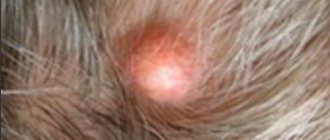
Causes of weeping dermatitis
The causes of weeping dermatitis are divided into several points: distant, close, obligate, selective factors.
Remote factors causing the development of the disease:
- Hereditary factor - dermatitis in infants in 40% of manifestations, occurs due to allergies of one or both parents;
- Predisposition – having once contracted any form of weeping dermatitis, 50% of patients remain sensitive to the disease;
- Low immunity;
- Acute and chronic diseases of internal organs;
Related factors that can trigger the development of the disease:
- Psychological illnesses, prolonged stress, nervousness - very often a strong nervous shock can cause a decrease in the body’s protective functions and, as a result, a decline in immunity.
- The entry of pathogenic substances into the human body - allergens, chemicals that have a detrimental effect on the skin.
- Diseases of the stomach and/or intestines - improper functioning or malfunction of these organs is the most common cause of weeping dermatitis.
Obligate factors (arising under the influence of external factors):
- Pathogenic radiation - radiation, prolonged exposure to direct sunlight;
- Overheating or, on the contrary, hypothermia of the body;
- Contact with chemicals – acid or alkali.
Selective factors:
- Allergy – food (to food or medicine);
- Allergies - to cosmetics, insect bites;
Weeping dermatitis is essentially an advanced stage of any other type of dermatitis (domestic, occupational, fungal, bacterial), in addition to the above, can occur as a result of improperly selected treatment or ignoring the disease.
Causes of venous dermatitis
Varicose eczema is usually caused by increased pressure in the veins of the legs. When the small valves inside the veins stop working, the upward movement of blood against gravity becomes difficult and it leaks back. Because of this, the pressure in the vessels increases, and this leads to the fact that the liquid part of the blood passes through the vascular wall and permeates the surrounding tissues. It is assumed that varicose eczema develops as a result of the immune system's reaction to this fluid.
Venous dermatitis affects people with varicose veins and is a sign that the veins in the lower extremities are not working properly. But in some patients, this condition occurs for no obvious reason. Research shows that 22% of patients with gravitational eczema do not have concomitant varicose veins.
Factors that increase the likelihood of this disease include:
- Gender, varicose dermatitis is more common in women;
- Obesity, which causes increased pressure in the leg veins;
- Pregnancy also increases venous pressure and makes the vascular wall more loose, pliable and permeable to fluid;
- Situations when you have to remain motionless for a long time, which leads to impaired blood circulation;
- Previous deep vein thrombosis is a condition in which blood clots called thrombi form in the veins of the legs. These blood clots damage the valves, which causes the veins to no longer cope with their function:
- Elderly age. As people age, they generally move less, which creates favorable conditions for microcirculation disorders and venous problems.
- Taking certain medications. Thus, drugs that are prescribed for hypertension, such as nifedipine, amlodipine and others with a similar effect, promote swelling and can provoke gravitational dermatitis.
Symptoms of weeping dermatitis
Symptoms of the disease may vary, depending on the age of the patient.
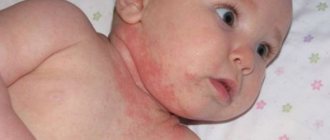
In adults, lesions form in natural folds of the skin, on the face and neck, arms and legs. A rash and erythema (redness) with cloudy contents appear; as the disease progresses, the rash opens, forming weeping erosions.
Common symptoms can be identified for all ages: swelling and redness of the skin at the locations of the lesions, the presence of a rash with cloudy contents.
The disease is characterized by severe itching - its intensity is influenced by the severity of damage to the nerve endings located in the skin; burning and painful sensations, a feeling of dryness or tightness; in addition, a person experiences emotional discomfort, since dermatitis has an unpleasant appearance.
Weeping dermatitis, if not properly treated, can have complications - damage to large areas of the skin, discharge of purulent contents (in cases of infection), and in rare cases, sepsis (blood poisoning) is possible.
You can see what weeping dermatitis looks like in the photo section.
Symptoms of venous dermatitis
As with other types of eczema, with varicose dermatitis the following changes are characteristic of the skin:
- Itching may be the first symptom; it appears unnoticed and gradually progresses, becoming more pronounced at night. Sometimes it is more pronounced on one of the lower extremities.
- Swelling, which is less in the morning, but intensifies in the evening.
- Dryness and flaking;
- Transparent discharge that dries out in the form of crusts. If an infection occurs, the liquid becomes cloudy, purulent, and the drying crusts turn yellow.
These changes primarily affect the inner surface of the ankle, and as the disease progresses, they spread to the foot and lower leg.
On lighter skin, the affected areas appear light brown or pink. In dark-skinned people, the lesion takes on a dark brown or grayish tint and can be difficult to notice. The disease occurs with periods of exacerbation, when symptoms intensify, and remission, when they disappear.
Feet often swell, especially at the end of the day or after periods of standing for a long time. Swelling most often occurs on the lower leg. Varicose veins may also be visible in the form of bluish tubercles and nodules, and spider veins are also characteristic.
Some people also experience these symptoms:
- Change in skin color, which becomes darker, brown, grayish, with a purple tint. This manifestation may appear before all other symptoms.
- The affected surface becomes sensitive and painful when touched.
- When saturated with liquid, the dermis thickens and becomes rougher to the touch; this condition is called lipodermatosclerosis.
- Areas of skin thinning (atrophy) appear that look like thin, whitish scars.
- Pain in the area affected by varicose eczema.
- Plaques and nodules of a purple hue on the legs and tops of the feet, in the place of which painful ulcers form.
- Venous dermatitis is often accompanied by other types of eczema, such as atopic or dyshidrotic.
If varicose eczema is not treated, a trophic ulcer may form on the lower leg. This is a wound that appears in the area of greatest damage to the skin, does not heal on its own, is prone to suppuration and is very difficult to treat. This is facilitated by poor blood supply to tissues compressed by edema.
Cellulite is another complication that develops if treatment is delayed. This is an inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue, which is accompanied by severe swelling, redness, pain, fever and discharge of pus. It occurs when pyogenic bacteria penetrate through damaged skin, and local disruption of microcirculation and decreased immunity contribute to the formation of an infectious focus.
Weeping dermatitis in a child
The occurrence of weeping dermatitis in children is due to the characteristics of the skin; at an early age, the skin does not have the same protective forces as the skin of an adult and is therefore more susceptible to the influence of pathogenic factors. The second reason may be weak immunity; children suffer from respiratory diseases more often than adults, and are more susceptible to the negative effects of external factors than adults.
Signs of the disease in children may vary depending on the age of the child:
Weeping dermatitis in infants often occurs on the bends of the elbows, knees and face, and very rarely occurs on other areas of the skin. Small cracks and ulcers may appear on the dermis; after a few days, crusts form on the affected areas.
In children over three years of age, lesions are localized on the hands, elbows, knees and neck. The skin in the affected areas is inflamed - swollen and acquires a bright red color, cracks and ulcers form, and the course of the disease is long. Subsequently, the skin at the former sites of outbreaks thickens and differs from healthy skin in a dark shade.
In adolescents, the disease proceeds in the same way as in children over three years of age, the only difference is the spontaneous course; there may be a sharp development or an independent decline in symptoms. With a sharp exacerbation of the disease, lesions can occupy large segments of the skin.
In the photo section, you can see what weeping dermatitis looks like in children.
Causes of dry dermatitis
Dry dermatitis, as doctors suggest, is based on a defect in the functioning of the immune system, which is inherited, from parents to children. Because of these features, the skin is much less protected than that of healthy people. The protective layer of fat on the surface becomes thinner, moisture easily evaporates, damage to the epithelium develops, which, together with the inflammatory reaction, gives symptoms of dry dermatitis. This disease can begin at any age, but most often starts in infancy and progresses with some improvement as one gets older. More than half of children with atopy “outgrow” this condition by school age, but exacerbations can, under certain conditions, occur throughout their lives.
Many different provoking factors have been identified, which for some patients play a large role in the formation of symptoms, while for others they do not in any way affect the course of the disease.
- Some products can provoke exacerbations of dry dermatitis. These include cow's milk, chicken eggs, nuts, especially peanuts, soybeans and wheat. Unfortunately, if symptoms have already appeared, simply removing the allergenic product from the diet will not help cope with the exacerbation.
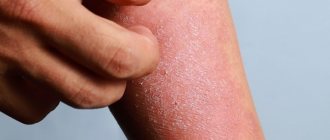
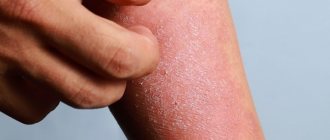
- Dry skin dermatitis can be caused by contact with harsh detergents, which most often appears on the hands; the symptoms can be seen in the photo. Soap washes away the lipid layer from the surface of the epithelium, which normally protects it from water evaporation.
- Dry air also provokes dermatitis, as it promotes evaporation, causing the skin to lose moisture. Damages form on the overdried and inflamed surface of the skin, and dermatitis develops. This often happens in winter when the batteries are running.
- Cold air is also an important risk factor. Firstly, at low temperatures the relative humidity of the air decreases, which promotes evaporation. Secondly, cold and frost, as well as temperature changes, themselves irritate delicate skin, destroy the protective functions of sebum, cause damage and inflammation. In winter, during the cold season, dry dermatitis often develops on the face, head, arms and legs - those areas of the body that are in more contact with the environment (see photo), and its treatment should consist of restoring the barrier role of the skin and protecting it from aggressive temperature. The condition is further aggravated by the fact that heating devices are actively operating in the premises, which contributes to even greater loss of fluid.
- Mechanical irritation of the skin contributes to the development of dry eczema. The reason may be tight cuffs and collar, uncut labels, rough seams that rub and damage the skin surface. The quality of the fabric itself is also important. Thus, itchy woolen items can cause severe aggravation of dermatitis, and synthetic fabrics have both an irritating and allergenic effect.
- If eczema in children does not always take the form of dry dermatitis, then with age the skin’s ability to produce sebum decreases, the function of the sebaceous glands is insufficient, and asteatosis develops. Therefore, the tendency to dry dermatitis increases significantly in older people.
Treatment of weeping dermatitis
Before starting treatment, it is necessary to conduct a diagnosis. Diagnosis is very important, since weeping dermatitis has a similar clinical picture to eczema; this is usually not difficult for a specialist, but for an accurate diagnosis, the specialist conducts the following studies:
- Scraping - to exclude other skin diseases and identify the possible causative agent of the disease;
- Tests to identify allergies and the source of allergies;
- A general blood and urine test is used to determine the cause of dermatitis and identify concomitant diseases.
Often, treatment involves complex therapy, which is aimed at eliminating the cause of weeping dermatitis and relieving the symptoms characteristic of it.
- Antihistamines (anti-allergic) drugs to relieve itching and swelling of tissues;
- Sometimes sorbents may be indicated (if dermatitis occurs due to allergies);
- Prebiotics to normalize intestinal microflora;
- Antibiotics - in case of secondary infection (when scratching, often in children)
- Local preparations for eliminating the inflammatory process, relieving the sensation of itching and for rapid tissue regeneration; a popular drug that copes with these purposes is Losterin.
- Antiseptic solutions are used to treat lesions when opening pustules (rashes).
- Severe itching can cause sleep disturbances and affect mental health, in these cases sedatives are indicated.
In addition to medications, it is recommended to follow a diet; this is one of the factors contributing to a rapid recovery. The diet involves eliminating foods that can cause allergic reactions (citrus fruits, nuts, honey, etc.).
For weeping dermatitis in infants, special attention is paid to correcting nutrition and following the mother’s diet if she is breastfeeding.
When weeping dermatitis passes into the chronic stage, medications are indicated to raise and strengthen the immune system.
Self-medication in this case is unacceptable, especially in relation to the treatment of children. The doctor prescribes medications based on test results and taking into account the characteristics of the body.
Dermatitis on legs
Venous dermatitis on the legs
Varicose dermatitis on the lower legs occurs as a result of trophic disorders.
It develops against the background of chronic uncompensated lymphovenous insufficiency.
Women suffer from this pathology 3 times more often than men.
Pathology usually occurs after 40 years.
Venous dermatitis often occurs on the legs during pregnancy.
This is due to an increase in the volume of circulating blood and a decrease in the tone of the veins due to hormonal changes.
The pregnancy hormone progesterone increases the permeability and distensibility of the venous wall.
Which leads to varicose veins and deterioration of blood supply to the skin of the lower extremities.
Varicose eczematous dermatitis on the legs does not develop instantly.
If the cause is not thrombosis or injury, and the pathology occurs against the background of varicose veins, then this process lasts for years.
Its appearance is promoted by venous stagnation.
Initially, signs of skin thickening appear, hair falls out, and swelling is observed.
Only after some time does stasis dermatitis occur.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers dilated veins.
The skin is atrophic, dry, thin, hyperpigmented.
Varicose eczema can spread to other parts of the body as the body becomes sensitized.
White plaques may appear on the skin.
Against their background, varicose ulcers develop - they are very painful.
In vascular dermatitis on the legs, the subcutaneous tissue is thickened.
Against this background, warty growths of the epidermis are possible.
Dry dermatitis on legs
Older people often develop dry dermatitis.
At risk are men over 65 years of age.
Pathology most often occurs in the winter season, while remission is observed in the summer.
The main localization of this type of dermatitis is the lower legs.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers dry skin.
Peeling is possible.
The disease has a chronic, long-term course.
The inflammatory process can last from several weeks to several months.
Very often, the disease develops against the background of constant degreasing of the skin - regular washing with soap.
Dry warm air also contributes to dry dermatitis.
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, older people should avoid frequent use of soap.
You should bathe more often in the shower rather than in the bath.
And also maintain the air humidity in the room where they spend most of their time at a level of at least 50%.
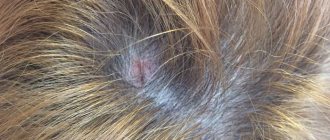
Seborrheic dermatitis on the legs
Seborrheic dermatitis occurs in areas where there is hair.
There are quite a lot of them on the legs, so the lower limbs are at risk.
Pathology can occur in people of any age, including children.
Men get sick more often.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not genetically transmitted, but there is a hereditary predisposition to it.
This disease is chronic with an undulating clinical course.
Periods of exacerbation and remission follow each other.
Usually there is an improvement in the summer, and an exacerbation in the fall.
People who suffer from seborrheic dermatitis are better off wearing shorts rather than trousers in the warmer months.
Because ultraviolet rays reduce the manifestations of the disease and prevent exacerbations.
Typically, the rash elements of seborrheic dermatitis look like greasy or dry patches with peeling.
These can also be large papules measuring 1-2 cm, with clear boundaries.
It may become wet and cracks may appear.
Infectious dermatitis on the legs
Sometimes skin inflammation is caused by infections.
The causative agents can be fungi, bacteria, viruses.
Frequent causative agents of skin infections are staphylococci and streptococci.
Infectious dermatitis may be accompanied by suppuration.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers:
- purulent crusts;
- continuous arrangement of morphological elements of the skin without layers of healthy skin;
- increase in lesions along the periphery;
- the presence of single papules or pustules around the main focus of infection.
There are a wide variety of infections that can affect the skin.
In each case, the symptoms will be different.
How to treat dermatitis on the legs
Treatment for dermatitis on the legs can vary depending on the type of disease.
Acute simple contact dermatitis (the result of a chemical burn) usually goes away on its own.
Treatment is not required - the manifestations of the disease disappear without any residual effects.
But in severe clinical cases, medical assistance may be needed.
It consists of treating the affected skin with antiseptic solutions.
This is required to prevent the addition of bacterial inflammation.
If there are large bubbles, they are punctured, but the tire is not removed.
To reduce symptoms - pain, itching, burning, swelling - weak local glucocorticoids are prescribed.
For severe inflammation, oral corticosteroids are prescribed.
For acute allergic dermatitis, the treatment is similar.
It is important to identify the allergen and avoid contact of the skin of the feet with it.
In cases of subacute or chronic allergic dermatitis, ointments with potent glucocorticoids are prescribed.
Oral corticosteroids may be used.
With atopic dermatitis, the main goal of treatment is to avoid further scratching of the skin.
Lotions with camphor or menthol help relieve itching.
These drugs have a distracting effect.
In the acute stage, ointments with corticosteroids are used to treat atopic dermatitis.
To prevent the addition of a secondary bacterial infection, use local medications with antibiotics.
For severe itching, take oral antihistamines.
When a secondary bacterial infection occurs, antibiotic tablets are prescribed.
It is possible to use intestinal sorbents internally to remove toxic metabolic products.
In the treatment of cold dermatitis, plasmapheresis is used to cleanse the blood of circulating immunoglobulins.
For kidney damage, cyclophosphamide is prescribed.
For inflammation of the skin and joints, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are indicated.
Treatment of venous dermatitis on the legs is carried out with the help of hormonal drugs.
Triamcinolone is administered locally.
It is important to avoid injury to the affected areas.
Treatment of the underlying disease – varicose veins – is required.
Sclerotherapy or surgery can be used for this.
Before radical treatment, a person wears tight bandages for the treatment of blood vessels or compression stockings, and takes venotonics (diosmin).
In the treatment of dry dermatitis, effective ointments containing vegetable oils are used.
You should install a humidifier in the bedroom.
You can take warm baths with added oils.
Foretal cream gives good results.
In cases of severe inflammation, corticosteroids of moderate strength are used.
They are used 2 times a day.
Hormones are canceled after the cracks in the skin disappear.
In the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis on the legs, drug and non-drug methods are used, depending on the severity of the pathology.
The patient is advised to spend more time in the sun.
Irradiation with an ultraviolet lamp can be carried out.
When a fungal process is attached, creams with ketoconazole are used.
Corticosteroid ointments (hydrocortisone) 2 times a day may be prescribed.
For maintenance therapy, 2% salicylic acid is used.
Non-hormonal cream Naftaderm is used.
Hydrocortisone may also be prescribed for maintenance treatment.
But in this case, regular medical examinations are required in order to promptly identify signs of incipient skin atrophy.
In the case of infectious dermatitis, identification of the pathogen is required
Then treatment is carried out with antibiotics, antimiotics or antiviral drugs.
The lesion is treated with antiseptic solutions.
For suppuration, broad-spectrum antibiotics (erythromycin, ceftriaxone, etc.) are indicated.
Alternative treatment for dermatitis on the legs
Some patients try to treat at home with folk remedies.
This approach is doomed to failure.
In folk medicine, all dermatitis is treated with the same means - without any diagnosis.
In addition, all the recipes used are ineffective.
In the best case, a person will be lucky and the dermatitis will go away on its own.
At worst, complications will arise as a result of an allergy to folk remedies or the spread of an infectious process.
Many dermatitis are dangerous to human health and life.
Therefore, treatment should only be done by a doctor.
What tests should I take?
It is not always possible for a doctor to clinically determine the origin of dermatitis.
After all, many inflammatory processes have similar external manifestations.
Therefore, tests are often required for dermatitis.
Basic laboratory tests that are used:
- Skin patch tests with allergens - to confirm allergic contact dermatitis.
- Allergic blood tests for immunoglobulins E.
- Scraping for fungus.
- Culture for infections.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Skin biopsy.
- Doppler testing of blood vessels for suspected varicose veins.
Which doctor should I contact?
If signs of dermatitis appear, you should consult a dermatologist or dermatovenerologist.
This specialist deals with skin diseases.
Good dermatologists work in our clinic.
You can contact one of them.
The doctor will find out the cause of dermatitis, its origin, and conduct targeted therapy.
It will be aimed not only at eliminating the symptoms of pathology.
But also to eliminate the main pathogenetic and etiological factors that led to inflammation.
This is required to ensure that dermatitis does not return in the future after treatment is completed.
If dermatitis appears on your legs, contact the author of this article, a dermatologist in Moscow with 15 years of experience.
Treatment of weeping dermatitis with folk remedies
Traditional medicine has many recipes to combat various dermatological pathologies. Methods of therapy may include tinctures, lotions, ointments, etc., based on herbs or other natural ingredients, but these remedies are ineffective or not effective at all. Herbal medicine can relieve some symptoms, but will not have a detrimental effect on the cause of dermatitis, and in some cases it will worsen the disease. Some traditional medicines can be used as an addition to the main treatment and should only be reported to a doctor. You should not prescribe any folk remedies yourself, especially if a child needs help.
Types of dry dermatitis
On the legs, the disease occupies the area of the legs and ankles. Several factors influence this. These areas often experience reduced blood flow and venous congestion. The cold often affects ankles, which are rarely adequately insulated. Mechanical rubbing of the area with the elastic bands of socks also plays a role.
On the hands, the pathological process is expressed on the dorsum of the hands. This is due to the fact that hands are often washed with soap, which dissolves sebum, thereby depriving the skin of adequate lipid protection. Moisture evaporates, the epithelium dries out, and symptoms of dermatitis develop. Hands are also often exposed to cold, frost and dry air, as they are not protected by clothing.
On the head, the cause of dry dermatitis can be a disruption in the functioning of the sebaceous glands, when excess sebum is produced, but instead of protecting the skin, it has an irritating effect, causing redness of the skin, itching and severe flaking, when numerous skin scales fall off on the patient’s clothes, they can be very noticeable, and this also affects social life.
Treatment of weeping dermatitis with Losterin
Improper skin care for dermatological diseases slows down recovery, so it is important to choose products suitable for problem skin that do not dry out, but at the same time cleanse. A common product is Losterin gel for showering or Losterin cream for skin care. Thanks to its composition, it protects the skin from dryness and cracks, helps reduce flaking and has a regenerating effect. Used for the treatment and prevention of weeping dermatitis.
Symptoms of infectious dermatitis
Manifestations of skin disease directly depend on the underlying pathology, including:
- diabetes;
- decreased immunity;
- regular stress;
- chicken pox;
- measles;
- atopic dermatitis suffered in childhood.
Infectious dermatitis is characterized by skin rashes, itching, peeling, redness, and swelling. In some diseases, it is accompanied by elevated body temperature, fever and fever.
These symptoms are provoked by household chemicals, uncomfortable tight shoes made of artificial materials, food, and medications. At risk are children, elderly people, smokers and alcohol addicts, as well as those who suffer from allergic diseases, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous system and respiratory organs.
Prevention of weeping dermatitis
It is easier to prevent any disease than to treat it, tinea versicolor is no exception, in order to avoid the development of the disease you should:
- Adhere to the rules of proper nutrition - to prevent diseases of the stomach and intestines;
- Treat acute and chronic diseases - they are often the main cause of reduced immunity;
- Maintain immunity, especially after illnesses, in the autumn-spring period, after long-term use of strong medications;
- For people prone to allergies, exclude allergens;
- Avoid stress, maintain psychological health, and consult a specialist if necessary.
If dermatitis does appear, then for a quick recovery and to prevent recurrence of the disease, you should:
- Follow the recommendations of your doctor, do not interrupt or stop treatment without consulting a doctor;
- Compliance with hygiene rules, proper treatment of affected skin areas;
- Avoid sources that provoke allergies.
Exclude pathogenic factors.
If symptoms indicating weeping dermatitis appear, you should immediately consult a doctor, this will allow you to start treatment on time, which will have a beneficial effect on the duration of therapy and reduce the risk of developing negative consequences and relapses.
Causes of itchy dermatitis
It is not known exactly what causes prurigo, or why the skin reacts the way it does. Once itching occurs, rubbing and scratching makes the nerve endings in the dermis thicker and even more susceptible to irritation. This leads to more itching, thus making the condition worse.
In half of the patients, the exact cause cannot be detected, but there are some combinations of diseases that may be related.
- Up to 80% of patients with pruritic dermatitis are also prone to atopy, and may have conditions such as asthma, eczema and seasonal pollen allergies.
- Prurigo nodosa also develops in people with venous eczema (a condition where skin lesions occur due to venous blood pooling in the legs), and may be associated with nummular eczema (which is characterized by a well-defined, coin-shaped rash).
- In some people, nodular prurigo may begin after an insect bite,
- Several diseases may be associated with nodular prurigo, which must be excluded when pruritic dermatitis appears. This is bullous pemphigoid, in which blisters filled with fluid appear on the skin, like after a burn. Dermatitis herpetiformis is characterized by small, round blisters and is a symptom of gluten intolerance.
In 30% of patients, pruritic dermatitis develops as a consequence of a systemic disease, and metabolic and biochemical causes play a role.
- Nutrient deficiency. Here, iron deficiency comes to the fore, which may be associated with a lack of this microelement in food, increased losses (in women with menstruation), or poor absorption in the intestine (with gluten intolerance, after removal of a section of the intestine).
- liver disease,
- Uremia (a condition that develops with kidney failure),
- Severe diabetes mellitus.
Less common causes include thyroid disease, stroke, calcium metabolism disorders, and lymphoma (blood disease).
For the remaining 20%, psychological factors such as depression, anxiety and psychosis play a role. But even ordinary emotional stress can become a trigger. When under stress, people are more prone to scratching the epithelium. Thus, stress worsens the course of prurigo.