Have you noticed that you have a lump on your hand? Has it been going on for quite some time now without you hitting anything or receiving any injuries? And is this uncharacteristic formation really bothering you? What could it be? And how to treat this same bump on the hand?
The appearance of this neoplasm can have several reasons and be a characteristic sign:
- Pathologies in the joints;
- Oncological processes;
- Benign formations (hygromas).
Why does hygroma occur?
A lump on the wrist joint is a kind of cyst, inside of which there is a mixture of serous fluid and fibrin in the form of a transparent jelly-like mass. The wall of the capsule consists of connective tissue, but its cells have degenerative changes. Therefore, the cause of the development of hygroma is considered to be the degeneration of connective cells into spindle-shaped and spherical ones.
That is why it is very important to completely remove all contents: if after the operation even a small fragment of altered cells remains, the likelihood of relapse will be much higher than, for example, with insufficiently qualified removal of fibroma or atheroma. There is no need to talk about conservative treatment at all: it is simply pointless.
Hygroma is often called the disease of pianists and tennis players, since the provoking factor is repeated trauma to the wrist or high load on it. Young women are more susceptible to pathology, but hereditary predisposition, according to scientists, is almost completely excluded.
Features of hand exostoses
The free part of the upper limb or the arm itself is formed:
- humerus;
- bones of the forearm - radius and ulna;
- bones of the hand - wrist bones, metacarpals and finger bones (phalanx).
Exostosis can form on each of them. But the long tubular bones are most often affected: the humerus, ulna and radius. In this case, osteochondroma is usually located in the joint area, which supports the theory that it is formed from a displaced part of the epiphyseal plate. Before the process of skeletal formation is completed, which usually occurs between 18 and 25 years, it is a layer of hyaline cartilage located immediately behind the epiphysis (head) of the tubular bone. Its cells constantly divide, causing the bone to grow in length.
As they move away from the epiphyseal plate, old cartilage cells are replaced by osteoblasts. As a result, dense bone is formed. Such areas are called bone metaphyses and it is in them that exostoses are usually found. After the completion of the formation of the skeleton, the epiphyseal plates are replaced by thin epiphyseal lines, and the process of formation of new cartilage cells stops. This is called the closure of growth zones. Therefore, osteochondromas are mainly first diagnosed in children and adolescents, and more often during the period of active growth - at 8-16 years.
In this case, exostoses go through the same formation path from cartilaginous formation to ossification. And their characteristic feature is the presence of a cartilaginous cap on the surface of the growth.
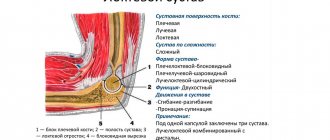
Since the metaphyses of the bones are located immediately behind the epiphyses, the presence of osteochondroma of the joint is often said. In hand this is:
- the shoulder joint, damage to which occurs due to the formation of exostosis in the area of the proximal epiphysis of the humerus or on the glenoid cavity of the scapula;
- the elbow joint, which is affected by the formation of exostosis at the distal epiphysis of the humerus or proximal epiphysis of the ulna or radius;
- small joints of the hands formed by the metacarpal, carpal bones and phalanges of the fingers.
Most often, exostosis is found in the elbow and shoulder joints. On the bones of the hand, such neoplasms form much less frequently.
In this case, exostosis of the arm bone can be either single (solitary) or only one of many present on other bones of the skeleton. In the latter case, they speak of the presence of multiple exostotic chondodysplasia, which is hereditary. This disease can lead to various complications, but the most dangerous is the malignancy of osteochondromas, which is observed 10 times more often than with solitary exostosis of the forearm, shoulder, etc.
How to treat
Conservative ways of solving the problem have been practiced for a long time. The formation was kneaded, crushed, the liquid was removed from it through punctures, and sclerosing drugs were injected. They used therapeutic mud, ointments with an anti-inflammatory effect, and physiotherapy. However, only in 10% of cases was it possible to achieve a positive effect: in the rest, relapses occurred.
After scientists discovered the ability of degenerated hygroma cells to restart the process of tumor formation, the conservative methods were done away with. The only treatment today is surgical excision, after which not a single fragment of tissue remains. Therefore, if in the case of other formations it is possible to remove atheroma with a laser or radio wave method, then with hygroma you will have to trust the surgeon and go for surgery, although some doctors practice endoscopic techniques.
Intervention is simply necessary if the tumor progresses seriously, causes severe pain and limits movement in the joints. You shouldn’t turn a blind eye to the aesthetic side of the issue: a lump on the wrist is always a cosmetic defect. After its removal, performance is restored and a normal lifestyle is established, and if endoscopic intervention is chosen as an intervention, recovery time is significantly reduced.
Hygroma of the wrist
27.09.2019
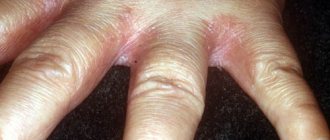
Wrist hygroma is a benign tumor , more precisely a formation that is localized mainly on the hand, in the area of the wrist and nearby joints . The formation of a tumor occurs in the tendon tissue, causing local swelling , redness and pain.
For some time the disease does not manifest itself in any way, but if left untreated it becomes chronic. The hygroma of the wrist may increase in volume, resembling a soft ball in appearance. Over time, the mobility of the hand is limited, the fluid-filled tissues of the hand become inflamed, making it difficult to carry out everyday activities.
Causes that provoke the appearance of hygroma of the hand
Despite the fact that the disease is a benign tumor , it never degenerates into a malignant one. Currently, doctors identify several reasons why hygroma of the hand develops.
- Constant physical activity on the wrist area. Various types of monotonous work associated with stress on the hand provoke inflammation and growth of formation. Most often, this is encountered by people whose work involves a computer, as well as those who work monotonously with their hands for a long time.
- Anatomical structure of the hand. In some people, the structure of the wrist is especially fragile; the surrounding tissues are located at the base of the surface of the hand and are not protected by anything, so they can be more often injured under load.
- Chronic course of bursitis and tendovaginitis. Inflammation of the soft tissues of the tendons and mucous bursae, which is permanent, can cause the formation of hygroma.
- Removal of the seal surgically . Unfortunately, removal of the lump does not exclude the reappearance of hygroma, since the disease has a tendency to recur.
- Female gender and heredity. According to statistics, women are more likely than men to develop the disease. The likelihood of getting a hand hygroma is higher if someone in the family has already been sick.
Symptoms, diagnosis
First of all, at the appointment, the doctor questions the patient and listens to the nature of the complaints. Next, he conducts an initial visual examination with palpation and palpation of the tumor. The patient is asked to rotate the hand in different directions and around its axis, identifying which movements cause pain. During palpation, the doctor determines the location of the ball and feels its soft contents.
For a more accurate diagnosis, the patient is prescribed an MRI and ultrasound of the wrist. Computer diagnostic methods are used when the question of surgical intervention is raised.
Symptoms of hygroma of the wrist are pronounced and noticeable externally:
- the neoplasm is clearly visible on the hand, it is round, similar to a ball;
- The seal is soft to the touch, but hurts when pressed;
- turning the hand will cause pain and discomfort;
- with prolonged loads on the hand, the hygroma increases in size;
- the skin at the site of the tumor is hyperemic and inflamed.
How is hygroma of the wrist treated?
Treatment of wrist hygroma is carried out mainly surgically . This method is chosen if the formation grows rapidly, becomes inflamed, infringing neighboring nerves and tissues. The surgeon can choose the method of excision of the tumor with complete removal of the formation. Hygroma can also be removed using laser surgery - this method is more gentle and does not leave a scar. There are also conservative treatment methods - the tumor is punctured and then medications are injected into the cavity. The disadvantage of conservative treatment is the high rate of relapse.
Timely seeking medical help will help avoid the disease becoming chronic.
Published in Surgery Premium Clinic
Symptoms
In children, exostoses rarely manifest themselves clinically, since they are usually completely cartilaginous structures and are small in size. Symptoms may occur during the period of active growth of the tumor, i.e. in adolescents. As a result, a lump may form on the hand. As a rule, it is painless, not adherent to the skin, dense and has a rough or smooth surface. This creates a cosmetic disadvantage, but is often the only manifestation of the disease.
Subungual exostoses of the fingers are extremely rare. In such cases, the neoplasm raises the nail plate, creating a risk of peeling or ingrowth.
In some cases, a growing osteochondroma provokes dysfunction of the joint next to which it is present, inflammation of its synovial bursa (bursitis) or tendons (tendinitis). The tumor can also compress nerves or blood vessels passing near it. This results in:
- discomfort or dull pain in the area of the formation of a tumor or joint, which occurs or intensifies when it is activated during movement;
- swelling, redness of soft tissues;
- restrictions of movement in the affected joint;
- sensations of numbness of the skin, goosebumps;
- hand muscle dystrophy.
Large exostoses can provoke deformation of the mother or neighboring bone, especially when they are located on the ulna or in the hand. The joint may also suffer. As a result, not only does the risk of fracture increase, but also the possible curvature of the upper limb. Sometimes in children, large exostoses injure the epiphyseal plates. This leads to disruption of their function and the growth of the affected bone lagging behind the healthy arm.
In isolated cases, rapid growth of osteochondroma is observed. This requires immediate contact with an orthopedic traumatologist, since such changes are characteristic of tumor malignancy. But if single exostoses degenerate into chondrosarcoma in less than 1% of cases, then with multiple osteochondromas the risk increases to 10%.
Diagnostics
The main diagnostic method is x-ray in 2 projections. The images visualize only the bone part of the tumor in the form of a neoplasm with clear boundaries and connected by a thin stalk or thick base to the mother bone. Thinning of the cortical bone is also observed, and the osteochondroma itself often has a “cauliflower” appearance due to areas of calcification in the cartilaginous cap.
The cartilage cap itself is not visible on x-rays, although its size is important in determining the likelihood of malignancy. Normally, the thickness of the cartilage layer should not exceed 1.5-2 cm. Therefore, in controversial cases, as well as in children with a high growth rate of osteochondroma, CT or MRI is often additionally prescribed. As a result, it is possible not only to accurately visualize the cartilage cap and measure its parameters, but also to determine the location of the neurovascular bundle, as well as assess the condition of the shoulder, elbow joint or hand. This makes it possible to develop optimal treatment tactics.
Treatment of hand exostosis
In the absence of clinical manifestations of osteochondroma, treatment is not carried out. In such situations, dynamic observation is sufficient to monitor the process of development of the tumor.
Conservative therapy is prescribed when bursitis, tendonitis or pain due to exostosis is diagnosed. It consists in the use of NSAIDs, sometimes in the intra-articular administration of corticosteroids, and in case of severe pain, in carrying out a drug blockade. Drug treatment can be supplemented with physiotherapeutic procedures, in particular:
- electrophoresis with the introduction of drugs;
- ultrasound therapy;
- Ural Federal District;
- laser therapy;
- magnetotherapy.
But conservative therapy is not able to lead to the resorption of osteochondral exostosis. It is aimed only at eliminating complications and improving the patient’s condition.
What causes hygroma?
The appearance of cysts on the hands sometimes does not have typical causes, but often occurs due to bruises, excessive stress on the joints, monotonous, rhythmic, prolonged movements, and genetic heredity.
Athletes have a high predisposition to the disease, since during training they perform exercises that greatly affect the arms and cause increased pressure in the upper extremities. For example, people who play table tennis, golf or badminton are at risk for mandatory hand hygroma surgery .
This is an industrial disease of many musicians who play the piano, violin, cello, etc. Many typists, seamstresses, and embroiderers very often encounter a similar diagnosis. Pathology has no age restrictions.