There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
Neoplasms, tumors on the skin: causes Types of neoplasms on the skin Symptoms and diagnosis Treatment methods Prevention of skin tumors
The term skin neoplasms refers to areas of pathological growth of the epidermis and dermis with an increase in the size or number of cells. These altered cells form tumor-like formations of limited size.
Usually the number of dying cells in the body is equal to the number of newly formed ones. But if the body is affected by unfavorable external or internal factors, uncontrolled cell proliferation is possible. Moreover, they can divide before they have fully matured, so they cannot fully perform the functions assigned to them. When it comes to malignant skin tumors, it is often extremely difficult to determine in which layer of the dermis the tumor originally originated.
Neoplasms, tumors on the skin: causes
There are quite a lot of various factors that can trigger the uncontrolled division of cellular elements of the dermis and lead to skin neoplasms. But among the most key reasons are frequent injuries, due to which cells must regenerate more often. As a result, uncontrolled proliferation of epidermal cells may begin. Various types of radiation (ultraviolet, X-ray, ionizing) can also act as provocateurs.
Hereditary predisposition, skin phototype, the presence of pigmentation, moles are important in provoking a neoplasm on the skin of the face or body. Usually these elements are benign, but some can undergo malignancy, which leads to their transformation into cancer.
ABCD principle
In dermatology, a simple rule is used to determine the signs of malignancy called ABCD. Each letter of the word corresponds to a specific characteristic of a mole:
A - asymmetry:
symmetrical (good) asymmetrical (bad).
B - random coloring:
uniform coloring (good) uneven coloring (bad).
B - height:
uniform height (good) uneven height (bad).
G - boundaries:
clear boundaries (good) unclear boundaries (bad).
D - diameter:
not growing (good) growing (bad).
Important: any changes in moles or their trauma is a reason to pay attention to them! Carefully examine all your formations; if you notice any suspicious signs, contact a specialist immediately!
Types of skin tumors
Any tumors or neoplasms localized on the skin can be classified into three large groups:
- benign elements;
- precancerous formations;
- malignant tumors.
Although benign skin tumors themselves do not threaten the patient’s life, if they are located in an inconvenient location and grow to large sizes, their presence leads to dysfunction of organs; they put pressure on nerve trunks, causing pain, and disrupt blood circulation, pinching arteries or veins.
If skin tumors classified as benign are constantly influenced by various external aggressive factors - infectious agents (bacteria, fungi or viruses), injuries, chemical irritants, radiation, a transition to precancerous and malignant lesions is possible. However, hereditary predisposition to such diseases is also important.
Types of benign skin tumors
Although cells in benign elements on the skin have lost control of division, they can be easily identified and partially retain their functional activity. Such tumors of the skin of the face or body tend to grow very slowly, pressing on the surrounding tissues, moving them, but without penetrating into the surrounding organs.
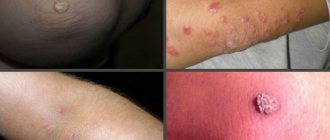
Various types of neoplasms on human skin are distinguished, depending on the predominant cells and localization of the process, the possibility of transition to more serious forms of the disease.
Lesions of adipose tissue can be in the form of lipoma and atheroma . The first has the appearance of a round formation from the fatty layer and does not have a tendency to develop into cancer. Atheroma is an epithelial cyst in origin; in rare cases it can transform into liposarcoma.
Viral elements - warts, papillomas, condylomas - look like bulges, growths on a stalk or a broad base. Some forms may become malignant due to frequent trauma, or initially have rapid growth and large size (Buschke's condyloma).
Dermatofibromas come from connective tissue, are more common in young women, grow slowly and have few symptoms. In extremely rare cases, they can become malignant. Externally they look like a nodule deep in the tissue with a convex hemisphere, smooth or slightly flaky surface.
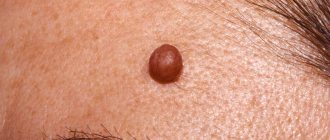
Nevi , moles are pigmented areas of the skin formed by clusters of pigment cells. Typically caused by excess sun exposure. Although they themselves are not dangerous, about half of all melanomas (skin cancer) form in the area of birthmarks or nevi.
Types of precancerous skin tumors
With increased congenital sensitivity of the skin to the sun and other types of irradiation, xeroderma pigmentosum may occur. It begins as a large number of freckles, which develop into wart-like growths. With frequent UV irradiation, the elements turn into different forms of cancer (squamous cell or basal cell).
Bowen's disease is a neoplasm in the form of spots and nodules, plaques or bumps that tend to merge and form surfaces that are covered with growths. It happens especially often in older people. Often develop into undifferentiated forms of skin cancer.
Keyer's disease is bright red nodules that have a velvety appearance, are prone to ulceration and become covered with papillomas. It rarely turns into cancer, but often gets injured, hurts and bleeds.
Senile keratomas are limited nodules in which the skin intensively divides, they turn into plaques and become covered with dense crusts.
Cutaneous horn - occurs in areas where the skin is injured. A cone-shaped skin compaction up to several millimeters long is formed. Prone to developing into cancer.
Malignant neoplasms of the skin
They account for up to 10% of all patrols. They occur more often in elderly patients; they differ from benign elements in that the formation cells are difficult to differentiate already in the initial stage of growth. Cells lose their functions, grow into neighboring organs and tissues, and metastasize through blood capillaries and lymphatic vessels. This group includes melanoma , as well as non-melanoma cancers (squamous cell, basal cell), epithelioma , Kaposi's sarcoma .
Gentle removal of tumors
New growths can regularly appear on human skin, which, as we indicated above, must be treated with caution and monitor for changes. The most effective treatment for skin lesions is laser techniques, which not only provide an excellent cosmetic effect, but also reduce the number of complications and relapses.
Therefore, if skin formations bother you and you want to get rid of them, there is an opportunity not to put off taking care of yourself and quickly and delicately remove them using the Deka SmartXide CO2 laser. In what cases should you apply for removal? If the neoplasm:
- was traumatized;
- changed shape or size;
- causes physical discomfort;
- aesthetically you don't like it.
Using a specific CO2 attachment, the laser precisely affects the tumor and does not affect healthy tissue. This gentle removal promotes rapid healing.The Deka SmartXide laser is an ablative CO2 laser that includes a fractional scanner and a dermatology attachment. The fractional scanner is used for laser resurfacing, but the dermatological attachment is designed to remove various tumors.
The SmartXide system is considered the “Gold Standard” in laser surgery due to its wavelength absorption, technology, ergonomics and ease of use.
Please note that when removing skin lesions, the laser affects only the pathological tissue to which the wave is directed, and it minimally affects the healthy skin around it. The specialist controls the depth of exposure and has the ability to remove the formation layer by layer, while virtually eliminating the possibility of scarring.
Why is it worth removing tumors with a laser?
Deka SmartXide laser technology has several advantages:
- painlessness of the procedure (anesthesia is either not used, or application or infiltration anesthesia is used);
- the risks of inflammation are minimized because the laser beam is sterile;
- gentle removal of the pathological focus;
- lack of blood, because only coagulation of blood vessels is carried out;
- no repeat sessions are required.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Typically, benign and malignant skin tumors begin as a small area of skin change: the appearance of growths, crusts, and round formations. In addition, any moles or nevi that change their size, shape, or color are dangerous. In these cases, if there are any changes in the epithelium and underlying tissues, targeted diagnosis of skin tumors is needed. It is performed by a dermatologist, and if there are signs of melanoma or another type of cancer, by a dermato-oncologist. The doctor will ask you in detail about the complaints, evaluate what the skin growths look like, clarify growth dynamics, color changes, additional complaints (itching, pain, ulcers, bleeding).
If a tumor is suspected, the doctor will perform a biopsy of the suspicious element, which will accurately determine the nature of the tumor.
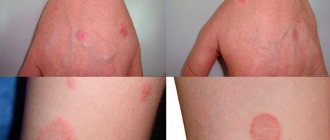
Dangerous degeneration of moles into melanoma!
Every year, doctors diagnose 200,000 patients with melanoma, and a third of cases are fatal. On average, after positive treatment results, patients with melanoma live about 5 years. These scary statistics are presented here so that you think about your health and pay attention to it.
How to spot melanoma?
Melanoma, in simple words, is a former mole. The harbingers are situations when a mole changes color, redness appears around the mole, grows unevenly, hurts, and bleeding appears. It is possible that new moles will appear during life, which look unusual and differ from those that previously existed on the body. Any changes or appearance of “unusual” moles require special attention and are a reason to consult a dermatologist.
Treatment methods
The main method of therapy is radical removal of the affected area with a small inclusion of healthy tissue. Benign elements are removed using the Surgitron apparatus, which avoids relapses, since the removed tissues are cauterized and there is no spread of tumor cells. Electrocoagulation of the affected areas is also used. Many clinics recommend radio wave therapy when removing skin tumors.
If it is cancer that cannot be removed, chemotherapy and radiation are used. With malignant processes, the prognosis is unfavorable, tumors can metastasize, so it is important to consult a doctor immediately at the first sign of skin problems. Modern removal techniques make it possible to prevent cancer and remove formations without scarring.
Malignant tumors
Neoplasms of this type grow rapidly, spread to surrounding tissues, and often create metastases due to the transfer of pathological cells through the lymphatic and circulatory systems. In such growths, the body’s control over cell division is lost, and the cells themselves lose the ability to perform direct functions.
Malignant tumors are quite difficult to treat; they are characterized by frequent relapses even after surgery. The stage of progression is determined by ultrasound and phototomography, and sometimes additional tests are prescribed.
The main signs of transformation of a stable borderline condition or a benign skin tumor into a malignant neoplasm are:
- rapid and sharp growth in size;
- pigmentation changing in saturation or color;
- ulceration, bleeding;
- spread of the tumor to nearby tissues.
Basalioma
A dangerous type of squamous cell carcinoma, formed from basal atypical cells of the dermis . At the initial stage, it looks like a white bunch with a dry surface, over time it increases in width and ulcerates, after which it transforms into a mushroom-shaped node or a deep ulcer protruding above the skin. Appears in areas of the body that are exposed to carcinogenic substances, elevated temperatures, and ultraviolet radiation. It is removed by standard methods - radiation, surgery, laser, cryo- or chemotherapy.
Fibrosarcoma
Appears in soft connective tissues, most often in the lower extremities. When placed superficially, it can protrude significantly above the skin . With deeper localization it is visually invisible. They classify poorly differentiated and differentiated fibrosarcoma, the latter is less dangerous - it does not create metastases and grows relatively slowly, but all two types have a high percentage of relapses after removal.
Melanoma
The most common type of cancer. As a rule, it is the result of malignancy of nevi and moles after strong ultraviolet irradiation or trauma. Creates metastases in almost any organ and often recurs. It is removed surgically, in combination with radiation and chemical therapy.
Liposarcoma
Tumor of adipose tissue. As a rule, it appears in men over 55 years of age. Usually formed against the background of benign neoplasms - atheromas and lipomas. Liposarcoma rarely metastasizes and grows slowly. It is removed by chemotherapy, surgery in combination with radiation therapy.
Hemorrhagic sarcomatosis, angiosarcoma, Kaposi's sarcoma
Numerous malignant neoplasms in the dermis. They have a structure of lilac, purple or violet spots without clear contours; over time, dense round nodes up to 2 in size, bluish in color, appear on them, which tend to ulcerate or unite.
As a rule, this type of sarcoma infects people with HIV, progresses in an aggressive form, and quickly leads to death.
Papillomas
These soft growths, mistaken for moles, are manifestations of a viral infection, which, as it spreads, leads to the formation of new growths. When injured by clothing and jewelry, the soft “pendants” can come off, ulcerate, and bleed. But the most dangerous complication of papillomas is degeneration into cancer. Therefore, these formations need to be removed.
Because the virus affects the entire body, cancerous tumors can occur in the genital tract, colon, and rectum. Patients suffering from papillomatosis (multiple papillomas) undergo a comprehensive examination and are prescribed antiviral treatment.
Warts
This is another viral type of skin tag that needs to be removed by combining topical treatment with an antiviral one. Warts spread over the surface of the skin, merging into large lesions. Contrary to ancient belief, the infection is “caught” not from frogs and toads, but from sick people, therefore, without removing the warts, a person infects those around him. Children are especially often infected.
Hemangiomas
These tumors arising from vascular tissue are:
- flat – red and or bluish birthmarks;
- cavernous - having the appearance of purple or bluish growths. When tension occurs, blood flows to the tumor, it increases in size, becoming more noticeable;
- combined and combined - consisting of convex and flat sections.
Cavernous hemangiomas, which grow, hurt, bleed and suppurate, must be removed. Other options are eliminated only for aesthetic reasons.
Why do you need to remove benign tumors?
Non-cancerous tumors can grow to enormous sizes. Wen (lipomas) and fibroids weighing several kilograms have been described. During the growth process, large tumors put pressure on tissues, blood vessels and nerves.
Neoplasia becomes inflamed and suppurates. The accumulation of pus can lead to cellulitis and blood poisoning. If accidentally injured, the tumors “get wet” and heal poorly.
Papillomas, warts and condylomas grow, forming large lesions. Growths located in the intimate area, on the edges of the lips and nasal mucosa, create inconvenience.
A benign tumor, especially located in open areas, often looks unaesthetic, causing problems with appearance.
How to avoid getting skin cancer? What to avoid?
Sunlight. The most proven cause of both types of skin cancer, as well as melanoma, is exposure to sunlight. If you like to travel to hot countries, have fair hair and skin, or your work involves prolonged exposure to the sun, you should seriously consider UV protection.
Precancerous skin diseases are the next factor that may precede the development of the squamous cell form: actinic (solar) keratoses and cheilitis, leukoplakia, human papillomavirus infection of the mucous membranes and genitals. This type of tumor can also develop against the background of scar changes after burns or radiation therapy.
Contact with carcinogens
Various chemicals can lead to the development of skin cancer: arsenic and petroleum products.
Weakened immune system. People taking immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant or people living with HIV have an increased risk of developing squamous cell skin cancer.
Pigmented nevi (moles, birthmarks)
Every person has several moles of different sizes on their body, but it is not necessary to remove them. There are nevi that need to be gotten rid of because of the risk of cancerous degeneration. To make it easier to remember, the signs of a “bad” mole are described by the AKORD system.
- A
- asymmetry. - K
- edge unevenness, scalloping. - O -
coloring. Malignant degeneration is indicated by the dark, almost black color of the neoplasm and the presence of areas of a different shade. - R
– size. Rapid growth of a mole is an unfavorable sign. You should consult a doctor if the nevus becomes more than 6 mm in diameter. - D
- dynamics, Dangerous signs - changes in the appearance of the mole, loss of hairs growing on it, bleeding, the appearance of nodules, crusts or ulcers, itching, burning and inflammation of the surrounding skin.
After removing the tumor, the tissue is examined for cancer cells.
Lipoma
This tumor is composed of fatty tissue. Wen formations can be single or multiple. Lipomas can grow, reaching a weight of several kilograms. Such large formations compress blood vessels and nerves, interfering with blood and lymph flow. Huge fatty tissues create many everyday problems - they impede movement and interfere with the selection of clothes. Cases of degeneration of wen into a malignant tumor - liposarcoma - have been described.
Therefore, if a lipoma is detected, you need to monitor it. Tumors that increase in size, cause pain, swelling, or are injured by clothing are removed. Small formations are cut off with a laser or electric knife, and for the resection of large lipomas, a surgical operation with suturing is performed. Therefore, it is recommended to remove wen before they reach an impressive size.