Services Doctors Results Reviews
Expert tested
Sharubina Karina Petrovna Trichologist, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist
Publication date: January 16, 2022
Review date: November 08, 2022
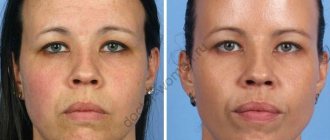
Who doesn't want to have beautiful, sensual lips? And, it would seem, the technique of lip augmentation has been worked out for years and decades. They are injected with hyaluronic acid, which immediately gives noticeable volume plus hydration.
However, not everything is so simple - in order to get truly beautiful lips, you need a very experienced doctor to do hyaluroplasty. Sometimes patients themselves are not responsible enough in choosing a doctor and a clinic, and then they come to other doctors and ask them to fix what happened and remove hyaluronic acid from their lips.
It happens that hyaluronic acid needs to be removed from tissues for medical reasons, without waiting for it to dissolve and leave them.
What problems require treatment with hyaluronidase?
Most often, patients come to the clinic after unsuccessful lip augmentation in two cases:
- When the drug shines through the mucous membrane because it was not injected deeply enough.
- When unsightly lumps appear on the lips because the drug was administered incorrectly or granulomas have formed.
Also, when introducing hyaluronic acid into different parts of the body, the following complications are possible:
- threatening necrosis of the skin and subcutaneous tissue around the lower lip;
- Tyndall effect or swelling under the eyes caused by too superficial placement of the drug;
- abscesses after increasing the volume of the cheeks;
- early and late allergic reactions.
Lumpiness of lips
Lip necrosis
Swelling of lips
Problems arise due to the administration of a low-quality drug or as a result of the administration of biological products under questionable sanitary conditions.
Many of these patients do not receive care from the esthetician who performed the cross-linked hyaluronic acid procedure because he is not qualified enough to resolve the medical problem in the event of an adverse event. A beauty salon is not a clinic! And a cosmetologist is not a doctor!
Is it even possible to remove biopolymer gel from lips?
Restoring the shape of the lips after previously injected silicone gel is an art.
When enlarging lips with gels, many believe that if necessary, “pumping out the gel” is a minor problem. After all, the gel was introduced through a thin puncture, which means it can be removed back in the same way. Unfortunately, everything is not as simple as it seems. This gel grows into the lip tissue, becomes overgrown with connective tissue (scar) and deforms the natural shape of the lips.
And in this case, lip correction turns into an extremely difficult task for the surgeon.
What complications after the injection of hyaluronic acid will hyaluronidase help with?
If you contact an experienced cosmetologist-dermatologist in a timely manner, he will be able to help in any situation, except blindness and skin necrosis. Of course, the introduction of hyaluronidase will not give anything if it was not hyaluronic acid that was used, but some other drug of unknown origin. Hyaluronidase acts on any cross-linked hyaluronic acid that is approved for injection in the European Union.
Hyaluronidase
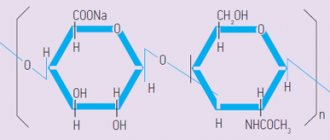
What is hyaluronic acid?
Let us remember that hyaluronic acid is a polysaccharide that is able to attract and retain large quantities of water molecules, providing excellent cell hydration. It is widely used in cosmetology for the correction of facial features, including lips. Natural and synthesized acid is used.
The main amount of all hyaluronic acid is concentrated in the skin; it is located in the connective tissue of the dermis between collagen and elastin fibers, as well as in the cells of the stratum corneum - corneocytes. If we draw some analogy and imagine our skin as a mattress, then we can say that collagen and elastin are springs, and hyaluronic acid is foam rubber that fills the space between them.
Hyaluronic acid is a natural component of our body. It is synthesized in it and participates in many biological processes. Its role in the body is truly invaluable. The most important and valuable quality is the ability to bind and retain water. It is known that one hyaluronic acid molecule binds 500 water molecules. It also has the so-called “diaper effect” - the ability not to release moisture from the skin.
Being an important component of the extracellular matrix, hyaluronate ensures the vital activity of cells, filling the space between them. Hyaluronic acid ensures the transport of oxygen, lymphocytes and other blood molecules and nutrients to the site of tissue damage and inflammation.
After 45 years, the amount of your own hyaluronic acid begins to decrease. Therefore, many resort to its artificial administration. Hyaluronoplasty helps trigger the production of your own hyaluronic acid, but other reactions also occur.
Zadiran Alina Valerievna
Dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist. Candidate of Medical Sciences
How quickly does hyaluronidase work?
The effect of hyaluronidase is immediate, but often causes swelling, so most often patients see the effect of complete dissolution of hyaluronidase only after 2-3 days.
- If it is necessary to dissolve only part of the hyaluronic acid, small doses of the enzyme must be administered every 10-14 days.
- If we are dealing with a serious complication and want to dissolve all the acid at once, large doses of the enzyme should be used.
Effect of hyaluronidase
Results and discussion of ultrasound examination and subsequent treatment
In the group of examined patients who were injected with filler based on hyaluronic acid, the gel was distributed by zone as follows (see table): 10 people (50%) - nasolacrimal groove, 6 people (30%) - infraorbital region (fossa canina), 5 people (25%) - the area of the cheekbone, 6 people (30%) - the area of the lips and nasolabial folds, 2 people (10%) - the area of the chin. In 5 cases (25%) the gel was adjacent to the vessels, in 12 (60%) fibrosis was detected. In 2 cases, non-hyaluronic preparations were injected.
Ultrasound revealed HA fillers as clear anechoic and hypoechoic loci of varying diameters from 3 to 15 mm. Based on the results of the ultrasound diagnostics, taking into account the anamnesis, the following data were obtained below.
In two patients, after multiple (8 and 11-fold) injections of hyaluronidase preparations into the area of the injection zone of Restylane Perlane gel (nasolacrimal grooves and the area of the zygomatic bone), examined after the last injection of hyaluronidase on the 7th and 14th days, gel loci were found in injection zones without signs of biodegradation. Moreover, in one of the cases, described in the clinical example below, an ultrasound was done on the 7th day after the administration of the hyaluronidase drug and on the 49th day, while the size of the filler bolus did not change. The drug Juvederm Voluma in a patient with a clinical picture of persistent edema, injected into the zygomatic-buccal area in a volume of 0.4 ml on each side, increased on the right side, according to ultrasound, three times the original volume, and its actual volume was 1. 7 cm3 ( Fig. 1A
).
In this case, the drug migrated from both sides from the injection zone to the area of the zygomatic bone, to the infraorbital region, was located in the fossa canina and came into contact with the branches of the infraorbital (infraorbital) neurovascular bundle, and was well palpated as a tissue compaction ( Fig. 1B
).
After administration of the Longidase drug on the second day, the gel locus on the right side decreased by half, but still remained one and a half times larger than the initial injected volume - 0.7 cm3 (Fig. 1B). On the opposite side, the size of the locus before the administration of Longidase and on the second day after administration were unchanged, 0.4 cm3 each. An interesting fact is that during a control study after the administration of Longidase, the gel was found in the nasolacrimal groove subcutaneously (Fig. 1D). During the initial ultrasound examination, there was no gel in this area, and initially no gel was injected into the area of the nasolacrimal grooves. It seems that in the area of edema of the tissues of the facial skeleton, the gel migrated presumably along a pressure gradient. The resistance index (RI) on Doppler examination (DI) of the facial artery upon admission and follow-up examination on the second day after Longidase administration on both sides was reduced to 0.50. The patient was prescribed phonophoresis with one percent hydrocortisone ointment. Over time, on the tenth day after the injection of Longidase and six procedures of phonophoresis with one percent hydrocortisone ointment, the patient experienced a significant improvement in the clinical picture, swelling of the face decreased, palpation of the facial tissues became soft, the actual volume of the bolus in the right infraorbital region was 0.33 cm3, IR increased from 0.50 to 0.61 ( Fig. 2
).
In a patient with complaints of overcorrection, nine months after injection of Juvederm Ultra 3 into the lips at the border of the transition of the red border into the mucosa, an ultrasound picture of fibrosis was revealed in the form of a hyperechoic cord on the red border of the lower lip, which was mistakenly interpreted by the patient as a bolus of filler.
In a patient with complaints of hypercorrection in the forehead after injection of a filler three years ago in China, presumably of a biopolymer nature, anechoic boluses of irregular shape were located throughout the face in the hypodermis, and in the forehead area - subdermally.
In another patient with complaints of lip asymmetry after surgical removal of a granuloma that developed after the injection of a gel of unknown nature, its unremoved remains were visualized like “moth eggs in a spider’s web.”
Rice. 1. Patient A., 36 years old, after injection of Juvederm Voluma into the cheek-zygomatic area with complaints of facial swelling and compaction in the right infraorbital zone: the volume of the gel bolus in the infraorbital zone upon admission before the administration of Longidase was 1.7 cm ( A); size of the gel bolus in the infraorbital zone upon admission before Longidase administration (B); volume of gel bolus in the infraorbital zone 2 days after Longidase injections (B); a bolus of gel subdermal over the orbicularis oculi muscle, which appeared in the nasolacrimal groove 2 days after the Longidase injection (D)
Rice. 2. Patient A., 36 years old, after injection of Juvederm Voluma into the cheek-zygomatic area in dynamics ten days after treatment with Longidase and six phonophoresis procedures with hydrocortisone: the volume of the gel bolus in the infraorbital zone decreased from 1.7 cm3 up to 0.33 cm3 (A); gel bolus size in the infraorbital zone (B)
Symptoms of Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome
The syndrome is manifested by swelling of the lips and cheeks.
Then the facial muscles gradually weaken. It becomes difficult for a person to close his eyes or talk, and liquid pours out of the corners of his mouth. 30 percent of patients experience dry or watery eyes. In 20%, the perception of sounds increases to such an extent that it becomes unpleasant. In a patient with Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, Restylane Perlane gel in the zygomatic bone area was visualized as clear anechoic loci. Restylane was visualized in his lips with signs of incomplete biodegradation in the form of anechoic and hypoechoic loci 14 months after the injection. The syndrome developed two months before the examination and, in our opinion, is not associated with the presence of filler. We found it interesting that 14 months after the injection, the filler was not completely biodegraded.
In the remaining 16 patients with complaints of swelling, asymmetry and overcorrection, the sonographic picture of a hyaluronic acid-based gel was combined with ultrasound signs of adipose tissue edema of the type of septal panniculitis in four cases, and fibrosis in 11 cases. Foci of fibrosis measuring four millimeters or more in diameter were clearly palpable in the lips (in 3 people) (Fig. 3), perceived by patients as an “unresolved gel,” as well as in the soft tissues of the face (in 2 people).
Rice. 3. Ultrasound picture of fibrosis in the lips
After the end of the first stage of treatment, positive dynamics were observed in patients with gels based on hyaluronic acid (80%), namely, a decrease in the size of the boluses and a change in their structure from clearly located hypoechoic and anechoic formations before treatment into heterogeneous structures replaced by echo-positive tissue, presumably fibrous . According to our observations, the degree of biodegradation and reduction in the size of the gel were influenced by the depth and size of the initial bolus. The deeper the bolus was and the larger its size, the less amenable to correction it was. In the area of fossa canina and the chin, the gel was the slowest to respond to therapy, decreasing by no more than 25% of the original size, while the gel with a more superficial occurrence decreased after the first stage of treatment by 40-60% and acquired the appearance of heterogeneous fragmented tissue during ultrasound examination. structures of increased echogenicity, which indirectly indicated replacement of the filler bolus with connective tissue (fibrosis).
Specialists of the Clinical Center for Maxillofacial, Reconstructive and Plastic Surgery of the Moscow State Medical University Clinic named after. A.I. Evdokimov in their work described various options for the outcome of the injected filler according to the data of an echographic study in dynamics. Our observations coincide with the data of researchers. The outcome after contouring with gels based on hyaluronic acid is fibrosis with varying degrees of severity [].
Rice. 4. Periorbital edema
An interesting fact is that out of 10 patients (50% of the total number of those examined) who complained of hypercorrection of the nasolacrimal grooves, in only five (25%) the gel in the area of the nasolacrimal groove was determined both above and below the orbicularis oculi muscle, At the same time, there was a clinical picture of edema of the periorbital zone. In the remaining five people (25%), the gel was located under the orbicularis oculi muscle, and there was also a clinical picture of swelling of the indicated area, which was perceived as overcorrection ( Fig. 4
). In the same 10 patients (50% of those examined), in 30% of cases (six people), the gel was located in the infraorbital region (fossa canina) in the deep layers. In another five patients (25%) in the area of the nasolacrimal groove, the gel was visualized along the angular artery and the dorsal nasal artery. Moreover, in five examined patients (25%), the gel was not just located along the vessel, but was in contact with it in different areas: in 2 cases (10%) with the facial artery in the projection of the nasolacrimal groove and in 2 more cases (10 %) - at the level of the exit of the infraorbital artery and nerve. In these five patients (25%), there was a decrease in the resistance index (RI) during Doppler examination of the facial artery and its branches, which correlated with the clinical picture of long-term (more than three weeks) edema. The resistance index was reduced at all points of the vessel with which the gel was in contact. At the same time, in patients with the gel located along the vessel, but not adjacent to it, a decrease in IR was not observed. Presumably, the mechanism for reducing IR may be associated with an imbalance of relaxing and constricting factors, one of which is nitric oxide. For example, in works studying the pathogenesis of the development of posthemorrhagic cerebral vasospasm, it was established that in the acute period there is a high functional nitrooxydergic vasorelaxation. From the second week of the hemorrhagic period, differences are observed in the clinical course of the disease and the dynamics of indicators of nitrooxydergic vasorelaxation: in the absence of ischemic complications, the level of nitrite was within the normal range, and apoplectiform vasospasm, on the contrary, occurred against the background of a significant decrease in the level of nitrite relative to the norm [].
In another study examining the pathogenesis of the development of infectious toxic shock, a significant increase in the level of nitrite as a metabolite of nitric oxide was found in patients with clinical infectious toxic shock, which was not observed in the group of severe patients without clinical shock []. Described in the works of E.I. Karpova, L.R. Mingazova, O.R. Eagle compression-ischemic syndrome, neuropathic disorders in the facial area after contour injection plastic surgery can lead to such an imbalance of relaxing and constricting factors [, ]. However, this issue requires additional research. Another study suggests that non-mechanical gel compression may maintain the clinical picture of persistent edema. Experimental work on mice showed that at the maximum level of pressure and stretching of soft tissues with fillers introduced into the area of vessel projection, no significant changes in the functioning of the vascular bed were detected []. Our studies indirectly confirm clinical manifestations using the instrumental method. Determination of the resistance index can be used for the differential diagnosis of compression-ischemic syndrome in the facial area.
After the first stage of treatment, patients with gel loci measuring more than 3 mm in diameter (25% of those examined) required a second stage of treatment - administration of the drug Longidaza under ultrasound guidance. Two weeks later, repeated ultrasound control was carried out. In the injection zone, signs of reduction, biodegradation and fragmentation of the gel into separate isoechoic areas less than 1-2 mm in size were observed.
Incorrect administration of hyaluronic acid – when and who to contact?
Below is a list of the most alarming symptoms that - if they occur after the injection of cross-linked hyaluronic acid - should prompt the patient to immediately seek help from a specialist experienced in treating complications in the field of aesthetic medicine:
- pain that is not relieved by over-the-counter pain medications;
- increased swelling of the face;
- dyspnea (shortness of breath);
- whitening, decrease or increase in skin temperature over the injection site of hyaluronic acid;
- suspicion of an abscess;
- heat.
Unsatisfactory aesthetic effect, asymmetry, visible lumps and translucency of the drug do not require urgent intervention.
The only correct address where you can eliminate the consequences of complications after using hyaluronic acid is the office of a dermatologist with experience in treating complications in the field of aesthetic medicine.
Materials and methods
The proposed method was tested on 20 patients. The group included women aged 25 to 44 years.
The structure of the complaints included:
- dissatisfaction with the aesthetic result – 100%;
- hypercorrection – 75%;
- asymmetry – 60%;
- swelling in the injection area – 50%.
The most common correction areas were: nasolacrimal grooves - 50%, lips - 30%, cheekbones - 10%, chin - 10%.
When collecting anamnesis, according to the patients, we identified the following distribution of installed fillers of various brands by zone (Table).
Table. Distribution of installed fillers of various brands by zone
| Introduction zone | Filler brand | Number of patients |
| Buccal-zygomatic region and nasolacrimal grooves | Restylane Perlane Juvederm Voluma Juvederm Volbella Reneal Princess Revanesse Unknown HA filler | 5 1 1 1 1 1 1 |
| Area of nasolabial folds and lips | Restylane Juvederm Ultra 3 Unknown filler (not hyaluronic acid) | 3 2 1 |
| Chin | Restylane Unknown HA filler | 1 1 |
| Forehead | Unknown filler (not hyaluronic acid) | 1 |
After collecting an anamnesis, an examination of the affected area, palpation, and then an ultrasound examination using the MyLab Twice device (manufactured by Esaote, Italy) were performed.
In four patients (20%), an initial ultrasound examination was performed after administration of drugs containing hyaluronidase. One of the four patients had a history of multiple injections into the lips with various fillers, followed by shape correction with hyaluronidase preparations. The last correction of asymmetry before admission to our clinic was carried out with the simultaneous administration of 6000 units of the drug “Longidaza” (two bottles in the lip area; a clinical example is described below). Three patients were admitted with swelling of the face and periorbital area. In one case, ultrasound was performed on the 14th day after the last administration of hyaluronidase preparations (in total, the patient had 11 injections of hyaluronidase preparations). In the second case, ultrasound was performed on the 7th day and dynamically on the 49th day after the last injection of hyaluronidase (there were eight injections in total). And in the third case, an ultrasound was performed before the administration of the drug "Langidaza", as well as over time after twice daily administration of the drug, 500 units on each side, for a total of 2000 units in two days.
Diagnostics.
During the ultrasound examination, we searched for subcutaneous fragments of the gel, clearly determined their localization relative to the anatomical structures of the facial skeleton and the depth of their occurrence from the epidermal layer of facial skin, established the longitudinal and transverse dimensions of the filler loci, noted the relationships of anatomical structures (vessels, facial muscles, nerve trunks of varying degrees branching, fibrous formations) and filler boluses. The structure of the surrounding tissues was also determined: increased pastiness, excessive fibrosis, other features, if any, for example, the presence of non-hyaluronic implants or changes in the speed of blood flow in the vessels of the facial skeleton in the event of gel contact with them.
Treatment.
After this, treatment began, which was carried out in two stages. At the first stage, depending on the clinical picture, a course of phonophoresis with one percent hydrocortisone ointment was prescribed in the amount of 6-10 procedures daily, followed by a control ultrasound of the affected areas, assessing the dynamics of the reduction in gel size after three weeks. After this, in patients with hyaluronic fillers, the swelling of the surrounding tissues decreased, the gel biodegraded: from anechoic and hypoechoic boluses with clear and fairly even contours before treatment, they took on the appearance of heterogeneous loci in structure with signs of fibrosis in the form of hyperechoic tender cords and phenomena of fragmentation of these boluses.
The remaining fragmented gel larger than 3 mm in diameter was then treated with a second stage of treatment. Under ultrasound control, the Longidase drug was injected directly into the filler focus (the deviation of the needle tip during ultrasound guidance did not exceed 1 mm), avoiding trauma to adjacent vessels and nerves, followed by repeated ultrasound control two weeks after the injection. To do this, the skin of the injection site was treated with an antiseptic and a sterile ultrasound gel was applied. Ultrasonic navigation was performed on the device using a linear sensor with a scanning frequency of 15-18 MHz in the small parts probe mode. The optimal route for inserting the needle into the gel was selected, taking into account the position of blood vessels, nerves and other anatomical structures, in order to avoid trauma. In this case, both the gray scale mode and the Doppler and energy mapping mode were used, which made it possible to obtain a higher-quality image and increase the accuracy and safety of drug administration. The injection of the Longidaza drug was carried out with an insulin syringe with a fixed needle, a dose of 75-500 international units (IU) per gel fragment (bolus), depending on the actual volume of the bolus, which can be calculated by the standard ultrasound machine program.
Such a targeted administration of the Longidaza drug in the described manner under ultrasound control makes it possible to minimize the risks of damage to adjacent vessels and nerves and to deliver the drug in a targeted manner, reducing its dose and volume.
The described treatment method was applied to patients with localization of the gel in various areas of the soft tissues of the face.