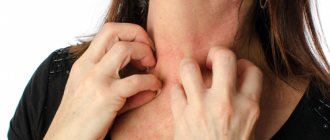
Preventive measures and effective treatment for ear itching
The main and key rule in order to ensure the health of the hearing organs is to maintain hygiene and keep them clean.
At the same time, you should not thoroughly clean them of sulfur every day. It plays an important role and is produced by the human body for a reason. It is required to avoid drying out of the outer part of the ear and is a serious barrier to various microorganisms that can harm health. What should be done, from the point of view of prevention, to avoid a situation where the ear is blocked and itches inside:
- You cannot clean the ear canal without lubricating or softening it with anything, in other words, “dry”. Doctors advise doing this after taking a shower or washing your hair.
- Cleaning your ears should only be done with means specifically designed for this purpose, such as cotton swabs. This is done to prevent damage to the eardrum, which can lead to hearing problems or complete loss. Cleaning should be done superficially.
- You should not strive to remove the maximum amount of earwax, be sure to remember that it protects the human ear from various bacteria and fungi. Of course, when earwax is produced in excess and your doctor advises it to be removed, this should be done on a regular basis. If this requirement is not met, a lot of sulfur will accumulate in the ear canal, it will thicken and turn into a plug. As a result, it will be impossible to cope with them at home; you will need to carry out the so-called rinsing with water and a syringe in the doctor’s office.
- In addition, many experts advise regularly wiping your phone and various personal items to remove bacteria from them. Also, it is not recommended to use other people’s hats. Be sure to use caps in the pool, which will protect against water getting into the ear canal.
So, what to do if the inside of your ears itch? The doctor prescribes treatment depending on the symptoms. Moreover, it is worth noting that you should not take any medications, because it will be very difficult for an otolaryngologist to make a correct diagnosis in such a situation. Symptoms accompanying itching in the ear canal can directly indicate infectious or any other problems, and in each individual case, treatment will be different. And it is a competent specialist who will be able to choose the most effective plan of action.
As a rule, when ear itching occurs, most people try to cope with it on their own, for example, by carrying out various hygienic actions. Quite often this method leads to success. However, if the problems are caused by serious reasons, then you should not worry or panic too much. In modern conditions, almost all problems can be corrected and cured, in addition, diseases in this area do not pose any threat to life.
If there is an effective and correct approach to correcting the situation that has arisen in the ear canal, it will be resolved with virtually no consequences. First, you should most accurately identify all the symptoms, both obvious and hidden. After this, it will be much simpler and easier to determine the real nature of the disease.
You cannot take any action on your own; only a specialist can fix everything correctly. The basis for treatment will be an examination of the patient, a thorough examination of the ear canal and the results of tests. You should also try not to scratch the skin, otherwise it will be much more difficult for the doctor to decide what to do if the inside of the ear itches.
Under no circumstances should you leave the situation to chance.
Separately, it is worth noting the situation in which, in some newspapers and magazines, attention is paid not to the medical side of the issue, but to the mental or even magical side. There are many signs
For example, what to do when the inside of your right ear itches, such sources say unequivocally - expect strong changes. In their opinion, the right ear is a clear harbinger of potentially good news. In turn, itching of the left ear, on the contrary, can bring troubles and failures, in other words, it is a negative factor. Moreover, the more it itches, the more changes and news will happen.
However, in most cases, one should not interpret omens, but rather deal with the situation from a scientific point of view.
Prevention
Measures to prevent itching in the ears:
- Rational ear hygiene without the use of matches with cotton wool, pins or hairpins,
- Wearing hypoallergenic jewelry,
- Maintaining the amount of earwax at an acceptable level,
- Periodic disinfection of mobile phone and headphones,
- Using earplugs when swimming in a pool or open water,
- Regularly washing your ears with soap and wiping them dry,
- Timely detection and treatment of diseases of the ENT organs,
- Fighting nasal congestion,
- Improving immunity: hardening the body, gymnastics, proper nutrition, walks in the fresh air.
Thus, the best prevention of itching in the ears is a set of publicly available measures and actions that are aimed at preventing otitis media of various origins and other dangerous diseases in which the ears itch inside and outside.
What is the cause of flaking in the ears?
Why do my ears itch? If a person is prone to frequent hygiene procedures, then this may be the cause of flaking and itching in the ears. Most otolaryngologists do not recommend cleaning your ears more than once every 5-7 days.
Even smooth movements with soft ear sticks can disrupt the integrity of the sensitive skin in the auricle. This results in shallow scratches, which, when healing, can itch the ears and cause discomfort in the auricle.
When we are not talking about carrying out frequent hygienic procedures, and the ear itches regularly, the cause of this phenomenon may be the presence of an inflammatory process in the area of the inner ear or an infectious invasion. In turn, peeling is an additional signal that there is a complex disease that requires qualified treatment.
The causes of peeling and itching in the hearing organs, on which the choice of treatment for the condition depends, may be different. Let's look at the most common of them.
Allergic reaction
The manifestation of allergies, when the ear itches, is not typical for most people. However, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body of each individual person, some patients experience allergies this way – peeling and itching in the hearing organs. The trigger for an allergic reaction can be insect bites, certain foods, medications, plants, etc.
Along with the fact that during an allergic reaction the ears begin to itch, the usual manifestations of allergies in the form of a skin rash may be absent and the person may not even be aware of the presence of such a condition.
There are many sweat and sebaceous glands in the head and neck area. When they function fully, the skin is normally moisturized and does not dry out.
But if the functioning of the glands is disrupted, for example, with excessive activity of the glands, the skin in the auricle becomes too oily.
Against this background, there is the development of a favorable breeding ground for pathogens, which in 9 out of 10 cases leads to a disease such as seborrhea - blockage of the sebaceous glands with subsequent inflammation.
During the inflammatory process, not only does the hearing organ begin to itch and pieces of the epithelium peel off, but a painful syndrome is also observed, causing significant discomfort to the person.
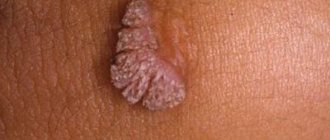
A fungal infection that parasitizes the ear is a fairly common occurrence. And all because such microorganisms choose the most inaccessible places for their parasitism, where a person cannot reach without outside help, not to mention diagnosing the problem. In view of this, the fight against harmful microorganisms becomes significantly more complicated.
If a patient has problems with dandruff, then it is more likely that the ears will begin to itch due to the formation of fungus in them.
Chronic diseases
Ears can also itch and peel due to the presence of certain chronic diseases:
All these diseases indirectly affect the health of the hearing organs. The negative impact of such pathological conditions manifests itself in the form of inflammation inside the ear canal, accompanied by itching, redness and peeling of the auricle and around it. The ear not only begins to itch, it dries out, and small cracks appear on it in places where the upper layer of the epidermis has peeled off.
In the case when we are talking specifically about the presence of a chronic disease that caused itching in the ear, then treating only the organ of hearing does not make any sense - therapy must be comprehensive.
The greatest danger for the patient is the chronic form of otitis media. In this case, after the appearance of itching in the ear and its peeling, swelling of the ear canal may occur, as well as partial or complete hearing loss.
Sometimes chronic otitis is accompanied by the appearance of ulcers in the Eustachian tube, after rupture of which the pus moves to the cerebral cortex
Therefore, when the ear begins to itch, it is extremely important to pay attention to this point.
Only a qualified specialist - an otolaryngologist - can determine the reason why the ear itches and flakes. Only this approach allows us to make a correct diagnosis when it comes to a chronic disease, allergy, fungus, etc., and prescribe the most appropriate treatment.
Associated symptoms
Based on the symptoms accompanying itching in the ears, the presence of the disease can be determined during diagnosis. The following accompanying symptoms often occur:
- Ear pain
, which increases with pressure on the tragus, as well as congestion, noise, redness and swelling. As a rule, a complex of such symptoms signals the presence of inflammatory processes. In advanced stages, fluid accumulations in the passages can also be detected. Temporary hearing loss often occurs. - A sore throat
. The discomfort in the ears that accompanies the symptom is most often a sign of the development of acute inflammatory processes in the mouth and throat, or sore throat. - The presence of yellowish and white discharge
, pus, pain and hearing loss. Usually signals the development of infectious processes. - Peeling of the skin
. Often indicates vitamin deficiency and allergic reactions.
How to treat ears if they itch inside
After accurately determining the nature of the disease, the doctor, if necessary, will prescribe conservative drug treatment. Depending on the etiology of the ear disease, antifungal, antihistamine, immunostimulating, antibacterial, symptomatic and other drugs are used.
If cases of burning inside the ear are isolated, and there are no other symptoms of any disease: no pain, no purulent discharge, no inflammation or fever, you can get rid of the unpleasant sensations by using a home cleansing procedure with folk remedies.
For example, rinse with hydrogen peroxide, or remove sulfur with cotton wool, lightly lubricated with mineral or vegetable (boiled) oil.
What reliable recipes do traditional healers offer:
Garlic oil.
You can make it yourself: leave ground garlic (2-3 cloves) for 24 hours with 50 ml of boiled sunflower (olive) oil. Or buy the product at the pharmacy. A turunda moistened with 3 drops of medicine is placed inside the ear canal at night.
Lavender and calendula oil.
Mix 3 drops of lavender essential oil with 1 tsp. calendula tincture, soak a tampon in the emulsion, squeeze it out and place it in the ear canal overnight, or simply lubricate the ear 3-4 times a day.
Celandine.
When infected with ear fungus, use an infusion or fresh juice of celandine inflorescences. To prepare the decoction you need 1 tsp. herbs pour 200 ml of boiling water, leave for 15 minutes. Only 3 drops of solution or juice are instilled into the ear in the morning and at night.
Hydrogen peroxide.
You can relieve the symptoms of burning inside the ear, and also disinfect the epithelium from bacterial flora and parasites. In Art. l. boiled water, dissolve 10 to 15 drops of 3% peroxide from the pharmacy. Pipette 4 drops into the ear canal, leave for 15 minutes, then rinse thoroughly.
Natural apple cider vinegar 4% naturally fermented.
The surface of the ear canal is lubricated to disinfect it from pathogenic microorganisms that cause an itchy burning sensation inside the ear.
Chamomile decoction.
Destroys fungal pathogens and relieves inflammation. Using a pipette, you need to rinse with the medicinal solution so that it flows out from the inside of the ear.
Tampons with propolis tincture.
They are considered an extremely effective remedy for getting rid of burning sensation caused by mechanical injuries to the ear cavity and fungus. This wonderful wound-healing anti-inflammatory agent is used only if there is no allergy to bee products.
Before instilling drops, it is important to make sure that the eardrum is intact, otherwise the penetration of the medicinal drug into the area of the inner ear can provoke an inflammatory process with serious health consequences
Treatment methods
Itching in the ears: how to treat the diseases that the problem causes? An otolaryngologist will help you get rid of prolonged itching. In this case, the doctor will necessarily carry out diagnostics, including:
- external and hardware examination of the ears and passages;
- blood tests;
- urine tests;
- smear examination for infection.
The list of events can be shortened or expanded in each individual case. Most often, a detailed examination and scraping examination is sufficient. Only after an accurate diagnosis can therapy be prescribed.
Drug treatment includes:
- The use of antibiotics (Tsipromed, Otof), as well as immunostimulants (Levomax, Polyoxidonium, Amiksin). Drugs are necessary to treat otitis media of various forms and stages of progression.
- Using ear drops (Polydex, Garazon). Used to treat otitis media and other infections inside the ear.
- Therapy with antimycotic agents (Nystatin, Clotrimazole, Amphotericin). Necessary for otomycosis, as well as for the prevention of fungus in otitis media and tissue damage inside the ears.
- Treatment with antihistamines (Suprastin, Cetrin, Loratadine). Eliminates symptoms of allergic reactions.
The use of traditional medicine recipes will help you quickly get rid of unpleasant sensations:
- Prepare tea tree oil. It is enough to purchase a pharmaceutical composition and use it for daily instillation of one drop into each passage.
- Grate a large onion. Use half for oral administration, squeeze juice from the second. Place four drops of the product into each ear canal before going to bed. The course of treatment is three to four days.
- Chop three or four cloves of garlic, pour three large tablespoons of olive oil into the product and stir. Heat the mixture over low heat for half an hour. Apply to the skin of the ears using a cotton swab two to three times a day.
- Pour a teaspoon of celandine into a glass of boiling water and simmer for fifteen minutes over low heat. Cool and strain the mixture. Place three to four drops in the right and left ears daily.
The recipes proposed above are effective for eliminating microbial and bacterial infections; they can also be useful for prevention of injuries and other diseases.
Drugs for treatment
Usually, for fungal infections of the ears, drugs such as Ketoconazole, Miconazole and others are used as treatment. For topical use, Chlornitrophenol, Bifonazole, etc. are prescribed.
During treatment with such drugs, a large number of dead fungi will form in the ears, so priority should be given to hygiene and ear care. Pathological discharge can only be removed by a doctor using special tampons or a probe. After the procedure, the patient is given a tampon with medication. Otomycosis can be considered successfully cured if after a month the analysis shows the absence of a pathogenic fungus.
Itching may occur with otitis media. This disease accompanies inflammation and pain in the ear. Treatment should be carried out with antibiotics, this can be Flemoxin Solutab, Sofradex or Otipax. Only the attending physician can prescribe an antibiotic, since all medications have contraindications and side effects.
If itching is caused by an allergy, you need to eliminate the allergen itself (for example, change the shampoo). Then you can move on to treating symptoms. For this purpose, antihistamines are used: Suprastin, Diazolin or Loratidine. If you have diabetes, you should take the same medications that were prescribed for the underlying disease.
Etiology
Most often, the problem of itching in the ears is short-term and does not pose a health risk. If accompanying symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor. Among the main causes of discomfort:
- increased sensitivity;
- accumulation of sulfur in the sink;
- exposure to irritants on the surface of the ear canals;
- hair growth in the passages;
- dry skin;
- hypothermia;
- age-related changes;
- disruption of the body's metabolic processes;
- injuries and damages;
- ingress of an insect or foreign body;
- skin diseases, ear mites;
- allergy;
- boil growth;
- changes in weather conditions;
- fungal pathologies;
- hormonal disorders;
- change in atmospheric pressure;
- otitis media of a bacterial nature;
- diabetes.
Sensations that are eliminated by mechanical action with hygiene products do not require treatment, but if improvement does not occur, you should consult a doctor.
Diseases
There are diseases of internal systems and skin that cause not only itching, but also burning, peeling, redness and pose a great threat to human health. The table describes the most common diseases with their symptoms and treatment methods.
| Name | Symptoms | Treatment methods |
| Ticks | Signs of the presence of parasites are a feeling that something is crawling under the skin, periodic itching, which intensifies at night. Another reliable sign is the presence of bites and redness on the skin. | In the fight against this parasite, several effective instillation agents are used - alcohol solution (70%), sodium chloride (9%). Yam, Demalan or sulfur ointment are suitable ointments. |
| Otomycosis | An infection of the outer ear caused by a fungus can develop in both adults and children. The risk of infection is high in patients with diabetes and a weakened immune system. Concomitant factors for the development of otomycosis are injury to the skin inside the auricle and canal, frequent exposure to moisture, and prolonged use of ear drops. If the sore is not treated, then over time the patient will experience not only unpleasant discomfort, but also a strong noise that covers the head, and later he faces complete ear congestion. Deep penetration of the fungus provokes pain, so at the first symptoms you need to seek help from a specialist. | Treatment of otomycosis takes a long time - it will take 2-3 weeks to destroy the fungal infection. First, a 3% peroxide solution is instilled into the ear canals, then Candibiotic drops. Frequency: 3 times a day. |
| Bacterial damage | Constant or periodic itching in the ears occurs due to the presence of bacteria inside the ears - staphylococcus or streptococcus. Unpleasant sensations are accompanied by a serious inflammatory process, periodic pain, and itching. | Complex treatment is prescribed using drops and ointments, which include Colistin, Neomycin and Polymyxin. Antibacterial agents include Quinozol, Tannin in glycerin, or Resorcinol. Broad-spectrum antibiotics such as Ampicillin are also prescribed. If necessary, the patient takes painkillers. |
| Skin diseases | Severe itching, peeling of the ear and canal can be caused by psoriasis, dermatitis of various etiologies or eczema. These skin lesions are contagious and can spread to any part of the body. | We need a vitamin and mineral complex to boost immunity and speed up recovery. Corticosteroids - Lemod, Celeston. Antihistamines - Fenistil, Ebastine. To dry the skin Zinc Oxide or Talc. |
| Otitis | Typically, itching and pain inside the ears occur with otitis externa. The inflammatory process is caused by injuries, frequent hypothermia or diseases of the ENT organs. | Several drugs are used for treatment - Otipax, Otofa, Amoxicillin. To eliminate the inflammatory process in the outer ear, the doctor prescribes steroid ointments or creams based on betamethasone (0.1%) or hydrocortisone (1%), as well as baby soap for ear care and ointment that contains antibiotics. |
| Diabetes | High blood sugar levels cause persistent or intermittent itching in the ears. | In this case, it is necessary to consult a specialist and take medications that normalize blood sugar levels. In addition to this, the doctor prescribes antipruritics - Fenistil. |
| Pathology of the liver and kidneys | Unpleasant sensations not only in the ear canal, but also on the skin of the whole body are caused by disruption of the kidneys and liver. This discomfort is caused by toxins that these organs secrete through the skin. | Once diagnosed, complex treatment is carried out to eliminate liver or kidney diseases along with ear itching. For severe and frequent itching, ointments are prescribed. |
| Idiopathic itching | The causes of such itching and burning have not yet been identified. Some experts claim that it is caused by mental or nervous disorders - frequent neuroses, stress. | Usually, with such a lesion, the doctor prescribes external treatment with Triderm or Pimafucort ointments. The course of therapy is 7-10 days. |
| Age-related changes | With age, every person undergoes a process of hormonal changes and disruptions in metabolic processes. Such changes provoke itching, both in the ears and in other parts of the body. | Immunomodulators - Wobenzym, vitamin-mineral complexes and lipoic acid. Additional dietary food. |
| Sulfur plugs | Itching, hearing loss, feeling of tightness in the ears. | If the cause of itching is excessive accumulation of sulfur or the formation of cerumen plug, the doctor removes it on an outpatient basis. |
Traditional methods
The advice that has been passed down to us as a heritage from our ancestors can also contribute to a quicker cure for various diseases that lead to the symptoms in question.
- Apple cider vinegar helps with ear fungus. It is used to dry the skin and destroy mycelium. Take a cotton pad, soak it in the liquid and wipe all affected areas. Do not bury it inside under any circumstances!
- A decoction of dry celandine herb will also help in the fight for health. You need to prepare 200 ml of water and 1 tsp. plants, combine everything and bring to a boil over low heat, or even better in a water bath. The decoction can only be used if the eardrum is not damaged. Children should not use this product.
- For eczema, one of the most effective remedies from traditional healers is St. John's wort oil. You can do it yourself. So: Collect only the flowers of the plant.
- Place in a container, compacting tightly.
- Fill with oil. Any neutral will do, even sunflower.
- Place on the sunny side of the window for 2-3 weeks.
- Shake the jar from time to time.
- The result is a concentrated oil that can be used successfully for other diseases.
Common diseases
It is not always possible to cope with constant itching in the ears by simply cleaning or washing. Severe itching may indicate a disease that requires treatment.
That is why it is important to know about the main causes of its manifestations, as well as the accompanying symptoms.
Otitis
Otitis is an inflammatory disease that develops in the ear. The pathology can be acute or chronic in nature. The infection usually enters the ear canals through the nasopharynx or from the external environment, concentrates on the inner ear and causes inflammation.
The disease is characterized by the development of the following phenomena:
- Otitis externa
. It is a mild form of the disease, in which severe pain occurs, especially when touched. This may cause hearing loss.
- Otitis of moderate severity
. In this case, the pathology spreads to the auditory tubes and forms deposits of secretions in the area of the eardrums. The progression of the disease is accompanied by a noticeable deterioration in hearing, the appearance of severe pain, and intoxication of the body. The peculiarity of the course is that when purulent stagnation is removed, the well-being and general condition of the patient improves significantly. - Labyrinthitis
. The disease is characterized by impaired orientation in space and the functioning of the vestibular apparatus. In this case, severe pain in the ears, headaches and dizziness, and partial hearing loss are observed.
Otomycosis
Severe itching in the ears, accompanied by the presence of discharge and crusts, indicates the development of a fungal infection. In addition, peeling of the skin and pain may occur. The progression of otomycosis to a severe form can cause damage to the bones of the skull.
Candida fungus enters the ear canals from the external environment due to weakened immunity. Also, progression of the disease can be a complication of chronic otitis media.
Skin pathologies
Dermatitis that develops on the walls of the auricle and canals is characterized by the formation of nodules, noticeable discomfort, as well as redness and peeling. After the appearance of scratching, the appearance of transparent and yellowish crusts may also be observed. Yellow spots form with seborrheic dermatitis, and peeling is also possible.
The progression of eczema is accompanied by the appearance of small blisters on the lobe and canals, redness and peeling. In this case, the itching can be unbearable, especially in the evening and at night.
https://youtube.com/watch?v=lL2hlsixNr4
Ear mite
The parasite can enter the human ear canals from animals or infected sick people. The presence of a tick is felt by the patient by constant movement; externally, the problem manifests itself by the appearance of redness, swelling and red dots on the skin. In this case, severe unbearable itching is possible, which intensifies in the evening and at night.
Allergic reactions
Allergies with formations on the skin occur, as a rule, both to food products and to cosmetics and household chemicals. Often the cause of redness and itching can be the use of inappropriate personal hygiene products. Diagnosis of the problem in this case is carried out with the participation of not only an ENT specialist, but also an allergist.
Furuncle
Inflammation of the hair follicle against a background of weakened immunity can result in a serious complication in the form of a painful abscess. As a rule, Staphylococcus aureus acts as the causative agent of infection. As the boil progresses, there is a significant deterioration in hearing, severe pain (especially upon palpation), swelling and redness. Externally, a boil appears as a reddish bump on the skin with a white or yellowish center.
Injuries and damage
Improper cleaning and the use of sharp instruments can damage the skin inside the shells, which often causes itching and pain. In addition, if infection penetrates into the resulting damage, inflammatory and purulent processes will occur. These phenomena, in turn, will make the unpleasant sensations long-lasting.
Bacterial infections
Getting into the ear canals from the outside and inside from fingers or non-sterile personal hygiene items, bacteria can cause complications, including inflammation of the inner ear. In this case, the skin and ears become very swollen, and clear liquid and pus are released from the labyrinth. The infection can also affect other areas of the skin near the canals, spreading through touching and scratching. Due to swelling, the patient begins to hear poorly, and the ear becomes blocked.
Allergy
Allergic reactions often manifest as itching in the ears. Allergens include cosmetics, insect bites, latex swimming caps, the use of headphones, poplar fluff, and dandruff. The otolaryngologist, together with the allergist, will conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient, identify the allergen and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Itching in the ears due to allergies can appear occasionally or bother the patient constantly. It is a signal from the body about a serious disorder. With allergic dermatitis, a keratinized rash appears on the skin, the skin thickens and becomes denser. If the ears itch and burn at the same time, the patient may be allergic to a fungus.
- Noise in the ears and head, causes and treatment. Folk remedies and medications for ear noise
Hygienic reasons
It happens that a person himself provokes pathological changes in the condition of the skin. This is especially true for the ears - surprisingly, most ear problems appear precisely because of improper hygienic care. If a person cleans their ears with a match, a knitting needle, a cotton swab, etc., the epidermis of the skin is injured and the nerve endings are irritated. In response to this, the sulfur glands begin to more actively synthesize sulfur - a secret that plays a vital role in protecting and moisturizing the ear canal.
Diligent ear cleansing usually leads to the opposite effect - an increase in the amount of wax.
The wax mass gradually moves to the outer edge of the ear canal - this is how self-cleaning of the ear occurs. This process is often accompanied by tickling and mild ear itching. To get rid of it, just rinse your ears with hydrogen peroxide or drip warm vegetable oil into the ear canal. This will help dissolve the sulfur and speed up its removal.
Many people, faced with excess wax formation in their ears, begin to clean them with even greater diligence. The irritated ear canal may begin to peel; crusts, fragments of dead epidermis and sulfur will accumulate in it. Under such conditions, the risk of infection of skin microdamages increases.
Inflammation of the outer ear often occurs as a result of scratching the skin of the auricle.
In some cases, excessive cleansing of the ears produces the opposite effect - the ear canal becomes dry and sensitive, and virtually no wax is produced. The skin may itch and peel. Without wax, the ear becomes more susceptible to various infections, primarily fungal.
How to properly care for your ears? The following rules should be followed:
- do not clean the ear canal with a cotton swab, match or other hard objects;
- wash the auricle every day, and the ear canal once a week (this cleans the visible part of the ear canal; you should not penetrate into the deep parts);
- avoid getting water deep into the ear canal;
- Regularly clean in-ear headphones, earplugs, etc. with alcohol;
- if there is a need to get rid of excess sulfur or cerumen plug, use non-mechanical cleansing methods (rinsing with peroxide, instilling vegetable oil, using cerumenolytics - drops to dissolve sulfur);
- do not use questionable methods of treatment (for example, wax candles for the ears - they are ineffective and dangerous).
Ears itch inside: reasons
There are a number of conditions and diseases that cause itching and even painful sensations. The causes of itching are as follows:
- Increased secretion and accumulation of wax in the ears;
- Rapid hair growth in the ears;
- Increased dryness of the ear canals;
- Irritation of unknown etiology;
- Injuries;
- Hypothermia of the body;
- Allergic reaction;
- Skin diseases of the external ear;
- Otitis;
- Diabetes;
- Boils;
- Problems with the body's metabolism;
- Ear mite.
Very often the ear hurts and itches very much with otitis media. This acute or chronic infectious inflammation is usually accompanied by redness and swelling of the ears. Microbes penetrate from the nasopharynx into the tympanic cavity through the Eustachian tube, and into the outer ear from the external environment. There are three types of otitis media:
- Outer. Inflammation affects the ear canal and the auricle itself. The pathology is accompanied by itching and discomfort in the ears, acute, throbbing, sometimes dull or pressing pain. Touching the ears is quite painful;
- Average. Exudate accumulates in the tympanic cavity, and the auditory tubes do not perform their function. There is a feeling of stuffiness in the ears, hearing acuity drops significantly, the patient feels throbbing pain and may observe purulent discharge;
- Labyrinthitis (inflammation of the inner ear). Symptoms of balance and hearing problems appear. A day after a vestibular disorder, a person feels that his ears are itchy and itchy, and later there is pain, which increases with sudden movements. If not treated promptly, deafness may occur.
Against the background of chronic otitis, as well as as a result of poor ear hygiene or damage to the integrity of the skin of the ear canals, otomycosis can develop. The cause of this pathology is a fungus of the genus Candida. The symptoms are as follows: a person’s ear is very itchy, white flakes appear, and skin hyperemia occurs. White crusts are usually visible on the outer ear. The danger of this disease is that the fungi can penetrate the labyrinth and then the bones of the skull.
If your ears are itchy and flaky, this could be a sign of an allergy. It can occur as a result of an insect bite, wearing headphones, dandruff, or using cosmetics. Unpleasant symptoms can occur only occasionally or constantly bother a person. Allergic dermatitis can lead to the appearance of a keratinized rash, thickening and hardening of the skin. The appearance of such a pathology in a child or adult requires contacting not only an otolaryngologist, but also an allergist, who will be able to formulate the most effective treatment tactics.
Many people complain that when they have a cold, their throat and ears often itch. This condition occurs as a result of inflammation of the laryngeal mucosa. The fact is that pathogenic microorganisms with mucus from the nose can penetrate the ear canals and larynx, provoking the further development of the inflammatory process. Usually, after recovery, the itchy sensation goes away.
It should be understood that the inside of the ears can itch due to dermatological problems. However, for some, the problem occurs only occasionally, causing minor discomfort. But sometimes the ears constantly itch, causing real suffering to the patient. They often turn red and become covered with nodules that burst open. After that, stains remain in their place, which constantly get wet and do not look very aesthetically pleasing. Subsequently, if this process is not treated, the epidermis thickens significantly, and pigment spots appear on its surface. With eczematous dermatitis, the ears become very flaky, and there is also severe itching and hyperemia of the skin of the ears. In addition, small bubbles with yellow and brown crusts appear on their surface. When the outer ear becomes infected with pathogenic fungi, seborrheic dermatitis occurs. The symptoms of this disease are as follows: irritated skin, plaques with yellow and greasy crusts. In this case, the skin can peel off not only in and around the ear, but also on the neck and cheeks. Psoriasis is also accompanied by similar symptoms. In this case, a person itches in and around the ear, and white peeling is also observed.
External otomycosis
If it itches a lot behind the ears, this may indicate a fungal infection. A disease such as external otomycosis develops very slowly. As a rule, the skin does not change. At first, the person feels only a slight itch. As its intensity increases, the ear constantly itches. Scratching leads to damage to the skin. And these are favorable conditions for contamination with fungi Penicillium, Candida, Aspergillus. With the development of the disease, in addition to itching, a burning sensation and a sensation of a foreign body also appear. The auricle becomes quite sensitive. The painful spasm is very strong. It intensifies during chewing, swallowing, and yawning. Most often, the pathology affects the skin of the outer ear. If a person has diabetes or leukemia, the damage may spread to the middle ear.
What causes external otomycosis? Main reasons:
- Poor hygiene.
- Inflammatory processes.
- Damage to the skin.
- Long-term use of antibacterial drugs.
This disease is highly treatable. Prescription of drugs is carried out on an individual basis. In difficult cases, combination therapy can be used.