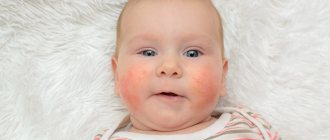
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, relapsing disease accompanied by inflammation of the skin.
Atopic dermatitis predominantly debuts in early childhood; most patients with atopic dermatitis experience stable remission by the age of 3. However, the disease can debut in adolescence and in adults; often after 3 years of age, a relapsing course of the disease is observed.
Atopic dermatitis may be the first step in the “atopic march,” in which patients eventually develop food allergies, bronchial asthma, and allergic rhinitis.
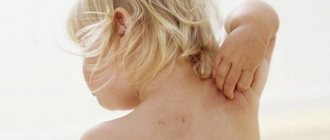
Features of dermatitis on the hands of children
Dermatitis in children is a local or widespread inflammatory process of the skin, which develops due to the direct or indirect effects of various internal and external factors.
Of all childhood diseases, almost half are dermatological. Most often, dermatitis in children occurs in the first year of their life. But cases of the disease occurring in preschool or school age are very rare.
Photo
To assess the condition of the skin during inflammation on the hands, we offer a photo of dermatitis.
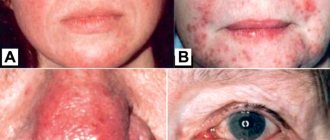
Manifestations and types of contact dermatitis
For irritant contact dermatitis to occur, a single exposure to the agent may be sufficient. Then the disease is called acute , redness of the skin occurs, often swelling, blisters, and the affected area becomes moist. All this is accompanied by burning, pain and often itching.
Chronic is more common - when there is prolonged contact with a substance that has a mild irritant effect. Then the skin becomes dry, red, flaky, thicker and cracks.
With irritant contact dermatitis, problems most often occur on the back of the hand and the skin between the fingers. But sometimes even areas covered by clothing, such as the genitals, are affected.
With allergic contact dermatitis, the boundaries of redness can be blurred, several areas are affected at once: eyelids, lips, etc. Pain and burning occur infrequently, but there is almost always itching. Visually, allergic and irritant contact dermatitis are quite similar.
If you suspect contact dermatitis, your doctor will first ask you about the specifics of your work (especially if you are undergoing a medical examination), as well as when your symptoms began and what you attribute to their worsening. Therefore, it is better to prepare and try to answer these questions for yourself before visiting the doctor. The doctor will also be interested in whether you have already had dermatitis and allergic diseases.
Causes of dermatitis on the hands of children
As a rule, dermatitis has several types, but the causes of this disease are always similar.
The main reasons for the development of dermatitis in children:
- Genetic predisposition
- Weakened immunity and digestive system of the baby
- Poor maternal nutrition during pregnancy
- Artificial feeding
- Presence of fungi and infections
- Poor nutrition during complementary feeding
- Poor skin care for your baby
- Chemical factors in contact with baby's skin
- Presence of viruses, bacteria and infections
- Adverse climatic conditions
Allergic dermatitis in children
The main feature of allergic dermatitis is that it is not a contagious disease. Allergic dermatitis is hereditary. The disease is characterized by the formation of a rash on the child’s skin, which can either disappear or appear again, which causes severe suffering to the baby.
Allergic dermatitis in children appears after reaching one year of age. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, the disease can become chronic.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease in children most often appear at the same time. And this greatly simplifies the process of treating a child.
The main symptoms of allergic dermatitis in children:
- Manifestation of allergies on the child’s legs, arms and face
- Inflammation of formations on the body
- The formations may dry out and become covered with a yellow crust
- Presence of itching
Professions - risk groups
This disease mainly affects medical workers, mechanics, builders, hairdressers, cosmetologists, makeup artists, cleaners, gardeners, agricultural workers, as well as people who work with food (waiters, cooks, etc.).
- The most common irritating agents are solvents, bleaches, medical alcohol, soaps, deodorants, cosmetics, sawdust, oils, and detergents.
- If you have to wash your hands regularly or the work itself involves the fact that they are often in a humid environment, then this is also a risk factor for the development of contact dermatitis.
- Allergic contact dermatitis can be caused by metals, formaldehyde (found in glue, solvents), plants, cosmetics, etc.
Atopic dermatitis in children
Atopic dermatitis is the most common type of dermatitis in children. Most often, this disease is inherited by the baby.
Nutritional factors that can cause the development of atopic dermatitis in children:
- Non-compliance with nutritional rules by pregnant or nursing mothers
- Consumption of foods by a child that do not contain the necessary immunoglobulins
- Eating large amounts of foods containing salt and sugar
- Overfeeding, which can lead to excess protein intake
Symptoms
Atopic dermatitis in children most often manifests itself in the first year of life.
The main symptoms of atopic dermatitis in children:
- Skin rashes accompanied by dryness and flaking
- Having severe itching
- Follicular hyperkeratosis of the elbows, shoulders and forearms
- Scratching of the skin
- Presence of recurrent conjunctivitis
- Development of urticaria
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
Main symptoms of atopic dermatitis:
- dry skin;
- itchy skin;
- skin rashes.
What criteria are used to diagnose atopic dermatitis
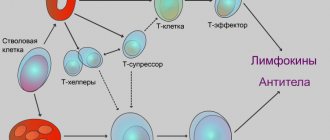
? There are no specific diagnostic markers of atopic dermatitis; the diagnosis of this disease is always clinical, that is, it is made based on the medical history, hereditary allergic history and clinical picture.
Contact dermatitis in children
Already from the very name of this type of dermatitis you can recognize the main feature of the disease. Contact dermatitis in children is usually called one of the varieties of allergic dermatitis, which is formed as a result of the interaction of the baby’s skin with a variety of external irritants. As a rule, the main irritants are the seams on the child's clothing that rub against the skin.
An article about treatment and photos of allergic dermatitis in adults addressed a similar issue.
Prolonged exposure of a child to sunlight can also lead to contact dermatitis. Products for daily child care in the form of creams, talcs and lotions can also cause the development of this disease.
Symptoms
The rash due to contact dermatitis appears only on the area of the skin that came into contact with the external irritant.
You might be interested! What is nodular dermatitis and is it dangerous for humans?
The main signs of contact dermatitis in children:
- The presence of edematous hyperemia of the skin with sharp boundaries
- Severe itching
- Burning of damaged areas
- Painful sensations
- The appearance of blisters
Contact dermatitis in a child can be either acute or chronic. Acute dermatitis is characterized by the period immediately after contact with an external irritant. Chronic contact dermatitis can occur after frequent exposure to an aggressive factor.
Review of remedies for atopic dermatitis
What products should be used to combat atopic dermatitis?
Anna Trushina, a dermatologist at the DocDeti clinic, will talk about the means used to treat and prevent atopic dermatitis.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disease. And to treat it, you need products for external use that affect the skin.
What medications are there?
For basic, permanent therapy, products with emollients are used. Such products are aimed at prevention and help relieve exacerbations.
Emollients soften, moisturize the skin, and replenish its barrier function. They increase the effectiveness of anti-inflammatory therapy, resist itching, skin soreness and eliminate flaking.
Release forms:
- Lotion and milk are the lightest form. They apply well in a thin layer, but the moisturizing effect is minimal. The product can be applied to hairy areas of the skin and to areas of acute inflammation.
- Creams are denser products than milk and lotions, but they are also comfortable to use. They can be used throughout the day - there will be no greasy residue left.
- Ointments and balms are the thickest and densest forms, good for very dry skin, thickened skin, with severe peeling, as well as for nighttime care.
What's within your means?
There is a large selection of available emollients on the market: La roche posay Lipikar, Bioderma Atoderm, Uriage Xemose, Topicrem DA, A-derma Exomega, Avene Xerocalm, Noreva Xerodiane, Emolium, Atopic, Cerave, Eucerin and many other products.
Something more serious
In case of exacerbation and the appearance of foci of inflammation, the doctor may prescribe reparants
- they speed up healing and relieve irritation. Products are used only in problem areas, and not on the entire skin. They do not replace products with emollients!
There are two forms of release of reparants; liquid lotion and balm or cream. It is not difficult to find these drugs in pharmacies - most contain Cica in their names.
Liquid medications help relieve inflammation and are often prescribed in a short course. These are Avene Cicalfate lotions, Bioderma Cicabio and Uriage Bariederm Cica spray.
Reparants in the form of creams and balms are used if necessary: A-derma dermalibur, La roche posay Cicaplast, Topicrem Cica, Avene Cicalfate (in the form of cream), Bioderma Cicabio (in the form of cream), Uriage Bariederm Cica (in the form of cream).
Nothing helps
There are cases when emollients and reparants cannot cope, then drug therapy comes to the rescue (prescribed by a dermatologist!).
1. topical glucocorticosteroids (hormones)
A large number of studies have confirmed that the drugs are effective and not dangerous when used externally. But remember that the attending physician must monitor the process.
GCS differ greatly from each other in terms of active substances, form and form of release of products (emulsions, creams, ointments, sprays, and so on).
2. calcineurin inhibitors - pimecrolimus and tacrolimus
Group of anti-inflammatory drugs. These are non-hormonal products that can help in delicate areas: facial skin, diaper area, folds - where the use of hormonal products is limited. These drugs are also suitable for long-term therapy.
3. antibiotic, antifungal drug
Prescribed alone or in combination with other medications if a complication occurs due to a secondary infection.
Additionally
The doctor may recommend syndets - products that cleanse the skin when bathing; they replace shower gel and soap.
Stop list
The pharmacy offers a wide selection of tar, ichthyol, and naphthalene preparations, but it is important to know that they are not treatments for atopic dermatitis.
Treatment of dermatitis on the hands of a child
It is necessary to begin treatment for dermatitis only after determining the symptoms and type of the disease itself.
Basically, topical drugs are prescribed for treatment:
- Bepanten, Fenistil - antihistamine ointments
- Pimafukort
- Advantan
If topical agents are ineffective, then specialists prescribe treatment with systemic medications.
Systemic medications:
- In order to moisturize a child's skin, doctors recommend using Exomega milk or Hydrolipidic cream.
- If the irritation of the formations becomes severe, then it is necessary to use antipruritic ointments such as: Elidel, Gistan.
- If the wounds on the baby’s body are wet, then it is best to use drying agents in the form of Zinc ointment or mash.
- If the disease is of an allergic type, then antihistamines should be used for treatment: Zyrtec, Telfast, which can get rid of negative symptoms.
Another important factor in treating a child for dermatitis is diet , which should contain a large amount of proteins, vitamins and microelements. If the baby is still breastfed, then the mother must follow the diet.
She should exclude from her diet:
- Chocolate
- Seafood
- Citrus
- Nuts
- Honey
If a child uses artificial nutrition, then you need to pay attention to the composition of the milk formula. As a rule, such food often contains cow's milk, which is an allergic product. A child under six months should not consume foods that can cause an allergic reaction.
Folk remedies for dermatitis on the hands of a child
Many people prefer treatment with traditional methods.
Of these, we can also highlight those that can cure dermatitis on the hands of a child:
- Chamomile baths can effectively deal with blisters on the skin. To prepare the solution, you need to mix 4 tablespoons of dry chamomile with 200 milliliters of boiling water. The solution should sit for about 20 minutes. After this, it can be added to the bathtub.
- Lotions can also be used to treat dermatitis in children. To prepare the lotions, you will need to take the juice of two medium lemons and add 1 teaspoon of sunflower or olive oil to it. Pour all this with 0.5 liters of water. A cotton pad or napkin is dipped into the resulting solution and applied to the affected areas of the body.
- Formations on the body are also allowed to be treated with ointment made from butter and St. John's wort. In order to prepare such an ointment, you need to mix St. John's wort juice with melted butter. The affected areas of the skin must be treated with ointment 2 times a day.
Preparations for external use
Dermatitis on the hands is often accompanied by itching, which gets worse at night. Many patients complain of waking up in the middle of the night and being unable to fall back to sleep. In such cases, it is recommended to wear cotton gloves before going to bed and take a light herbal sleeping pill.
Acute inflammatory process is relieved with glucocorticoid ointments or creams. Depending on the severity of the lesion, the use of drugs of weak or moderate effect is prescribed. If skin lesions spread and affect not only the skin of the hands, but also other parts of the body, the use of strong hormonal drugs is necessary. Since dermatitis on the hands is accompanied by swelling and burning, patients are often prescribed creams. Due to their structure, they have a cooling effect, which helps reduce swelling, and a rapid antipruritic effect. Weak hormones include hydrocortisone, and moderate hormones include prednisolone, fluocortolone, and prednicarbate. Glucocorticoid creams are used for a limited amount of time, usually no longer than a week.
Relieving acute inflammation is only the first step of therapy. The chronic stage is also characterized by itching (albeit not as intense) and, most importantly, dry skin. Dryness provokes peeling and cracks that interfere with the healing of the skin. To normalize metabolic processes in the skin, including water balance, it is necessary to resort to additional hydration. The greatest effect comes from applying creams after hygiene procedures. Under the influence of warm (but not hot) water, the epidermis softens, and the crusts dissolve and come off.
However, it is worth noting that washing your hands with soap will most likely lead to a negative result, since alkali dries out the skin and, once it gets into the wounds, causes tingling and exudate. Delicate care is provided by special medicinal and cosmetic care products for inflamed skin. Thus, “Losterin” body gel, which can also be used as hand soap, does not contain surfactants, fragrances or dyes. And 4 types of vegetable oils in its composition, deresined naphthalan and Japanese sophora extract provide both cleansing, bactericidal effect, and moisturizing of the skin. In the acute period, it is recommended to cleanse the skin of the hands with micellar water and clean soft wipes.
After water procedures, the skin is carefully blotted (do not wipe!) with a towel and moisturizer is applied. For hand skin dermatitis, creams containing vegetable oils and panthenol are useful, which create a thin fatty film on the surface of the skin and do not allow the liquid to evaporate. Vegetable oils can be applied to the skin in the form of lotions, or they can be included in creams. Traditionally, olive, flaxseed, sea buckthorn, sunflower oil, avocado and jojoba oils are used in dermatology. In addition, products with the addition of plant extracts and vitamins are needed. These components provide nutrition to skin cells and accelerate regeneration. Preparations containing tar, naphthalan, salicylic acid, and zinc help relieve skin itching.
The restoration of epithelial cells is facilitated by preparations with propolis. This natural remedy has desensitizing, anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties due to its composition. Propolis contains flavonoids, aromatic and fatty acids, free amino acids, proteins, alcohols, minerals, sugars, vitamins, steroids, and many microelements. However, ointments, sprays and creams with propolis can be prescribed only to those people who are not allergic to honey and pollen. In other cases, the product may cause a severe allergic reaction.
In most cases, chronic dermatitis on the hands can be treated with external herbal medicine. It can be combined with hygienic procedures. For example, after an evening shower, it is useful to take hand baths with extracts or infusions of pine needles, chamomile flowers, oak bark, calendula, birch buds, string, burdock root, plantain leaves, poplar buds, and lungwort. After a 10-minute bath, the skin of the hands is also dried with a towel and moisturizer is applied.
Possible consequences
As mentioned earlier, treatment of dermatitis should not be delayed for a long time. Otherwise it may cause complications. This especially applies to allergic dermatitis. Lack of treatment for this type of disease can lead to a chronic form of dermatitis.
In its chronic form, the disease can last for several years and cause a lot of moral and physical problems. Also, if treatment is not timely, this can lead to bacterial infection and the appearance of a fungal infection that can affect damaged areas of the epidermis.
Dangerous symptoms of dermatitis
If you have signs of contact dermatitis, consult your doctor. The doctor will make a diagnosis and prescribe treatment that will alleviate your condition. You should not hesitate if, along with redness on the skin, signs of infection appear (pus, fever), or if you feel that the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract (it hurts to breathe) or the gastrointestinal tract (it hurts to chew and swallow) are damaged.
To diagnose and treat contact dermatitis, make an appointment with a dermatologist - call +7 (495) 120-08-07.
Prevention
Regardless of the type of dermatitis on a child’s hands, it is necessary to follow some general preventive rules:
- Hardening
- Proper baby skin care
- Using good baby skin care products
- Clothes made from natural materials
- Baby's diapers must be changed every 4 hours or when soiled.
- Proper diet
If a child has atopic dermatitis, then contact of the baby with household or food allergens should be excluded.
Preparations for internal use
Thus, tableted antihistamines are prescribed to inhibit inflammatory processes and reduce the harmful effects of allergens. Depending on the degree of damage, drugs are prescribed for a period of 2 weeks to several months. To treat dermatitis on the hands, products of various generations are used.
First generation antihistamines (diphenhydramine, mebhydrolin, chloropyramine, clemastine, cyprohepadine, promethazine, quifenadine) have a powerful antipruritic and decongestant effect, and also reduce muscle tone and cause drowsiness. They are recommended for therapy in the acute period.
Second-generation drugs have virtually no effect on the nervous system and do not reduce physical activity, but can negatively affect the functioning of the heart, so they should not be taken by people with cardiac diseases and elderly patients. Second generation antiallergic drugs include terfenadine, astemizole, acrivastine, dimethendene, loratadine.
If it is impossible to provide the patient with bed (home) treatment, third generation . They do not affect the functioning of the brain and heart muscle, which means they can be taken by people whose work involves mental activity. Third generation antihistamines on the pharmaceutical market include cetirizine, fexofenadine, desoloratadine, and hifenadine.
To quickly remove allergens from the body, medications are prescribed that stabilize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract. Sorbents absorb and remove toxins accumulated in the liver and intestines from the body. These include activated carbon, enterosgel.