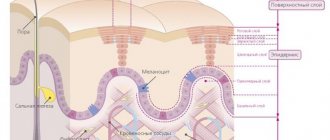
When it comes to the uniqueness of each individual person, we mean not only the details of appearance, the originality of the pattern of lines on the palms, but also the characteristics of the skin. Did you know that the structure, color shade and phototype of the skin is unique? It depends on the combination of genes from both parents, as well as non-standard combinations formed when germ cells join. Human skin is determined by genetics, and will have its qualities throughout life, regardless of what external influence is exerted on the integument.
How to determine your phototype
It is quite easy to determine the phototype of your skin, using the generally accepted classification, which is a synthesis of the scales of two authors: one proposed by Fitzpatrick, and the second by Harold F. Lancer. There are six phototypes in total, the first four of which are characteristic of the population of Europe, as well as of Russia.
So, to determine which phototype your skin belongs to, we suggest answering a few questions:
- What color are your eyes?
- Light
- Blue, gray, green
- Dark
- Brown
- Black
- What is your skin color?
- Pink
- Pale
- Beige
- Brown
- Dark brown
- What kind of hair do you have?
- Ginger
- Blonde or light brown
- Chestnut or light brown
- Dark blond or brown
- Black
- Do you have freckles on your face and body?
- Quite a lot all over the body
- Small amount on face and body
- Very little on the face
- Virtually none
- Not at all
- What happens to your skin after prolonged exposure to the sun?
- Painful blisters and peeling skin
- Painless blisters and peeling skin
- Mild peeling, burning
- Unpleasant sensations are rare
- No burns and/or peeling
- How does your skin tan?
- Never tans
- In rare cases
- Sometimes
- Often
- Always
- How tan does your skin get?
- Doesn't become
- Slightly tanned
- Well tanned
- Very tanned
- Very dark
Skin phototypes according to Fitzpatrick
Dermatologist Thomas Fitzpatrick is called the father of modern dermatology. He was one of the first to study malignant melanoma and its dependence on ultraviolet radiation and sunburn of the skin. In 1975, a doctor developed a scale of skin types based on the level of sensitivity to ultraviolet light - what we call Fitzpatrick skin phototypes.
How many Fitzpatrick skin types are there and what are the features of each of them? There are 6 phototypes in total. Let's look at their detailed description from lightest (the skin produces little melanin) to darkest (high levels of melanin).
Celtic skin type
Skin: very light, milky white or pinkish beige with freckles.
Hair: very light or red.
Eyes: often blue, gray or green.
Location: Celtic (Scandinavian) skin type is found mainly among people from Great Britain and northern Europe.
Reaction to ultraviolet radiation: the skin does not tan, there is a high risk of sunburn and hyperpigmentation, there is a tendency to photoaging.
Recommendations: Avoid direct sunlight or use sunscreen with a high protection factor (SPF 50 or higher). When the sun is inactive (in winter or in cloudy weather) without adequate protection, it is permissible to stay in the air for up to 67 minutes, under the scorching sun - only 5-7 minutes.
Nordic skin type
Skin: light, sometimes freckled
Hair: light blond, blond, light brown.
Eyes: blue, gray, green.
Location: the Nordic phototype can often be found among the inhabitants of the central and northern parts of the European continent.
Reaction to ultraviolet radiation: the skin becomes slightly tanned, which fades quickly, there is a high risk of sunburn, and there is a tendency to photoaging.
Recommendations: sunscreen with SPF 30-50. Without SPF products, it is safe to stay in the inactive sun for up to 100 minutes, and in the active sun for up to 10 minutes.
Dark European skin type
Skin: darkish or ivory.
Hair: from dark blond to light or dark brown
Eyes: light brown, hazel
Location: the dark European type in some sources is called Central European, since the owners of this phototype live in the central part of the European continent.
Reaction to ultraviolet radiation: the skin is well covered with a lasting tan, the risk of sunburn is low, and there is a tendency to photoaging.
Recommendations: sunscreen with SPF 30. Without protection, it is safe to be under the inactive sun for no more than 200 minutes, with high solar activity - up to 20 minutes.
Mediterranean skin type
Skin: dark.
Hair: brown, dark brown.
Eyes: brown, black.
Location: owners of the Mediterranean phototype live in the south of Europe, Asia, South America and the Caucasus region.
Reaction to ultraviolet light: the skin tans very well, but is prone to photoaging, the risk of sunburn is minimal.
Recommendations: sunscreen with SPF 20-30. Without protection, you can stay under the inactive sun for up to 300 minutes, with active solar radiation - up to 30 minutes.
Indonesian skin type
Skin: yellowish, brown.
Hair: dark brown, black.
Eyes: brown or black.
Location: the Indonesian phototype is typical for residents of the south and east of the Asian continent.
Reaction to ultraviolet light: the skin tans easily, the risk of sunburn is extremely low, there is a tendency to photoaging.
Recommendations: sunscreen with SPF 10-20. It is safe to stay under the inactive sun for 400 minutes; during peak solar activity, it is better to reduce your exposure to direct rays to 40 minutes.
African American skin type
Skin: very dark.
Hair: dark brown, black.
Eyes: brown, black.
Location: African-American (African) skin phototype is typical for the population of Africa, America and the indigenous people of Australia.
Reaction to ultraviolet light: tanning matches the natural skin tone, the risk of sunburn tends to zero, photoaging is possible.
Recommendations: it is permissible to do without special sunscreens, provided that the exposure time is reasonable. When the sun is inactive, it is safe to stay outside for about 500 minutes, and with high solar activity - 50 minutes.
Phototypes: cheat sheet
| Skin type | Phototype | Ethnic scale |
| I | Prone to burns when tanning, does not acquire a bronze tint, and does not tan at all | Irish, Scots |
| II | Characterized by the occurrence of sunburn and the difficulty of obtaining a tan. Owners of this type of skin | central Europeans |
| III | It may succumb to the negative effects of the sun and become covered in blisters, but it is extremely rare. As a rule, the skin easily gets a golden tan, and after a while it becomes dark. | Italians, Portuguese |
| IV | Virtually no burns, quickly acquires an even, attractive tan | Natural olive or yellow skin tone (Hispanics, fair Hispanics) |
| V | It is distinguished by its natural dark complexion. Has a brown tint. Suitable for quick and easy tanning | Natural dark, brown skin (East Indian) |
| VI | Natural black leather | Naturally black leather |
Having correctly determined your phototype, you can more intelligently approach the choice of decorative cosmetics, as well as care products and protective products that protect the skin from burns. Also, having information about your phototype, you can avoid mistakes that arise when carrying out a number of procedures (laser rejuvenation, cosmetic procedures, etc.).
A professional cosmetologist at the Abrielle Aesthetic Surgery Clinic can choose the right skin care for your phototype. To schedule a consultation, call the clinic and 8(921)99-22-335.
Application in cosmetology
In addition to the features of care and sun protection, phototypes are taken into account when using a variety of light cosmetology techniques, primarily laser. The action of pulsed light with a certain wavelength, that is, a laser, is used by cosmetologists for cleansing, lifting, and hair removal. Before using such techniques, the cosmetologist must take into account the skin phototype.
Incorrectly selected laser beam power can lead to burns.
35+ points
Skin type VI (“African”)
Dark brown or black leather. The sixth phototype is characteristic of people from the African continent and the aborigines of Australia. Natural skin protection against UV exposure can be considered ideal, since it allows you to constantly be exposed to direct rays of the sun without any damage.
If you score 13 points or less, you have fragile beauty and are at risk for developing melanoma. Things are a little better for the “European dark” (III) type. It is this phototype that predominates in Russia from Kaliningrad to Kamchatka. The incidence of skin cancer, scientifically called melanoma, has doubled in Russia over the past decades.
The incidence of skin cancer among representatives of phototypes IV, V and VI has not changed for decades. Among the indigenous population of Russia, these phototypes are rare. The number of mulattoes does not exceed 0.5% of the population of the Russian Federation, but we will also voice recommendations for them.
Fitzpatrick classification
There are many gradations and systems that define the so-called “skin passport”. One of the most convenient and widespread of them is the classification of the famous American dermatologist Thomas B. Fitzpatrick, developed in 1975. His scale divides all people into 6 categories depending on the saturation of the dermis with melanin and its reaction to the action of ultraviolet radiation. In addition to natural skin color, the Fitzpatrick phototype takes into account hair and eye color .
Differences in male and female skin
Men and women have different skin, different problems associated with it, and, as a result, their care secrets are also different. And all this follows from biologically inherent differences in the structure of the skin.
Well, everyone has their secrets. In order to know how to preserve your beauty longer, let's consider a few key points.
Sensitivity
Even though men's skin is thicker than women's, it is more sensitive. This is directly related to the effects the skin undergoes. Environmental impact due to the specifics of the work (we are talking about professions that involve physical activity), shaving stubble - all this destroys the hydrolipid layer of the skin. But if we consider the vulnerability of the skin in terms of reaction to ultraviolet rays, then women's skin is more sensitive.
The structure of the skin largely depends on the activity of the sebaceous glands. In women's skin, estrogen is responsible for controlling them, and this causes less oil to be produced. Therefore, men's skin is naturally oilier.
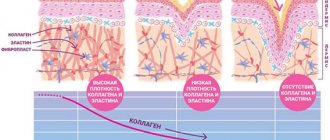
Estrogen and collagen are responsible for the strength and elasticity of the skin. On average, skin thins by 1% over the course of a year. Due to the fact that after menopause, women undergo a complete restructuring of their bodies, they often look older than men. Moreover, the reaction to the sun's rays also increases with age, so protective measures should become stronger from year to year.
Upon reaching the age of 50, men have an increased risk of developing melanoma compared to women. This is primarily due to the rhythm of life - they spend more time outside, and their skin is more exposed to ultraviolet rays. This is also directly related to the fact that men use protective equipment much less often than women. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly visit a dermatologist and monitor any new growths that appear on the skin.
Cosmetics and procedures
Cosmetics created to combat the signs of skin aging are different for men and women because there are significant differences in the functional and chemical composition. Therefore, it is better not to use universal products, but to select them together with a specialist and based on your skin type and phototype.
There is no clear answer to the question of what ultraviolet rays bring more benefit or harm. Those who excessively sunbathe, especially at an advanced age, increase the risk of melanoma. But at the same time, a lack of sunny color can result in a low level of vitamin D in the body, which can lead to increased fatigue and even become a prerequisite for the formation of a depressive state. Moreover, then the consequences will be sad for both men and women.
The truth is that everything should be in moderation, within reasonable limits. If you exceed the norm for sun exposure or visit the solarium too often, you can get a burn, which can have serious consequences not only for the condition of the skin, but also for the entire body. But you shouldn’t avoid sunlight either, since nature itself has provided for everything.
Heliotherapy (sunlight treatment)
The mentality stipulates that women visit the solarium more often than men. And not the least role in this is played by the deep-rooted stereotype about the harmful effects of solarium on the body (men are not afraid of the risk associated with the release of adrenaline into the blood, but they are always very afraid of getting sick). Women, on the contrary, over the centuries have formed the habit of living according to the principle: “Beauty requires sacrifice” - this explains everything.
And despite all this, heliotherapy affects the body of men and women absolutely equally
Ultraviolet rays (whether live or artificial) provoke the production of melanin in the skin, which affects the change in skin tone. Moreover, even in terms of tanning intensity, there are virtually no differences between male and female skin, although the chemical composition is somewhat different
Be careful! Possible contraindications:
Prohibitions on visiting a solarium or the beach may be associated solely with the presence of some personal medical contraindications, but they do not depend on gender. For women, however, this list is still longer: in addition to dysfunction of the thyroid gland, this also includes cysts, polyps, fibroids and mastopathy.