Traumatologist-orthopedist
Shelepov
Alexander Sergeevich
13 years of experience
Doctor
Make an appointment
An accumulation of clots or liquid blood in the soft tissues of the body, formed due to rupture of blood vessels, is called a hematoma. The most common type of pathology is an ordinary bruise. However, this concept includes much more severe and complex cases that cannot be left without qualified medical care. Blood flowing from the vessel irritates the tissues surrounding it, resulting in pain, tissue swelling and other signs of developing inflammation. In addition, the hematoma compresses the tissues or organs located next to it, which can lead to the development of complications.
General information
The main cause of hematomas are bruises - closed injuries to soft tissues resulting from a blow or fall. A strong blow leads to rupture of the walls of small blood vessels, due to which blood begins to flow through the breakout sites into the subcutaneous tissue, soft tissues or body cavities. Hematomas form in different parts of the body - on the limbs, torso and even on the head. In addition to bruises, hematomas are caused by intense compression and stretching of tissues due to dislocations or fractures.
Small lesions, as a rule, do not require any treatment and resolve on their own within a few days. When large hematomas form, there is a risk of infection and the development of suppuration. Most often, hematomas form in representatives of younger age groups - children, adolescents and young people, who are characterized by high physical activity. Another “risk group” are people with increased fragility of the vascular wall, as well as with blood clotting disorders.
Orthopedics and traumatology services at CELT
The administration of CELT JSC regularly updates the price list posted on the clinic’s website. However, in order to avoid possible misunderstandings, we ask you to clarify the cost of services by phone: +7
| Service name | Price in rubles |
| Appointment with a surgical doctor (primary, for complex programs) | 3 000 |
| X-ray of the chest organs (survey) | 2 500 |
| Ultrasound of soft tissues, lymph nodes (one anatomical zone) | 2 300 |
All services
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
Why does a hematoma change color?
Doctors identify three distinct stages of a hematoma through which it must go before completely disappearing. Each of them is characterized by a certain skin color, through which the hemorrhage is visible.
- Appearance of a bruise. Immediately after a soft tissue bruise, a sharp pain is felt, the area of skin in the damaged area becomes purplish-red and swells due to tissue swelling, then the red color gradually changes to blue. The red color comes from red blood cells containing large amounts of hemoglobin. After a few hours, hemoglobin begins to break down, and the bruise site turns blue. Due to swelling and inflammation of the tissue in the damaged area, the temperature rises.
- Greening. After two or three days, swelling and temperature decrease, the condition of the tissues more or less returns to normal, but minor pain when pressed remains. The blue tint of the skin gradually turns into a greenish color.
- Yellowing. By about the fifth day, the swelling completely disappears, the remaining hemoglobin disintegrates and is removed from the tissues. The site of the bruise becomes yellowish, then acquires its normal color.
Visual symptoms of hematomas are most clearly visible in cases where the effusion of blood occurs in the subcutaneous layer. If a clot forms in the deeper layers of soft tissue, then only a small but painful swelling is noticeable on the outside. Such formations are much more dangerous, since the process occurs unnoticed and can be accompanied by complications.
Are you experiencing symptoms of a hematoma?
Only a doctor can accurately diagnose the disease. Don't delay your consultation - call
Symptoms
A bruise on the skin is always clearly visible. At first it has a purplish-blue color, and then begins to “bloom”, acquiring yellow and green colors. If a sufficiently large amount of blood accumulates under the skin, a protruding lump forms. At first it is very painful to feel, but later the pain goes away.
The outpouring of blood into the internal organs and into the substance of the brain is preceded by trauma. The main symptom is pain. In this case, the hematoma is not visible externally. If bleeding continues, the victim becomes pale, weak, and dizzy. With chronic internal bleeding, anemia comes to the fore. Bleeding in the brain is especially dangerous. Compression of brain structures may occur, sometimes leading to death.
Types of damage
The faster a hematoma forms, the more difficult the recovery. Injuries of this type are divided into:
- lungs that develop within a day, accompanied by mild pain and not requiring special treatment;
- moderate severity, the appearance of which requires no more than 5-6 hours, accompanied by noticeable swelling and pain, worsening the motor function of the limb;
- severe, forming within 2 hours after a bruise, accompanied by dysfunction of the limb, acute pain and noticeable swelling.
Treatment of moderate and severe hematomas should be carried out under the supervision of a physician to eliminate possible negative consequences of injury.
In addition to the severity of the damage, there are other criteria for classifying hematomas:
- by depth of location - under the skin, under the mucous membrane, deep in the muscle tissue, under the fascia, etc.;
- according to the state of spilled blood - uncoagulated (fresh), coagulated and lysed (filled with old blood that is not capable of clotting);
- by the nature of blood distribution - diffuse (blood permeates the tissue and spreads quickly), cavitary (blood accumulates in the cavity between the tissues) and encysted (over time, the cavity filled with blood is surrounded by a “bag” of connective tissue);
- according to the condition of the vessel - pulsating (blood flows freely from the vessel and flows back) and non-pulsating (the rupture of the vessel is quickly sealed by a thrombus).
Almost always, hemorrhage poses a health hazard, so to eliminate its consequences, you need to seek medical help immediately after the injury.
Paint bags are swelling that occurs as a result of aging of the body.
Age-related changes are the reasons that can also contribute to the formation of puffiness. With age, the aging process in the human body accelerates.
They make the skin less elastic due to the loss of natural elastin. Without exception, under the skin of the face, in the area of the lower eyelid, above the cheekbones, there are skin hernias filled with fat (sufas). They have a clear border at the bottom; this skin tissue bridge holds the fat and prevents it from sliding onto the cheeks.
While the skin is young and elastic under its tight, stretched top, the bags are invisible. They appear only in difficult situations (for example, critical days, severe lack of sleep). But with age, these formations become more and more noticeable, as the skin becomes less elastic and the bridge sags.
They acquire a bluish tint, become loose, and begin to absorb a lot of moisture. This happens especially quickly during the period of restructuring of the body (menopause), kidney disease, and heart disease.
One of the manifestations of this process will be the separating skin tissue forming a groove in the upper part of the cheekbone. If at a young age it is invisible, then over time it becomes more noticeable.
It provokes the formation of wrinkles around the eyes. “Bruises under the eyes” or “bags under the eyes” formed by lipid deposits are difficult to treat with simple compresses or ointments, and with age they become more and more difficult to remove.
Examination methods
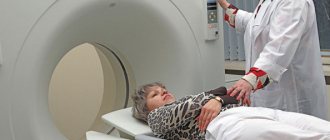
To diagnose hematomas, you need to contact a traumatologist. When the hemorrhage is localized deep in muscle tissue, joints or internal organs, a visual examination provides too little information for the doctor to objectively assess the severity of the lesion and the degree of danger of injury. In such situations, the patient is prescribed:
- Ultrasound of a damaged body part, organ or joint;
- X-ray of the damaged part of the body;
- CT or MRI;
- puncture (puncture with a special needle) of a joint or organ in which blood is believed to have accumulated.
Based on the examination results, the doctor prescribes appropriate procedures.
Treatment
Minor bruises can be treated conservatively: physiotherapeutic procedures and medications are prescribed.
In case of large accumulations of blood, the hematoma is treated surgically: it is opened, the blood or pus is evacuated, washed with antiseptics and drainage is installed. Antibiotics are prescribed if necessary.
When hemorrhaging into internal organs, it is often necessary to perform surgical intervention, during which it is necessary not only to remove the spilled blood, but also to stop the bleeding.
The multidisciplinary CELT clinic employs experienced traumatologists and surgeons who perform operations on hematomas of various locations. Modern techniques used in our clinic help provide effective treatment and minimize the risk of complications.
How to remove hematomas?
After establishing the nature and characteristics of the hematoma, treatment is prescribed in accordance with the information received:
- prescribe UHF procedures;
- a surgical opening is performed to remove accumulated clots and rinse the cavity;
- the patient is hospitalized in the surgical department for opening and drainage, followed by antibiotic therapy.
Recovery time depends on the extent of the lesion, the presence or absence of infection and other factors.
Swelling of the eyelids and cheekbones caused by illness and disruption of the usual lifestyle
The first type of swelling can occur as a result of many reasons. Its treatment will depend on the factors that caused the swelling. Here, the primary disease should be treated first.
Swelling in the cheekbone area goes away after treatment for the underlying disease. In some cases, lifestyle changes may be necessary to reduce swelling on the face. Treatment of the edema itself in these cases will not bring results.
Factors and diseases that cause swelling on the cheekbones
Among the widespread factors of swelling in the eyes and cheekbones of the face there are several large groups. All causes can be divided into 3 groups.
Violation of the usual routine
Sleep disturbances. Often, lack of sleep, especially if sleep is interrupted at the stage of falling asleep, causes unpleasant swelling on the cheekbones. The person gets a tired and dissatisfied look and with too much time spent in the evening, excessive doses of alcohol; after tears;
Frequently asked questions
How to get rid of a hematoma using traditional methods?
Folk remedies only help with minor and non-dangerous superficial damage. To speed up resorption, you can apply a compress of mashed cabbage leaves, bodyagu mixed with Vaseline, or tampons soaked in a mummy solution to the bruise. For deep or extensive injuries, you should consult a doctor.
Why is a hematoma dangerous?
The greatest danger to health, and sometimes to life, are hematomas that form deep in the tissues, inside organs or joints. Large hemorrhage is dangerous due to the possible development of infection, inflammation and suppuration. If the joint is damaged, bursitis, synovitis or hemarthrosis may develop, resulting in disability. Blood in the peritoneal cavity leads to peritonitis. Brain hematomas lead to dysfunction of this organ with serious consequences in the form of deterioration of cognitive functions, paralysis of body parts, etc.
How to treat a hematoma in the first hours after injury?
Immediately after a bruise, it is necessary to provide first aid to the victim: apply ice to the injured area, then tightly bandage the injured limb to block the flow of blood into the tissue. The dressing should not remain on for more than two hours. During this time, it is necessary to get to the emergency room, where the patient will receive the necessary professional help.
Ways to deal with bruises on the face
Both pharmaceutical products and many traditional medicine recipes will help eliminate such an unpleasant problem. But before you raise the question of how to remove a bruise on your face, you should think about the true reasons for this phenomenon. The simplest option is when a dark spot appears due to mechanical impact. But if a bruise occurs for no apparent reason, it is worth contacting a specialist to exclude or diagnose a pathology that may manifest itself in this way.
If you suspect any disease, you need to stop self-medication and carry out timely diagnosis to prevent it from developing into a more severe form. Only the necessary therapeutic methods will eliminate the pathology and consequently prevent the occurrence of abrasions.
What can you do yourself?
You should use any medications only as prescribed by a specialist. You can adjust your diet yourself. Diversify your daily menu with foods rich in vitamins, especially P and C. These include bananas, herbs, rosehip infusions, cucumbers, salads, citrus fruits, black currants.
If you associate the appearance of bruises with taking medications, stop using them and consult your doctor.