, and reduces the size of warts.
- Oxolinic ointment. Relieves pain and relieves physical discomfort. Use for 1.5 weeks freezes the tumor.
- Carbolic acid. Has a disinfecting effect.
- Etc.
If conservative therapy does not bring the desired effect, the patient will be offered other ways to relieve itching.
Folk remedies
In addition to drug treatment, it is permissible to use traditional medicine. It is believed that some of the home recipes may well help get rid of benign growths and associated discomfort.
If the papilloma grows and itches, it is recommended to use the following methods:
Apply to the affected area, cover the skin with a bandage. Do this bandage twice a day for a week.
Steam the papilloma, apply a rich cream. Lubricate the tumor with freshly squeezed celandine juice. Please note: it is important not to affect healthy nearby tissue. Repeat the procedure every 2-3 days until the growth is completely removed.
Alcohol infusion of calendula can be purchased at a pharmacy or made yourself. To do this, add 10 grams. calendula flowers in a small container with alcohol (70%). The mixture must be infused for 2 weeks, then strained. It is recommended to wipe the resulting decoction on the affected areas. Use several times a day.
Brew 3 leaves with a glass of boiling water, keep on low heat until the water partially boils away. Remove from heat, add boiled water. Treat the skin with the resulting decoction at least three times a day (more often is allowed).
Soak a clean cloth with ointment or tincture and, if possible, fix it on the injured area. To relieve unpleasant symptoms, hold the compress for at least 10 minutes.
- Any medicinal plants.
To make lotions or compresses, pour boiling water (250-300 ml) into 1-2 tbsp. l. plants or flowers. The mixture is infused and cooled, after which it is used for its intended purpose. The most suitable plants are string, chamomile, mint, calendula.
The easiest way to temporarily relieve the itching is to lightly press the wart with a clean finger.
Please note: removing papilloma yourself can provoke infection and will only worsen the situation.
Surgical intervention
Conservative therapy can be used as an additional treatment to surgery. This applies in the following cases:
- if the papilloma itches.
- The growth has increased in size.
- A color change has occurred.
- There is severe irritation and an inflammatory process in the active stage.
The operation to remove papilloma is carried out according to the indications of the attending physician. The procedure does not take much time and significantly improves the condition of the skin affected by pathology.
There are several methods for removing papillomas, but cryodestruction is most often used. The essence of the procedure is to freeze tumors by exposing them to liquid nitrogen. The likelihood of relapse after such an operation is extremely low, and no scars or cicatrices remain in place of the previous wart.
The method of removing papillomas with a laser can be used, regardless of the size of the growth and its location. After such exposure, no traces remain, and the risk of re-infection is also minimized.
Why does itching occur after removal?
Itching of papillomas is not the only inconvenience. Discomfort may occur even after the growth is removed. If the place where the papilloma was continues to itch, it is important to correctly diagnose the cause of what is happening. Here are some of them:
- partial preservation of pathogenic cells. If the tumor is not completely removed, there is a high probability of relapse.
- Injury to adjacent tissues during surgery. The presence of itching indicates healing of the affected area.
- Restoration of the skin after removal of papilloma. This reaction of the body is considered normal and goes away on its own after some time.
What to do if it itches at the site of papilloma removal
Removing tumors does not guarantee that they will not appear again. It is necessary to eliminate the cause - HPV. If this is not done, the virus can become active at any time and tumors will appear again.
The main reason that the skin itches after papilloma removal is precisely the activation of HPV. The place where the operation to eliminate the tumor was performed is the most vulnerable at first. General therapy, as well as compliance with all medical recommendations, will help reduce the risk of recurrence of papillomas. If itching occurs after removal, you should immediately inform your doctor.
Removal of papillomas
When papillomas appear on the body, it is necessary to remove them, since they contain a large concentration of viruses.
The removal procedure is one of the stages of complex HPV therapy.
If the growths are not removed, the patient will pose a danger to the people around him and be a source of infection.
Due to the inconvenient location of papillomas on the body, they are subject to frequent trauma, so this factor is an indication for their removal.
At the present stage, in order to get rid of growths, hardware technologies are used that can quickly destroy the tumor.
The patient does not require special preparation and the recovery period is reduced.
Methods for removing papillomas
- Using a laser beam. The technique allows you to remove growths in one session. The removal method is painless, since local anesthesia is performed before excision. The risk of relapse is minimal.
- The use of liquid nitrogen (cryodestruction) to remove papilloma. Under the influence of low temperature, the growth freezes and then dies. During the healing process, the place where the growth was located itches. This method is not used in the facial area, since the likelihood of scar formation remains high.
- Diathermocoagulation (electrocoagulation). Electric current is used for removal. There is no risk of bleeding, since coagulation of blood vessels occurs during the burning process.
- Radio wave technique. Refers to gentle methods of removing tumors. The procedure is characterized by the absence of pain, bleeding and precise execution. After removal, no scars are formed.
The advantages of two useful methods are that they make it possible to take biomaterial for histology.
In the presence of large papillomas, removal is carried out using a scalpel.
The procedure is performed under local anesthesia.
After removing the pathological tissue, sutures are applied and a sterile gauze bandage is applied over them.
The rehabilitation period lasts longer than with other methods.
The resulting biomaterial can be subjected to histological analysis.