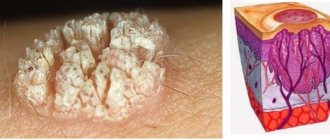
Causes of dermatomycosis
Speaking about the etiology of the disease, it is important to take into account that the causative agents are a variety of fungi: microsporum, trichophyton, epidermophyton (the latter group includes varieties of this type of fungus, all of them are united under the common name “dermatophytes”). It is always extremely difficult to identify pathogens in body tissues, since a specialist must first isolate a pure culture for research.
Another difficulty is that the causative agents of dermatomycosis are very common, so infection occurs easily, and in some cases such manifestations may have something in common with epidemic symptoms. Most often, dermatomycosis is characteristic of countries with a tropical climate, that is, humid and hot, since fungi usually multiply actively at a temperature of 25-30 degrees Celsius. The summer season and alkaline environment are ideal for them. At the same time, experts say that children are much more likely than adults to become infected.
As a rule, the pathogen appears on the skin after a person has been in contact with the lesion for some time. Doctors distinguish three main types of pathogens:
- bestiality;
- geophilic;
- anthropophilic.
The source of infection in the first case is animals, or rather, parasites living in their bodies. This includes parasites that use domestic dogs, cats or cattle as hosts.
In the second case, we are talking about pathogens living in the ground and soil. A person can work or simply come into contact with the ground without using protective equipment, and as a result become infected.
The third case is parasites that live in the body of a person who is a carrier of the disease. The very fact of infection occurs through contact.
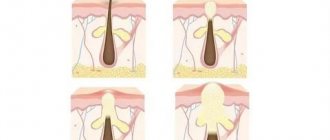
The development of dermatomycosis is expressed in the fact that conidia and hyphal fragments of pathogens enter the hair, upper layers of the skin, and nails (that is, those tissues that contain keratin). The degree of infection in dermatophytes is quite low, so tissue damage does not appear in healthy people. However, pathogens have a characteristic feature: they can subject keratin to complete destruction and destruction.
Pathogens located in the hair shaft can be divided into two types based on their growth. First: endothrix begin to grow from the skin into the hair and follicles, but they do not go beyond the boundaries of the hair shaft itself. Second: ectothrix grow directly into the hair directly from the hair follicle.
Much in the occurrence and development of the disease depends on the characteristics of the person’s body. Some types of dermatomycosis may be characteristic exclusively of an adult, while others - only of a child. In many ways, the disease is caused not only by age, but also by the secretion of the sebaceous glands, the composition of sweat and many other characteristic features.
Primary infection with dermatomycosis is a consequence of sensitization, after which it is time for a relapse to develop. Immunodeficiency largely determines the level of risk of dermatomycosis. In addition, various metabolic disorders, poor nutrition, problems with the hormonal system, and vitamin deficiency can also become a favorable background for infection. It is also important to remember that the fungus penetrates damaged skin faster, so people with ulcers, wounds and scratches on the skin are at particular risk.
Conidia, hyphae, and spores penetrate hair, nails and skin. Since the nutrient medium for the fungus is, first of all, keratin, the epidermis after infection begins to deteriorate at a rapid pace. In this case, healthy areas of the skin are also affected.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease mainly concerns compliance with hygiene standards that exclude infection (including self-infection) with a dangerous fungus. Here are the recommendations given by experts:
- You cannot use other people’s towels and combs;
- You should have wet wipes with you (at work, while traveling) to keep your hands and face clean;
- after swimming in the sea, pool, bath, the skin between the toes should always be wiped;
- do not wear tight clothes and underwear, preferring a loose fit;
- do not touch stray animals, and regularly show pets to the veterinarian.
Remember that when the first signs of dermatomycosis appear, you should immediately contact a dermatologist. Only a doctor can prescribe effective treatment, and you can get rid of these unpleasant diseases forever.
Symptoms of ringworm
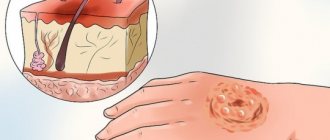
Dermatomycosis does not pose an immediate threat to the life of its carrier. Reproduction of pathogens is observed on the skin and other tissues, often all this is limited to external signs and manifestations. So what worries the patient most is not how dangerous the disease is, but how he himself now looks. If we are talking about skin lesions, then in this case for dermatomycosis the symptoms appear in the form of scaly plaques. They are usually red in color, can be located in groups or individually, each plaque is less than 5 cm in diameter. Such diseases are characterized by the brightness of the damaged areas and their itching.
Dermatomycosis on the head is caused by the pathogen microsporum. Their symptoms manifest themselves in increased hair fragility, as the endothrix fungus penetrates the hair shaft. If the ectothrix fungus is to blame, then the hair begins to fall out as the follicles are destroyed under the influence of the pathogen.
There are other symptoms of dermatomycosis, which arise depending on what kind of disease the patient has. For example, with dermatomycosis of the mustache and beard, the clinical picture is somewhat different. The pathogen causes the appearance of pustules, and subsequently the follicles begin to be damaged. Often these affected areas become infected for the second time, so diagnosing the disease is not difficult, taking as a basis the presence of areas where swelling forms, and the lesions themselves become covered with a crust with bloody discharge. The causative agent in these cases is trichophyton.
Inguinal dermatomycosis is characterized by rashes of pustules, extensive peeling, and pyoderma appears in the groin and genital area. The causative agent is the same trichophyton in several of its forms.
Symptoms of dermatomycosis of the body are characterized by the same manifestations: peeling in localized foci, pyoderma, erythema and pustular rashes.
If we consider cases of tinea pedis, it should be noted that skin lesions here are usually located between the toes, as well as on the feet themselves. The pathogen trichophyton causes scales, cracks, skin erosion, and sometimes small blisters.
A disease such as favus is expressed in damage to nails, hair and skin. In this case, the course of the disease is chronic, and infection occurs through direct contact with the carrier. In the scuticular form, a week after the infection itself, erythema is observed near the follicles, which later transforms into pseudopustules and ulcers. After this, the skin begins to atrophy and cicatricial alopecia occurs. In this case, the hair does not fall out, but becomes lifeless and dull. As for the impetiginous form, in this case the clinical picture is different: brown crusts appear on the patient’s skin, under which the same alopecia is hidden. If favus of nails is observed, it is expressed in their fragility, the nails acquire a yellowish color.
Onychomycosis affects the fingernails and toenails; they begin to peel, become rough and thicken. The causative agent is trichophyton; in some cases, the disease can be caused by various types of candida fungus.
Causes of skin mycosis
The main cause of the disease is fungal microorganisms, which, through microtraumas and scratches, enter the subcutaneous tissue and are absorbed by the mucous membrane. Spores can accumulate in the lungs, gradually weakening the immune system. The predisposition to infection, as well as the mechanism of the disease, depends on the general condition of the body.
The appearance of mycosis may be preceded by:
- Past infectious diseases.
- General weakening of the immune system.
- Taking antibiotics, steroids.
- Poor hygiene.
- Unbalanced diet.
- Trophic ulcers and varicose veins.
- HIV infections.
- Diabetes.
Important! Modern medicine identifies 16 varieties of microsporum and 22 types of fungal parasites that pose a danger to humans and require an individual choice of treatment methods. Therefore, you should not self-medicate. After all, it is possible to establish the cause of the pathology and choose a treatment method only after diagnostics in the laboratory.
Diagnosis of dermatomycosis
Superficial mycoses can be detected already during an external examination. The fact is that with dermatomycosis, symptoms and treatment are closely related, so first the doctor must correctly determine which pathogen caused the disease, diagnose it, and then prescribe treatment depending on the type of pathogen. Typically, ringworm is characterized by a rash with red edges. However, the final diagnosis is manifested in clinical examinations under a microscope, or more precisely, in the examination of culture taken by scraping.
The scales of nails and skin must be examined. The patient may need to have a blood test and allergy tests. A dermatologist is not limited to an external examination, because only a thorough examination will help identify the true causes of the disease.
Classification
Dermatomycoses are classified according to location:
- smooth body skin;
- scalp and beard;
- nails;
- groin area;
- stop.
Depending on the pathogen, dermatomycosis is classified into:
- keratomycosis: nodular microsporia, lichen versicolor;
- dermatophytosis: athlete's foot, athlete's foot, trichophytosis, imbricate mycosis, favus, rubrophytosis;
- deep mycoses: aspergillosis, chromomycosis, blastomycosis, sporotrichosis, etc.;
- candidiasis: superficial, visceral and chronic generalized;
- pseudomycosis: actinomycosis, trichomycosis, erythrase, etc.
Treatment of dermatomycosis
Antifungal ointments and formulations are successfully used to treat such diseases; these products can be purchased at the pharmacy without a prescription. This remedy must be used 1-2 times a day, and within a week the results of treatment will become noticeable. However, in no case should the course of treatment be interrupted if the patient believes that things are getting better. Only long-term use of antifungal agents can completely rid a person of the disease.
Sometimes ointments may not help, this applies to the disease in an advanced stage. In this case, stronger oral medications are prescribed. It should be remembered that the affected areas of the skin should never be wetted; they should be dry and clean. If bubbles appear, it is forbidden to open them, as this will provoke further development of the infection. If the patient is being treated for inguinal ringworm, he must pay close attention to the quality of his underwear and change it daily. For tinea pedis, clotrimazole powder is used to treat shoes.
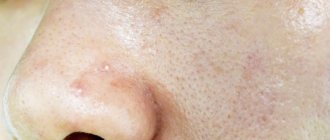
Photo of dermatomycosis in humans
In the photo you can see various manifestations of dermatomycosis in humans:
Depending on the symptoms of ringworm, treatment for a person will also differ. Accurate diagnosis is necessary.
What it is? Terms and Definitions
Skin mycoses
– fungal infections of the skin and its appendages (hair, nails) by pathogenic fungi of various types. In fact, this is a large group of diseases united by a single criterion - the causative agent. Mycoses can manifest themselves in different ways, affecting only the skin or its appendages, some can simultaneously cause systemic lesions, that is, extend their effect to internal organs. Approaches to the treatment of different mycosis also differ: some require the use of local, topical drugs, such as ointments or creams for mycosis, some are supplemented with tablets for mycosis, oral forms of systemic drugs, in some cases doctors are forced to expand the range the drugs used against mycosis in order to first stabilize the patient’s condition and then rid him of the pathogenic fungus.
Dermatomycosis of smooth skin
This type of fungal disease is more common in warm countries, where the human body initially produces more sweat, which means the natural moisture of the smooth skin increases. Very often professional athletes who subject their bodies to grueling training suffer from this disease.
This type of dermatomycosis manifests itself in the formation of a lesion in the form of a ring with small bubbles inside, accompanied by severe itching.
Often a secondary infection of bacterial origin is also associated with the fungus. As a result, even scarring can be observed. After healing, areas of redness remain.
Risk factors
Some diseases may predispose to the development of mycoses:
- AIDS
- diabetes mellitus and endocrine diseases
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract and urinary system
Treatment with certain drugs can also provoke the disease: we are talking about long-term use of corticosteroids, immunosuppressants and antibiotics.
Very often, mycoses occur in athletes, military personnel, and heavy industry workers. After all, people from these areas often use shared showers and locker rooms, wear overalls and heavy closed shoes.⁶
Photos before and after
You can evaluate how mycosis of smooth skin is eliminated in our clinic from the photos taken before and after treatment. In 90% of cases, it is possible to achieve results without traces of the disease. If treatment is not done in a timely manner, complications may result, leaving barely noticeable scars and other changes in the epidermis. Therefore, to achieve maximum effectiveness of treatment, we recommend contacting a specialist when the first symptoms appear.
We are waiting for your questions by phone in Moscow. To make an appointment with a dermatologist, leave a request on the website.