Senile itch
Age-related changes affect all human organs, including the skin.
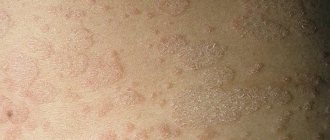
In older people, the skin becomes thinner, dries out, and becomes sensitive to allergens and mechanical irritants. These factors, as well as various diseases of internal organs and systems, cause the so-called senile itch - an unpleasant sensation that can be constant or occur periodically. Senile, or senile, itching can cover the entire body or only certain areas. The pathological condition is accompanied by peeling of the skin. Most often, unpleasant sensations occur in the evening and at night.
Allergic reactions
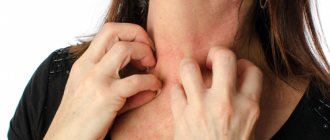
Allergic itching of the neck in front is most common in women who wear massive metal jewelry. Constant friction disrupts the integrity of the epithelium, which causes itching and irritation. Dermatologists advise wearing jewelry no more than five hours a day. In summer, this period should be reduced as much as possible. After removing jewelry, it is recommended to treat it with hydrogen peroxide to remove dirt, dust, dead cells and bacteria.
In women, the front of the neck often itches with redness.
Before putting on such jewelry, the neck is treated with special antiseptic compounds. This area collects dirt, sebum and sweat. You should not wash irritated areas with soap solutions. The ideal way would be a regular hygienic shower. Irritated areas are treated with soft wipes soaked in water.
The skin reacts with itching in the front of the neck and to synthetic clothing, washing powders with phosphates, creams, deodorants, and lotions. In this case, it is necessary to determine the type of allergen and completely eliminate it: wash off cosmetics from the body, remove clothes, use only high-quality cotton underwear. Medicines such as Tavegil or Zodak will also help to cope with unpleasant symptoms. In what other cases does the front of the neck itch?
Causes of senile itching
The main reason for the condition is natural aging of the body. As a person ages, the synthesis of hormones “responsible” for the elasticity of the skin decreases. Metabolism slows down, resulting in slower tissue regeneration. The skin becomes dry and wrinkled.
Several contributing factors increase the likelihood of aging itch. These include:
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- diabetes;
- renal failure;
- liver diseases;
- atherosclerosis;
- atrophy of the skin glands;
- cognitive disorders;
- violations of water-salt metabolism;
- dehydration.
Often, an unpleasant sensation can appear due to changes in air temperature, wearing synthetic clothing, swimming in too hard water or using products with an inappropriate pH level.
Thyroid diseases
The thyroid gland is a rather vulnerable organ in the human body. Its pathologies can cause itching on the front of the neck, since the skin may suffer from hormonal disorders. Such diseases usually develop for the following reasons:
- lack of iodine;
- reduction in the amount of protein in food;
- intake of nicotine and alcohol;
- lack of microelements with high iodine levels;
- unfavorable environmental conditions.
Therapy for endocrine diseases should begin with the elimination of provoking factors. The patient must rule out the causes, adjust the diet and quality of food, and forget bad habits.
Symptoms of pathology
Characteristic signs help identify senile body itching:
- thinning and drying of the skin (skin becomes papery);
- the appearance of red spots, rashes, pustules on the body;
- absence of scratches and wounds in areas of the body that are prone to itching;
- itching worsens in the evening and at night;
- The duration of discomfort can range from several days to several months.
Sometimes patients may itch different parts of their body every day.
Demodicosis
The neck may itch with the development of certain pathologies of internal organs: endocrine and fungal diseases.
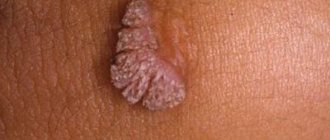
Demodicosis is a fungal infection of skin areas, which is accompanied by severe itching and peeling. The itchy area first acquires a yellowish, then brownish tint. Demodicosis is also called ringworm. It occurs on the scalp and, if left untreated, spreads to the neck, chest and face.
The patient develops round purulent rashes that turn red and itch. When the tick that causes the disease penetrates the sebaceous glands, there is a decrease in the functioning of the endocrine and immune systems, and the gastrointestinal tract suffers. Scratching can make the situation worse.
When the front of the neck itches, the cause may be neurodermatitis.
Diagnostics
With a similar problem, patients come to see a dermatologist. As a rule, the diagnosis is made based on a survey and examination.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the dermatoscopy method is used - studying the biomaterial using magnifying lenses.
In some cases, it is appropriate to conduct additional examination:
- take blood, urine and stool tests;
- test for allergens.
If the cause of the pathology is a disease of the internal organs, the patient is referred to a therapist or other specialized specialist who will supervise the underlying disease.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a pathological process that occurs as a result of stress and constant psycho-emotional tension. It is most common among people who engage in mental activity. The disease begins with the formation of red spots on the neck, most often in the front, which begin to peel and itch a little later. This is a chronic pathology that cannot be cured. Patients are advised to rest more, eat well, avoid emotional overload and the use of alcoholic beverages. Therapy is prescribed to achieve periods of remission and reduce the manifestation of unpleasant symptoms. Sometimes the skin on the front of the neck itches due to thyroid pathologies.
How to treat?
The goal of therapy for senile skin itching is to relieve symptoms. Several techniques are used to alleviate the condition. The choice of treatment regimen depends on the cause that provoked the pathology and the nature of the manifestations.
Preparations for senile itching
The following types of drugs are used to treat senile itching:
- antihistamines (Diazolin, Diphenhydramine, Suprastin);
- neuroleptics (Promazine, Clozapine);
- immunostimulants (Cycloferon, Echinacea tincture);
- corticosteroids (Betazon, Betaderm, Kremgen);
- vitamin complexes;
- alcohol tinctures;
- pharmaceutical ointments and creams with a soothing and cooling effect (Fenistil, Clotrimazole, Menovazan, etc.).
Corticosteroid drugs are taken only as prescribed and under the supervision of the attending physician. In general, hormone therapy is used for patients with autoimmune diseases, with the doctor carefully weighing the benefits and risks of treatment for each patient.
If the cause of itching is stress and other cognitive conditions, the patient is prescribed mild sedatives: valerian infusion, Novopassit, etc.
You can quickly stop an attack with warm water. The itchy area is showered with water for a few minutes. Before water procedures, you can apply 2-3 drops of peach tree essential oil to the skin.
Body hygiene
When symptoms of senile itching appear, it is important to pay attention to hygiene. For bathing, you need to use soft products with a neutral pH, and if possible, wash with water that is not too hard.
When bathing, do not use hard washcloths or scrubs.
The patient's underwear and bedding should be made from natural fabrics.
Senile body itch and diet
If you have senile itching, you should exclude the following foods from your diet:
- grilled meat;
- marinades;
- baked goods;
- citrus;
- coffee;
- spices;
- alcoholic drinks.
The diet includes seafood, herbs, fresh vegetables, pumpkin seeds, nuts, and unrefined oils.
Folk remedies
Some types of senile itching can be successfully treated with folk remedies.
Traditional methods of treatment:
- herbal baths;
- applying vegetable oil to flaky areas;
- using homemade ointment made from aloe and Vaseline.
Before using unconventional recipes, you should consult your doctor.
Other techniques
For patients who experience itchy skin as a response to stress, it is very important to control their emotions. In such cases, it is useful to do yoga, auto-training, and use various relaxation techniques.
Neurodermatitis
This is a disease of nervous origin and requires complex treatment. Patients undergo therapy with a psychotherapist and a neurologist.
Signs of neurodermatitis are roughened upper layers of skin, hyperemia, pain during touch, roughness, the appearance of tubercles, irritation and severe itching at night. The disease can spread to other areas, accompanied by an inflammatory process.
Why does the front of the neck itch and turn red?
Popular questions about senile itch
Can it develop in young people?
Young people may also suffer from itchy skin, but the term “senile itch” is not applied to them.
Where is itching most often located?
The localization of pathology is individual. The patient may itch the whole body or individual areas, and it may be different every day.
Which doctor treats senile itch?
If unpleasant symptoms appear, you should consult a dermatologist. If the patient has a history of chronic diseases, you should also visit a specialized specialist.
Option to choose a specialist
The need for treatment measures determines the need to select a medical center that meets the search criteria, which includes the availability of qualified personnel in various specialized areas, laboratory capabilities and instrumental equipment, as well as a course of treatment procedures.
Commercial centers fully cover this range of services, and you can choose an acceptable and convenient location through our Help Desk for private clinics in Moscow “Your Doctor”, a visit to which allows you to immediately sign up for an hour-long visit to a specialist or register a dermatologist’s home call
.
Common symptoms and manipulations in dermatology:
- Skin rashes
- Calling a dermatologist to your home
- Itching in the urethra
- Itchy skin
- Skin rash
- Prevention of casual sex
- Skin neoplasms
- Pyoderma
- Pityriasis rosea
- Streptoderma
- Scabies
- Peeling skin
- Fungal infections
- Skin infection
- Pus on the skin
- Blisters on the skin
- Papillomas on the foreskin
- Sexually transmitted diseases
- Skin structure
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.
Author:
Kasabov Vadim Vladimirovich Dermatovenerologist
Back to section
Care Tips
- Prevention of scratching: short-filed nails, lightly rubbing itchy areas.
- After washing, dry your skin carefully using wet movements, use a soft towel or a hair dryer on a cold setting.
- Avoid long hot baths. Try a bath with sodium bicarbonate (baking soda) or medicated oils.
- Use loose clothing and loose bedding/blankets.
- Avoid overheating and sweating, especially during night sleep.
- Increase the humidity in the bedroom so that your skin loses less moisture.
- Wear cotton gloves at night to prevent scratching.
- Avoid damaging the skin with alcohol-containing rubbing, woolen clothing, and excessive hygiene procedures.
- Cleanse your skin gently using moisturizers.
- Use cooling, soft compresses.
- You can use an anesthetic mixture: aftershave cream with menthol 50 ml, Diphenhydramine 1% 3–5 ml, Lidocaine 2% 1–2 ml, Novocaine 0.5% 5–10 ml. Mix and serve chilled.
- Use relaxation and positive visualization techniques.
Acne
In the cervical-collar area, with the development of acne, characteristic rashes appear that itch. Scratching is strictly prohibited. Initially, specialists find out the cause of such itching on the front of the neck, and then prescribe treatment methods.
The culprits in the development of acne may be:
- regular contact with the allergen;
- neglect of hygiene measures;
- viral and bacterial infections of lymph nodes;
- diseases of the digestive system.
Severe itching of the neck in front, peeling of the skin and burning cause the patient a lot of inconvenience and discomfort, which makes him overly irritable and apathetic.
Classification
By prevalence
Localized:
- non-specific:
dry skin, parasitic diseases, skin diseases (eczema, bullous pemphigoid, etc.), fungal skin lesions, allergic skin manifestations, insect bites, contact dermatitis;
- specific for oncological diseases:
melanomatosis (for cancer of the anus and vulva), glioblastoma, metastatic skin lesions, paraneoplastic syndrome.
Generalized:
- non-specific:
primary skin diseases, endocrine diseases (hypothyroidism, thyrotoxicosis, diabetes mellitus), carcinoid syndrome, diseases accompanied by cholestasis, blood diseases (for example, Vaquez disease), neurological diseases, senile pruritus, psychogenic pruritus, pruritus caused by infectious diseases, iatrogenic pruritus ( side effects of drugs);
- specific for oncological diseases:
chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin's disease, lymphomas, mycosis fungoides (a type of T-cell lymphoma), multiple myeloma, paraneoplastic syndrome.
By genesis
Central:
• neuropathic: brain abscess, brain injury, brain tumor, multiple sclerosis;
• neurogenic: cholestasis, opioids, paraneoplastic process;
• psychogenic: psychosomatic disorder manifested by itching.
Peripheral:
• cutaneous, “pruritoceptive”: cutaneous mastocytosis, medications (± rash), infestations (scabies, lice, fleas, mites), primary skin diseases, plant burns, urticaria;
• neuropathic: postherpetic neuralgia.
Mixed: central and peripheral – uremia.
Diffuse goiter
This disease is associated with a high concentration of thyroid hormones in the blood. Symptoms of diffuse goiter are worsening mood, increased irritability, inflammation of the skin on the neck and itching. Inflammatory reactions contribute to an increase in goiter, which is sometimes easy to determine even visually.
Diffuse goiter is also accompanied by rapid heartbeat, bulging eyes, deformation of the eyelids, and severe burning in the thyroid gland.
The front of the neck often itches with redness. The cause may be acne.
Prevention of tingling
When you first encounter a situation where the skin all over your body becomes prickly, you need to change your daily habits, supplement your daily routine with exercise, and review your wardrobe. The list of measures to prevent discomfort may include:
- Frequent changes of position during prolonged sedentary work (10 to 20 times per hour);
- short but mandatory breaks during long and monotonous work at least every 15-20 minutes;
- Replacing tight clothing with loose ones made from natural fabrics;
- avoidance of too tight belts and tight shoes;
- control posture in a sitting position;
- exercises for the spine, massage, going to the gym or swimming pool;
- prevention of hypothermia;
- change your diet as directed by your doctor.
Treatment options
In some cases, a skin biopsy, nerve biopsy, or cerebrospinal fluid test may be performed.
- Depending on the diagnosis, the doctor will recommend the best treatment option, taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient. The prescribed medications and procedures depend on the type of disease. Such treatments include:
- antihistamines for allergic reactions;
- sedatives for stressful situations, nervous disorders;
- cold showers or compresses, creams and ointments with a similar effect to relieve anxiety symptoms;
- drugs that stimulate blood circulation and relieve inflammation in case of carpal tunnel syndrome with tingling in the hands;
- For paresthesia, B vitamins, antioxidants, and drugs that reduce blood viscosity and stimulate blood flow are prescribed;
- for the same purpose, different types of physiotherapy are prescribed;
Infusions of collected herbs (chestnut, parsley, birch leaves, nettle, jeweler, willow bark, chestnut cake) are used as a treatment method.