Home / Papillomas
| Pharm. groups | Active substance | Trade names |
| Antiseptics and disinfectants | Phenol | Feresol |
| Antiseptics and disinfectants in combinations | Verrukacid ® | |
| Homeopathic remedies | Edas-801 Thuja oil | |
| Dermatotropic agents in combinations | Solcoderm | |
| Other immunomodulators | Immunomax | |
| Inosine pranobex | Isoprinosine | |
| Normomed ® | ||
| Antiviral (except HIV) drugs | Sodium deoxyribonucleate with iron complex | Ferrovir ® |
Official website of the RLS ® company. Home Encyclopedia of medicines and pharmaceutical assortment of goods of the Russian Internet. The directory of medicines Rlsnet.ru provides users with access to instructions, prices and descriptions of medicines, dietary supplements, medical products, medical devices and other goods. The pharmacological reference book includes information on the composition and form of release, pharmacological action, indications for use, contraindications, side effects, drug interactions, method of use of drugs, pharmaceutical companies. The medicinal reference book contains prices for medicines and pharmaceutical market products in Moscow and other cities of Russia.
Transfer, copying, distribution of information without the permission of RLS-Patent LLC is prohibited. When quoting information materials published on the pages of the website www.rlsnet.ru, a link to the source of information is required.
Lots more interesting things
© REGISTER OF MEDICINES OF RUSSIA ® RLS ®, 2000-2019.
All rights reserved.
Commercial use of materials is not permitted.
The information is intended for medical professionals.
TOC o «1-6″ p» » hzu
Warts are a group of benign skin growths caused by various types of human papillomavirus (HPV).
CLASSIFICATION ICD 10
B 07 Viral warts
EPIDEMIOLOGY
· The frequency of warts in the general population is 7 – 10%
· Among all forms of dermatosis, simple warts make up about 70%, plantar warts – about 30%, flat warts – about 4%.
· Children, adolescents and young adults are more often affected
– HPV-2 and HPV-3 – causative agents of vulgar (common) warts;
– HPV-2 and HPV-4 – palmar-plantar;
– HPV-1 – hyperkeratotic.
Source of infection: sick people
· Routes of transmission of infection: direct or indirect contact (through household objects)
The spread of the virus in the body occurs through autoinoculation
· Incubation period – from several days to 5-8 months
– microtrauma of the hands and feet
– contact with a patient with manifest form
– imbalance of the immune system (HIV infection, oncopathology, long-term immunosuppressive therapy, etc.)
– illness of one of the family members
– wearing socks made of synthetic materials, constantly wearing sneakers, boots, shoes made of synthetic materials during the day,
– wearing someone else’s shoes, stockings, socks, using someone else’s cutting tools, towels, other care and personal hygiene items,
– exposure to conditions of high temperature and humidity, including in production,
– visiting public baths, saunas, swimming pools,
– non-compliance with the rules of sanitation and hygiene: personal and industrial
PREVENTION
· Elimination of risk factors
· Wearing cotton socks, daily change of socks, stockings, tights
· Comfortable shoes made from natural materials, change shoes throughout the day
· When visiting baths, saunas, swimming pools, you must use individual rubber shoes, carry out individual disinfection of the skin of the feet: 1-2% iodine solution, 2% alcohol solution of salicylic acid, Formidron liquid and others
· Disinfection of inventory and equipment, replacement of wooden objects with rubber and plastic ones in industrial showers, gyms, public baths and swimming pools
· Sanitary educational work: holding lectures and seminars with service workers (baths, sports institutions), workers who visit showers every day, athletes, military personnel, medical workers to familiarize themselves with the typical manifestations of warts, new treatments and preventive measures; use of visual aids and reminders.
SCREENING
· Timely identification of patients with warts: examination of the patient’s skin during active observation by specialists of any profile or during any visit to a family doctor (general practitioner) or pediatrician. In the presence of exophytic formations of the hands and feet - referral to a dermatologist
Active identification of patients when examining family members of the sick person
· Active identification of patients during medical examinations of employees of children's, sports and medical institutions, enterprises providing sanitary and hygienic services to the population (baths, manicure and pedicure rooms); athletes; workers who visit industrial showers every day; military personnel)
DIAGNOSTICS
HISTORY AND PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
History of risk factors
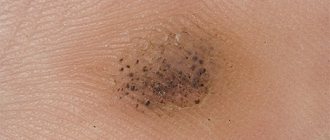
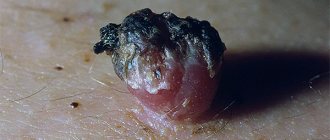
· Common warts are usually located on the fingers in the periungual area. They are clearly defined dense hemispherical papules of flesh-colored or grayish-yellow color from 2 to 7 mm in diameter with a rough, papillary surface, often with hyperkeratotic layers. They can be single or multiple, with one of the warts, the “maternal” one, usually being larger in size. There is usually no sensation.
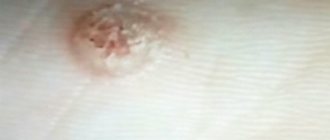
· Flat warts - always multiple, prone to grouping, clearly defined dense flat papules from 1 to 5 mm in diameter, rising above the surface of the skin by 1 - 2 mm. Their color does not differ from healthy skin or has a pink or beige tint; outlines - round, oval or polygonal; surface is smooth. Favorite localization is the dorsum of the hands, the face (usually the forehead and cheeks). There is usually no sensation.
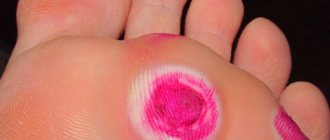
· Plantar warts are located, as a rule, on the supporting areas of the soles: in the projection of the heads of the metatarsal bones, on the heels, and on the pads of the toes. At the beginning of the disease, a small shiny flat papule of flesh-colored or yellowish-gray color appears, slightly rising above the skin or lying at the same level with it. Over time, its size increases, reaching 1 cm, the consistency becomes hard, the surface becomes rough, hyperkeratotic. Sometimes the center of the element may crumble, exposing the papillary surface. Formations are often single. Multiple small warts can merge with each other, forming a “mosaic” lesion. The rashes are painful and disrupt the patient’s performance and lifestyle.
Short description
Warts, or skin papilloma according to the ICD, have the same nature for all types, types and locations. Modern research has clearly established and proven that all papillomas of the skin, mucous membranes, and internal organs are of a viral nature.
They are caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Based on the ICD tenth revision, they belong primarily to group B, which includes all kinds of infections of a viral nature, accompanied by affecting the mucous membranes and skin.
It should be clarified that each of the classes below has its own subparagraphs and certain exceptions, but they are not indicated due to the fact that the information provided is aimed at highlighting the problem of papillomas.
Classes B00 – B09 include:
- A viral disease where changes are observed in the skin and mucous membranes:
- B00 Infections caused by the herpes simplex virus;
- B01 Chicken pox;
- B02 Herpes zoster;
- B03 Natural smallpox (considered eliminated since 1980, but retained in the classification due to its extreme danger);
- B04 Infections associated with monkeypox;
- B05 Measles;
- B06 Rubella;
- B07 Warts caused by a virus.
2. Includes all simple papillomas.
Warts are a skin disease caused by a filterable virus and characterized by small tumor-like benign formations of a non-inflammatory nature.
Warts are benign skin growths caused by various types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Frequency. Warts are a common dermatosis, accounting for 7–10% of the general population. The predominant age is children and youth.
Classification • Palmar - plantar • • Deep hyperkeratotic • • Superficial - mosaic • Flat (juvenile) • Condylomas acuminate.
Mechanism of infection
Infection is facilitated by microtraumas to the skin - scratches, wounds, abrasions. The routes of transmission of the virus are as follows:
- the most common way is sexual intercourse;
- failure to maintain personal hygiene when visiting public toilets, showers, gyms, baths, etc.;
- infection can occur from an infected mother to a child during childbirth;
- self-infection - damage to one’s own tumors when shaving, rubbing with clothes, etc.
Reference! The virus is extremely unstable in the environment, so most often infection occurs directly through contact with a carrier.
Etiology and pathogenesis of the disease
The virus enters the human body mainly during unprotected sexual contact (vaginal, oral, anal), in a public place (bath, sauna, swimming pool, cosmetologist's office) through microcracks in the skin or through mother to child.
The pathogen exists in epithelial cells, and the immune system fights it. If a person’s defenses are strong, self-healing occurs. In other cases, papillomas appear, which can be caused by the following factors:
- weakened immunity due to viral and infectious diseases;
- violation or lack of personal hygiene;
- promiscuity;
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits (alcohol, drugs, smoking);
- exposure to stress;
- hormonal imbalances.
The algorithm for the development of the disease is as follows: first, the virus enters the body of a healthy person, and immunity is mobilized. It fights against it for a long time, after which it either completely “eliminates” the pest, or sharply weakens under the influence of some factors (surgical intervention, severe hypothermia, pregnancy).
While the immune system is not working, the virus begins to actively infect the DNA of epithelial cells, turning them into atypical ones. The altered cells grow and divide, resulting in the formation of a cluster of those same cells above the skin or mucous membrane - papillomas, warts or condylomas.
Causes
Etiology, pathogenesis. The causative agent is the filterable virus Tumefaciens verrucarum. The disease is transmitted through direct contact with a patient, as well as through shared objects. Incubation period - 4 - 5 months. The state of the central nervous system plays a certain role in pathogenesis.
Etiology and pathogenesis • HPV - 2 and HPV - 3 - common warts; HPV - 1 - hyperkeratotic; HPV - 2 and HPV - 4 - superficial varieties of palmar-plantar warts; HPV - 3 - flat warts • Incubation period - from several days to 8 months. The route of transmission is contact - household.
Genetic aspects. There are several hereditary diseases that are accompanied by the appearance of warty growths on the skin, for example: • Epidermodysplasia verruciformis (226400, r).
Hereditary predisposition to the development of multiple viral warts • Verrucous X - linked epidermodysplasia (305350, À) • Van den Bosch syndrome (*314500, À): mental retardation, choroidal atrophy, warty acrokeratosis, anhidrosis, skeletal deformities.
Risk factors are decreased immunological reactivity of the body, increased sweating of the hands and feet.
Pathomorphology. Acanthosis, papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis with areas of parakeratosis, vacuolar degeneration of cells of the spinous and granular layers of the epidermis.
HPV types according to ICD-10 code and their features
Depending on the location and type of papilloma according to ICD-10, there are multiple points classified as pathologies of various organs and systems, classifying them. This is due to the fact that treatment methods and prognosis for such growths are determined not so much by the HPV itself, but by the location, including the thoracic region, and the type of its manifestations.
We recommend reading: Papillomas treatment at homeHistology of papillomasDrugs for the treatment of plantar warts
Skin papilloma code according to ICD10, the most common case, belongs to the category of benign skin diseases of a different nature, relative to processes group D23. It is classified according to the location of growths on the body:
- D23.0 lips;
- D23.1 Eyelids and commissure;
- D23.2 Ear, including external auditory canal;
- D23.3 Other areas of the face (cheekbones, cheeks, nose, chin);
- D23.4 head and neck;
- D23.5 back, chest, abdomen;
- D23.6 arms and area of the shoulder joint;
- D23.7 legs and around the hip joint;
- D23.9 Unspecified location.
Treatment of all kinds of growths caused by a virus depends primarily on its location. Thus, formations classified by the international code according to ICD-10 as skin papillomas of the eyelid, regardless of their location, are subject to standard treatment methods in the form of cryodestruction, thermocoagulation, laser removal and the use of antiviral or immunostimulating agents.
ICD-10 papilloma of the nose, mouth, pharynx, eyelid and larynx, breast papilloma fall under several points at once, but they require similar treatment in the form of minor operations that are insignificant in terms of trauma. Treatment with conventional methods is quite difficult due to the impossibility of their use in a single area.
What is this code: definition and general information
ICD-10 is the International Classification of Diseases, without which it is difficult to imagine the activities of medical workers. Essentially, this is a list of diseases with a description of survival and mortality statistics, symptoms and treatment. Thanks to this document, the doctor can easily gain access to the necessary data.
Since everything changes in the world, some diseases disappear, others are discovered, the ICD periodically needs correction. The document is revised every ten years under the guidance of the World Health Organization.
Currently, the current classification is ICD-10, and the number 10 means that it has been revised for the tenth time. Scientists are also engaged in modifying and simplifying an existing document, and if everything goes according to plan, ICD-11 will come into force in 2022. We recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material: papilloma ICD 10.
Symptoms (signs)
Most often, warts appear on the hands. This localization is typical for children and adolescents. Simple warts are hard formations ranging in size from 1 mm. Such formations tend to merge and therefore often cover large areas.
Plantar warts can cause pain when walking and are often confused with calluses, however, unlike warts, calluses have a smooth surface and skin pattern. Flat warts have the color of normal skin and are represented by dense papules. Their shape can be different, and they are often accompanied by itching, hyperemia, pain and inflammation.
• Common warts •• Single or multiple nodules with a diameter of 0.2–0.5 cm, hemispherical in shape, clearly defined, dense, grayish-yellow in color, with hyperkeratosis on the surface •• Localization - easily injured areas, i.e. fingers, hands, knees.
• Plantar warts (horny wart, palmoplantar wart) •• Rash elements. First, a small shiny, subsequently keratinizing papule or plaque of a yellowish-gray color with a rough, uneven surface.
The formation is usually single, but 3–6 or more warts are found. Small elements can merge to form a “mosaic” wart.
Warts located in places of pressure are painful •• Localization: soles in the projection of the heads of the metatarsal bones, heels, toes, other supporting areas of the foot.
• Warts are flat •• Flat, well-demarcated papules with a smooth surface, 1–5 mm in diameter, raised 1–2 mm above the surrounding skin. The color is light brown, pink or normal skin. Always multiple isolated elements arranged in groups; in places of injury, a linear arrangement is possible •• Localization: favorite localization is the face, dorsum of the hands, legs.
Diagnostic methods
Diagnosing the disease is not difficult. Upon visual inspection of the formation, a specialist will determine the presence of the disease.
If papillomas are localized on the genitals, a woman should consult a gynecologist, and a man should consult an andrologist. At the same time, a visual examination is most often enough for women, and men will have to undergo urethroscopy, since genital warts in men can also affect the urethra.
To finally verify the correctness of the diagnosis, as well as to determine the type of disease according to the ICD, it is necessary to undergo an additional examination - PCR. To do this, the patient must donate blood and scrapings. Treatment of papilloma according to ICD 10.
Treatment of papilloma is based on its removal. There are many ways to remove a growth, and the optimal method is determined by a specialist based on the localization of the formation and the extent of the affected area.
- removal with a scalpel;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- cryotherapy.
Reference! You can also remove warts using folk remedies. This will take more time, but the result usually takes place. Most often, plants are used that contain a large amount of phytoncides - celandine, Kalanchoe, garlic and others.
Immunomodulatory drugs
In addition, patients are prescribed immunomodulatory drugs:
- drug Lykopid;
- drugs from the interferon group - Viferon, Kipferon;
- herbal immunomodulators – Panavir, echinacea preparations.
Antiviral drugs
Antiviral agents may be prescribed:
The goal of treatment is to reduce the activity of the virus, strengthen the immune system and prevent the spread of growths on the skin and internal organs.
The diagnosis is usually straightforward and is based on the clinical picture. Differential diagnosis for plantar warts is carried out with a callus, which is a continuous horny layer without a papillary structure; for genital warts - with condylomas lata (manifestations of secondary syphilis), which have a dense consistency, a wide base and often a macerated surface on which the pathogen - treponema pallidum - is found.
Treatment method
Treatment of viral tumors is always complex and, as a rule, long-term. Almost always, the doctor recommends first removing the growth surgically or with a more modern method (cryosurgery, laser removal, electrocoagulation), and then prescribing antiviral drugs and immunomodulators.
Conservative therapy using pharmaceutical and folk remedies is not always effective.
Non-drug
Non-drug treatment is the fastest and most effective way to get rid of growths with a low chance of recurrence. In most cases, drug therapy cannot completely cope with the virus and lead to getting rid of papilloma.
Surgical removal
If the papilloma has a clear border and is large in size, surgical removal of the growth would be advisable. In this case, local anesthesia is used. In the operating room, the doctor makes an incision, removes the contents of the resulting skin “hole,” including some healthy cells, and applies sutures.
The disadvantages of the method include pain, the need to care for a fresh wound (treat it with an antiseptic), a long rehabilitation period and the formation of a suture or scar. However, if surgically removed, the papilloma tissue can be used for biopsy.
Folk remedies
Many people, even in the 21st century, remain supporters of alternative medicine, believing that nothing can cope with diseases better than medicinal herbs and herbal infusions.
The main way to eliminate papilloma using folk remedies is cauterization. To do this, use iodine, garlic juice, celandine, aloe, apple cider vinegar, fresh potato juice, essential oils and much more.
A person who is a fan of traditional medicine recipes dips cotton wool or gauze in the chosen remedy and applies it to the affected area. Thus, over time, the papilloma dries up and falls off, but this is not a fact.
Treatment with folk remedies takes a long time, affects neighboring healthy areas of skin and makes it impossible to examine a tissue sample to determine the risk of cancer.
Medication
Drug treatment is often ineffective when the papilloma has long been formed. As a rule, therapy with pharmaceutical products is necessary either at an early stage of the disease, or after surgical removal, or in cases where the wart cannot be removed surgically.
Immunomodulatory drugs
Immunomodulators are drugs that help strengthen the immune system. For HPV, tablets, ointments and gels can be prescribed. As a rule, local therapy is effective only in the initial stages of human papillomavirus disease.
Immunomodulators are herbal and contain interferon. The latter include the popular and effective Viferon, Interferon, Isoprinosine, Genferon. Herbal preparations may include Derinat, Dermesil drops or Echinacea-based tablets.
When taking immunomodulatory drugs, it is imperative to supplement therapy with antiviral agents.
Antiviral drugs
Among the tablets, Isoprinosin, Immunosin, Novirin, Allizarin have proven themselves well. Popular ointments include Viferon, Panavir, Superchistotel, and Acyclovir.
Antiviral therapy is determined by the doctor, as is the dosage and course of treatment. You cannot prescribe medications on your own, especially without diagnosing the disease.
What tests are needed?
If a woman notices neoplasms, it is necessary to consult a specialist to establish a correct and accurate diagnosis.
- A cytological smear helps to find an atypical cellular form in the uterus. If the age is over thirty years, then a screening test is recommended; it is carried out in combination with a smear and determines the necessary information about the virus. For girls under thirty years of age, this procedure is prescribed if the smear results are positive. If atypical cells are found, additional treatment is prescribed.
- There are no screening tests for men; a physical examination method is used for them. This examination includes an external examination of the genital organ and anus. Experts recommend that men who practice homosexual relations undergo periodic anal smears at least once a year.
- More often than not, a physical examination is sufficient to correctly make this diagnosis. A special substance changes the color of the growths and highlights them for better detection. A weak solution of acetic acid is also used to detect the disease; a strong burning sensation and discomfort will be felt in the infected areas.
Locations
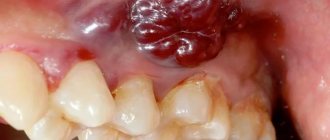
All neoplasms associated with papillomavirus can appear on any part of the body. Even the eyelids, fingers, soles and internal organs are not excluded.
REFERENCE! Genital warts affect only the mucous membrane of the genital organs or the oral cavity.
Different strains of viruses and, accordingly, types of papillomas love different parts of the body: filiform, for example, prefer places with thin skin (armpits, eyelids), flat and plantar papillomas prefer rough skin (sole, palms).
If we talk about the frequency of occurrence, the leadership belongs to the area of the genital organs and anus. Also, papillomas are often found on the face (forehead, chin, eyelids, nasolabial fold), neck, and armpit area.
Prevention of infection
This virus can only be transmitted by another person who is a carrier of genital warts. It happens that the carrier has no symptoms or external signs of the disease at all, but this does not exclude the possibility of illness from him.
- Sexual activity is the most common cause of transmission of this disease.
- The likelihood of the disease is much higher in men whose sexual life is based on homosexual relationships.
- Young people and their active sexual relationships with a large number of partners are also at increased risk of infection.
- Sex with a partner who has recently been ill and is still infected is the most common cause of genital warts in a healthy person.
- The possibility of transmission through various household items, such as someone else's towel, is much less likely.
- There are cases of condylomas appearing after visiting public swimming pools, saunas and baths.
- Children, including very young children, are also susceptible to the formation of condylomas.
- There is a chance of catching this virus during childbirth, when the baby passes through the mother’s genitals.
- In everyday life, using the wearer’s personal hygiene products, the child’s chance of getting sick is extremely small.
Unfortunately, absolutely all people become infected with HPV by the age of 18–20 years of age. This is due to the fact that it is transmitted from infected people to uninfected people through ordinary skin contact.
Since the entire adult population is a virus carrier of these infectious agents, they constantly infect the younger generation. The exception is the strain that causes anogenital warts - it is transmitted only through sexual contact.
Unfortunately, by the age of 20, almost all people are infected with the papilloma virus, this happens because the virus is transmitted through any skin contact (with the exception of anogenital warts, which are transmitted only through intimate intimacy).
To prevent the infection from worsening, you must:
- undergo a diagnostic examination every six months;
- strengthen immunity;
- If necessary, remove any warts that appear.
To prevent HPV infection you must:
- observe hygiene rules;
- use barrier methods of contraception;
- Get vaccinated with Gardasil or Cevarix.
Pregnant women are advised to promptly diagnose the disease and receive treatment to avoid transmitting the virus to their child.
Asymptomatic carriers of the virus need to undergo cytostatic therapy as a preventive measure - they will inhibit the development of infection.
Preventive therapy
In order not to encounter such a nuisance as a wart, you need to follow simple preventive measures.
- Avoid promiscuity and unprotected contact.
- Wash your hands often with soap, especially after being in public places.
- Maintain personal hygiene.
- Choose the right skin care products and underwear.
- Visit your doctor regularly and undergo routine examinations.
- Eat right, exercise.
- To refuse from bad habits.
- Toughen up and walk more in the fresh air.
For some reason, many people believe that papillomas and warts appear only in old age. In fact, activation of HPV can occur at any age if a person is infected with it after the first sexual contact or from a sick mother.
Under no circumstances should you remove warts and growths yourself or prescribe medications without medical advice. As a rule, therapy should include removal of the growth by any available method, antiviral measures, strengthening the immune system and further observation by a doctor.
Treatment
The correct treatment is determined by a specialist who, based on the shape and size, will determine chemical or destructive treatment.
- For one or several small formations, the cauterization method is used with solutions of solcoders, pedophylline and condiline. Pedophyllin inhibits the development of condylomas, the other two substances destroy formations.
- A special spray - epigen, has an antiviral, anti-inflammatory effect, stimulates increased immunity, it is used in local form. Also, a special ointment with identical properties is applied to genital warts.
- It is necessary, in combination with local treatment, to carry out immune-stimulating and antiviral therapy. These could be suppositories for rectal administration against this virus. Genferon stops the reproduction and growth of condylomas. The action of Panavir is similar; it is available in the form of suppositories and ointments. Taking cycloferon stimulates the immune system to fight the disease.
- Also, special drugs for condylomas are taken orally, which increase the level of interferon, for example, isoprinosine. Often, taking this drug stops growth and destroys formations.
Treatment. Electrocoagulation, diathermocoagulation, cryodestruction with liquid nitrogen, solid carbonic acid, lubrication with thuja tincture, application of 5% tebrofen ointment.
For multiple warts - hypnotherapy, burnt magnesia orally (0.5 - 1 g 3 times a day), Fowler's solution (5 drops 3 times a day). For plantar warts, injections with a 1% novocaine solution (2 - 3 ml), surgical excision, and electrophoresis of a 10% novocaine solution are also indicated; for flat warts - lubrication (3 - 7 times) with fresh celandine juice, vitamin B12 intramuscularly, UV irradiation.
Diagnosis code according to ICD-10 • B07
• For flat warts •• Orally magnesium oxide 0.15–0.25 g 3 times a day for 2–3 weeks •• Local keratolytic ointments with salicylic and benzoic acids, tretinoin 2 times a day for 4–6 weeks , phonophoresis with 50% interferon ointment.
The external manifestation of the human papillomavirus is papillomas on the skin. New growths, popularly called warts, are benign in nature. But a seemingly harmless growth can undergo malignancy and transform into a cancerous tumor.
Herpes zoster is a disease that can go away on its own and without complications. But it still brings physical and moral inconvenience, so it is better to consult a doctor at the first manifestation of symptoms. The doctor will be able to reduce pain and itching, burning, and also prevent possible painful consequences and complications.
Is shingles really such a simple disease? If so, what are the consequences of neglecting its appearance?
Viral wart in a child
Principles of treatment
In pediatric dermatology, there is a rule: viral warts that do not bother the child and do not have a risk of malignancy require only active observation.
Such formations can spontaneously regress within two years. It is imperative to treat warts in patients with immunodeficiency conditions to avoid self-infection. Therapy is also indicated if the wart causes itching, pain, creates psychological discomfort, or bleeds. The main method of treating a viral wart in a child remains removal by destruction. An immunologist may prescribe antiviral therapy with interferon drugs.
Physical destruction
For children, this type of therapy is a priority, as it has no toxic side effects. The choice of method depends on the location of the wart, its type, and size. Any of the techniques is performed against the background of local anesthesia (anesthetic cream or infiltrative anesthesia with lidocaine solution):
- Cryodestruction.
The essence of the method is the effect of liquid nitrogen on the proliferation zone. A contact cryoprobe with special attachments is used. Exposure time is up to five minutes. Repeated procedures are carried out if necessary after 1–2 weeks. - Electrocoagulation.
The destruction of a viral wart occurs as a result of the action of a low power electric current. The coagulator provokes layer-by-layer thermal damage to pathological tissue. The technique is bloodless, allowing you to work as accurately as possible in the hearth. - Radiocoagulation.
With this type of destruction, electromagnetic waves are used. Under the influence of radio waves, intercellular connections are broken, the pathological tissue is stratified and destroyed. - Laser destruction.
Wart removal occurs through laser ablation. Depending on the size of the formation, exposure to the beam lasts up to 2-3 minutes. If there is a need for repetition, the next manipulation is carried out after 1 month.
Chemical destruction
The basis of the technique is the application of local agents with a keratolytic effect for the purpose of cytolysis of pathological tissues. Several acids are approved for use in children: salicylic 15-40%, oxalic, acetic, lactic, nitric in various combinations. The treatment regimen depends on the course of the disease. The drug of choice for the treatment of flat warts is creams based on trans-retinoic acid (a form of vitamin A). The course of use is long - up to three months.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is justified if there is a risk of atypical transformation of a viral wart in a child, with a large area of damage. Methods of surgical correction:
- Blunt excision
. To remove the formation, non-sharp surgical instruments are used - specially designed scissors. The method is considered the most effective in children. Has the smallest number of relapses – about 10%. - Curettage.
It involves peeling off a wart with a surgical curette. Efficiency is enhanced by parallel cryodestruction. Curettage is used for medium-sized viral warts. - Excision.
Full surgical treatment with removal of the wart with a scalpel within healthy tissue. The method is traumatic, so it is used when absolutely necessary. Excision is indicated for deep damage to the dermis.