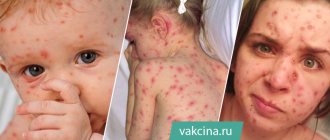
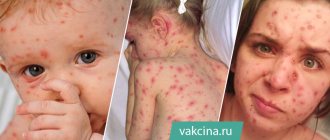
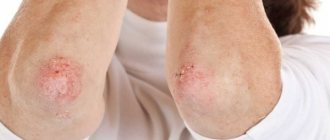
Furunculosis – a disease manifested in the appearance on the skin of two or more foci of purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. These lesions are called “boils”. Furunculosis in children requires special attention from adults, and before using any treatment (especially antibiotics), the exact causes of the disease should be determined. In addition, not all treatment methods can be applied in pediatrics.
Boils are formed as a result of penetration of golden (sometimes white) staphylococcus into the hair follicle and sebaceous gland. Furunculosis is an unpleasant and quite dangerous disease, especially when this problem occurs in a child, and pustules appear on the face or in the neck area.
Description of the disease
Boils can occur in both young children and adolescents. Today they are the most common purulent skin lesion. Inflammation can affect any area where there are hair follicles. Most often, boils appear on the child’s head and neck, less often on the body (in the groin, on the back or stomach, under the armpit), on the legs and arms. The main feature of the course of this pathology in children is the high risk of inflammation spreading to neighboring tissues and structures, as well as its spread through the bloodstream, leading to the development of dangerous complications.
Price
Allergology-immunology
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an allergist-immunologist, primary | 3 500 ₽ |
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
Furunculosis is a purulent-necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and surrounding subcutaneous fat. Formed on the hairy parts of the skin. The causative agent of the infection is usually Staphylococcus aureus.
Furunculosis is more common in people with weakened immune systems, adolescents and adults. Furunculosis is rare in children and the elderly. The disease affects men more than women. Unsanitary living conditions increase the risk of infection.
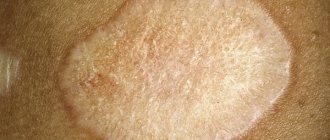
Boils may disappear without any treatment. Sometimes they burst on their own and heal without a trace within 2 days to 3 weeks. However, after healing, they can lead to a complication of furunculosis such as scars. If the abscess is accompanied by fever, pain and other symptoms that affect well-being, the person should seek medical help.
Three or more episodes within 12 months are defined as recurrent furunculosis. In this case, you should also consult a doctor, even if the boils tend to heal on their own.
Causes of boils in children
Most often, inflammation develops due to tissue damage by Staphylococcus aureus, less often the causative agent is other groups of staphylococci or streptococci. All of them are on the skin almost constantly, but in a normal state of immunity they cannot cause disease. The pathological process starts when exposed to certain unfavorable factors:
- wounds, scratches on the skin;
- skin diseases (eczema, atopic dermatitis);
- decreased immunity due to acute respiratory viral infections, operations, injuries, exacerbation of chronic diseases);
- congenital immunodeficiency conditions;
- diabetes mellitus and metabolic disorders (often cause the constant appearance of boils in a child);
- chronic infections: tuberculosis, pyelonephritis, sinusitis, etc.
Consultations with other specialists
Contacting specialists in various fields of medicine is necessary, since boils of bacterial origin (staphylococcus) can provoke:
- formation of a focus of chronic infection (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis);
- diseases and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract (cholecystitis, dysbacteriosis, etc.).
The formation of boils may indicate a urinary tract infection, iron deficiency anemia, immune diseases, or the presence of a latent infection (herpes, cytomegalovirus infection).
Pathogenesis and stages of development
During the development process, the boil goes through three successive stages:
- initial (infiltration): the inflammatory process begins at the mouth of the follicle and gradually spreads;
- necrotic (maturation): inflammation engulfs the entire cavity of the follicle, causing necrosis and purulent melting of tissue; the process lasts from several days to 2 weeks and ends with a rupture of the skin over the center of the boil;
- healing stage: after the pus has drained and the cavity of the lesion has been cleaned, it gradually scars with the formation of a scar.
Symptoms of a boil in a child
The main symptoms of a boil in a one-year-old child, preschool and school-age children are the same and depend on the stage of development of the disease.
At the initial stage, an area of redness appears on the skin, which gradually increases, but practically does not cause discomfort. As the pathology progresses, a purulent area appears in the center of the lesion, and the area of inflammation increases in size and becomes sharply painful. Then a necrotic rod is formed inside the cavity, which from the outside looks like a dark dot in the very center of the boil. After a few days, the abscess breaks through, its contents come out, after which the healing process begins. A small boil, especially if it is located on a child's hand, foot or finger, rarely causes general symptoms. With multiple inflammatory foci, as well as when localized in an area with a large number of blood and lymphatic vessels (face, neck, groin, armpits), the baby may have a fever, weakness, malaise and other signs of general intoxication.
Symptoms of furunculosis
Boils are red, swollen, and painful nodules of varying sizes. The larger they become, the more painful the sensation. The surrounding skin is usually red and inflamed. The nodules quickly fill with pus and may burst at the last stage of furunculosis. If several adjacent follicles are infected, they may grow together and form a larger nodule called a carbuncle. A carbuncle is a collection of boils.
Fever and swollen lymph nodes with furunculosis are rare, but possible.
Boils and carbuncles usually affect the thighs, armpits, buttocks, face and neck. They occur in areas prone to hair formation, sweat and friction.
Diagnosis of boils in children
Diagnosis and treatment of boils in children is carried out by a dermatologist, often requiring the help of a surgeon and/or otolaryngologist. Making a diagnosis is not difficult, since the formation is clearly visible during a routine examination. If boils appear in a child too often and/or in large numbers, a more detailed examination is required to clarify the cause of this condition. Depending on the situation, the following is prescribed:
- microscopy and bacterial culture of the abscess contents;
- general and biochemical blood test;
- glucose tolerance test for suspected diabetes mellitus;
- study of the state of immunity;
- Ultrasound of internal organs, examination of the nasal cavity and sinuses, chest x-ray and other studies aimed at searching for chronic foci of inflammation.
Pediatric doctors of other specialties often join the examination: endocrinologists, pulmonologists, gastroenterologists and immunologists.
In addition, if you suspect the development of a boil, it is imperative to involve a pediatric surgeon in the diagnosis. His intervention will help to promptly notice the formation of an abscess and take the necessary measures (opening the abscess, washing the cavity, bandaging).
What is paronychia and how does it differ from felon?
In short, felon is a general medical name for various types of purulent inflammation of the tissues of the hands and feet. These inflammations can have different localizations on the affected limb, being cutaneous, subcutaneous, articular and even bone. Paronychia is a special case of panaritium: it is an inflammation of the tissue around the nail plate. Sometimes paronychia is called periungual felon. Paronychia in children occurs mainly as a result of mechanical trauma. It can happen during a manicure or pedicure, or while playing - a child can injure the skin near the nail or plant a splinter, get burned, or spend some time in tight, uncomfortable shoes. The child may unsuccessfully bite or tear off an interfering hangnail or bite his nails. Of course, the wound itself does not necessarily lead to tissue inflammation. Therefore, any cuts and punctures of the skin should be treated with an antiseptic as soon as possible. But if an infection gets into the wound, the tissues turn red, swell, and later pus may appear - these are already manifestations of paronychia. Less commonly, it happens that paronychia is not preceded by trauma. In adult patients, the cause is most often a fungus, in children - staphylococcus and streptococcus. In general, children suffer from paronychia more often than adults because they are more likely to be injured and have poor hygiene.
Treatment of boils in children
If the child’s boil is small in size and is not located on the face, neck or knee, treatment at home is allowed. In case of extensive lesions or multiple purulent foci, hospitalization is required.
With a relatively mild course of the disease, conservative treatment is sufficient, which depends on the stage of development of the disease:
- at the initial stage, alcohol solutions and dry heat are used to accelerate ripening;
- at the necrotic stage, antibacterial agents, proteolytic drugs and regular wound washing are necessary;
- at the healing stage, agents are used that accelerate regeneration in combination with antibacterial treatment.
In more severe cases, local treatment is supplemented with systemic drugs: antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs, immunostimulants, etc. If the infection spreads to adjacent tissues with the development of abscesses or phlegmons, surgical assistance is required: opening and draining the abscess.
Prevention of furunculosis
Ways to prevent the disease include:
- keeping skin clean by washing regularly;
- immediate disinfection of all skin wounds, cuts and abrasions, even the smallest ones;
- Cover any cuts with a sterile dressing to prevent infection.
Eating a healthy, balanced diet and regular exercise will improve your overall health and immune system, reducing the risk of developing not only furunculosis, but all diseases in general.
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Prognosis and prevention
Single boils that occur without complications completely disappear within 2-3 weeks.
With relatively frequent relapses (exacerbations once a year or more often), the likelihood of complications is much higher. In this case, regular monitoring, immunostimulating procedures, and treatment of underlying diseases are required. Prevention of the development of boils in children includes careful skin care, regular hardening and strengthening of the immune system, timely treatment of acute and chronic diseases.
A boil is not just a pimple. An abscess can cause severe complications, including sepsis and meningitis, which is why any such formation on the body of a child or teenager requires careful monitoring. The specialists of the SM-Doctor clinic will select the optimal method of treating and preventing this problem.
Which doctor should I make an appointment with if my child has an inflamed finger?
If you have recently discovered inflammation around your child's nail, it makes sense to first make an appointment with your pediatrician. In children, paronychia often causes not only local pain and discomfort, but also a general deterioration in well-being: fever, tearfulness and moodiness from a constant irritant, sleep disturbances. You may even experience weakness and nausea. All these are consequences of intoxication. Therefore, you need to contact your pediatrician as soon as possible. If you leave it too long, there is a chance that the infection will affect the nail, and then it may even have to be removed - partially or completely. After examining the finger, a competent pediatrician will either prescribe conservative therapy for local treatment of the damaged area, or, if the infection has already developed to a purulent stage, refer the little patient to a specialist - a pediatric surgeon. If you find pus on your own, you can immediately make an appointment at a children's clinic directly with a surgeon, bypassing the pediatrician.