From this article you will learn:
- why do acne appear on the chin, forehead or cheeks,
- reasons for their development in women,
- the most effective remedies for acne on the face,
- use of phototherapy (IPL) and laser.
The article was written by a specialist with higher medical education.
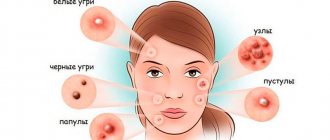
Pimples on the face are inflammatory formations on the skin, which are a consequence of the formation of acne (open and closed comedones) in the hair follicles and their subsequent infection. There are 2 types of acne - the so-called “papules” and “pustules”. Papules look like inflamed bumps on the skin, but they do not contain pus inside. Pustules are classic pimples in which a blister of pus has already formed.
Papules can be independent formations and, persisting for up to 2 months, can then disappear without a trace. However, most often papules turn into pustules. In general, the term “acne” is a colloquial expression, and it is correct to call this disease papulopustular acne. This form is usually preceded by the comedonal form of acne, which is nothing more than acne. The formation of blackheads (sebaceous plugs) in the hair follicles is a necessary basis for the subsequent formation of acne.
Types of acne on the face in teenagers (papules) -
Pimples in the form of pustules -
Pustules and papules are superficial inflammatory elements. Pustules go through their full development cycle in an average of 10-12 days, and after they disappear, a bright hyperpigmented spot remains in their place. As we said above, papules can persist from 10 days to 2 months, and they can either turn into pustules or disappear without a trace (or rather, weakly pigmented spots remain in their place). You probably already realized that it is useless to squeeze out papules, and this can only lead to increased inflammation and suppuration.
Getting rid of acne on your face if you have mild acne (moderate amount of superficial inflammatory elements) is not very difficult. However, in a number of patients, deep inflammatory elements can also form - these include the so-called indurative, abscessing, phlegmonous, draining, and conglobate acne. After the disappearance of such inflammatory elements, superficial or deep atrophic scars remain in their place, less often keloid scars.
The most common location of acne is if we talk about the face, then most often acne appears on the forehead, as well as acne on the chin. No less common localization are pimples on the cheeks or in the area of the ears. Some patients may experience acne on the scalp (in the scalp), as well as in the back and shoulders. This localization is due to the fact that it is in these areas that the skin contains the maximum number of sebaceous glands - about 400 to 800 per 1 cm2.
Acne on the face in teenagers: causes
We have already said above that it all starts with the comedonal form of acne, i.e. since the appearance of acne. The main reason for the formation of acne in adolescence is an increase in the production of androgens during puberty (puberty). The main androgen in girls is androstenedione, and in boys it is testosterone. Puberty for girls begins at approximately 12-13 years of age, for boys at 14-15 years of age. It is during this period that approximately 85% of adolescents experience the first manifestations of the comedonal form of acne (acne).
Let us remember that the main elements of acne are comedones (white or blackheads), which are non-inflammatory formations. In the middle and late teenage period, against the background of comedones, inflammatory elements (papules and pustules) already begin to predominate, which will indicate the transformation of the comedonal form of acne into the papulopustular form. The course of mild forms of acne usually lasts no more than 4-5 years, but the course of moderate-severe forms can last even 10-12 or more years.
The most striking clinical picture of acne (blackheads and pimples) is observed in girls between the ages of 17 and 18, and in boys between the ages of 19 and 21. It should be noted that girls are less fortunate and are characterized by a longer course of acne, which is also due to the presence of the menstrual cycle. In particular, it is known that in the period from 2 to 7 days after ovulation, acne symptoms intensify in girls. This is due to an increase in the concentration of luteinizing hormone during this period, and the conversion of androstenedione (this is the main androgen secreted by the ovaries) into testosterone.
Important: let's look at how androgens are associated with the appearance of acne and pimples... The fact is that the sebaceous glands have receptors for androgens, and therefore an increased concentration of the latter automatically leads to hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands. As a result, they begin to produce too much sebum, which contributes to the formation of fatty plugs in the lumen of the hair follicles, which are called acne or comedones.
Pimples on the forehead or chin in women: causes
Why do acne form on the chin in women? The reasons here may also be hidden in hormonal background. The fact is that increased concentrations of androgens can occur not only in adolescents. Clinical studies show that 30% of women with acne have laboratory confirmed absolute hyperandrogenism, i.e. increased production of androgens of ovarian or adrenal origin.
Acne in middle-aged women is most often localized in the chin and cheeks; sometimes women also experience acne on the forehead:
We have already said above that in women, in the period from 2 to 7 days after ovulation, current symptoms of acne may arise or intensify. This is due to peak concentrations of luteinizing hormone, which promotes the transformation of androstenedione into testosterone, and the latter, thanks to enzymes, is already converted into dihydrotestosterone. Therefore, taking into account all the above-mentioned causes of acne in women, a remedy for acne on the face, such as oral contraceptives or antiandrogens, can be used as part of complex therapy.
Another cause of acne in women may be the use of oral contraceptives based on pure progesterone. This is due to the fact that sebocytes (these are the cells of the sebaceous glands that produce fatty secretions) have receptors not only for androgens, but also for progesterone. However, the largest group of adult acne patients (both women and men) do not have an increase in androgen production, but they still have overactive sebaceous glands. What this is connected with - read below.
Other causes of acne in adults -
As we said above, the sebaceous glands have receptors for androgens. The fact is that hyperactivity of the sebaceous glands can occur even with normal concentrations of androgens (if these receptors, due to genetics, have increased sensitivity to androgens). The receptors become more sensitive to androgens due to increased activity of the following enzymes: 17-β GSD, 3-β GSD, and 5 α-reductase. The first 2 enzymes convert dehydroepiandrosterone and androstenedione into free testosterone, and 5 α-reductase further converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (24stoma.ru).
In general, it is precisely due to the increased activity of these enzymes that in men and women there is an increase in the concentration of dihydrotestosterone (even if the level of androgens is normal). It is dihydrotestosterone that is the main and direct hormonal stimulator of the activity of the sebaceous glands. Studies have shown that in patients with acne and pimples, the synthesis of dihydrotestosterone in the sebaceous glands is increased from 2 to 30 times - compared to patients without acne symptoms. And, by the way, one of the markers of increased activity of these enzymes is the presence of androgenic alopecia in the patient (which occurs not only in men).
Key Factors in Acne Formation –
You probably already realized that overproduction of sebaceous gland secretions is one of the main reasons why acne appears on the face. But this factor is far from the only one. This also includes the process of follicular hyperkeratosis, and in addition, the bacteria Propionibacterium acne (P.acne), which live both on the surface of the skin and subsequently in the ducts of the sebaceous glands, are also important.
- Hyperproduction of sebaceous gland secretions – it is caused by increased production of androgens, as well as increased sensitivity of sebaceous gland receptors to androgens. We have already described this process above, but as it turned out, what is important here is not only that there is an increase in the secretion production of the sebaceous glands. A very important point is the change in the chemical composition of the secretion of the sebaceous glands (sebum). In particular, against the background of increased secretion, there is a decrease in the content of linoleic acid in the sebum.
The function of the latter is to regulate the processes of differentiation and desquamation of follicular and epidermal keratinocytes. The stratum corneum of the epidermis of the skin consists of epidermal keratinocytes, and follicular keratinocytes line the lumen of the hair follicle. A decrease in the content of linoleic acid in sebum causes follicular hyperkeratosis, which is one of the most important factors in the development of acne and pimples (we will talk about follicular hyperkeratosis below).Simultaneously with the decrease in the concentration of linoleic acid, the content of unsaturated fatty acids in the sebum increases (from 5 to 20%). Such acids are comedogenic and also contribute to the development of follicular hyperkeratosis and the onset of inflammation. And lastly, an increase in sebum secretion also leads to the fact that follicular keratinocytes begin to release an inflammatory mediator called IL-1α (interleukin-1α). This mediator also promotes follicular hyperkeratosis and the development of inflammation.
- Follicular hyperkeratosis - the lumen of the hair follicle is covered with layers of follicular keratinocytes of varying degrees of differentiation.
When their cell layers are renewed, a constant process of exfoliation of their surface layer occurs. A low concentration of linoleic acid in sebum leads to: 1) hyperproliferation of follicular keratinocytes, i.e. to a sharp increase in the number of their layers and their thickness, 2) to a disruption in the desquamation of keratinocytes into the lumen of the hair follicle. Follicular hyperkeratosis, together with an increase in sebum production, leads to the formation of fatty plugs (comedones) in the lumen of the follicles, obstruction of the follicles and the onset of the inflammatory process. Moreover, at the first stage, inflammation is not associated with a sharp increase in the number of P. acne bacteria in the lumen of the follicle and its damage, but is associated with the production of interleukin-1α by follicular keratinocytes, as well as with an increase in the concentration of free fatty acids. - The presence and activity of the bacteria "P. acnes" - the bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (and to a lesser extent Staphylococcus epidermidis) - are the main microorganisms that are involved in the formation of acne.
These bacteria are representatives of the normal opportunistic skin flora, which is also present on the skin of people without acne symptoms. For a long time, the importance of these bacteria was underestimated; for example, it was believed that they were only responsible for the development of local inflammation in the hair follicle. However, this bacterium also affects the formation of comedones (blackheads) themselves. In particular, the increase in the content of free unsaturated fatty acids in sebum occurs precisely thanks to the enzymes (lipases) of these bacteria. These enzymes break down di- and tri-glycerides contained in the secretions of the sebaceous glands into free fatty acids. And as we said above, free fatty acids are comedogenic and contribute to follicular hyperkeratosis and the development of inflammation. In addition, the listed bacteria secrete enzymes, which subsequently lead to rupture of the walls of the hair follicle - as a result of which the entire contents of the follicle are poured into the surrounding tissue, which leads to a pronounced local inflammatory reaction.
What factors can aggravate the appearance of acne -
- use of comedogenic cosmetics,
- insufficient cleansing of the skin from water- and fat-soluble contaminants,
- medications (prednisolone, steroid hormones, drugs with lithium, anticonvulsants, iodides and bromides),
- active sweating.
How to dry acne at home?
There are many quick, safe and effective ways to dry out pimples. If acne appears constantly and affects large areas of the skin, then you should consult a dermatologist for the selection of comprehensive specialized treatment. However, if we are talking about several rashes, it is quite possible to cope with them on your own.
Ultraviolet
Regular sunlight is great at fighting inflammation. During the tanning process, the production of vitamin D is activated, the activity of bacteria on the surface of the skin is reduced, and swelling is reduced. Regularly exposing your face to the sun for a short period of time is a good acne prevention. It is important not to forget to cleanse and moisturize the skin, since under the influence of high temperatures and sunlight, the skin becomes more vulnerable, and the sebaceous and sweat glands become more active.
Many people use the solarium as an accessible source of ultraviolet radiation during the off-season and bad weather. The potential harm from artificial sun is much greater than the expected benefits. Firstly, tanning from lamps is much more intense, and the skin can behave unpredictably. Secondly, sensitivity to ultraviolet radiation is higher in inflamed skin. There is a high risk of getting burns and peeling at the site of pimples.
Important! For artificial tanning, special protective equipment is used. These are mainly oil-based creams and emulsions. It is highly undesirable to use such cosmetics on acne-prone skin.
Sorbents and minerals
An excellent way to remove excess sebum and stop the activity of the sebaceous glands is to apply homemade or pharmaceutical products with sorbents or minerals to the pimple. Activated carbon or polysorb literally pulls fat out of the pores along with bacteria and dirt. Zinc oxide, calcium carbonate, colloidal silver and other mineral salts and compounds have excellent drying properties. They can be found in drying ointments, talkers, and specialized care cosmetics for problem skin.
The simplest folk remedy for drying out acne based on sorbents and minerals is ordinary toothpaste. Due to calcium and enzymes in the composition, it dissolves and removes dirt from pores, narrows them and reduces the activity of the sebaceous glands. Menthol reduces itching and swelling. In order to quickly dry a pimple, you need to apply a small amount of toothpaste to it, leave it for 10-15 minutes, and then rinse thoroughly with warm water.
Plant based products
Many natural extracts and oils have the ability to relieve inflammation, dry and heal the skin. Modern cosmetology in the treatment of acne largely relies on natural ingredients or their synthetic analogues. In particular, the following are widely used to dry out acne: essential oils of peppermint and tea tree, fir and rosemary, decoction of chamomile, green tea or calendula. Freshwater sponge powder - badyagi - will help quickly eliminate inflammation. The natural diversity of medicinal herbs and fruits is so great that everyone can find a remedy that suits them. It is enough to study the properties of plants a little and approach the issue with common sense.
The most effective remedies for acne on the face -
How to remove acne from the face quickly and without complications? The most difficult thing here is to choose the right combination of drugs and draw up a treatment regimen taking into account the specific clinical situation. Below you can see that the approach to treating acne on the face may differ - depending on the predominance of different types of inflammatory elements (papules or pustules), as well as on the severity of the disease. The most effective remedies for acne on the face:
- antibiotics,
- products with benzoyl peroxide,
- topical retinoids,
- oral contraceptives in women,
- phototherapy (IPL), photodynamic therapy and lasers,
- comedones extraction method.
Only a dermatologist or a dermatologist-cosmetologist can professionally treat acne on the face. Unfortunately, in most cases, patients seek consultation with a specialist late, and this leads to complications - the appearance of persistent age spots, as well as superficial atrophic scars. Below you can see a treatment plan for acne, which is based on recommendations from the most famous English-language textbook for dermatologists around the world, Fitzpatrick's Dermatology.
How to get rid of acne on your face (according to Fitzpatrick's Dermatology):
Below we will look at all the types of drugs that are indicated in this scheme, and now you will know for sure which ointment for acne on the face will be the best in your case. Please note that azelaic and salicylic acids are not the main remedy for acne on the face, and can only be used as “second-tier” drugs. You can find out more about them at the link above. At the same link you can learn about the use of oral contraceptives in women.
How to get rid of acne at home using cosmetics
To get rid of acne forever, stock up not only with patience, but also with a decent arsenal of skincare products with sebum-regulating, exfoliating and anti-inflammatory ingredients. The minimum program is a gel or foam cleanser, makeup remover, toner, scrub and face mask.
Antibiotics for acne treatment –
Antibacterial drugs for the treatment of acne can be used both for external use (usually in the form of gels) and in the form of tablets for oral administration. Modern research shows that antibacterial therapy in patients with acne is not very effective, because Over time, it causes the formation of resistant strains of bacteria and, as a result, leads to more severe acne. But in some cases, antibiotic therapy for acne is still necessary, and in addition, there are ways to reduce the risk of bacterial resistance to antibiotics.
a) Mild to moderate papulopustular acne:
Antibiotics, if prescribed, are only externally. These may be drugs such as Dalacin, Clindovit or Clindatop. These drugs are monocomponent gels containing the antibiotic clindamycin. In addition, there are drugs in the form of solutions for topical use, for example, the drug Zerkalin. This drug is clindamycin based, but it also contains alcohol, which is actually not very good for acne patients (especially if you are also using retinoids and benzoyl peroxide).
Another drug - Zinerit (in the form of a solution that is applied using an applicator) - is based on erythromycin, but there are now many resistant strains of the bacterium P.acnes to this antibiotic. There are also combination preparations that, in addition to the antibiotic, may additionally contain either the retinoid adapalene or benzoyl peroxide. An example of several combination preparations in the form of gels:
- Klenzit-S – contains clindamycin 1% + adapalene 0.1%,
- Indoxyl – contains clindamycin 1% + benzoyl peroxide 5%.
Photos of some drugs –
Important: for papulopustular acne of mild or moderate severity, antibacterial gels are prescribed primarily only in cases where the predominant inflammatory elements in the patient are pustules with pus. In this case, in addition to the external antibiotic, we must simultaneously use + external retinoids, + benzoyl peroxide.
And here you may ask: why is it recommended to also use benzoyl peroxide when prescribing an antibiotic gel? Isn't one antibiotic enough? The fact is that the use of benzoyl peroxide together with an antibiotic greatly reduces the risk of P.acnes bacteria developing resistance to antibiotics. Including the development of such resistance contributes to the transformation of mild forms of acne into forms with a more severe course.
As for patients whose inflammatory elements are represented predominantly by papules (i.e., without pus), it is irrational to prescribe antibiotics in this case. It is optimal to use only a combination of external preparations “benzoyl peroxide + retinoid”.
b) Papulopustular form of severe acne:
For severe papulopustular acne, antibiotics are prescribed only orally (i.e. in tablets for oral administration), plus we prescribe externally retinoids + benzoyl peroxide. For systemic antibiotic therapy, drugs from the tetracycline group will be primarily used - this can be either tetracycline itself or its derivatives - doxycycline and minocycline. Only a doctor can determine the optimal dosage for each individual patient.
As for tetracycline, the average daily dosage is usually 1000 mg, but in serious cases the dose can be increased to 3500 mg per day (such doses can only be used under monitoring of liver function). Tetracycline can be taken only 1 hour before meals or 2 hours after; the duration of administration is determined by the doctor, but not more than 8 weeks. However, this drug has serious age restrictions, and in recent years more resistant strains of P. acnes have been discovered.
Much fewer resistant P. acnes strains have been found to lipophilic tetracyclines (such as doxycycline and minocycline). Doxycycline is taken at a dose of 100 to 200 mg per day orally for no more than 8 weeks, regardless of meals. However, it induces photosensitivity in the summer and therefore in summer it is better to use another antibiotic (azithromycin). Minocycline is also taken at a dose of 100-200 mg per day, but this drug can cause blue-black pigmentation in different areas of the skin. This pigmentation most often occurs in the area of atrophic scars and acne scars.
A good drug of doxycycline is
Antibiotics of the Macrolide group - previously a drug such as erythromycin was widely used, but now there are a lot of resistant strains of P.acnes to it. It is more preferable to prescribe azithromycin in a dose of 250 to 500 mg (taken only 3 times a week). Unfortunately, this drug may have side effects such as diarrhea, and therefore it is best to take it only with parallel medications to restore intestinal microflora. Azithromycin is a good alternative for patients who cannot use doxycycline.
Antibiotics of the Lincosamide group - clindamycin belongs to this group of antibiotics. But its use is justified only for external therapy (with the composition of products for external use), and when taken orally, there is too high a risk of getting a severe form of anibio-associated diarrhea, which is called pseudomembranous colitis. This is such a terrible thing (with a high mortality rate) that don’t even think about taking clindamycin tablets.
Drugs of the sulfone group - these include the drug Dapsone, but it can only be used if the patient develops resistance to other antibiotics (i.e. this drug will not be the first choice drug). Antibiotic resistance should be suspected if there is no response to treatment after 6 weeks of antibiotics. Moreover, in cases where we assume resistance, it is very important for us to exclude the development of gram-negative folliculitis in the patient (usually it occurs precisely after long-term use of antibiotics in the past).
Important: the most painful area of antibiotic therapy in the treatment of acne is the development of resistant strains of P.acnes and S.epidermidis. Concurrent use of topical benzoyl peroxide products with antibiotics, and avoidance of frequent changes between different antibiotics, are the best ways to prevent antibiotic resistance in P. acnes and S. epidermidis. Phototherapy procedures (IPL), photodynamic therapy, and the use of lasers can help reduce the need for antibiotics. We will tell you more about them at the end of the article.
Preparations with benzoyl peroxide –
Benzoyl peroxide is a bactericidal component and is probably the best remedy for acne (it can even be called the gold standard of therapy). This is a bactericidal component that effectively inhibits the growth of P. acnes bacteria, leading to the development of local inflammation in the area of hair follicles and the appearance of papules and pustules (pimples). It is very important that benzoyl peroxide, unlike antibiotics, does not cause the emergence of antibiotic-resistant microflora.
Professional pharmaceutical preparations with benzoyl peroxide are produced in the form of a gel (usually with a concentration of 2.5 or 5%). For the first month, in order to get the skin accustomed to benzoyl peroxide, it is optimal to use a concentration of 2.5%, and then switch to 5% of the product. If you use more concentrated products at once, irritation will likely appear on the skin. The classic monocomponent preparation with benzoyl peroxide 2.5 or 5% is Baziron-gel.
Combination drugs - but there are drugs where benzoyl peroxide is combined with an antibiotic or retinoid. As you will see below, each of these drugs will be effective in slightly different clinical situations, for example, depending on what type of inflammatory components (papules or pustules) you have. Examples of combination drugs for acne treatment:
- Indoxyl (UK) – benzoyl peroxide 5% + clindamycin 1%.
- Effezel (France) – benzoyl peroxide 2.5% + retinoid adapalene 0.1%.
How to choose the right drugs:
1) For mild to moderate papulopustular acne, the choice depends on the predominance of certain inflammatory elements. If papules predominate (without pus inside), then in this case the combination of “benzoyl peroxide + retinoid” will be optimal. For example, this could be the combination drug Effezel. But for patients with sensitive skin, it is better to use a combination of two monodrugs - benzoyl peroxide in the morning and a retinoid in the evening.
Thus, you can use the drug “Baziron” with benzene peroxide in the morning, and in the evening – one of two drugs “Klenzit” or “Differin” (containing the retinoid adapalene) of your choice. But if you have pustules with pus, then to the above combination of “benzoyl peroxide + retinoid” we also add external use of an antibiotic.
2) For severe papulopustular acne, we also use “benzoyl peroxide + retinoid” for external use, and also add systemic antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics for this form are used only orally, in long courses of up to 6-8 weeks (see above).
Side effects of benzoyl peroxide: Be aware that itching, burning sensation, dryness, tightness, redness, or flaking of the skin may occur after use. But usually these effects are not too pronounced. If you use the drug during active sunny periods, be sure to use sunscreen, because Benzoyl peroxide makes facial skin more sensitive to sunlight.
Drying ointments
In order to quickly cope with an annoying and painful rash, it is good to always have a ready-made ointment with drying properties in your home medicine cabinet.
Salicylic ointment
An ointment based on acetylsalicylic acid quickly relieves inflammation and dries out acne. Before use, the skin must be thoroughly cleaned, then applied to the area of the rash. The greatest effect can be achieved if you use the ointment under the bandage at night. It is important to use salicylic ointment only on the site of the pimple, as it greatly dries out the skin and can cause irritation in healthy areas.
Zinc ointment
Products based on zinc oxide are also applied pointwise. They quickly stop the process of microbial proliferation, narrow pores and regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands. After use, zinc ointment is washed off with water or tonic. Half an hour is enough to obtain a noticeable visual effect.
Ointment based on badyagi
The freshwater sponge spongilla has long been known for its property of improving metabolic processes in the skin. When used on problem areas, it reduces sebum production, relieves swelling, improves blood circulation and lymph flow. The pimple almost immediately noticeably decreases in size, heals faster, and is less likely to be complicated by tissue suppuration.
Antibiotic ointments
This is a fairly radical means of getting rid of acne. Ointments with antibacterial components, provided the pathogens are sensitive to the active substance, almost instantly stop the inflammatory process. All of them have an antiseborrheic and drying effect. The main disadvantage of such ointments is the development of microbial tolerance. After several uses, the bacteria lose their susceptibility to the antibiotic, and the ointment stops working. Only a doctor can prescribe any antibiotics in all forms and only if indicated.
Topical retinoids (adapalene)
In fact, this is the most important ointment for acne on the face. Topical retinoids are intended for external use. Such drugs are prescribed - 1) for the comedonal form of acne, which means acne, 2) for the papulopustular form of acne (i.e. in the presence of pimples). Previously, the topical retinoid tretinoin was used to treat acne, but it had a lot of side effects, and now there are much safer 4th generation topical retinoids, for example, adapalene.
Such drugs are monocomponent and combined. Monopreparations based on adapalene include Differin, Klenzit or Adaklin. A number of drugs of this type are produced only in the form of gels, but some manufacturers produce drugs with adapalene in both gel and cream form. Gel products will be more effective, but facial acne cream is more suitable for patients with dry and/or sensitive skin (and will help reduce the risk of irritation in such patients).
Examples of combination drugs with retinoids are 1) Klenzit-S, containing adapalene together with the antibiotic clindamycin, 2) Effezel, containing adapalene in combination with benzoyl peroxide. The choice of drug will depend on the severity of the acne, as well as on which inflammatory elements predominate in you (papules or pustules). All this information is schematically reflected in Table 1, which we placed before the description of groups of drugs for the treatment of acne.
How to treat facial acne with retinoids:
- Preparations containing adapalene should be used once a day before bedtime. Before applying a retinoid, you should wash your face with a mild cleanser. Before applying the retinoid, the skin must be completely dry, because... otherwise severe irritation will develop. To get your skin used to it and not be too irritated, start using the drug 3 times a week. After 1-2 weeks, switch to daily use.
When can you expect results: skin oiliness decreases sharply within a few days from the first use. As for acne and pimples, the first noticeable result can be seen only after about 4 weeks of therapy. Good results can be seen after about 8 weeks of using retinoids, but for radical improvement a full course is required, which lasts at least 12 weeks (3 months).
Use of oral retinoids:
In addition to topical retinoids intended for external use, there are also so-called systemic retinoids for oral administration. Such drugs (Acnecutane or Roaccutane) contain the retinoid isotretinoin. These drugs are very effective for treating acne, but they also have very serious side effects. Therefore, such drugs are used only in difficult situations, for example, for the treatment of nodular and conglobate forms of acne.
Use of oral contraceptives in women:
As for the use of oral contraceptives in women, you can read more about this method of treatment in the article at the link below:
→ Oral contraceptives for acne in women
Masks for drying out acne
There are many effective recipes for face masks that reduce the activity of the sebaceous glands and fight pathogens in the skin. You can make them at home from the ingredients you have on hand.
Clay based
It is now easy to buy dry, ready-made cosmetic clay powder in pharmacies. Suitable for drying masks: white, blue or pink. Before use, the clay is diluted to a paste.
You can do this using:
- decoction of medicinal plants: chamomile, calendula, peppermint;
- cream 15% fat;
- cucumber, lemon, potato juice;
- water with the addition of a drop of essential oil of tea tree, rosemary, lemon or other citrus fruits, mint, eucalyptus.
Leave the clay mask on for 15 to 30 minutes, then rinse thoroughly and moisturize the skin with tonic.
Potato mask
One raw potato is grated on a fine grater and mixed with egg white until a thick, homogeneous mass is obtained. Apply the mask to problem areas, cover with cling film or warm gauze and leave for up to half an hour. Afterwards you need to wash your face. This mask will quickly get rid of blackheads, reduce skin oiliness, relieve inflammation, and tighten enlarged pores.
Film mask with activated carbon
You can quickly dry out acne, shrink pores and cleanse the skin using a film mask. To prepare it, one plate or teaspoon of gelatin is dissolved in a small amount of warm water. While the gelatin is swelling, you need to grind several tablets of activated carbon into powder. It is mixed with a gelatin solution until a “milk” is obtained. Apply the mask with a brush to problem areas, and remove after complete drying.
Rice mask
Two tablespoons of rice flour are mixed with warm honey and a few drops of lemon juice. The resulting paste is evenly applied to the face. After 15-20 minutes, wash off with active movements. Rice particles act as a soft peeling, delicately removing particles of the epidermis along with impurities. Honey relieves inflammation and destroys pathogens in the pores. The mask is not suitable for people with sensitive skin and allergies to bee products.
Squeezing pimples and blackheads (comedone extraction)
For comedonal and papulopustular forms of acne, invasive methods are sometimes used, for example, comedonal extraction. Extraction means their removal/squeezing out - using special comedones extractor tools, or by palpation. Moreover, we are talking about the removal of macrocomedones, i.e. large eels. But squeezing out pimples (papules and pustules) can, at best, lead to the appearance of a hyperpigmented spot in this area in the future.
In the worst case, self-squeezing pimples and blackheads can lead to the spread of inflammation and the formation of deep subcutaneous pimples, which will leave superficial or deep atrophic scars on the skin. Therefore, only comedones (acne) can be squeezed out, and secondly, this should only be done by a dermatologist or a dermato-cosmetologist. The procedure is called “mechanical facial cleansing.”
Mechanical facial cleansing: video
Important: keep in mind that the removal of comedones is much easier and without complications if the patient has previously used topical retinoids for at least 3-4 weeks. The fact is that topical retinoids (adapalene) also have comedonolytic properties.
Why do you need to dry out acne?
If you do not perform any manipulations with acne, the healing process will depend entirely on the immune system, the structure of the epidermis and the activity of the sebaceous glands. If the skin is too oily, and the immune system is low, if there are factors in a person’s life that negatively affect health (for example, bad habits, poor environment, stress, poor diet, hormonal imbalance, and others), then you may not be able to wait for isolated rashes to heal on their own. Instead, the condition of the skin will worsen, bacteria will spread throughout the entire area of the epidermis, and instead of several pimples, the person will face acne. Therefore, it is important to dry acne in a timely manner.
Pharmacy or folk remedies that dry out acne work in several directions. All of them are important for timely treatment of acne.
Reduced activity of the sebaceous glands
First of all, it is necessary to deprive the pathogens of their nutrient substrate. To do this, the inflamed sebaceous gland must get rid of excess secretion and stop producing it in excessive quantities. When drying, the production of sebum in the required area is temporarily blocked. That is why products for actively reducing acne are applied pointwise.
Reducing inflammation
Externally, acne manifests itself as a painful swelling - a papule. A focus of inflammation develops inside it. It may consist only of swollen, inflamed cells of the epidermis or contain a purulent infiltrate inside, which over time appears outside in the form of a pustule. Inflammation is often accompanied by itching and pain. Drying pimples is necessary to reduce external manifestations and unpleasant internal sensations. The less the pimple bothers you, the less desire you have to scratch it and touch it with your hands. When scratched or touched, the infection can spread to neighboring areas and lead to the appearance of entire conglomerates of acne.
Acceleration of regeneration
After the inflammation is relieved and bacterial activity is stopped, the skin will begin to restore its structure. The wound from the bursting pustule will close with a thin film, under which new cells will actively divide. If the tissue around the pimple is not injured by squeezing, then the blood supply and lymph flow in this area will remain normal, which means that healing will proceed quickly and without scar formation. Many drying agents contain components that have a beneficial effect on regeneration, nourish the epidermis, and accelerate blood flow.
Phototherapy and lasers for acne treatment
Phototherapy and lasers are used to treat acne - either endogenous porphyrins contained in P. acnes, or sources of exogenous porphyrins are additionally applied to the skin before the procedure. Porphyrins have the property of absorbing light in the blue regions of the spectrum (wavelength 415 nm), which leads to the formation of unstable oxygen and, as a result, to the destruction of pathogenic bacteria P.acnes. The FDA recommends Lumenis devices (for example, the IPL module of the M-22 device), which use high-intensity light from the blue part of the spectrum, for the treatment of papulopustular acne, i.e. acne.
Light from the red part of the spectrum can also be useful because... Compared to blue light, it has a stronger anti-inflammatory effect (although it has a lesser effect on porphyrins). Therefore, a combination of light from the blue and red parts of the spectrum will be even more useful. Facial procedures are carried out 2 times a week for 15 minutes. According to the dermatology textbook Fitzpatrick's Dermatology, after a 4-week course of therapy in 80% of patients, the number of acne decreased by 60%. But in the absence of supporting procedures, their number returns to the original level - within 3-6 months.
Photodynamic therapy is even more effective in treating acne. It consists of applying exogenous porphyrins to the skin 1 hour before the procedure (aminolevulinic acid/ALA), after which exposure to a high-power light source occurs. The latter can be pulsed dye lasers, intense pulsed light or a broadband light source in the red part of the spectrum. ALA is metabolized in the sebaceous glands and hair follicle to porphyrins, which when exposed to light lead to the release of unstable oxygen, which damages the sebaceous glands. Several photodynamic therapy treatments can provide improvement for up to 5 months.
Pulsed KTP laser (wavelength 532 nm) - also leads to a reduction in the number of acne by about 40%. Use this laser 2 times a week for 2 weeks (a total of 4 treatments are required). In addition, some of the non-ablative infrared lasers at 1450 nm and 1320 nm wavelengths may also be useful for treating acne. they cause thermal damage to the sebaceous glands. However, any of these lasers requires a course of several treatments (and the improvement lasts up to about 6 months).
One of the newest acne treatment devices is the Isolaz device (from Solta Medical). The nozzle of the device is made in the form of a photo-pneumatic device, which creates negative pressure that sucks out the fatty secretion from the mouths of the hair follicles. Immediately after this, broadband pulsed light (wavelength from 400 to 1200 nm) is turned on, which acts on the P. acnes porphyrins, destroying these bacteria, and also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
What do phototherapy and lasers do?
Regular use in courses not only improves the course of acne, thereby reducing the number of inflammatory elements. The use of phototherapy (IPL) and lasers in courses often avoids the need for oral medications (antibiotics, isotretinoin), as well as the numerous side effects associated with them. But the cost of such treatment is high. We hope that our article on the topic: How to remove acne on your face was useful to you!
Sources:
1. Higher medical education of the author of the article, 2. Textbook on dermatology “Fitzpatrick's Dermatology” (8th edition), 3. “Modern methods of treatment and rehabilitation of patients with acne vulgaris” (Barinova), 4. “Acne from the position of evidence-based medicine” (Anisimova), 5. “Cellular mechanisms of barrier protective functions of the skin and their disorders in skin diseases” (Medelets).
Conclusion
It is very important to promptly help the skin cope with inflammation. Even a single pimple can become the beginning of acne or leave an unaesthetic scar. Under no circumstances should pimples be squeezed out or burned with caustic acid or alcohol solutions. The choice of drying agents with a delicate action is quite large. You just need to choose the one that suits your skin type and lifestyle and be patient. With proper care and treatment, soon the pimple will no longer even be an unpleasant memory.
Please rate this article.
Click on the heart to vote.
Overall rating 4 / 5. Voted: 4
No votes yet. You will be the first!
I'm sorry you didn't like the article. We will try to improve it according to your feedback.
How to make the text better?
Please tell me how we can improve the article?