March 24, 2021
Atopic dermatitis is quite common, with an average of 1 in 12 people suffering from it. It is impossible to completely cure dermatitis, so treatment usually comes down to daily care that maintains a state of remission. Let's look at how to care for dermatitis so that there are no relapses.
Classification of dermatitis
There are the following types of dermatitis:
- Contact . This is an inflammation of the skin that occurs after direct contact with an irritant. Absolutely any substance can act as an irritant; it all depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. There are also substances that cause the development of contact dermatitis in all people (skin injuries, nettles, exposure to low or high temperatures, acids, caustic alkalis and a number of others).
- Atopic . This form of the disease has a neuro-allergic origin and a chronic course.
- Toxidermy . This is a toxic-allergic skin reaction that occurs in response to the penetration of an allergen into the body. An example of toxicoderma is urticaria.
- Seborrheic dermatitis . Caused by a yeast-like fungus, it occurs chronically, most often affecting the skin of the face.
- Other types of dermatitis . These include eczema, rosacea, pimples, acne and a number of other pathological conditions of the body, which are considered as separate diseases.
According to the course, dermatitis can be acute and chronic. According to the degree of prevalence, general (diffuse) and local (local) dermatitis are distinguished.
Causes of dermatitis
The main reasons for the development of the disease are:
- hereditary predisposition - if the parents were diagnosed with dermatitis, this sharply increases the likelihood of the child developing this pathology;
- acquired predisposition - people who suffered from atopic dermatitis in childhood are more likely to develop dermatitis in adulthood;
- stress, nervous tension;
- weakened immune system;
- exposure to high or low temperatures on the body;
- the entry into the blood of various irritants that can cause the development of dermatitis (some medications, chemicals, food, pollen and a number of others);
- irradiation of the skin with quartz lamps, radiation, and sunlight.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in children and adults
An integrated approach is required, including:
- Correction of disturbed neuroimmune endocrine mechanisms (or the consequences caused by them).
- Prevention of complications caused by immunodeficiency.
- Relief of symptoms (primarily itching) with ointments, creams, injections.
- Prevention of exacerbations by identifying and eliminating the provoking factor (or factors) from the body’s “field of vision”. The main role belongs to diet, regular wet cleaning, refusal to wear clothes and use of hygiene products (and household chemicals) that can provoke an exacerbation.
- Increasing stress resistance and normalizing the psychological climate in the family, school, work, etc.
Physiotherapy and staying in a dry, hot climate have a good effect.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in infants
The above is relevant for all ages. In maintaining (and returning) the baby’s health, the nutrition and emotional state of the mother and the microclimate in the family play an important role.
The following can provoke the manifestation of the disease in an infant:
- transfer to artificial feeding;
- severe emotional stress (for example, fear);
- the climate in the house is too hot (the air temperature is constantly above 24 degrees);
- exposure to direct sunlight;
- bathing too often using alkaline products;
- acute infectious diseases;
- vaccinations;
- use of hygiene products not intended for infants;
- insufficiency of enzyme systems and, as a consequence, incomplete absorption of food, etc.
Symptoms of dermatitis
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the type of dermatitis. Common symptoms that are characteristic of most dermatitis are:
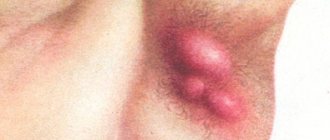
- Skin itching . Its intensity depends on how strongly the nerve endings are irritated. The discrepancy between skin manifestations and itching (for example, there are few rashes, but the itching is severe) is a sign of an allergic reaction of the body in atopic dermatitis.
- Erythema (redness) . It occurs as a result of increased filling of the skin capillaries with blood. In acute dermatitis, the skin is swollen, with uneven edges. In the chronic form of the disease, there may be no erythema at all. When you press on the skin at the site of inflammation, the redness temporarily disappears. Erythema should be distinguished from subcutaneous hemorrhage.
- Eczema (appearance of rashes) . The appearance of the rash depends on the type of dermatitis. Most often, the rashes are localized on the face, limbs, groin, and sides of the torso.
- Exudation . Most often, the formation of exudate occurs in acute forms of dermatitis. With chronic dermatitis, cracks in the skin and self-scratching are observed, which the patient does due to severe itching.
- Peeling of the skin . Occurs due to excessive dryness of the skin caused by dysfunction of the sebaceous glands and dehydration. Most often, this symptom occurs in chronic inflammatory and allergic dermatitis.
It is no longer news that most of the products that are used in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the head and the appearance of dandruff contain various antifungal components and hormones, but do not always give the expected effect. When you stop using them, the symptoms of the disease return, and long-term use of products containing glucocorticosteroids threatens the development of various side effects.
Are there still no effective shampoos developed for seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff?
Developed!
Naftaderm® shampoo is a unique product with naftalan oil extract. It not only effectively combats the symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, but also helps reduce the activity of sebum synthesis.
- Contains highly active substances from naftalan oil;
- Has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects;
- Normalizes skin pH and does not cause the skin to feel dry even with prolonged use.
Naftaderm® shampoo
is a natural composition with naftalan oil. Just imagine that more than 50% of people have experienced mild manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis in the form of dandruff at least once in their lives.
So, what is seborrheic dermatitis?
This is a chronic recurrent skin disease associated with increased secretion of sebum. Against this background, a change in the composition of the skin microflora occurs due to the individual sensitivity of the body to the waste products of fungi.
When should you sound the alarm and how to recognize seborrheic dermatitis?
Our body is able to send us signals so that we can prevent the development of more severe manifestations of the disease.
The lesions in this disease are located on the scalp, face (in the area of the beard and mustache, nose, at the border of hair growth), ears, postauricular folds, neck, chest, back, armpits and genitals.
Characteristic signs of seborrheic dermatitis:
- redness
- peeling
- white or yellowish greasy scales on hair, shoulders, clothing, headdress, comb
- itchy scalp
- wet crusts and cracks in the armpits, groin areas, in the folds behind the ears and under the mammary glands
- increased skin oiliness
- dullness and brittleness of hair
What factors can provoke exacerbation of seborrheic dermatitis and the appearance of dandruff?
- hereditary predisposition
- hormonal disorders
- diseases of the digestive, endocrine systems, lungs, neurological diseases, hypovitaminosis, immunodeficiencies
- infectious diseases (HIV, hepatitis)
- mental and physical stress
- improper scalp care (over-drying with a hairdryer, frequent coloring, exposure to air conditioners)
- exposure to air conditioners, high humidity
- use of drugs
How to solve the problem of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp and dandruff?
Remember that untimely identification of the causes of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff, as well as improper treatment, can lead to the spread of the process to the skin of the face and body, and frequent exacerbations contribute to hair loss.
The main directions of action of means for eliminating dandruff and treating seborrheic dermatitis:
- reduction of inflammation
- stopping peeling
- eliminating itching
- stopping the proliferation of fungi and bacteria
before use
after use
Naftaderm® shampoo with naftalan oil extract eliminates all symptoms of the disease, and above all the main cause of seborrheic dermatitis.
Features of Naftaderm® shampoo
- The active composition of Naftaderm® shampoo is medicinal naftalan oil, which is extracted only from natural deposits in Azerbaijan. The composition of this oil includes various substances: polycyclic saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons, naphthenic acids, various trace elements, nitrogenous bases, etc.
- For the production of Naftaderm® shampoo, only purified pharmaceutical substance is used. Ordinary Naftalan oil contains a large number of harmful impurities and bacteria. Naftalan® refined oil was obtained as a result of multi-stage purification; it is included in the State Register and standardized for density, viscosity, boiling point, water content and naphthenic acids.
- The unique manufacturing technology of Naftaderm® shampoo allows you to maintain a high concentration of active substances. The effectiveness of products containing naftalan oil has been tested in preclinical studies on animals.
- Naftaderm® shampoo is able to reduce the intensity of sebum production, thereby acting on the main links in the pathogenesis of seborrheic dermatitis. Regular use of shampoo helps to gradually reduce itching, flaking and oily skin.
- Naftaderm® shampoo has a balanced composition. When creating the product, scientists carefully studied the proportions of all constituent substances. Thanks to this, it carefully cares for the hair, giving it a natural shine and saturating it with minerals and trace elements.
- Naftaderm® shampoo is safe for long-term use. The product does not contain artificial colors, fragrances or preservatives, therefore it is safe.
- Naftaderm® shampoo is effective in the complex treatment of seborrheic dermatitis. The effectiveness of the shampoo has been repeatedly confirmed by clinical trials. The shampoo has been tested by dermatologists and patients.
- Naftaderm® shampoo can be used to prevent dandruff and exacerbations of seborrheic dermatitis. Developed by dermatologists, an effective scheme for using shampoo allows you to achieve stable remission of seborrheic dermatitis and prevent its exacerbation.
How to use Naftaderm® shampoo correctly?
- Apply a small amount of Naftaderm® shampoo with massaging circular movements onto damp hair from base to ends.
- Leave Naftaderm® shampoo on your head for 3–5 minutes
- Rinse hair and apply Naftaderm® shampoo again
- Rinse your hair thoroughly, then squeeze it lightly.
It is recommended to use Naftaderm® shampoo 2-3 times a week for 2 months. To prevent relapses, you can continue to use shampoo once a week for another 2 months.
Important to remember!
Successful treatment of seborrheic dermatitis depends on proper nutrition and a healthy lifestyle. In the diet, it is recommended to limit foods containing easily digestible carbohydrates, spicy, fried, smoked foods, pickled foods and alcohol.
Forget about the unpleasant symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff! Make a choice in favor of natural sources of health for your skin and hair with Naftaderm® shampoo!
Author:
Kalinina Olesya Vladimirovna, Candidate of Medical Sciences, dermatologist of the National Center for Retinoids
Seal
Diagnosis of dermatitis
The main methods for diagnosing dermatitis are:
- collecting anamnesis, questioning and external examination of the patient;
- blood test (general, biochemical, hormones);
- taking biological material from the affected areas of the skin, microscopic examination and inoculation on nutrient media - is carried out to confirm or refute the fungal nature of dermatitis;
- various allergy tests are carried out to diagnose allergic dermatitis.
The diagnosis is made by an allergist or dermatologist. It is important to identify dermatitis in the early stages and begin timely treatment. Otherwise, a number of complications may develop and the disease may become chronic, which is difficult to treat.
Treatment of dermatitis
First of all, it is necessary to exclude the patient’s contact with the provoking factor that causes the development of dermatitis.
To improve the general condition, the patient is prescribed a hypoallergenic diet . To reduce inflammation, itching, and swelling, taking antihistamines is indicated. Modern antiallergic drugs do not cause drowsiness and give a minimum of side effects, which allows the patient to lead a full life.
If necessary, treatment may be prescribed to remove toxins from the body. For this purpose, the patient is prescribed enterosorbents. Sensitization of the body is also reduced by drugs containing calcium.
Local treatment of dermatitis includes applying hormonal ointments to the affected areas. It should be remembered that only the attending physician can prescribe them. He also determines the dosage and duration of administration, depending on the severity of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient’s body. Self-medication is unacceptable!
If dermatitis occurs with the formation of pustules and vesicles, then the blisters are carefully opened in accordance with the rules of antiseptics and asepsis, after which they are treated with aniline dyes. Contrary to popular belief, only the edges of the wound can be treated with iodine solutions to prevent further spread of infection.
To relieve neurological disorders caused by itching, the use of mild sedative herbal preparations (valerian, motherwort) is indicated.
If the cause of dermatitis is hypofunction of the pancreas, then taking enzyme preparations after each meal is indicated.
For dysbacteriosis, taking prebiotics and probiotics and fermented milk products is indicated. As soon as normal microflora in the intestines is restored, dermatitis disappears on its own.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic dermatological disease, which is characterized by inflammation of the surface layer of the epidermis, severe itching, dryness and the presence of specific rashes. This disease is detected in a person’s infancy, after which it accompanies him throughout his life. During its course, periods of improvement are replaced by exacerbations. The disease not only affects the general health of a person, but also leads to aesthetic and psychological problems. Regular skin rashes, itching and extreme dryness create discomfort, which interferes with normal life. Very often, dermatological problems affect the psycho-emotional state of the patient. Typically, such people withdraw into themselves, find it difficult to make contact with outsiders, are mostly depressed, and suffer from insomnia and other nervous disorders. It is impossible to completely cure it, but with the help of complex therapy the condition can be improved.
SPECIFICITY OF THE DISEASE IN CHILDREN In a newborn under the age of three months, a dermatological disease manifests itself primarily by external symptoms on the skin. Any changes in the state of the epidermis are characterized by the following stages:
- exudation - the release of natural fluid containing protein and other cells onto the surface of the skin;
- the formation of “serous wells” - weeping affected areas of the epidermis, which independently open and lead to the leakage of purulent contents to the surface. Usually, with strong scratching, such erosive formations can turn into a huge wound;
- the appearance of crusts;
- exfoliation of cells.
They appear mainly on the skin of the face (with the exception of the nasolabial area), on the elbows and knees. Itching of the skin can be very severe, which leads to anxiety and tearfulness in the baby. And scratching wounds aggravates the course of the dermatological disease, which leads to sleep disturbances and other neurological problems.
ATOPIC DERMATITIS IN A TEENS For a child in adolescence, this form of dermatological disease is characterized by the formation of large, painful papules. The upper layers of the epidermis are thick, the pattern of blood vessels is enhanced, and pigmentation is clearly impaired. When scratching and mechanical impact on the skin, hemorrhagic crusts appear mainly in the area around the eyes, corners of the mouth, chest, hands, elbows and knees. The teenager has a stable form of light dermographism of the skin. Treatment at this stage is prescribed to each patient individually by a qualified specialist.
ATOPIC DERMATITIS IN MATURE PATIENTS Therapy for this skin disease in adults has its own specifics. It usually goes away after puberty. If this does not happen, then it remains with the person for the rest of his life. In medical practice, cases of self-healing of the disease in a child during the period of active growth have been recorded. However, increased sensitivity of the skin may persist.
The disease in an adult combines all of the above symptoms. The surface layer of the epidermis is very dry, the pattern of the vascular network is strongly pronounced, and the pigmentation is clearly changed. Severe scratching of the skin can cause an infection, which often aggravates the course of the disease. Periods of exacerbation and improvement of the patient's condition follow each other at certain intervals.
APPEARANCE OF COMPLICATIONS DURING THE PROCESS OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS Basically, all complications in this disease are associated with mechanical damage to the surface layer of the epidermis, as a result of which any infection can be introduced inside. When the skin is damaged, the immune system also decreases, and this is a favorable environment for the proliferation of pathogens. All these factors together significantly complicate the treatment of the disease.
The most common complications of atopy are bacterial. When bacteria penetrate into the damaged area, a purulent lesion - pyoderma - can develop. The causative agents of this dermatological disease are pyogenic cocci, including streptococci, gonococci, and staphylococci. Popular symptoms of this disease are purulent rashes on the skin of the body and face. When dried, they form yellow crusts. Other signs of pyoderma include extreme fatigue, weakness, and fever.
In addition to bacterial complications, various viral lesions are often associated with atopic dermatitis. With them, various rashes appear on the skin, including vesicles (formations with a clear liquid). Mostly viral lesions are observed in the facial skin and mucous membranes.
Another common complication of this type of dermatitis, which is typical for childhood, is fungal infection. Very often, infants develop thrush, the causative agent of which is the Candida fungus. Dermatitis in mature people, which is associated with a fungus, manifests itself with various signs, including the formation of plaque in the skin folds.
REASONS FOR ATOPIC DERMATITIS How to cure atopic dermatitis? To do this, it is important to identify its root cause. As medical practice shows, it can be caused by a combination of external and internal factors. This dermatological disease is one of the genetically determined ones, so parents who suffer from it very often have children with similar symptoms. Doctors have confirmed that almost 50% of patients whose relatives have had cases of atopic dermatitis have a predisposition to various allergic reactions. In the case where both parents of a child are susceptible to atopic dermatitis, the probability of having a child with a similar dermatological disease is about 80 percent.
Genetic predisposition and the presence of this disease can be identified already in the first year of life. They usually manifest themselves in the form of a specific allergic reaction – inflammation and the appearance of rashes on the skin. Signs necessarily appear before 5-6 years of age. If allergies do not appear at school age, then parents with atopic dermatitis can be calm about the disease in their baby. However, sometimes symptoms of this disease can appear during adolescence. They can be aggravated by various factors, which include:
- decreased immune system;
- unfavorable environmental conditions;
- climate – high temperature or humidity;
- unbalanced diet;
- lack of vitamins and iron;
- infections;
- psychological factors and others.
Basically, this type of dermatitis is accompanied by other allergic diseases - rhinitis or bronchial asthma. It cannot be completely cured, but with the help of specific procedures and medications, the condition of the skin and quality of life can be significantly improved. With systematic implementation, remission can be achieved.
How to cure atopic dermatitis? To answer this difficult question, it is necessary to first analyze the classification. According to research by doctors, several of its forms can be distinguished - the stage of exacerbation, remission and the stage preceding the aggravation. It is called incomplete remission. Complete remission means the body is healthier and there are no symptoms. The forms of the disease are also classified depending on age - infant (from 1 to 3 years), childhood (from 4 to 12 years), youth (from 13 to 18 years) and adult (after 19 years) can be distinguished.
Also, depending on the severity of the symptoms of this disease, experts distinguish three different forms - mild, moderate and severe. This division is due to the duration of periods of deterioration, as well as the severity of clinical manifestations.
SIGNS OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS The first symptoms of this disease are in a child from birth to six months, but only if he has a tendency to allergic reactions. Doctors have determined that breastfed babies are less susceptible to allergies. Together with mother's milk, they receive antibodies that help the fragile body fight allergens. Also, the first signs may appear when introducing complementary foods, which usually begins at the age of six months, or when switching to an adapted milk formula.
During puberty, when active production of hormones occurs, in more than half of patients, all symptoms of atopy completely disappear. However, if they remain, they will cause discomfort for the rest of a person’s life. Typically, primary forms of atopy progress to adulthood, the symptoms of which are more pronounced.
According to the characteristics of the course of the disease, doctors distinguish two stages - acute and chronic. Each of them has its own symptoms and severity of clinical symptoms. In the first option, there is a change in shade in the affected areas, hyperemia and severe swelling. In some other cases, the course of the disease can be aggravated by numerous rashes in the form of nodules, erosive formations, dryness and increased peeling. The most characteristic sign of atopy is the release of natural fluid containing protein and other cells on the surface of the skin. This leads to the formation of weeping wounds and ulcers. With constant scratching of these formations, a viral or bacterial infection can join the dermatitis, which will lead to various complications and aggravate the course of the disease. The most dangerous of them are the appearance of papules and pustules.
The chronic form of this disease is characterized by thickening of the skin and the appearance of a noticeable pattern on it. It is also characterized by the following symptoms:
- numerous wrinkles in the lower eyelid area of the child;
- the skin on the feet is swollen with multiple small cracks;
- alopecia in the occipital area.
In mature people, other symptoms of the disease can be identified. A characteristic sign of this dermatological disease for different forms is severe itching. Other symptoms may vary depending on the person's age.
THERAPY OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS If signs of atopy have been detected in a child, adolescent or adult and the diagnosis has been confirmed, it is important to begin complex treatment in a timely manner. It is aimed at achieving certain objectives, including:
- removal of toxins and allergens from the body;
- reducing the severity of allergy symptoms;
- reducing the body's hypersensitivity to certain allergic substances;
- relief from severe itching;
- therapy for secondary infections;
- preventing exacerbation of the disease.
Atopy, the causes of which can vary depending on the age and health of the patient, cannot be completely cured. But drug and non-drug therapy can significantly alleviate the patient’s condition. To do this, it is important for the patient to follow all the specialist’s recommendations.
BALANCED NUTRITION IN ILLNESS To prevent relapse and alleviate the patient’s health during the period of exacerbation of the disease, it is necessary to choose the right diet. It should not include food products that contain a large number of allergens. You need to pay special attention to it when feeding infants, in which case all restrictions are imposed on the mother. It is necessary to exclude from her diet all foods to which the baby is hypersensitive. Typically these include dairy products and chicken eggs.
Also, the diet should not include fatty, fried and salty foods, smoked sausages, fish and meat with a high fat content, and highly colored foods. Also, you should not eat sweet foods, citrus fruits, nuts, as well as fish eggs and mushrooms, as they have a strong effect on the gastrointestinal tract.
When preparing food, the patient should reduce the amount of salt, and should not consume pickled and salty canned foods. To meet the need for nutrients found in some prohibited foods, you can take fat tablets. For more detailed information on creating a balanced diet, you should consult a nutritionist. He will be able to choose an individual nutrition plan.
DRUG TREATMENT OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS When treating this disease, the primary goal is to eliminate uncomfortable itching. It leads to constant scratching, which can cause infection of the affected area and lead to other more dangerous complications. To combat this unpleasant symptom of atopy, doctors prescribe special medications.
Antihistamines are good at eliminating itching of the skin, but also remove excessive swelling of the mucous membranes. This allows you to prevent common complications of dermatological disease. It is important to take into account that regular use of most of these drugs can cause the body to develop a lack of sensitivity to them in the future. This will cause the medication to stop working. To avoid this, experts recommend not taking antihistamines for more than a week. Also, many similar medications (Suprastin, Diazolin, as well as Tavigil and others) have a slight relaxing effect, which is important to take into account for those people whose work involves high attention.
There are several hormonal-based anti-allergy medications. Their intake is possible only for a short period of time with a gradual decrease in quantity. It is used only in the presence of severe itching, as well as in the absence of effect from the use of other drugs and medications.
If there are symptoms of intoxication, the doctor may prescribe additional intake of sorbent substances. They bind allergens and remove them from the body. Enterosorbents, which include charcoal, polysorb, enterosgel and others, are suitable for the child.
Intensive treatment of atopy is carried out when symptoms are severe using droppers to administer certain medications orally, including saline. In very difficult situations, blood purification may be prescribed. Depending on how you feel, this procedure is carried out every day or several times a week.
The use of special external preparations – ointments, creams, gels and other cosmetics – is important in the treatment of many dermatological diseases. Dermatologists often prescribe corticosteroids for therapy. The most common is Elidel. The main advantage of this medication is that it can be used to treat small children from birth to 3 months.
If there are weeping wounds and ulcers on the patient’s skin, they need to be dried. For this purpose, special cosmetic preparations are used. The selection of medications depends on the location of the lesions, the stage of the disease and the characteristics of the patient.
When a secondary viral or bacterial infection occurs, patients are prescribed antibacterial therapy. The selection of drugs in this case should be based on the results of tests carried out to determine the pathogen. A drug can be prescribed simultaneously with antibiotics to strengthen the immune system and prevent the development of intestinal dysbiosis.
Atopy therapy can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist after a thorough diagnosis of the patient’s condition. To achieve maximum effect, the treatment program is selected individually.
PREVENTION OF THE APPEARANCE OF ATOPIC DERMATITIS Therapy of this disease in people of mature age requires compliance with preventive measures. Today, this dermatological disease cannot be completely cured, since it occurs in the presence of factors that do not depend on the person. But with a competent approach to treatment, any patient can alleviate the course of the disease, improve well-being and reduce symptoms of exacerbation. To do this, it is important to avoid certain factors, which will prevent relapse.
All activities carried out as part of prevention can be divided into primary and secondary. The first group primarily includes careful management of a woman during preparation for childbirth. It is important to prevent the development of severe toxicosis and the use of potent medications. A pregnant woman should eat a balanced diet and avoid eating certain foods that can lead to allergies.
A newborn baby should be breastfed for as long as possible. It is not recommended to introduce complementary foods early and transfer the baby to an adapted milk formula. A nursing mother should also carefully monitor her diet and exclude highly allergenic foods from it, and be careful when consuming vegetables and fruits. You should not take strong medications during breastfeeding.
Secondary prevention measures are aimed at preventing exposure to external factors that provoke allergies. It is important to take care of your skin carefully and not use cosmetics that contain dangerous chemical dyes, fragrances and other aggressive ingredients.
You should also avoid wearing tight-fitting underwear, using hard washcloths and hot water. It is important to carry out comprehensive skin care, which includes hydration, nutrition and protection from adverse external factors.
Patients with atopy should carefully approach the choice of professional activity. It should not be associated with concentration and contact with chemicals, dust, and oils. You have the opportunity to make an appointment right now by filling out the online form on our website or by calling 91-80-70. Treatment of atopic dermatitis from 815 rubles
Folk remedies for dermatitis
Dermatitis can be quite successfully treated at home using traditional methods, but to do this you need to accurately determine the cause of the disease. Most often, decoctions, infusions, lotions and ointments for external use made from natural ingredients are used to treat skin diseases. Folk remedies for the treatment of dermatitis have a fairly mild and delicate effect, so when using them it is necessary to prepare for a long course of therapy.
Tar soap for healthy skin
Tar soap is used as an independent medicine for the treatment of skin diseases, as well as to consolidate the results after using lotions or ointments based on various phytoextracts.
Tar soap is suitable for the following health-improving procedures: compresses, massages, applications, baths; it is also enriched with cosmetics intended for the care of inflamed skin (shampoos, creams, soaps).
Herbs
Medicinal herbs help get rid of dermatitis:
- celandine. This is one of the most effective remedies for treating problem skin. It is most convenient to use ready-made celandine juice. The juice is diluted in water in a ratio of 1:2, a gauze swab is moistened in the resulting composition and applications are made for 10 - 15 minutes. A herbal decoction is used in a similar way. If there is no allergy to bee products, honey is added to the application solution;
- series. To prepare an infusion or decoction, 1 tbsp is required. dry plant and half a glass of water. You need to brew the herb with boiling water in the evening and leave it to brew overnight. The result should be a dark brown infusion; wet gauze compresses are made from it 3-4 times a day;
- Sophora japonica. The fruits of Sophora japonica are an effective remedy for dermatitis, eczema and other skin diseases. The infusion is prepared as if from a series. The finished product is slightly warmed up and used as a lotion on the affected areas;
- cornflower flowers. An infusion of cornflower flowers is taken orally; to prepare it, take 10 g of crushed raw materials and pour a glass of boiling water. Take the product orally, a quarter glass three times a day.
Tea tree
Tea tree oil is considered a very strong antiseptic, with antifungal, antiviral, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial properties. When treating dermatitis, it is used as an independent remedy or added to other drugs to enhance the therapeutic effect. Tea tree oil goes well with tar oil and any other oil solution.
The use of this product involves applying it to the affected area. To do this, you need to drop a few drops of oil onto the skin and rub it with light massage movements along the entire perimeter of the inflammation.
Tar
Effectively treats even severe forms of dermatitis - eczema and psoriasis. Tar is applied to the skin directly during an exacerbation of the disease and left for a couple of hours or added to other medicines, for example, to water and alcohol tinctures.
Potato
Soothes and heals the skin. To make a compress, wash the potatoes, peel them, and grate them. The mixture is spread on gauze folded in three layers and applied to the sore spot. After two hours, you can remove the compress and put on a new one. At night, the skin is additionally lubricated with propolis ointment 10%.
Geranium
Geranium oil is easy to make yourself. To do this, crushed flowers and leaves of the medicinal plant are crushed, 2 tbsp are measured. and pour into a glass jar. Next, the geranium is poured with a glass of refined sunflower oil and infused for 5 days in a dark place. After five days, the jar is moved to light, for example, on a window, and kept for another month and a half. The finished oil infusion is filtered, poured into a dark glass container, closed with a tight lid and sent to the refrigerator for storage. You can use geranium oil in the same way as tea tree oil.
Alcohol tinctures for dermatitis
Alcohol tinctures help get rid of rashes and improve skin condition in a fairly short time. There are several proven recipes for tinctures for dermatitis:
- Combine 0.5 tsp. lemon juice and vodka with 1 tsp. ground eggshells. The finished medicine is stored in the refrigerator. Take the composition orally, 1 tsp. twice a day. The course of treatment is from 1 to 3 months.
- Mix and grind 10 g of black elderberry, St. John's wort, elm bark, 15 g of calamus roots, 5 g of elecampane roots. Pour boiling water (100 ml) over the herbal mixture and leave for 24 hours. After a day, filter the water infusion, boil it, add 100 g of vodka. The mixture should still sit for about 10 hours, after which it can be consumed. Take the composition 2 times a day, 2 tsp, diluted in half a glass of boiled water. The course of treatment is 14 days.
Murom County Children's Hospital
The issues of caring for the skin of a child in the first years of life remain relevant to this day. Due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of children (thin and sensitive surface layer of the epidermis, well-developed capillary network, lack of local immunity), the protective function of the skin, protecting against adverse external influences, is significantly reduced in them. At the same time, the resorption (absorbing) and respiratory functions of the skin are increased.
The influence of various damaging factors, improper use of care products: creams, powders, soaps, as well as diapers - all this can lead to disruption of the normal condition of the skin.
One of the most common skin changes is diaper dermatitis, the incidence of which ranges from 35 to 50%. It is observed more often in girls.
Using disposable and gauze diapers and over-steaming a baby can sometimes lead to diaper rash or even diaper dermatitis. This does not seem to be a very serious problem and is easy to deal with. But it is not so. In addition, skin irritation causes a lot of trouble for the child, as a result of which he is constantly capricious and exhausts both himself and you.
It is important to know why diaper rash and diaper rash occur. This is necessary in order to cope with these phenomena.
Causes of diaper rash and diaper dermatitis
Most often, the main cause is prolonged contact of the child's skin with moisture or baby stool. And no matter how well the diaper absorbs, with prolonged use the result is the same - irritation.
But this is far from the only reason for the appearance of diaper rash and diaper dermatitis. Therefore, we will dwell in more detail on the most common ones.
Diaper rash and diaper dermatitis, which appear as a result of skin contact with urine.
The problem is based on the pH level of the child’s urine, which changes due to several reasons.
First, let's start with the fact that the child's urine itself is sterile, there are no microbes in it. If a baby stays in the same diaper for a long time, bacteria grow rapidly, which changes the pH level, resulting in irritation on the skin.
Another reason for changes in the acid-base balance may be the food the child consumes. The risk of diaper rash or diaper dermatitis in this case increases as soon as you start introducing complementary foods, since various substances appear in the urine, which are excreted along with the urine and, with prolonged contact, irritate the baby’s skin.
Diaper rash and diaper dermatitis, which appear as a result of skin contact with feces.
Feces contain substances that irritate the baby's skin. Here, an important role is played by the quality of the digestive system (with diarrhea, the number of bowel movements increases - the irritation is stronger), and what the child eats.
Diaper dermatitis may be accompanied by skin candidiasis (thrush). Thrush can also appear when either a child takes antibiotics or a mother who is breastfeeding her baby.
Diaper rash and diaper dermatitis, which appear as a reaction to baby cosmetics used.
Anything that a child’s skin comes into contact with, including creams, lotions, and powders, poses a potential threat. Some substances worsen the condition of already irritated skin, creams that are too greasy make the bottom sweat more, and if you apply diaper cream with unwashed hands, you risk introducing various infections to the baby’s skin.
Here are just some of the causes of diaper rash and diaper rash. Now let’s move from identifying problems to solving them.
Methods for treating diaper rash and diaper dermatitis
Cleanliness is the key to health! In the fight against dermatitis, it is important to follow the rules of personal hygiene, both for children and adults. In addition, you should carefully select diapers, soaps, shampoos, wipes, lotions, etc. First things first:
Change diapers as often as possible.
Wash or dry your baby's skin every time.
Do not forget that the diaper should only be put on a dry bottom. Remove moisture with gentle movements.
Don't forget about diaper cream. If you have an allergic reaction, try a different brand.
The cream should be slightly absorbed before putting on the diaper.
If your baby's skin is too irritated, do not use wet wipes or soap to clean your baby's skin. It is best to wash the child with boiled water or herbal infusion. For this purpose, you can brew chamomile, string, calendula, and celandine. Or dilute a weak solution of potassium permanganate. And then apply the cream.
Baby cream with herbal extracts is also suitable for baby skin care.
If diaper rash or diaper dermatitis appeared when you started introducing complementary foods, treat them first, and only then continue to expand the diet.
If your baby is sweating, bathe him in warm water. You can again add a decoction of herbs to it.
Air your baby's bottom for at least 15 minutes a day.
Use only products intended for child care.
For diaper dermatitis, the use of creams and ointments is recommended to treat the affected areas of the skin. Desitin ointment has a tightening effect, which reduces the flow of mucus and other secretions to the affected areas of the skin. In addition, a protective barrier is created against irritating factors.
The components of the cream "Drapolen" have a local antiseptic, disinfectant, protective and hydrating effect.
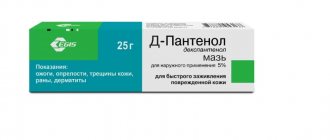
Ointments "d-Panthenol" and "Bepanten", containing dexapanthenol, stimulate epithelialization of the skin (promote rapid healing), and in addition, have an anti-inflammatory effect.
The drug used should be applied daily in a thin layer to the affected areas of the baby's skin during swaddling until the symptoms of diaper dermatitis disappear.
Treatment for an infection caused by Candida albicans is to apply topical creams or powders with antifungal medications as recommended by your doctor.
If you are unable to get rid of the irritation within 3 days, be sure to see a doctor as it could be an infection.
In general, caring for a child is not difficult, it is important to know the rules and do everything in a timely manner.
Prevention of dermatitis
The main measures to prevent the disease are:
- proper nutrition - avoiding junk food, introducing fresh fruits and vegetables into the diet;
- use of personal protective equipment when working in hazardous industries and contacting household chemicals;
- timely treatment of diseases of internal organs that can lead to the development of dermatitis;
- regular sanitation of foci of chronic infection in the body;
- rejection of bad habits;
- avoidance of stress and other psycho-emotional disorders;
- compliance with hygiene rules;
- normalization of work and rest regimes;
- hardening the body, strengthening the immune defense;
- giving up a sedentary lifestyle - walking in the fresh air, exercising;
- when in the sun, use special sunscreens;
- Seeing a doctor when the first symptoms of dermatitis appear - this will help diagnose the disease at an early stage, which will significantly facilitate subsequent treatment and help avoid the transition of dermatitis to a chronic form.
Causes of atopic dermatitis
The systems and mechanisms woven into its cause-and-effect network are mostly known, but it has not yet been possible to identify a universal root cause. The clinical manifestations of the disease are striking in their diversity. It is possible (some researchers are inclined to think this way) that it does not exist, and the wide range of symptoms collectively called “atopic dermatitis” may be the result of various combinations of causes, conditions and provoking factors.
The skin is a large and important organ of the immune system. It is the first (together with other “borderline” tissues - the epithelium of the bronchi, gastrointestinal tract, genitourinary system) to meet everything and everyone trying to penetrate the body or settle on its borders. Meets and assesses the degree of danger. And if necessary, it destroys (on its own or with the involvement of “special forces” - T and B-cell immunity).
Any inflammation is precisely designed to play a protective role: to surround and localize the “enemy”, preventing it from penetrating deeper; attract additional help to the site of the invasion and destroy both the actual or potential “enemy” and its products dangerous to the body (for example, toxins).
The “unusuality” of inflammatory skin damage in atomic dermatitis lies in the fact that this hypertrophied protective reaction develops without visible external causes (purulent complications do not count). And it happens “at the wrong time” and “in the wrong place” due to internal failures in neuroimmunoendocrine regulatory processes. These failures ultimately lead to the fact that immune mechanisms, recognized to be protective, are perverted and turned against one’s own cells (so-called autoimmune reactions), causing their death. This in turn is manifested by a variety of skin symptoms characteristic of this disease.
At the moment, a huge amount of material has been accumulated all over the world regarding the possible causes, conditions, provoking factors and clinical manifestations of atopic dermatitis in children and adults. Let's look at them in more detail.
Genetic predisposition
The role of the genetic factor in the development of this disease is beyond doubt. If one of the parents is sick, the disease manifests itself in children in more than fifty percent of cases. When both parents suffer from atopic dermatitis, the child's chance of developing the disease increases to eighty percent.
What is inherited?
The risk of developing atopic dermatitis is also quite high in those children whose parents (or parent) suffer from any other ailment from the group of atopic diseases. This group, in addition to atopic dermatitis, also includes bronchial asthma, cataracts, and rhinitis. In fact, diseases of this group are united by the nature of disturbances in the body’s reactions to external influences, and not by the organ that suffers from them.
That is, it is not specific mechanisms of skin damage that are inherited, but the above-mentioned malfunctions in the functioning of the body’s most important regulatory systems - nervous, immune and endocrine. Which leads to different types of pathological scenarios of reaction to internal and/or external provoking factors.
Theories explaining the causes and mechanisms of development of this disease
- One of the leading ones is the theory of allergic genesis. Within its framework, the main reason is the innate heightened sensitivity of the body (mediated by the hyperproduction of antibodies of the immunoglobulin E class) to everything “foreign, different, different” (literal translation of the root of the word “allergen”), seeking to enter the body through its borders - mucous membranes and skin, be they of a biological or chemical nature (food, wool, dust, household chemicals, bacteria, fungi, etc.).
- Its complementary component (as indicated by the results of scientific research) are congenital (or acquired) disorders also in the cellular link of the protective reactions of the immune system.
- The active participation of autoimmune mechanisms is recognized both in the manifestation of the symptoms of the disease and in the complication of its course.
- There are also so-called pseudoallergic forms of the disease, in which specific humoral and cellular reactions of immune defense are not involved.
- A significant role is given to the participation of the central nervous system (the so-called neuro-allergic theory). In particular, chronic stress and psycho-emotional trauma are considered significant provoking factors in the manifestation and/or exacerbation of the disease. For children, a significant triggering factor is the unfavorable atmosphere in the family, preschool and neighborhood institutions.
Currently, different classifications of atopic dermatitis have been proposed, based on the predominance of certain immune mechanisms (humoral or cellular).
Triggers of atopic dermatitis
In most cases, there is a clear relationship between interaction with the allergen and the onset or exacerbation of the disease.
The triggering factors for the onset and/or exacerbation of the disease may include:
1. Food allergens (this can be any food product!). They occupy a leading position, especially in early childhood.
Separately, it is worth mentioning the dependence of the prevailing food triggers on age.
In the first year of life these are: plant and animal proteins (cereals, soy, cow's milk, seafood and fish).
For infants, the main risk factor for the manifestation of the disease is an early transition to artificial formula and complementary feeding using products with a high allergenic potential (cow's milk, for example).
At an older age, the following products are added (in descending order of risk):
- eggs, mushrooms, honey, chocolate, tomatoes, carrots;
- corn, peas, buckwheat, rice, potatoes, green peppers, bananas, peaches, cranberries, apricots.
In addition, a relationship was found between poor nutrition of children (the predominance of proteins and carbohydrates, especially in refined foods, against the background of a lack of vegetables and fruits) and an increased risk of developing the disease.
Adults are most sensitive to (in order of decreasing effect):
- cereals (rye, wheat, barley, oats, rice, buckwheat);
- fish;
- peas and carrots;
- eggs, milk, almonds, pork, cheese.
Smoked foods, dyes, preservatives and food additives also provoke exacerbation.
2. Inhalant allergens.
By the age of seven, food allergens give way to inhalant allergens:
- pet hair;
- house and/or industrial dust;
- environmental pollution;
- plant pollen;
- tobacco smoke;
- household chemicals and hygiene products.
For adults, the most active triggers are not food, but pollen and house dust. The latter is by and large very heterogeneous and contains various types of foreign substances (pollen, wool, dandruff, mold, household chemicals, and epidermal mites).
3. Other provocateurs of the onset and exacerbation of the disease at any age are:
- viruses, fungi, parasites, bacteria (and their toxins);
- heat (especially constantly high temperature in the living room) and cold;
- excessive dampness and low humidity;
- woolen and synthetic clothing;
- medications and vaccines (aspirin, antibiotics, hormones).
Factors that aggravate the course of the disease:
- infectious diseases;
- congenital and acquired metabolic pathologies;
- neurological disorders;
- stress (acute and chronic) and psycho-emotional trauma;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (for example, in infants, the manifestation of atopic dermatitis and a severe course can be provoked by immaturity/insufficiency of enzyme systems, which results in incomplete absorption of consumed protein).
Summarizing the above, we can say that a favorable “soil” for the development of atopic dermatitis is a combination of hereditarily determined disorders in the humoral and cellular components of the immune response, abnormalities in the functioning of the nervous, endocrine, digestive, and cardiovascular systems. And various irritants of living and inanimate nature can act as factors that provoke the primary manifestation and/or exacerbation of the disease.
Where to buy natural remedies to treat dermatitis
Medicinal products made according to folk recipes, as well as ingredients for their preparation at home, can be ordered in the Russian Roots online store. The order will be promptly delivered to Moscow and the Moscow region by courier, and to other regions of the country by mail.
You can also buy everything you need to treat dermatitis in one of the capital’s herbal pharmacies.
Attention! All materials published on our website are protected by copyright. When re-publishing, attribution and a link to the original source are required.