Dermatology specialists disagree on which list of diseases to classify as itchy skin disorders. According to the general idea of dermatosis of this nature, it is formed by most types of neurodermatitis, which in 99% of cases is accompanied by itchy discomfort. In addition to neurodermatitis, dermatosis with severe itching is often classified as:
- dermatosis and dermatitis of pregnant women;
- urticaria (better known in the practice of treating dermatosis as urticaria);
- acariasis - acarodermatitis or itchy scabies;
- psoriatic pathologies;
- contact, allergic, atopic, seborrheic dermatitis.
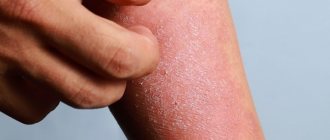
Scratching the skin when itching
It is important to know about the vicious circle “itching – scratching – itching”.
This means that when the skin is damaged, followed by inflammation, itching is provoked. In the skin, inflammatory cells release itch mediators, which again increase inflammation. The itching signal is transmitted to the brain, causing a person to need to scratch. Scratching leads to disruption of the skin (excoriation), which again increases inflammation. The skin becomes more vulnerable to internal and external irritants. This is a vicious circle that is difficult to stop. The vicious circle of “itching – scratching – itching” disrupts sleep, reduces concentration and perception processes.
Prevention of itchy dermatitis
The most important method of preventing this condition is to control the underlying disease. When we know what can cause a problem, it is easier to prevent it.
- Food rich in iron will help prevent deficiency of this trace element, which will protect against prurigo. Iron is found in beef, liver, eggs, buckwheat, and apples.
- A hypoallergenic diet will help protect against eczema, another condition associated with itchy dermatitis. If you are prone to atopy, exclude nuts, soy, chicken eggs, whole milk and seafood from your diet.
- If prurigo is associated with celiac disease, gluten-containing products should be removed from the menu. This is wheat, products made from wheat flour, semolina porridge, bread kvass. Products containing rye and barley cereals are also dangerous.
- Managing stress helps a lot in preventing itching. Adequate sleep, calmness, and avoidance of emotional situations are important. It is useful to master breathing techniques and stress management.
- Protecting your skin from irritation and dryness is also an important preventative measure. Avoid prolonged contact with water, sweating, and staying in hot rooms. Use hypoallergenic skin care products. Use a humidifier and drink at least two liters of clean water a day.
Unfortunately, this disease has not been sufficiently studied, and it is not clear what exactly leads to its appearance, so there are no preventive measures that will guarantee that prurigo will not develop. But by following these tips, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of illness.
Types of skin itching
At the appointment, doctors usually clarify with the patient the following characteristics of itching due to dermatitis:
- Intensity: weak, moderate, intense;
- constant or increasing at certain times of the day, for example, in the evening and at night;
- permanent or periodic;
- common – itchy skin all over the body;
These criteria allow you to more accurately determine the causes of itchy skin and prescribe the necessary treatment.
It should be remembered that scratching itchy areas of the skin is dangerous due to possible microbial infection - the so-called secondary infection, which can significantly worsen the condition of the skin and complicate treatment.
Types of dermatitis and diagnosis
Pruritic dermatoses and dermatitis are a group of diseases that are completely different in nature, which are united by a common symptom - itchy skin. It is not always easy to distinguish them even for an experienced specialist.
Table of itchy skin diseases, diagnosis
| Disease | Itching | Localization | Nature of the rash | Age of onset |
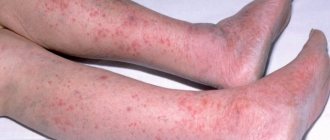
| Allergic contact dermatitis | Pronounced or strong, burning sensation | Any where the skin comes into contact with the allergen | Bubbles against the background of redness of the skin, clear boundaries of the lesion | Any |
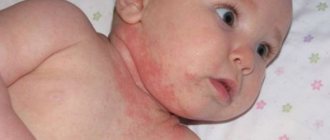
| Atopic dermatitis | Pronounced or strong | Face, limbs; depends on the patient's age | Bubbles against a background of redness, weeping, crusts, cracks | Most often children's, can be any |
| Psoriasis | From weak to strong depending on the stage of the process | Scalp, natural skin folds or friction points | Psoriatic plaques with gray scales | Any |
| Seborrheic dermatitis | Weak to moderate, may be absent | Scalp, nasolabial folds, upper third of the body | Areas of redness with accumulation of yellow, greasy scales | Teenage, adult |
| Scabies | Strong, unbearable, worse at night | Between the fingers, stomach, groin, buttocks | Red spots or papules arranged in pairs | Anyone, usually children |
| Herpetic infection | Severe, burning skin | Most often the face (lips), along the nerves (shingles) | Small tense bubbles | Anyone, for shingles most often an adult |
| Microbial eczema | Moderate, burning, soreness | Most often limbs, asymmetrically, legs | Bright red spots 1-3 cm with clear boundaries, weeping, blisters and crusts | Anyone, usually an adult |
Recognizing the cause of skin rashes
Since cutaneous dermatosis with a pronounced itching effect can act as an independent disease or a symptom complex against the background of other diseases, its diagnosis should be carried out at several levels.
- OAM, OAC, BAC to exclude neurology, against the background of which dermatosis with an itchy manifestation very often develops;
- An objective examination with a theoretical analysis of information about a person’s heredity, everyday life, habits, behavior in order to determine the likelihood of allergic dermatosis.
- Samples and tests, if necessary (to identify the agent or clarify the degree of its influence).
- Laboratory analysis (microscopy of cells in dermatosis) with scraping.
- Translucency.
How to get rid of itchy skin
Before relieving the itching of dermatitis, it is necessary to establish its cause, since in most cases it will be difficult to get rid of the itching without eliminating the cause.
Regardless of the causes of itching, treatment usually uses remedies aimed at alleviating the patient’s condition, relieving the urge to scratch, and preventing the development of secondary infection in areas of scratching.
Among skin diseases, common causes of itching are atopic dermatitis, eczema, neurodermatitis, seborrheic dermatitis, and psoriasis.
Medicine knows about 2,000 different skin diseases, which are united by a common medical term - dermatoses.
Among them, psoriasis and atopic dermatitis are the most common. The head of the clinic of dermatovenerology and allergology-immunology of the European Medical Center, candidate of medical sciences, doctor of the highest category Eva Pechatnikova and you understand these common skin diseases and find out the most effective treatment methods phototherapy of the European Medical Center Dmitry Serov.
Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis: more similarities or differences?
Despite the fact that psoriasis and atopic dermatitis belong to the same group of diseases (dermatosis), they are completely different skin problems. Atopic dermatitis belongs to a group of allergic diseases, usually hereditary. Polypous rhinosinusitis, bronchial asthma, hay fever (pollen allergy) are all diseases similar to atopic dermatitis. Psoriasis has a completely different pathogenesis, which often causes inflammatory processes in the joints, kidneys and other organs and tissues. Thus, these skin problems have different clinical presentations. Moreover, they can be combined, that is, one patient can have both atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
The only thing that is similar between these diseases is the prominent role of cytokines.
Cytokines are pro-inflammatory proteins that are secreted by immune cells (T-lymphocytes, B-lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, etc.). There are several groups of these protein formations, but the common property of all cytokines is their influence on immune cells, stimulating their development and transmitting information from cell to cell. In other words, cytokines are regulators of the body's immune responses. In the event of a violation of coordination of actions between immune cells, cytokines provoke processes that intensify rashes in both atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
How do atopic dermatitis and psoriasis manifest?
Psoriasis affects about 3-7% of the world's population. This disease has no age limit, but is most often diagnosed in patients 29-36 years old. Typically, psoriasis appears as pink, scaly patches on the elbows and knees and on the scalp. Sometimes defects appear on the nails. In advanced forms of the disease, the entire body may be covered in pink, itchy plaques.
The main manifestations of atopic dermatitis (or neurodermatitis) are skin rashes, most often in areas of large folds, face and neck. The main distinguishing symptom of this disease is itching. As a rule, neurodermatitis manifests itself in childhood, and then becomes chronic and accompanies a person throughout his life.
How dangerous are these diseases?
If dermatosis is not detected in time, it often leads to complications. Advanced forms of psoriasis are dangerous for the development of psoriatic arthritis, that is, damage to the joints. In this case, complex treatment requires the help of not only a dermatologist, but also a rheumatologist.
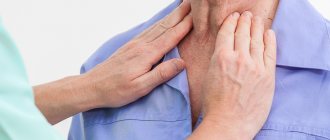
Exacerbation of atopic dermatitis provokes inflammation of the lymph nodes (in the cervical, axillary, inguinal, femoral areas), ophthalmological abnormalities (recurrent conjunctivitis and ectropion, that is, eversion of the eyelid). In addition, there is confirmed medical evidence that patients with atopic dermatitis are more likely to suffer from herpes simplex virus and HPV. Often, bacterial and fungal infections develop in parallel with atopic dermatitis.
Causes of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
The main and proven cause of both atopic dermatitis and psoriasis is genetic predisposition. For example, if one of the parents is a carrier of atopic dermatitis, then with a 50% chance the disease will be passed on to the child. If the carrier is the mother, then this probability increases.
Regarding psoriasis, we can say that this skin disease is not fungal, that is, it cannot be infected through household contact. Psoriasis can develop under the influence of stress, infectious diseases and trauma.
How is the disease diagnosed?
There are a number of tests that are always performed when you first visit your doctor. If necessary, the diagnosis is established using histological examination. But in most cases, a general clinical picture is enough to make a conclusion.
Traditional and modern treatments
When treating skin diseases, the doctor is guided by the rule of the so-called therapeutic ladder. The specialist begins by prescribing the simplest treatment methods. If such practices are ineffective, the doctor moves to the next stage of treatment, where systemic and biological therapy drugs can be used. Thus, the first stage is standard methods, the second is physiotherapeutic techniques, the third is systemic, and then biological therapy.
Laser therapy, ultrasound, magnetic therapy, and phototherapy are used as physiotherapeutic treatments. This type of treatment is very effective. However, it is worth noting that physiotherapy is not used in the acute phase of skin diseases. During periods of severe inflammation, treatment procedures can aggravate the situation and provoke the appearance of new lesions.
One of the ways to alleviate the manifestations of psoriasis is plasmapheresis - a procedure for cleansing the blood of toxins, poisons, salts and other harmful substances. It is important for people with psoriasis to watch their diet, eat a low-calorie diet, and avoid fried foods and alcohol. Psychotherapeutic sessions with a specialist are also a necessary element of treatment. The specialist helps the patient understand what disturbances in the psycho-emotional state could cause psoriasis, and in the future they work together on the optimal ways to respond to the triggers.
Of course, drug therapy is also used to treat skin diseases. Often, patient treatment is supplemented by the prescription of antihistamines, antibacterial, antiviral, and antimycotic agents. To restore damaged skin, emollients and moisturizers with a predominance of ceramides, lipid components of the cell membrane, are used. For mild cases of the disease, doctors recommend taking calcineurin inhibitors, that is, non-steroidal immunomodulators. In case of severe manifestations of atopic dermatitis, cyclosporine is prescribed. This remedy is very effective, but it cannot be abused over a long period of time (more than 1-2 years). This is due to the toxicity of some substances included in its composition.
To maintain a state of remission in patients, experts recommend, first of all, special skin care. To do this, every time after taking a shower, it is necessary to apply emollients to the skin - products whose composition is completely identical to the composition of the lipid mantle of our skin.
The above methods are used to treat both psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. The specific method of therapy for each patient is selected by the doctor based on the overall clinical picture. It is worth noting that in the treatment process, an important point is close interaction between doctors: dermatologists, allergists, rheumatologists. It is teamwork that allows us to achieve guaranteed positive results from the therapy.
Biological therapy - a revolution in the treatment of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis
Biological therapy completely changes the paradigm of treatment of skin diseases and helps to achieve sustainable remission.
The essence of this modern therapy is that it affects cytokines, that is, information molecules that cause the development of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis. It is biological drugs that make it possible to “freeze” the development of the disease. Previously, such medicines could only be found abroad, but now they are available in Russia.
A few years ago, getting rid of 50% of all skin rashes was considered an excellent result. Now, with the help of biological therapy, doctors are able to clear the patient’s skin almost 100%. At the moment, there is no type of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis for specialists that they cannot cope with.
As a result of treatment, the patient forgets about the existence of his illness. Unlike other types of systemic therapy, drugs consisting of large protein molecules do not have harmful effects on internal organs. Therefore, they can be appointed on a permanent basis.
The principle of action of biological drugs can be illustrated by the example of dupilumab, a drug based on monoclonal antibodies. This biological drug blocks inflammatory processes caused by cytokines. Thus, treatment with dupiluamab reduces the concentration of biomarkers in the blood that provoke a severe course of the skin disease. Such biological therapy is effective due to its selectivity and helps where all other methods have failed. Contraindications to the use of drugs obtained by innovative genetic engineering methods depend on the patient’s individual tolerance to certain substances.
Quality of life of patients after treatment
Even with severe forms of psoriasis and atopic dermatitis, doctors restore quality of life to patients. Those who could not attend work due to joint disease and significant skin damage can now live an absolutely normal life, have a family, children, etc. Some patients could not leave the house, were forced to leave work, fell into deep depression, and did not see any prospects for a complete cure. And it was biological therapy that was able to help them start a new life without discomfort.
Treatment of itchy skin with medications
Considering that itching can be provoked not only by mechanical and chemical irritants, but also by emotional factors, treatment should be comprehensive and aimed at eliminating the cause.
Medical recommendations for the treatment of skin itching due to dermatitis highlight the following means to reduce the intensity of itching:
- Systemic medications for skin itching in dermatitis: antihistamines, mast cell membrane stabilizers, systemic hormonal agents, antidepressants, sedatives, immunosuppressants.
- External medications, which include external anesthetics, hormonal agents, tacrolimus, zinc, menthol and camphor.
Skin cap for itchy skin due to dermatitis
To combat skin itching in atopic, seborrheic dermatitis, eczema and psoriasis in adults and children from 1 year of age, external medications based on zinc pyriton activated SKIN-CAP have been successfully used, which:
- can help reduce the severity of skin itching within 5-7 days [1] after the start of use;
- reduce the need to use hormonal [2] and antihistamines [1];
- help prevent the development of secondary infections when scratching, thanks to the antibacterial and antifungal activity of activated zinc pyrithione;
- have a high level of safety, unlike, for example, hormonal ointments, since they have only one contraindication in the form of individual intolerance to the components of the drug [2].
Anti-itching cream for dermatitis and Skin-cap aerosol can be used in children from the age of 1 year.
Symptoms of itchy dermatitis
- Simple prurigo is characterized by the appearance of symmetrically located areas with intense itching. There, over time, small dome-shaped flesh-colored bumps (papules) form, which itch intensely. Sometimes they transform into blisters containing clear liquid. To a greater extent, the disease affects the outer surfaces of the arms and buttocks, but can also be located in other areas of the head, neck, torso and limbs. This type of prurigo can affect people of any age; it occurs in both children and adults. Over time, the papules that appeared at the beginning of the disease are scratched off and disappear, but new ones are formed. This condition leads to a significant deterioration in quality of life, the itching worsens at night and interferes with sleep.
- Pigmented prurigo is a simple variant when pigment accumulates in papules and they change color and become darker than the underlying skin.
- With nodular prurigo, dense bumps and pimples appear on the skin, similar to warts, which bring a lot of discomfort. They may be darker than the skin surrounding these lesions. Their surface is rough, it is noticeably thickened, and many scratches and scratches are visible. The nodules are usually no more than a centimeter in diameter, they are very dense to the touch, can be sensitive, ulcerate, crust over and itch. The arms and legs are the areas most commonly affected, but the back, buttocks, shoulders and chest can also be affected by the disease. Scars and cicatrices are noticeable, differing in color from the underlying epithelium, which form at the site of scratching. Nodular prurigo is more common in young and middle age (30 - 60 years), equally common in men and women, and in representatives of all nationalities. The number of nodules gradually increases. This variant of prurigo is difficult to treat.
For diagnosis, a doctor usually only needs to examine the patient. The very appearance of skin rashes in combination with itching indicates itchy dermatitis. In some cases, a piece of the rash is taken and a biopsy is performed to clarify the diagnosis.