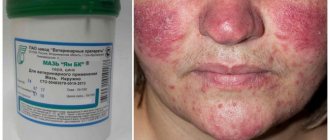
Few people know that skin diseases can be successfully treated with ASD-2. Dermatitis, eczema, and lichen are quite common today. Many of them are not only accompanied by painful symptoms, but are also difficult to treat. They also cause aesthetic discomfort, as they are often localized in prominent areas of the body.
ASD will help in the fight against various ailments of the dermis, both inflammatory and bacterial and infectious in nature. What ailments does the elixir treat, and how to use it? Let's talk about this.
ASD-3 reanimates the skin
The third fraction ASD drug is effective in the fight against many diseases of the dermis. It is effective in the fight against fungal infections, sluggish and long-term non-healing wounds, inflammatory processes, eczema, psoriasis, dermatitis, fistulas, and demodicosis.
This product, unlike ASD-2F, is intended exclusively for external use. It is used to treat affected areas of the skin and is used for compresses and rinses. There are several options for using the third fraction antiseptic stimulant, depending on the disease. The standard regimen for using the drug is as follows.
Veterinary
11.11.2015
The whole truth about ASD
July 2014 marked the 105th anniversary of the birth of Alexei Vlasovich Dorogov, the author of the biological drug antiseptic Dorogov stimulant (ASD), which, by his own admission, was invented in March 1948 on his personal initiative, and not by order of I. IN.
Stalin. In the first years of its existence, the drug ASD experienced a period of enormous popularity, then almost complete oblivion for 50 years, and is currently experiencing a period of renewed interest in it among specialists. The history of the creation of the drug ASD, its fate, like the fate of its author, is of certain interest. As is clear from archival documents, A.V. In 1948, Dorogov worked as a senior researcher at the Laboratory of Equine Infectious Anemia at the All-Union Institute of Experimental Veterinary Medicine (VIEV). According to the author (Report of A.V. Dorogov for 1949, VIEV Archive, p. 566), when searching for new medicinal drugs, he paid special attention to the original works of V.P. Filatov on the use of highly active tissue substances (stimulants), which are not destroyed by boiling and repeated autoclaving, do not contain proteins and hormones. Working on his own initiative for almost two years with the tissues of horses suffering from infectious anemia, he developed a new technology for obtaining a biogenic stimulant. Unlike the works of V.P. Filatov and academician M.P. Tushnova, A.V. Dorogov took a different path: he used the method of high-temperature digestion of animal tissues in the absence of free access of air, followed by collection of digestion products by condensation by cooling. As a result, the author obtained a dark liquid (fraction 1), which, when left to rest, separates into two fractions - light (fraction 2) and dark (fraction 3).
The author tested the medicinal properties of the drugs on animals for various pathological processes and found that they have the ability to stimulate the body as a whole and increase the reactogenicity of tissues exposed to the pathological process. In experiments on rabbits with pyemia, fraction 2, administered intravenously in doses of 0.3–0.5 ml, stopped the general septic process, caused the opening of subcutaneous purulent foci and led to a rapid recovery of the animals.
Already in the first studies it was shown that the effect of the drug ASD is complex and affects many body systems. The effect of the drug is being studied for various infectious diseases of animals and a number of human diseases. Positive results are obtained in the treatment of purulent wounds, eczema, trophic ulcers, furunculosis, lichen, and inflammatory processes of the genital organs. It should be noted that the treatment of people by A.V. Dorogov conducts this at his own peril and risk, without official permission. The author of the drug has the opinion that ASD is a therapeutic drug that is effective for most human and animal diseases.
Director of VIEV Professor N.I. At the end of 1949, Leonov submitted a report to the Secretary of the Central Committee of the All-Union Communist Party of Bolsheviks G.M. Malenkov about the invention of A.V. Dorogov of a promising medicine, which “in case of military necessity, after some refinement, will be one of the most universal and most effective means of treating shock, nervous injuries, gangrene, purulent wounds in hospitals,” and with a request for help in organizing widespread trials of the drug ASD in medical institutions, as well as in financing the organization of production of the drug for more active testing in veterinary medicine. N.I. Leonov simultaneously appeals to the USSR Minister of Health Smirnov to receive A.V. Dorogov with a report on the drug ASD. As a result, on April 28, 1950, the Council of Ministers of the USSR adopted Resolution No. 1739-680c, which obliges the Ministry of Health to organize a trial of the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug ASD for the treatment of eczema, purulent osteomyelitis, varicose and trophic ulcers, pulmonary and bone tuberculosis and leprosy. By decision of the State Staff Commission under the Council of Ministers of the USSR dated May 27, 1950 No. 2305c, the staff of the tissue therapy laboratory at VIEV was approved. From that moment on, professors and employees of the VIEV laboratories, as well as the Scientific Research Chemical and Pharmaceutical Institute named after ASD, were involved in the study of the ASD drug. S. Ordzhonikidze, Central Dermatovenerological Institute, Central Institute of Traumatology and Orthopedics, Hospital named after. Botkin and the Institute of Tuberculosis of the Academy of Medical Sciences.
Experiments conducted on farms with cattle suffering from trichomoniasis showed that the drug ASD (fraction 2) not only killed trichomonas, but also eliminated painful phenomena in the genital apparatus in a shorter period of time and restored its hormonal function. When treating pulmonary and bone tuberculosis in humans with the drug ASD in inpatient conditions, in some cases an improvement in the general condition of the patients was noted, but complete recovery of the patients was not observed. Similar results were obtained in the treatment of animals: in experiments with experimentally induced tuberculosis, the drug ASD did not have a therapeutic effect. In experiments on the treatment of brucellosis in cows under production conditions, there were isolated facts of a positive effect on accelerating the elimination of complications in the form of bursitis, arthritis, metritis and retained placenta, but no elimination of the infection was observed on the farm. Similar results were obtained in the treatment of horse washing. A positive effect was observed only when fraction 2 was used in the early stages of the disease. Administration of the drug for prophylactic purposes did not give a positive result (Report by Orlov E.S. et al., 1950).
According to the Central Dermatovenerological Institute and the Zagorsk Leprosy Clinic, when treating human skin diseases (eczema, athlete's foot, neurodermatitis, sycosis, lichen, neurotrophic ulcers) with ASD drugs, there is a rapid improvement in the general condition of patients and in almost all cases their complete recovery. Based on data from these institutions, the Pharmacological Committee of the Scientific Medical Council of the USSR Ministry of Health (Protocol No. 5 of March 17, 1951) authorized the use of ASD drugs for the treatment of human skin diseases. Similar results were obtained in animals with necrobacteriosis, eczema, dermatitis, trophic ulcers and infected slow-healing wounds.
However, these were preliminary studies. More extensive testing of the drug was required, which was in short supply because... the laboratory produced only 5–10 liters per day. In 1950, the laboratory commissioned three installations and in 1952 produced 17.5 tons of the drug, which made it possible to conduct extensive testing of the drug under production conditions. In 1953, the USSR Ministry of Health organized the production of ASD at the Akrikhin chemical and pharmaceutical enterprise, and in 1954, the USSR Ministry of Agriculture organized the production of ASD at the Gusevsky crealine plant, then at several biological enterprises. The organization of these productions is advised by A.V. Dorogov. However, in the 60s. ASD production is gradually being phased out, and by the 90s. it is preserved only at the Armavir biofactory.
The chemical composition of ASD fractions is very complex. Fraction 2, according to A.V. Nikolaev (1959), contains a large amount of nitrogenous compounds in the form of acid amides and ammonium salts of organic acids, organic compounds containing sulfur. The third fraction contains many nitrogenous compounds of phenols and carboxylic acids. Modern methods of gas chromatography-mass spectrometry reveal over 60 different compounds in the third fraction. It is very difficult to determine which substance is the active principle or whether they have an effect in combination.
The study of the therapeutic effectiveness of the drug ASD by medical institutes was completed, judging by the archival data of VIEV, at the end of 1950. At VIEV, research was continued as planned by many laboratories, in addition to the laboratory of tissue therapy, until 1958. About 50 specialists from the institute were involved in the work and a significant number of local veterinarians. Until 1954, scientific work on most topics was led by Alexey Vlasovich. Unfortunately, Dorogov had conflicts with the administration of the institute, which ended with his dismissal on April 25, 1955 under Article 47 of the Labor Code by order No. 54. He died on October 8, 1957 in the prime of his creative powers, veterinary science in his person lost an extraordinary scientist.
Work journals A.V. We did not find Dorogov in the archives of the institute. The technology he used for producing ASD can only be judged from a short explanatory note to the application for an invention filed by A.V. Dorogov to the Directorate for Inventions and Discoveries of the State Technical University of the USSR (Application No. 425080-x, priority dated 08/04/1950).
In 2003, after studying documents and testing a number of different technology options, the experimental production laboratory of VIEV restored Alexey Vlasovich’s technology. In the process of numerous experiments, it turned out that the rate of heating of the entire mass of raw materials loaded into the apparatus, the accuracy of maintaining a certain temperature, as well as the quality of the raw materials in terms of protein content are critical. All this was taken into account, and production of the drug began, first in the experimental laboratory of VIEV, then on an industrial scale in the city of Bobrov. The resulting drug is registered for use in veterinary practice as Antiseptic Stimulator D-2 and Antiseptic Stimulator D-3 fraction. Testing it in laboratory conditions using modern methods and in production conditions showed full compliance with the ASD developed at VIEV.
FGBNU All-Russian Research Institute of Experimental Veterinary Medicine named after. Ya.R. Kovalenko 109428, Moscow, Ryazansky prospect, 24, building 1
Tel
LLC "BIOSTIM"
397705, Voronezh region, Bobrov, Bityug station, 5, office 1
Tel
Number of hits: 17897 Author: G. Nadtochey, Ph.D. biol. Sciences, Head of the Laboratory of Biophysics VIEV N. Kukonin, Director of BIOSTIM LLC
Standard application scheme
- Every day, after pre-treating the affected area of skin with 3% hydrogen peroxide or a weak solution of potassium permanganate, apply a gauze pad soaked in a 20 or 50% oil solution (depending on how advanced the process is).
- The best oil is olive oil, but it is possible to use sunflower oil that has been purified and boiled in a water bath.
- Parchment paper is placed on top of the napkin with the oil mixture, then a thick layer of cotton wool, after which the compress is fixed with a bandage.
- The procedure is carried out 1-2 times a day, until the tissues are completely healed and complete recovery.
ASD fraction 2 for facial skin
The medicine promotes cell regeneration and rejuvenation of the body. For external use, you can use fraction 3, but this product is very aggressive and should be mixed with vegetable fats.
ASD for facial skin standard application scheme for fraction 2:
- 30 drops per 100 ml of cold and boiled liquid:
- twice a day before meals 30 minutes;
- The reception lasts for 5 days.
Then they pause for 3 days.
The product can be used in cosmetology. To do this, you need to choose the right cream, preferably for children. It is necessary to add a few drops of the drug to the cream, stir and rub into the skin of the face until completely absorbed. The result is a unique and inexpensive skin care product. It is well absorbed into the skin of the face and provides excellent care for skin where there is a rash or acne.
Summary table of regimens and dosages for the treatment of various skin pathologies
Depending on the ailment, the method of application of the composition, regimen and dosage may vary slightly. Options for using the medicine for skin diseases can be seen in the table.
| A drug | Disease | Way | Scheme | Dosage | Well |
| ASD-3F | Fungal infections | Treatment of affected areas | 3 times a day | The drug in its pure form | Until complete recovery |
| ASD-3F | Acne, bedsores, dermatitis, eczema, chronic inflammatory diseases | Treatment of affected areas, including 2mm of healthy skin | 2-3 times a day | 20% oil solution (for mild lesions) and 50% solution for severe lesions | Until complete recovery |
| ASD-3F | Demodicosis | Treatment of affected areas | 2-3 times a day | Ointment: 1 teaspoon ASD-3, 1 tablespoon Vaseline. | 7 days, 2 weeks break, 7 days |
| ASD-3F | Psoriasis | Lotions | 2-3 times a day | 2% solution in oil | Until symptoms resolve |
| ASD-3F | Non-healing wounds and fistulas | Lotions | 1 time per day, at night | 20 - 50% solution in oil | Until complete recovery |
External therapy for skin lesions of various origins
I.V. SALIMOVA
, Doctor of Medical Sciences,
V.I.
AVERINA , Ph.D.
, FMBC named after. A.I. Burnazyan FMBA of Russia The relevance of the problem of local therapy in cosmetology and dermatology is due to the growing need of the population for quality medical care.
A person’s appearance plays an important role in his life, and the condition of his skin speaks volumes. A prosperous person has healthy and well-groomed skin - the result of a healthy lifestyle, balanced nutrition and careful care. Over the past decades, due to various reasons, there has been a directional trend towards an increase in the incidence of skin, hair and nails throughout the world. Manifestations of skin diseases are easily accessible to external influences, so external treatment has long been widely used in dermatology. Local therapy, like general therapy, always requires an individual approach. In some cases, it is aimed at suppressing and eliminating the immediate cause of the disease (etiological therapy: for example, prescribing antimicrobial agents for superficial pyoderma, fungicidal agents for dermatophytosis, or antiparasitic agents for scabies and lice. However, more often external therapy is symptomatic and is aimed at eliminating and resolving emerging in the skin of pathological changes and accompanying subjective sensations.In some cases, external therapy is prescribed to protect the affected areas of the skin from the effects of external irritants.
The success of external therapy depends on correct consideration of the nature of the developed dermatosis (acute, subacute, chronic), the stage of the process (progressive, stationary, regressive), the depth and localization of the lesions, the pharmacological properties of the prescribed medication, indications and contraindications for its use, the concentration and dosage form of the external facilities. The most demonstrative example is eczema, in which external therapy depends on the form of eczema, its stage, location and other factors. Strict individualization of external treatment and constant monitoring of the patient are necessary, since it is often necessary to replace drugs (if they are intolerant or get used to them) or change the dose.
One of the basic rules of local treatment for a number of skin diseases is to first use a weak concentration of drugs with a gradual increase and transition to more active drugs. At the same time, there are forms and stages of skin diseases in which the use of potent local drugs is indicated (some infectious dermatoses - trichomycosis, scabies, etc.).
In acute and subacute forms of the inflammatory process, you should use mainly dosage forms with the surface action of the agents they contain (lotions, shaken suspensions, powders and pastes). In the case of chronic and deep processes, one should prefer dosage forms that allow the substances to act more deeply (ointments, compresses, etc.). However, there are exceptions to this rule. For example, glucocorticoid ointments can be used in the acute stage of the inflammatory process, since the effect of the steroid covers the “adverse” effect of the ointment base.
The general rule for the use of topical drugs is: the more acute the inflammatory process, the more superficially the dosage form and the anti-inflammatory substances included in it should act. Thus, lotions, powders, shaken mixtures act more superficially than pastes, and pastes - more superficially than ointments, compresses, etc. The concentration of the medication included in the dosage form is also important. That is, the choice of dosage forms is determined not by the etiology of dermatosis, but by the degree of severity of inflammation, the localization of the lesion and its prevalence.
External agents, according to the degree of their effect in depth, can be arranged in ascending order: powders, lotions, shaken mixtures, pastes, ointments, compresses, glues, patches, varnishes.
The wrong choice of dosage form usually leads to an exacerbation of the disease. In this regard, it is necessary to know well what dosage forms for external therapy are, their mechanism of action, indications and contraindications for use, and methods of use. Dosage forms of external therapy used in dermatology
All pharmacological agents of external therapy are divided into indifferent and those with a specific pharmacological effect. Indifferent agents, the effect of which is determined only by their physical properties, include: water, chemically neutral powdery substances, oils, fats, fat-like substances, gels, collodions. They usually form the basis of dosage forms of external therapy. Drugs that have a certain pharmacological effect are divided into a number of groups according to their most characteristic therapeutic effect. Depending on the purpose pursued by external therapy in each specific case, they are included in different dosage forms. This makes it possible:
• obtain a certain therapeutic effect due to the physical properties of the forms themselves; • use different concentrations of medicinal substances; • inject drugs into the skin to varying depths.
The most commonly used dosage forms are: powder, lotions, gel, paste, aerosol, cream, ointment, varnish, patch.
Powders consist of powdery substances that are applied to the affected area in an even thin layer. The powder dries and degreases (due to hygroscopicity) the skin, cools it (as a result of increased heat transfer) and helps to narrow the superficial blood vessels of the skin. This helps reduce hyperemia, swelling (especially in skin folds), sensations of heat and itching. However, when the lesions become wet, powder is not used, because together with the exudate they form crusts that intensify the inflammatory process and irritate the skin. Powders are used against excessive sweating and increased sebum secretion.
Powders consist of mineral or plant powders. The most common mineral substances in powders include magnesium silicate - talc (Talcum), zinc oxide (Zincum oxydatum), and plant substances - wheat starch (Amylum tritici). Starch can be fermented, so it should not be consumed if there is excessive sweating, especially in the skin folds. Some drugs in powder form are added to powders for the treatment of erosions and ulcers.
Lubrication is carried out with aqueous or alcoholic solutions of aniline dyes (for example, brilliant green), aqueous-alcoholic solutions of menthol (1-2%), silver nitrate (2-10%), fucorcin.
Lotions in the form of aqueous and alcoholic solutions are often used in dermatology as an anti-inflammatory, astringent or disinfectant. Moisten 4-6 gauze napkins or soft cloth with cooled medicinal solutions, wring them out and apply them to the affected wet area. The lotions are changed after 5-15 minutes (as they dry and warm up) for 1-1.5 hours; The entire procedure is repeated several times a day. Most often, a 1-2% solution of tannin, 0.25-0.5%, a solution of silver nitrate (lapis), a 2-3% solution of boric acid, 0.25-0.3% is used for lotions. lead water (Aqua plumbi). Lotions with a solution of boric acid are prescribed with caution due to possible toxic effects.
If there is a purulent infection in the foci of acute inflammatory lesions, then disinfectant lotions are used: 0.1% solution of ethacridine lactate (rivanol), solutions of furatsilin (1:5,000), potassium permanganate (0.05%), resorcinol (1-2 %).
Wet-dry dressing. This dressing is prepared according to the same principle as the lotion, but there are more layers of gauze (8-12) and the dressing is changed much less frequently (every 1/2-1 hour or more) as it dries. These dressings help to subside the symptoms of acute inflammation, since the slowly evaporating liquid causes cooling of the skin (however, less actively than the lotion).
Agitated suspensions (chatterers) are used for acute, subacute and aggravated skin inflammations (dermatitis, eczema, etc.), lack of weeping and excessive dryness of the affected skin areas. The advantage of shaken suspensions is the possibility of their use without applying bandages. Water suspensions (“chatter”) are preferable for oily skin, oil suspensions for dry skin. The main components of water mash are indifferent powders (30%) suspended in water with the addition of glycerin (10-20%). After shaking, the suspension is evenly applied with a cotton-gauze swab 2 times a day. The surface anti-inflammatory effect is due to increased heat transfer during the evaporation of water and the subsequent action in the same direction of the powders included in the composition (zinc oxide, talc, white clay, starch).
Pastes are a mixture of equal parts by mass of indifferent powders (zinc oxide, talc, starch, etc.) and a fatty base (lanolin, petroleum jelly, etc.). Pastes act more deeply than shaken mixtures, but are less active than ointments; they have an anti-inflammatory and drying effect. The viscous consistency of the pastes allows you to apply them without a bandage. Do not use them on the scalp when it gets wet. The paste is applied to the skin 1-2 times a day; Once every 3 days, it is removed with a swab moistened with vegetable oil. By reducing the amount of powdery substances, soft pastes can be prepared. According to indications, naphthalan, ichthyol, sulfur preparations, tar, etc. are added to the paste.
Compresses have a warming effect and are designed to absorb skin infiltrates, reduce inflammation, and protect affected areas from external influences. For compresses, alcohol, drilling fluid, and lead water are mainly used.
Oils in their pure form (peach, flaxseed, sunflower, olive, etc.) are used to cleanse affected areas of the skin from secondary pathological deposits and remove remnants of used medicinal substances.
The cream is used for dry skin, decreased elasticity and minor inflammation. Lanolin (animal fat) included in the cream makes the skin softer and more elastic. The water in the cream cools the skin and has an anti-inflammatory effect. The cream is well tolerated by the skin, but for children, Vaseline, which irritates the skin, is replaced with castor or sunflower oil. Unna's cream is widely used, as well as “Children's”, “Spermaceti”, “Delight” and others produced by the perfume industry. In Unna's cream, instead of Vaseline, it is more advisable to use vegetable oil (olive, peach, sunflower, castor): Lanolini, Ol. Helyanthi, Aq. destill. aa.
Ointments, creams and aerosols containing corticosteroids and having an anti-inflammatory and hyposensitizing effect are widely used in medical practice. In case of severe inflammation or weeping, it is more advisable to use aerosols.
Gel. In dermatology, hydrogels, which are a colloidal dosage form, are more often used. The gel has a gelatinous consistency that can retain its shape and has elasticity and plasticity. According to the mechanism of action, hydrogels are close to mash, and in consistency - to an ointment free of fats. To make gels, hydrophilic substances (gelatin, agar-agar, gum arabic, etc.) are used, which swell in water to form a colloidal system. They add various pharmacological agents (glucocorticosteroids, fungicidal, antibacterial, etc.), which quickly penetrate the skin.
Varnish is a liquid that quickly dries on the surface of the leather to form a thin film. Most often, the varnish consists of a collodion into which various medicinal substances are introduced (Ac. salicylicum, resorcinum, gryseofulvinum, etc.). Typically, varnish is used when you want to have a deep effect on the tissue (for example, on the nail plate) and in a limited area.
Varnishes like Loceryl and Batrafen are widely used for the treatment of onychomycosis.
The ointment contains one or more medicinal substances, evenly mixed with a fatty ointment base (vaseline, lanolin, lard, naphthalan, etc.), which must be chemically neutral (so as not to cause skin irritation) and have a soft, elastic consistency that does not change under influence of body temperature.
Ointment bases made from synthetic substances are increasingly used: polymers of ethylene oxides, cellulose derivatives, esters of sorbitan and higher fatty acids, etc. Ointments on such a basis penetrate the skin better and are more easily freed from the drugs included in them, do not oxidize or decompose, and are well tolerated skin.
Ointments have a deep effect, so they are prescribed for chronic and subacute diseases, and for inflammatory infiltrate in the skin. Use 2-10% sulfur ointment, 2-3% tar, 1-3% white mercury, 2% salicylic, 2-5% ichthyol, 2-3% naphthalan ointment and etc. They use ointments with antibiotics (2.5-5% erythromycin, tetracycline, lincomycin, etc.). In the treatment of vesicular lichen and herpes zoster, interferon, oxolinic ointment, acyclovir, etc. are used.
Patient first aid kit
Local therapy products are divided into prescription drugs and those approved for sale without a doctor’s prescription. There are quite a lot of the latter on the market, and it is sometimes difficult for patients to navigate their choice. Meanwhile, in everyday life, various skin problems are often encountered, including microtraumas of the skin - cuts, minor injuries, superficial burns, scratches and abrasions. Therefore, the presence in every home medicine cabinet of a product that can cope with most of these problems seems quite justified.
To speed up regeneration processes and reduce inflammation in skin microtraumas, dry skin, and burns, the “Keeper” balm is widely used. The drug has an analgesic, regenerating, antiseptic effect. Promotes rapid resorption of wounds, accelerates the process of healing damage by regulating the regenerative process. The composition of the drug includes: corn oils, sea buckthorn, essential oils of eucalyptus and lavender, vitamins A, E, auxiliary components. Oils ensure rapid conductivity of active substances, due to which the speed of the regeneration process becomes faster and the barrier functions of the skin increase. Naftalan is one of the main components of the Guardian balm, has unique healing properties and has a healing effect on human skin. Vitamins A and E, which are part of the Guardian balm, are natural antioxidants, accelerate cell division processes, help increase skin elasticity, prevent scar formation, and protect the skin from adverse environmental factors.
In everyday practice, the balm is used:
• for mechanical damage to the skin (abrasions, wounds, scratches, cuts), • burns caused by exposure to high temperatures or UV rays, • frostbite and chapping, • urticaria, allergic skin irritations, • bruises, skin hematomas, • calluses, cracks, • excessive peeling, dry skin, • insect bites, nettle burns, etc., • as a symptomatic and prophylactic remedy for dry skin.
The balm is applied to damaged areas of the skin in an even thin layer, rubbing in a little, three times a day. For hematomas and bruises, it can be used as a compress. The average duration of therapy is 3–9 days and depends on the severity of the disease and symptoms. "Keeper" is not used for the treatment of open wounds. An important positive property of the balm is the absence of hormonal and antibiotic components in its composition. This makes it accessible to a wide range of people, including elderly patients, people with a history of allergies, and severe concomitant pathologies. Literature
1. Ayzyatulov R.F. Clinical dermatology. Donetsk: Donechchina, 2002. 2. Arabian E.R. Some “psychosomatic” dermatoses in the practice of a dermatocosmetologist. Sat. Art. NGO of cosmetologists. SPb., 2002, 4: 31-35. 3. Belousova T.A., Goryachkina M.V. Modern ideas about the structure and function of the skin barrier and therapeutic possibilities for correcting its disorders. 4. Volkova E.N. Rational therapy of combined skin lesions - dermatoses of combined etiology. E.N. Volkova, D.A. Lange. Dermatology [Electronic resource]. Electronic journal, 2011, 4. Access mode to the journal: https://www.consilium-medicum.com/magazines/magazines/cm/article/21324 5. Gadzhigoroeva A.G. Minoxidil in the treatment of alopecia. To help the practitioner, 2006, 5: 87-92. 6. Dashkova N.A. Acne: the nature of its occurrence and development, issues of systematization and modern guidelines in the choice of therapy. ON THE. Dashkova, M.F. Logachev. To help the practitioner, 2006, 4: 8-13. 7. Dermatovenerology: National guidelines. Yu.K. Skripkin, Yu.S. Butova, O.L. Ivanova. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2011. 8. Dermatovenereology: Textbook for medical universities. A.V. Samtsov, V.V. Barbinov. St. Petersburg: SpetsLit, 2008. 9. Dermatological reference book. A.T. Sosnovsky, N.Z. Yagovdik, I.N. Belugina. 2nd ed., revised. and additional Minsk: Higher School, 2001. 10. Dribnokhod Yu.Yu. Cosmetology. 6th ed. Rostov n/d: Phoenix, 2010. 11. Zabarova V.A. Plants are sources of essential and vegetable oils used in dermatology. Russian Journal of Skin and Venereal Diseases, 2004, 2: 71-72. 12. Skin and venereal diseases: textbook. allowance. N.Z. Yagovdik, M.V. Kachuk, V.G. Pankratov. Minsk: Higher School, 1999. 13. Skin and venereal diseases. Yu.K. Skripkin, A.A. Kubanova, V.G. Akimov. M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2009. 14. Kochergin N.G., Belousova T.A. Problems of dry skin therapy. Attending Physician, 2009, 8: 36-39. 15. Kozin V.M. Dermatology: textbook. allowance. Minsk: Higher School, 1999. 16. Korobkova E.V. A combination of AHA acids and natural adaptogen β-1,3-glucan in cosmetic preparations for home and professional use. Sat. Art. NGO of cosmetologists. St. Petersburg, 2000, 2: 25-29. 17. Korotky N.P. Atopic dermatitis - treatment recommendations. To help the practitioner, 2006, 3: 58-59. 18. Korsun V.M. Herbal medicine for skin diseases: reference book. ed. V.F. Korsun, A.E. Sitkevich, Yu.A. Zakharov. Minsk: Higher School, 2001. 19. Mashkovsky M.D. Medicines. Vol. 1 and 2. 14th ed. M.: New Wave, 2000. 20. Monakhov K.N. “Basic” skin care for patients with atopic dermatitis. Sat. Art. NGO of cosmetologists. SPb., 2005, 5: 57-62. 21. Novoselov V.S. The place of photoprotectors in dermatological practice. V.S. Novoselov, A.V. Novoselov, A.E. Bogadelnikova. Dermatology [Electronic resource]. Electronic journal, 2008, 1. Journal access mode: https://www.consilium-medicum.com/dermotology/article/15766/ 22. Pavlova N.N. A little about shampoos. Sat. Art. NGO of cosmetologists. St. Petersburg, 2004, 5: 13-14. 23. Pashinyan A.G. Modern moisturizing products for sensitive skin. A.G. Pashinyan, E.S. Gordienko, D.G. Dzhavaeva A. 24. Perlamutrov Yu.N. Comparative assessment of the effectiveness of various treatment methods for rosacea. Yu.N. Perlamutrov, V.Sh. Saydalieva, K.B. Olkhovskaya. To help the practitioner, 2011, 3: 73-79. 25. The use of silver preparations in medicine: Sat. scientific tr. Ed. EAT. Blagitko. Novosibirsk, 2002. 26. Guide to dermatocosmetology. E.R. Arabian, E.V. Sokolovsky. St. Petersburg: Foliant Publishing House LLC, 2008. 27. Skripkin Yu.K. Modern view on pathogenetic therapy of atopic dermatitis. Yu.K. Skripkin, A.S. Dvornikov, L.S. Kruglova, P.A. Skripkina. To help the practitioner, 2006, 4: 36-39. 28. Tarasenko G.N. Treatment of chronic dermatoses with glucocorticoids. G.N. Tarasenko, I.V. Patronov, Yu.G. Tarasenko. Military Medical Journal, 2000, 1: 60. 29. Topical corticosteroids in dermatological practice. G.I. Sukolin, K.I. Plakhov, N.A. Imaeva et al. Farmateka, 2004: 12: 49-52. 30. Topical steroids in the treatment of dermatoses with severe hyperkeratosis. K.M. Lomonosov, D.V. Ignatiev. Dermatology [Electronic resource]. Electronic journal, 2009, 2. Journal access mode: https://www.consilium-medicum.com/dermotology/article/18741/ 31. Ferzhtek O. Cosmetology and dermatology: Trans. from Czech M.: Medicine, 1990. 32. Hill S. Study of the pharmacokinetics of 1% Lamisil cream when applied topically. S. Hill, R. Thomas, S. Schmit, A. Finlay. Bulletin of Dermatology and Venereology, 2011, 3: 120-125. 33. Shimansky N.L. Evolution of glucocorticosteroids used in dermatology. Farmateka, 2005, 3: 51-54. 34. Ebner F, Heller A, Rippke F, Tausch I. Topical use of dexpanthenol in skin disorders. Amer. J. Clinic. Dermatol., 2002, 3: 427-433.
Effect of antiseptic stimulator ASD-3 on the skin
ASD-3F has a pronounced anti-inflammatory, regenerating, analgesic, antifungal, wound-healing, antibacterial and antiseptic effect. The use of the composition for the treatment of skin ailments promotes:
- increasing the protective properties of the skin;
- improving the functioning of the reticuloendothelial system;
- improvement of tissue trophism, metabolism;
- destruction of pathogenic microflora;
- eliminating painful sensations;
- minimizing the inflammatory process;
- healing, regeneration of affected tissues;
- preventing cell oxidation;
- increasing the protective qualities of plasma membranes, accelerating the biosynthesis of new substances and metabolic processes.
The medicine easily overcomes tissue barriers. It is completely natural and therefore safe. ASD-3 can be used externally even during pregnancy and childhood. The elixir has no contraindications or side effects; it has an extremely beneficial effect on the body.
Conclusion about the drug
The drug ASD fraction 2 and ASD fraction 3 are a dubious remedy for the treatment of psoriasis.
There are few reviews on forums on the treatment of psoriasis, mostly negative. Patients often note a pungent odor , which is not surprising: the drug is made from animal tissue, and the chemical composition contains ammonia. Some patients stop taking the drug because nausea occurs. There are only isolated reviews about positive results for psoriasis. There are no medical studies of the drug in humans in the public domain.
In addition, there are some signs of “divorce ”:
- the drug “cures” all diseases - however, many still suffer from psoriasis;
- the price ranges from 190 to 4500 rubles. for packaging - some entrepreneurs especially want to make money on the medicine;
- The description does not indicate contraindications or side effects.
We do not recommend treating psoriasis with the ASD fraction. Why test the effect of a dubious drug on yourself if there are proven methods ? Read about these methods:
- Shampoos for psoriasis;
- Ointments for psoriasis;
- How 311 nm treats psoriasis;
- Diet for psoriasis.
In treating the disease, it is effective to use these measures comprehensively so that the remission is long-lasting and the psoriasis does not bother you.
Answers to common questions
Question No. 1. Where can I buy medicines?
Dorogovaya balm can be purchased on various Internet sites, for example, https://www.vetmag.ru and in pet stores. Sold at a cost of 200-300 rubles for 1 package of 100 ml. Aisida cosmetics can be ordered on the website https://www.aicida.ru/ and in a network of pharmacies - for example, Asia in Moscow or Violet in St. Petersburg. ASD ointment fraction 3 can also be purchased on websites, the cost is 25 hryvnia per 1 piece (about 60 rubles).
Question No. 2. Can the products be used by children and pregnant women?
Yes, since there are no contraindications for use. However, it is advisable to consult your doctor first.
ASD-2 fractions in the treatment of acne (acne)
ASD-2 will help get rid of acne. This truly effective remedy not only eliminates external defects, but also stabilizes the functioning of the body, preventing the appearance of a rash in the future. By strengthening the immune system, it minimizes the activity of the sebaceous glands and normalizes blood circulation. The rash goes away quickly, clearing the skin.
The drug does not contain any chemical additives, therefore, regardless of individual characteristics, the body does not reject it. Treating acne with ASD-2 is simple and effective.