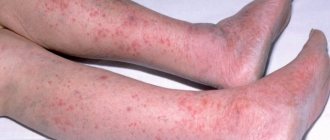
Atopic dermatitis (AD) in children is one of the most common diseases of young children. This disease is an allergic inflammation of the skin, which is characterized by itching, as well as frequent relapses and age-related characteristics of the skin rash. As a rule, dermatitis appears at an early age; if left untreated, it continues to progress into older age, which significantly worsens the quality of life of patients and their families.
For the development of this pathology, a hereditary predisposition to the development of allergies is of great importance. Therefore, this disease is often combined with other forms of allergies, for example, bronchial asthma, allergic conjunctivitis and rhinitis, food allergies. There is such a thing as “atopic march” . Atopic march is a natural progression of allergic diseases. As a rule, it all starts with a food allergy, which often gives impetus to the development of atopic dermatitis. In the absence of adequate treatment, the march progresses. Over time, the child develops allergic rhinitis. Over time, a more dangerous, in some cases, life-threatening condition arises - bronchial asthma.
Prevalence of atopic dermatitis in children
It is safe to say that this disease can occur in any country, in both males and females. Dermatitis occurs in different age categories. The prevalence of AD is higher in residents of economically developed countries, which may be due to the urban lifestyle of this population. According to the protocol for the treatment of AD in children, the prevalence of this pathology in the Russian Federation ranges from 6 to 15% according to ISSAC. ISAAC is a standardized epidemiological study - the International Study of Asthma and Allergy in Childhood. Repeated studies within the framework of this program show a significant increase in the prevalence of AD in children of the Russian Federation.
Research shows a significant increase in the prevalence of atopic dermatitis in children in the Russian Federation.
Also, the expert committee on asthma and allergy of the WHO European Bureau developed and approved another program - GA2LEN. GA2LEN (Global Allergy and Asthma European Network) studied the incidence of allergic pathology among adolescents aged 15 to 18 years. According to the study, the presence of symptoms of AD occurred in 33% of adolescents, the prevalence of AD according to questionnaires was 10%, and a confirmed diagnosis was found in 7% of adolescents. Girls have 1.5 times more than boys.
Antimicrobial and antiseptic agents
Fukaseptol and Fukortsin (solutions for external use, 10 and 25 ml in bottles) are red liquids of similar composition with a characteristic odor of aniline dye (fuchsine). Fukaseptol is manufactured using a new technology that allows the composition of the drug to be kept stable throughout the entire shelf life. The components of fucorcin may precipitate during long-term storage. Both drugs have an excellent antimicrobial and antifungal effect without interfering with healing. Used for application to scabs, scratching areas, and pustules. It is not recommended to lubricate fresh wounds, because... The alcohol contained in the composition causes a burning sensation. Large surfaces of skin should not be treated. After the solution has dried, pastes, ointments and creams can be applied to the skin.
An alcohol solution of methylene blue 1% has similar indications and application features. When applied to large areas of skin, the child’s urine turns blue.
Hydrogen peroxide 3% causes a tingling sensation when applied to the skin, but is always well tolerated. It is used to treat fresh wounds and scratches.
Furacilin solution 0.02%, made from powder and tablets of 0.2 g, belongs to another group of antiseptics - nitrofurans. Due to their weak effect and frequent cases of increased inflammation, nitrofurans in the treatment of allergic diseases have given way to stronger antiseptics - halogen-containing ones (chlorhexidine - 0.05% solution, 100 ml in a vial) and Miramistin (0.01% solution, 100 ml in a vial) .). Both solutions are aqueous, they can be used to treat fresh wounds and scratches without the risk of causing pain in the child, however, aqueous solutions take a long time to dry, and the skin treatment process, which is always unpleasant for children, is delayed.
Antibiotic ointments are used with caution for atopic dermatitis, as they are often allergenic. This group is dominated by domestic drugs, with the exception of ointments Bactroban (contains 2% mupirocin), Baneocin, Fucidin. Combined ointments Baneocin (contains bacitracin and neomycin), Levomekol ointment (contains chloramphenicol and methyluracil), Levosin ointment (contains chloramphenicol, methyluracil, sulfadimethoxin), in our experience, do not have any significant advantages. Unfortunately, the fatty base of domestic ointments with antibiotics does not contribute to the drying out and falling off of the crusts, rather softening them, so dermatologists prefer to use pastes with antibiotics (1% erythromycin, 2-5% lincomycin), prepared according to a prescription at the pharmacy. Fuzidin gel and Fucidin cream (contains 2% fusidic acid) have some advantage since there are still few resistant strains of microorganisms to the fusidic acid contained in the drug.
Silver sulfathiazole preparations are much better tolerated, although less commonly used - Argosulfan cream and ointment, containing 2% silver sulfathiazole in 40 g tubes, Dermazin cream, 1%, 50 g each, Sulfargin ointment in 50 g tubes. They should not be used Use for allergies to sulfonamide and sulfur-containing drugs.
Bismuth preparations (dermatol ointment 10%, xeroform ointment 10%) are inexpensive domestic preparations that have an excellent effect (antiseptic, drying and anti-inflammatory), however, they have a strong unpleasant odor and are rarely available in pharmacies.
Skin-cap preparations (70 and 100 ml aerosol, 50 g cream) also combine antiseptic and anti-inflammatory properties; high cost limits their widespread use.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children
In this article, we will pay great attention to the treatment of this disease, and will also talk about the main features of the use of medications in children with atopic dermatitis.
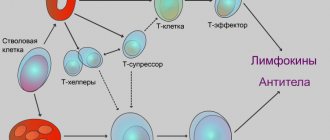
The basis of treatment is external therapy using various medications. The goal of external (local) therapy is the complete elimination of inflammatory changes, itching, as well as restoration of the water-lipid layer of the skin. Local glucocorticosteroids (hormones), calcineurin inhibitors, and emollients are used as such agents. We will pay special attention to emollients. Emollients are medicinal cosmetics that care for the skin and prevent dry skin. In some cases, systemic therapy is also prescribed. Systemic therapy refers to the use of drugs that are administered orally. Antihistamines are most often used as systemic therapy.
Below we consider the most common drugs for the treatment of blood pressure in children.
The goal of local therapy for atopic dermatitis is the complete elimination of inflammatory changes and itching.
Hormones
Local glucocorticosteroids (MGS) are used as hormones. They are the most powerful drugs at the onset of the disease, which allows the symptoms of this disease to be eliminated in the shortest possible time. The duration of use of these drugs should not exceed two weeks. If possible, use of MGCs should be short.
What parents should remember when using these products:
- It is not recommended to mix MHA with other agents.
- When the symptoms of the disease decrease, it is necessary to reduce the amount and frequency of MHA use.
- In the event of a bacterial or fungal infection, it is necessary to use a combination of MHA with antibacterial and antifungal drugs.
- Do not apply these medications under closed dressings.
- With long-term use, complications may develop. Such complications include: stretch marks, telangiectasia, skin atrophy. Striae are white to pink stripes on the skin. Telangiectasia is popularly called “spider veins”. This complication is a vascular formation with dilated vessels. Atrophy is characterized by a skin defect with a change in its volume and elastic properties.
Local hormones exist in different classes, depending on the strength of their action. The most common MGCs are: celestoderm, elokom, lokoid, dermovate, cutivate.
Calcineurin inhibitors (CI)
A special feature of these drugs is the absence of complications inherent to hormones. They can be used together with hormones. After eliminating symptoms, MGC can be replaced with IR, which will avoid the development of complications. The two most common medications in this group are pimecrolimus and tacrolimus. Pimecrolimus is used for mild cases, while tacrolimus is used for severe cases.
How to get rid of allergic dermatitis in a baby?
25.01.2021
Allergic dermatitis in children is quite common. This form of the disease occurs mainly in the first six months of life, that is, in infants, and can continue into adulthood.
With allergic dermatitis, inflammation occurs on the skin caused by external or internal irritants. light appears in any part of the body, most often on the face .
In some cases, dermatitis goes away quite quickly and on its own, but sometimes it can get worse over time. The affected areas turn into weeping wounds and ulcers, and the itching only intensifies.
Letting such a disease take its course or self-medicate would be an extremely frivolous activity. To avoid unpleasant consequences, the most reasonable thing would be timely intervention by a specialist and timely prevention in the future.
The symptoms of allergic dermatitis in an adult and an infant are significantly different. As a rule, if an allergy once, this trouble will accompany him throughout his life. But whether the allergic reaction that appears in a child becomes permanent depends directly on the cause that caused it.
What could be the factors contributing to the development of dermatitis in a child?
- Food allergies
- Overfeeding
- Heredity
- External factors
After identifying the causes, preventive measures should be taken, which, in turn, can be divided into certain groups.
- Limiting unwanted substances entering the blood . To do this, you need to achieve stable and free functioning of the gastrointestinal tract of the mother who is breastfeeding and the child herself. A woman should reduce her consumption of fatty and spicy foods and avoid sweets as much as possible. Another important preventative measure is to control the amount of food consumed by the child. It is impossible to overfeed a baby while breastfeeding. But if there is complementary feeding with a mixture, then there is a possibility of oversaturation. This is due to the fact that the feeling of satisfying hunger does not come immediately, and the hole in the nipple is not always small. In this case, excess food is not digested and accumulates in the intestines , turning into poison
- Maximum reduction in sweating. Everyone knows that sweat is a kind of riddler of harmful substances from the body. But the baby’s delicate skin suffers from contact with such secretions. To prevent such unpleasant consequences, it is important to maintain a comfortable temperature (about 20°C) and air humidity in the house, and also not to overwrap the child
- Preventing contact with the irritant. Dermatitis does not only occur due to certain foods, but can also be caused by external factors. These include detergents containing harmful substances, indoor dust, unnatural fabric, etc.
Perhaps, the measures to prevent the causes of dermatitis described in this block are the most basic, and they have long been known to everyone. It is advisable to boil the baby's clothes or wash them with a hypoallergenic detergent and rinse in boiled water. The same applies to clothing items of an adult in contact with a child and bedding. All these items must be ironed.
All child’s toys must be disinfected with a special agent. You also need to bathe your baby in boiled water, using herbal decoctions. Frequent use of soap is not recommended due to the fact that it washes away the natural oily film from the skin.
Compliance with all of the above preventive measures will help parents significantly reduce the likelihood of their child developing this disease, but the risk still remains. If it was not possible to avoid the appearance of dermatitis , it is important to immediately consult a doctor to identify the causes and prescribe competent, qualified treatment.
Primary diagnosis, which includes a number of procedures, is carried out either by a pediatric therapist or an allergist-dermatologist. Otherwise, complications are possible, in particular infection of wounds and scratches. Elevated temperature, which is characteristic of an infectious process, in turn, leads to increased sweating , which only worsens the situation.
To summarize, it would be advisable to once again recall that allergic dermatitis is a serious disease that is fraught with serious consequences if it is not treated in a timely and incorrect manner.
Published in Dermatology Premium Clinic
Anti-inflammatory and antipruritic drugs
ASD paste 5% is an excellent drug that successfully competes in the strength of its action with corticosteroid ointments. Previously, it could be produced in a pharmacy with a prescription, but due to the strong unpleasant odor and the reduction in the number of manufacturing pharmacies, this is now very difficult to do.
Elidel (contains pimecrolimus, 1% cream, 15, 30 and 100 g) is a relatively new anti-inflammatory drug that interferes with the production and release of biologically active substances from lymphocytes and mast cells (involved in cell inflammation). Can be used in children from 3 months of age. Use is contraindicated in case of infected rashes (appearance of pustules, crusts, weeping); it is not recommended to combine with other external agents. The use of the drug is limited by its high cost.
Preparations containing zinc oxide (Zindol zinc paste and ointment suspension) have a moderate anti-inflammatory and drying effect, but are widely used in pediatric practice, since they almost never cause side effects, are cheap and accessible.
Ichthyol ointment 10 and 20% is a drug with a moderate anti-inflammatory and absorbable effect, used during the period when acute inflammation is over and skin density is preserved. The effect of the ointment is enhanced by applying occlusive dressings (compress paper or a piece of cellophane is placed on top of the ointment and covered with a bandage), they also prevent the laundry from staining the dark brown color characteristic of this ointment.
Naftaderm
(10% naftalan oil liniment in tubes of 35 g) is an anti-inflammatory, antipruritic, analgesic, wound-healing drug, which also has the property of enhancing the effect of other externally applied agents, therefore it is usually used in combination with other external drugs. Its disadvantage is a specific oily smell.
Ointments related to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (indomethacin ointment 10% and gel 5% and 10%, Butadione 5%, etc.) are rarely used for treatment, as they are not effective enough and sometimes cause allergic skin reactions.
The use of Lead water or lotion (0.5% solution of lead acetate - 100 ml per bottle) is one of the ancient ways to relieve acute inflammation. Other preparations for lotions are not currently available in finished form.
External antihistamines, for example, Fenistil (1% gel in tubes of 20 and 30 g), unfortunately, are not often effective for atopic dermatitis. They are useful in the first hours of an exacerbation, as well as with concomitant urticaria or a hyperergic reaction to insect bites in the summer.
Diet for pregnant and lactating women
If, during the period of bearing a child, a woman does not monitor her diet, then the risk of the baby developing dermatitis increases. On average it increases by 15-20%.
What foods are prohibited for pregnant and nursing mothers:
- Fatty and fried foods, chocolate and drinks containing caffeine.
- Exotic fruits because they may contain harmful preservatives.
- Carbonated drinks, smoked foods, salty canned food and processed foods will cause swelling and increase blood pressure levels.
- Sweets in large quantities, fatty sauces and pickled dishes, garlic, onions.
- Red and orange fruits and vegetables are often the cause of food allergies.
The diet should be balanced; a woman is recommended to eat food in small portions; if she is very hungry, then have snacks. Drink kefir and eat apples.
Diet for adults and teenagers
There are no serious differences and consists in following basic rules. Food allergies occur more often in children than in adolescents and adults.
What should be excluded from the diet:
- coffee and drinks containing high concentrations of caffeine;
- strong tea with herbs and berries - can lead to a rash on the body;
- various types of alcohol, since its consumption leads to the accumulation of toxins and harmful substances;
- bakery and pasta products made from refined flour;
- various sushi, snacks rich in herbs and spices are also prohibited.
Over the years, with the correct menu design, it will be possible to remove from the diet those foods that are most dangerous for humans. So, teenagers and adults are not prohibited from eating carrots, bananas, soybeans, and potatoes. They are conditionally safe for the body. But they are prohibited for children.
Disputes also arise regarding cheeses; preference is given to those that are not high in fat, but it is better not to give them to children.
Why is nutrition so important for atopic dermatitis?
The main causes of atopic skin rash include poor nutrition.
Some people have intolerance to certain foods and food allergies occur, which triggers an allergic reaction and the appearance of dermatitis. Various studies have found that in most patients diagnosed with atopic dermatitis, diet alleviates the symptoms of the disease and helps control the course of the disease. This occurs due to the fact that foods that can cause an allergic reaction are excluded from the diet. At the same time, the diet itself becomes more moderate, healthy and varied.
Excluded from food
- All products containing cow's milk proteins (including whole milk, all fermented milk products, cheese, cottage cheese, butter), milk products from other animals, beef, veal.
- Highly allergenic foods - eggs, peanuts, nuts, fish, seafood, soy;
- Products that often cause both allergic and non-immune (pseudo-allergic) reactions (caviar, mushrooms, honey, chocolate, coffee, cocoa, citrus fruits, kiwi, pineapples);
- Broths, marinades, salty and spicy dishes, canned food, smoked meat and fish, spices;
- Products containing artificial additives - dyes, flavors, preservatives;
- Products containing histamine liberators and histamine (sauerkraut, sorrel, spinach);
- Products that irritate the gastrointestinal tract and change the taste of milk - onions, garlic, radishes, radishes.
Disease prevention
The following recommendations are aimed at preventing episodes of illness and minimizing the effects of dryness after bathing:
- Moisturize your skin at least twice a day. Use creams, ointments, or lotions that lock in moisture. Select one or more products suitable for your child.
- Try to identify and avoid triggers that make the condition worse. Prevent stress, negative effects of pollen dust. Dress your child according to the season to prevent him from sweating.
- Infants and children may experience flare-ups when consuming certain foods, such as eggs, milk, soy, and wheat. Talk to your doctor about how to identify possible food allergens.
- Use only mild soap. Choose products with a neutral pH level. Antibacterial soap removes natural oils and dries out the skin.
Water procedures should not exceed 10-15 minutes. After your bath, dry your skin gently with a soft towel and apply a moisturizer.
Allowed subject to individual tolerance
- Vegetables and fruits of green and white color (all types of cabbage, zucchini, squash, sweet potato, Jerusalem artichoke, apples, pears, yellow plums, white currants, white raisins, etc.)
- Soups – vegetarian;
- Meat – turkey, rabbit, lean pork (boiled, stewed, steamed);
- Cereals (buckwheat, corn, rice, oatmeal, millet, pearl barley);
- Pasta;
- Wheat, wheat-rye bread;
- Drinks – tea, compotes, fruit drinks from the above mentioned fruits.
The author of the article is professor, doctor of medical sciences. Svetlana Gennadievna Makarova
How do food allergies manifest?
The initial symptoms that may occur in the first days and weeks of a child’s life often do not in themselves indicate an allergy. These may be skin manifestations: redness, diaper rash, a small rash. Symptoms from the gastrointestinal tract may also appear. They will also be general, nonspecific, as doctors say. Excessive regurgitation and/or vomiting, colic, and constipation are possible. It is believed that at least 10-15% of cases of colic in infants are associated with food allergies.
Even refusal to take the product or anxiety after eating can be confirmation of an allergic reaction. Dyspepsia, diarrhea, lack of weight gain, abdominal pain, severe colic and persistent constipation are possible. With an allergy to CMP, blood can often be observed in the stool of children. Cow's milk proteins are the most common cause of allergic enterocolitis in children of the first year of life.
Please note: there are cases when the only symptom of an allergy to CMP in children is chronic iron deficiency anemia.