According to the burn center of the children's city clinical hospital No. 9 named after. G.N. Speransky in Moscow, burns rank third in terms of injuries, with children accounting for ¾ of all cases. Most often, burns occur in young children under 5 years of age. Thermal burns in children occur more often than chemical and electrical burns.
Children's skin is much more delicate than adults, so any burn, even minor, can cause significant harm. Therefore, you should definitely consult a doctor about how to treat a burn in a child.
What are they and how do they manifest themselves?
- Thermal: flame, hot liquid and steam, heating radiators, hot water pipes and other hot objects.
- Chemical: acids and alkalis - often included in household chemicals.
- Electrical: lightning, current.
- Radiation: ultraviolet, radiation.
- Mixed: several factors from the above.
Almost all burns are thermal: damage to the skin, and sometimes mucous membranes, muscles and bones, as a result of exposure to high temperatures. They most often affect children, and in 95% of cases the cause is a flame.
According to Russian clinical guidelines, there are three degrees of depth of skin damage for thermal burns:
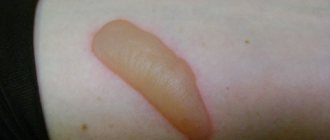
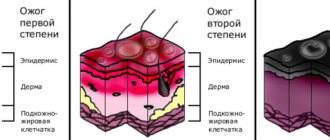
- Only the epidermis is the topmost layer. The skin turns red and swells. The pain is usually minor because the nerve endings are deeper. After 2-4 days, the dead epithelium sloughs off. There are no scars left.
- The epidermis and upper dermis is a layer rich in blood vessels and nerve endings between the epidermis and subcutaneous fat. In addition to redness and swelling, small blisters with cloudy or bloody contents appear - this is when the epidermis peels off and the void between it and the dermis is filled with blood and lymph. Second degree burns are very painful because the nerve endings are left without their protection - the epidermis. In 1-2 weeks, the lower layer of the dermis, closest to the subcutaneous fat, is renewed and the wound heals. Scars may remain if a large area of skin is affected.
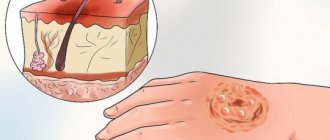
- Full thickness skin, subcutaneous fat, muscles and bones. A dense brown or black crust forms over the burn, which “sticks together” with the tissues below. The blisters merge with each other, and ulcers then appear in their place. Pain occurs only at the time of injury. Then pressure or slight discomfort is felt, and there is no pain even when touching the wound - because all the receptors have died. When the dead tissue begins to be replaced by new tissue, pain appears again. Amputation of the burned limb and plastic surgery of defects may be required. Scars always remain.
Types of burns
Thermal burns in children most often occur at home.
Children can be scalded by boiling water, burned near a fire, on a stove or an iron. Even too hot water during bathing can injure delicate skin. Electrical burns account for about 4% of injuries. Chemical burns occur even less frequently and are usually associated with parental carelessness when storing household chemicals.
In summer, you should pay close attention to sunburns: they are not as harmless as they seem. It is necessary to have special means on hand and know what to apply to a child’s burn in order to minimize the negative consequences. But first of all, it is important to quickly take him to a cool place, in the shade.
Why does it hurt so much
The skin is the largest organ: 4−6% of the total body weight. It contains up to 82% water and a third of the total blood volume. There are 2 million nerve endings in the skin, 1.5 million of them are pain receptors.
Temperatures above 44 °C destroy skin proteins - the integrity of the cell membranes is disrupted and water from the cells goes into the space between them. This can be illustrated using an egg as an example. It contains approximately 73% water, 13% protein, 12% fat and minerals. When cooked, the proteins in the cell membrane are destroyed and folded - water comes out. The same thing happens to the skin, only the water goes into other tissues. Therefore, swelling occurs.
Then platelets stick together in the vessels of the dermis and clog the lumen. The blood supply to the burned area is reduced, which can lead to complete tissue death if help is not provided in time. A burn also leads to the release of substances into the blood that provoke inflammation.
Treatment of scars after burns
If you are interested in how to get rid of the external consequences of a burn, you need to know that in case of serious damage to the skin, the scar will remain in any case. Here you will need the help of a cosmetologist who will help restore the normal appearance of the skin.
Typically, for such an operation, a scar excision technique is used, after which several cosmetic sutures are applied to the tissue. When the sutures are removed, the damaged area is treated with ointments that prevent the formation of new scars on the skin.
For particularly difficult cases, for example, burns from boiling water, the laser resurfacing technique is used. Modern equipment allows you to completely remove scars and achieve perfect skin. If the severity of the burn is insignificant, chemical peeling with fruit acids is recommended.
How to prevent
GMS Clinic pediatrician Maria Fadeeva recommends:
- Keep matches and lighters out of the reach of children
- keep hot foods and drinks away from the edge of the table
- Place irons and curling irons that are turned on so that the child cannot reach them
- cook on the back burners, turn the handles of pots and pans towards the wall or to the side so that the child cannot accidentally grab them
- use protective devices that block the switching on of stoves
- do not carry the child in your arms while preparing food
The kitchen is no place for a small child, especially when preparing food.
- Do not leave your child unattended in a room with heaters on.
- Check the temperature in the bathroom before bathing children
- Keep children away from bonfires and do not set off fireworks nearby
- Avoid inhalation over hot decoctions and boiled potatoes for ARVI - this is ineffective and creates a high risk of burns to the respiratory tract and face.
Preventing burns in a child at home
Young children get most burns due to parental negligence. Kids don’t yet know that hot things are dangerous and that fire shouldn’t be touched, so it’s important not to leave such things unattended. When children get older, you need to explain to them why certain objects should not be touched. Many children try to break the ban without explanation simply out of curiosity.
Before bathing or feeding hot food, be sure to first check the degree of heating, because children are more sensitive to temperature.
First aid
The Russian Ministry of Emergency Situations recommends not to panic, cool the burn, cover the affected area with a clean cloth, give painkillers and call an ambulance if necessary.
Maria Fadeeva tells more:
The most important thing is to stop exposure to the damaging factor: remove the child from fire, hot water or hot objects. For shallow burns, rinse the affected area of skin with running water, and if the skin looks purple and/or blisters appear, immerse it in cool water no higher than 15 ºС for no longer than 20 minutes. For extensive burns, cover the skin with a clean, non-stick cloth, such as cotton. Small areas can be kept open. If the pain is severe, you can give your child ibuprofen or paracetamol and, if possible, raise the burned part of the body above the level of the heart - this slows down the blood flow to the area, reduces swelling and pain. If there is itching, you can take antihistamines.
What to do for burns
First of all, it is necessary to stop the effect of the traumatic factor. In case of burns from boiling water in children, it is necessary to remove their wet clothes, being careful not to damage the blisters. Extinguish open flames with thick cloth. Do not pour water on the fire, as this creates steam, which can also burn the child or you. If your hair catches fire, for example when blowing out candles on a cake, you should also use a cloth to knock down the flame to prevent it from spreading.
In case of a slight burn in a child (1-2 degrees), if possible, cool the injured area under running cold, but not ice-cold water, at a temperature of approximately +10...+20 ℃, or cover the burn site with a clean cloth moistened with water.
If the injury is mild, you can treat the burn site with a special spray. To reduce pain, you can give a mild over-the-counter pain reliever according to the age of the victim. It is necessary to calm and distract the child if possible.
A more severe burn should not be cooled with running water. It is necessary to call a doctor, cover the affected area with a clean cloth to prevent infection, give pain relief and wait for the doctors to arrive, or take the child to a medical facility yourself.
What not to do
Pediatrician at the Fantasy Children's Clinic, Ph.D. Svetlana Mukhortova does not recommend:
- Lubricate the burn with vegetable oil, cream, sour cream and other fermented milk products. A film forms on the skin, air stops flowing to the wound - it overheats, and the depth of the lesion increases. Lactic acids and fermentation products can introduce microbes into the wound
- treat burned skin with brilliant green, iodine, cosmetic lotions - alcohol dries out the skin and causes burning and pain
- apply bandages with urine to the wound. The effectiveness of urine therapy has not been proven
- puncture blisters - microbes with liquid can enter the wound. The blisters will open on their own - as a rule, this happens when the skin has already been renewed and the wound has “healed”
- remove stuck clothing yourself so as not to injure the burn site
- apply snow and ice longer: burned skin does not feel temperature changes - you can get frostbite
- sprinkle the burn with soda, flour, mustard powder, starch or baby powder - the film prevents cooling, and small particles can fester
- apply tight bandages and seal the wound with adhesive tape - air access is reduced
- rinse with running water if bubbles open - this is painful and can lead to germs penetrating deeper.
Popular questions and answers
In order not to miss complications in case of burns in a child, we will learn how to act from a pediatrician, the head of the children's clinic of the Maternity Hospital No. 4 at the City Clinical Hospital named after. V.V. Vinogradov Vladislav Zyablitsky.
When should you see a doctor if your child has a burn?
Ideally, always, even if the burn is tiny, you should not risk the child’s health. The doctor should at least examine the baby to determine the depth of tissue damage and determine treatment tactics. After all, with different degrees of burns, the treatment is different.
What can be the consequences of a burn in a child?
In addition to the usual complications in the form of damage to the skin, mucous membranes and the appearance of blisters, secondary complications are also possible that appear after a while. The addition of an infection can also lead to gangrene - you will have to remove the limb to save your life. Blood clots may form, bleeding and ulcers may occur. Even after the burn has healed, there may be problems - eczema and dermatitis, scars, baldness. The prognosis depends on the area and depth of the burns, age and correctly provided first aid. In such a matter it is better to be on the safe side.
When to call an ambulance
“For extensive burns. In the first degree - only redness of the skin - you can seek medical help if the pain and swelling increases,” says Svetlana Mukhortova.
Maria Fadeeva also recommends seeing a doctor if:
- burned skin of the face, fingers and toes, feet, joints, genitals
- The burn area is larger than the child's palm
- the victim is less than 5 years old
- body temperature rises, redness increases, sensitivity disappears at the burn site
- there is a suspicion of a burn to the respiratory tract or eyes - this is possible after fires, falling into a fire, inhalation over hot steam
Remedies for burns
How to treat a burn, and what kind of surgical assistance can be provided independently in the field or at home?
The use of creams such as Levomikol or Rescuer is guaranteed to help with minor injuries, such as briefly touching a hot pan. Dexpanthenol works very well for first degree burns. If the degree of damage is more serious, creams can only be used as a preventive measure and there is no point in relying on them.
Anti-burn products such as sprays or gels - for example, Burnshield Anti-burn Hydrogel - are more effective because they are dispersed and are better absorbed by the skin. These drugs combine two functions - anti-inflammatory and analgesic.
Buy
Buy
Buy
There is another type of treatment - special anti-burn dressings. They are recommended when the patient needs to be outdoors. Such dressings prevent dirt and dust from entering the wound.
What else can you do at home?
To speed up the healing of superficial burns, preparations with dexpanthenol are recommended - preferably in the form of sprays, so as not to create a film over the affected area. It is applied to the wound 2-4 hours after the burn and only in the first degree. Sometimes it is allowed to treat a child at home and for burns with small blisters. In this case, it is necessary to promptly change clean bandages and, if the doctor prescribes, treat the wound with chlorhexidine.
In 2008, WHO issued a report on the prevention of childhood injuries. Pediatricians have developed a brochure for children, “Live an interesting and safe life”: it is written in simple language that children can understand and is presented in the form of stories and entertaining quizzes, and the advice from it is still relevant today.
Treatment of a burn in a child
After first aid is provided, the child is taken to the doctor, and he determines further treatment. Regardless of the degree of damage, all burns go through three stages of healing: inflammation, regeneration, scar formation. Each stage requires different medications and wound care.
When the burn is fresh, the wound is cleaned of dead skin, if any, to prevent damage to blisters and infection. For this purpose, bandages and antiseptics are used. Next, new tissue begins to form - to speed up the process, special ointments and vitamins are used. After scar formation, the skin recovers, but sometimes the scars are very large. Then physical therapy, laser resurfacing, softening creams, and resolving scars may be prescribed.
Diagnostics
Even with a minor burn, a child is treated only under the supervision of a doctor. The doctor determines the degree of damage and the area of the burn, and, if necessary, sends the child to the burn department at the hospital. A lesion area of more than 10% almost always leads to hospitalization, at least for observation on the first day.
The diagnosis is made based on external examination. The area and depth of the lesion is written as a fraction: the numerator indicates the burn area and depth, and the denominator indicates the degree of the burn. Blood tests may be ordered, especially if the burn is severe.
It is important
Concussion in a child and how to recognize it in time
Modern methods of treatment
A moderate burn usually takes about 2-3 weeks to heal. In severe cases, if the injury has affected joints, ligaments and other deep tissues, the victim may spend a long time in the burn department.
Wounds are constantly treated with antiseptics, since infection is very dangerous. Special dressings are used to protect the exposed surface of the burn. One of the modern methods is the application of hydrogel dressings. The hydrogel swells when it absorbs fluid from the wound and turns into a gel. This maintains a humid environment. The bandage itself does not cause allergies and allows air to pass through so that the wound heals faster. Hydrogel bandages and dressings are impregnated with special substances with an analgesic and disinfecting effect. Some have silver ions added.
The hydrogel is transparent, so you can monitor the condition of the burn directly through it without removing the bandage each time. What is very important is that the hydrogel does not stick to the skin - burns constantly get wet, and usually the bandages have to be soaked so as not to tear off the dried bandage from the wound.
For minor burns, hydrogel is not required - it is enough to periodically treat the inflamed skin with antiseptics and drugs that accelerate regeneration.