March 24, 2021
Atopic dermatitis is quite common, with an average of 1 in 12 people suffering from it. It is impossible to completely cure dermatitis, so treatment usually comes down to daily care that maintains a state of remission. Let's look at how to care for dermatitis so that there are no relapses.
Seeing a doctor
Dermatological diseases are varied and insidious, and sometimes without a specialist’s opinion and tests it is impossible to make an accurate diagnosis. If you have not been to a doctor before, then if red rashes, peeling or itching appear, it is better to immediately make an appointment with a dermatologist. Do not self-diagnose, and certainly do not prescribe treatment based on a diagnosis you made yourself. Thus, care for allergic dermatitis is fundamentally different from the treatment of psoriasis, and outwardly these diseases can be confused.
Bath for allergies
An allergic reaction can manifest itself in the form of skin rashes, a profuse runny nose or watery eyes, and disorders of the digestive system. The body produces a large amount of toxic substances, which are the cause of the disease.
The removal of toxins from the body is facilitated by exposure to elevated temperatures, sudden changes in temperature in the external environment, massage manipulations and high humidity. A sauna or bathhouse has this effect on the body.
Visiting a sauna or steam bath for allergies and urticaria is the best solution. Exposure to elevated environmental temperatures mobilizes the body's protective properties and also helps restore the function of the skin. Under the influence of hot steam, the pores open and the sweating process accelerates. With sweat, waste and toxins are removed through the pores. A contrast shower will help wash away harmful substances from the body and improve the condition of cells by reducing the toxic load.
Getting rid of the causes of atopic dermatitis
Now scientists classify atopic dermatitis as a neuro-allergic disease. This means that the course of the disease can be caused and aggravated by both allergens and nervous disorders. Accordingly, an important part of care for atopic dermatitis consists of eliminating allergens and causes of nervousness.
Eliminating allergens
Even if you are not a pronounced allergy sufferer, it is worth taking care of your surroundings and eliminating possible allergens. Adults often have food allergies: chocolate, citrus fruits, eggs, seafood, nuts and berries. Milk protein intolerance is common in children under three years of age.
Dust is one of the most common allergens. More precisely, not the dust itself, but the waste products of dust mites that live in it. Wet cleaning should become a regular ritual.
Allergies can also be caused by household chemicals. Aggressive cleaning powders, dishwashing detergents, washing powder - all this can provoke exacerbations. Choose the most gentle formulations, give preference to special children's washing powders and use household chemicals only with gloves.
Getting rid of nervous disorders
Don't underestimate the impact of your psychological state on your health. It is emotional stress that often leads to relapses of atopic dermatitis, so skin care includes visits to a psychotherapist.
How to avoid an allergy attack?
- always have medicines with you - they can be useful not only to you, but also to those around you;
- be attentive and careful while on vacation - bites from unknown (and also known) insects, animals, pollen from flowering shrubs and herbs can cause an allergy attack;
- Be wary of unfamiliar, especially exotic, vegetables, fruits, dishes - it is unknown how your body will react to a new product, so if you really want to try it, eat a very small piece and wait a while. People prone to allergies should generally refrain from such experiments;
- do not neglect the rules for using cosmetics - not so long ago the whole world was shocked by the story of a French woman who used hair dye and received severe swelling of her head. We trust manufacturers so much and take our health lightly that we very rarely test cosmetics before use - this is absolutely forbidden to do, especially if you bought the product for the first time. Lipstick, face and body creams, oils, paints, and perfumes can cause serious health problems and long-term treatment.
If you suddenly discover an allergy to a particular product, this is a serious reason to consult a doctor: the disease not only overshadows everyday life and holidays, deprives you of productivity and vigor, but can also lead to asthma and other serious pathologies.
The information provided is for informational purposes only. If you have any health problems, first of all, you should seek advice from a specialist.
← Previous articleNext article →
Skin care for atopic dermatitis
The second half of treatment is the elimination of symptoms, namely dryness, itching, redness and pain. Daily care consists of gentle cleansers and intense moisturizers. Areas affected by atopic dermatitis require gentle skin care products. During an exacerbation, patients with dermatitis need anti-inflammatory drugs. Many of these medications are hormonal and should only be taken as directed by a doctor. A dermatologist can also prescribe special procedures (wraps, lotions, applications, etc.).
Facial skin care for dermatitis
If facial skin is damaged, it is necessary to change your daily care to a more gentle one. Hydrophilic oils for washing are an excellent choice - they do not dry the skin, carefully remove impurities and do not cause irritation.
Bath procedures
For dermatitis, it is better to shorten the duration of any water procedures: instead of taking a long bath, take a quick shower. Reduce the temperature of the water for washing - hot water quickly deprives the skin of moisture. For people with dermatitis, the optimal temperature is 32–35°C.
Try to avoid aggressive exfoliators, hard washcloths, and scrubs. Instead, choose gentle cleansers such as gels and oils that do not contain soap. Immediately after your shower, apply moisturizer to prevent your skin from losing moisture. This is especially important in winter, when both cold air and central heating dry out the skin.
In children, care for atopic dermatitis is absolutely similar. Pay special attention to the choice of moisturizers, look for hypoallergenic formulations approved by pediatric dermatologists.
How to diagnose allergies?
Allergies occur when a person’s immune system reacts to environmental substances that are harmless to most people. These substances are known as allergens. They are found in dust, pet dander, pollen, insects, mites, mold, food and some medications.
What happens during an allergic reaction?
When a person who is allergic to a particular allergen comes into contact with it, an allergic reaction occurs. If an allergen, for example pollen, enters the body for the first time, it stimulates the production of antibodies and the formation of sensitized lymphocytes. When the pollen allergen comes into contact with antibodies again, antigen-antibody complexes are formed. The complexes are fixed on the surface of mast cells, causing their degranulation. As a result, histamine and other inflammatory mediators are released. Since mast cells are ubiquitous, an allergic reaction can occur in any organ. In humans, small vessels and bronchi are more often affected, so the clinical manifestations of their damage appear first.
Allergies come in a variety of forms: respiratory tract allergies (allergic rhinitis and bronchial asthma), allergic conjunctivitis, allergic dermatitis, allergic enteropathy and the most severe and life-threatening condition - anaphylactic shock.
Depending on the form, symptoms vary widely.
The most typical symptoms of allergic reactions are:
- spontaneous runny nose;
- frequent sneezing;
- tearfulness;
- rash;
- itching;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
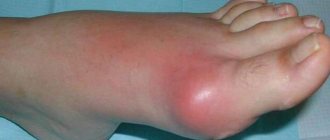
- redness;
- edema;
- temperature increase.
Allergic reactions occur within 30 minutes after contact with the allergen.
The correct diagnosis can be made based on medical history and symptoms, and can be confirmed by a special allergy test.
Seeking medical help is especially important for children, since a single primary allergy can quickly develop into multiple allergies, and allergic rhinitis can cause asthma. Early diagnosis is justified because it allows for preventive treatment, minimizing the impact of allergies in the future.
History taking
Special attention is paid to collecting anamnesis. The presence of allergy symptoms, especially when identifying associations with triggers described by the patient himself, speaks in favor of an allergic component.
Allergies often appear after eating certain foods, inhaling pollen, contact with animals, insect bites, taking certain medications, etc.
In patients with contact dermatitis or skin allergies, a history of exposure to latex, metals, fabric fibers, detergents, etc. is significant.
When a food allergy is identified, the patient is recommended to keep a food diary, which allows a more targeted understanding of which product is the trigger of the allergic reaction.
List of questions asked by an allergist during an appointment:
- What is the time of onset of the reaction after ingestion of the suspected food?
- Is there a consistent association of symptoms with certain foods?
- How much of a potentially allergenic food triggers symptoms?
- Does anyone else in the family who consumed the food exhibit similar symptoms?
Family history of allergies
When collecting anamnestic data, the doctor is always interested in whether any of the family members have had or are suffering from allergies. Finding first-degree relatives, such as parents and siblings, who suffer from allergies is important in diagnosing atopic conditions.
Atopy
- This is a genetic (hereditary) tendency for the development of allergic diseases. People with atopy are said to be atopic.
The tendency to atopy is determined by both genes and environmental factors.
Allergy tests
Skin tests (allergy tests) and blood tests help determine whether a person actually has an allergy.
Skin tests confirm the allergic nature of the disease. They are performed in the office of an allergist and allow you to quickly get an answer. Skin testing “provokes” an allergic reaction by introducing a small amount of an allergen—a substance that doctors believe you may be allergic to. If you have an allergy, your skin will react and something similar to a mosquito bite will appear where the allergen is applied.
There are three main types of skin tests: patch tests, prick tests and skin prick tests.
1).
Patch tests. When testing using patches, the doctor sticks test strips impregnated with the allergen.
The patient must undergo them for about 2 days, after which the doctor will evaluate the results at a follow-up appointment. This testing is used to diagnose contact allergies. 2).
Scarification tests. It involves applying the allergen to scratches, which the doctor makes with a lancet or needle.
Scratches occur on the forearm or upper back. If a reaction occurs at the site of damage to the skin - redness, scratching, etc., then this is a sure sign of an allergy. This method is the most popular in our country. 3).
Prick tests. The method is similar to the previous one, only instead of scratching the skin is pierced with a thin needle. The method is easier to tolerate, but less common in our country.
When preparing for skin testing, it is important to stop taking antihistamines two weeks in advance; 7 days before their placement, stop using antiallergic ointments.
Standard contraindications to skin allergy testing are:
- exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- the presence of diseases in the acute stage;
- exacerbation of allergies.
It is advisable to perform skin tests only when the child reaches 5 years of age. If there are clear indications, then you can resort to them earlier, starting from 2 years of age.
Blood test for IgE
In the blood, the total level of IgE and the presence of specific immunoglobulins can be determined. The total level of immunoglobulin E (IgE) in the blood indicates a tendency to allergies.
A blood test for specific IgE is used to confirm the results of skin tests. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) antibodies are substances produced by the body during an allergic reaction to a specific allergen. If high levels of specific IgE are detected in the blood, and there is a corresponding history, then these data together help confirm the allergic nature of the disease. However, an elevated result does not always indicate an allergic component. The laboratory test result should support clinical findings and skin testing in favor of an allergy. A negative result of laboratory testing for IgE, on the contrary, in 90% indicates the absence of pathology.
Skin care for seborrheic dermatitis
If with atopic dermatitis the skin dries and cracks, then with seborrheic dermatitis it begins to become shiny, and oily scales may appear on it. In children under 3 years of age, the disease usually appears on the top of the head. Skin care for seborrheic dermatitis in this case comes down to the use of special shampoos prescribed by a dermatologist. It is important to stop the itching, because a child can scratch the affected area and accidentally cause an infection.
For seborrheic dermatitis, agents that reduce skin inflammation are used: keratolytics, corticosteroids, antifungals.
They should only be used as prescribed by a doctor. If seborrhea has become chronic, a dermatologist may prescribe oral antifungal medications. March 24, 2021
Author of the article: dermatologist Mak Vladimir Fedorovich
When your own people become strangers
In order to better understand the nature of such disorders, consider several unusual types of “biological allergies”:
Allergy to sweat.
Sweat is secreted through the sweat glands and is accompanied by the elimination of nitrogenous base breakdown products from the body. This allergy in medicine is called “cholinergic urticaria”, since the symptoms of the attack correspond to the classic signs of urticaria. A person who is allergic to his own sweat notices the appearance of pinkish-pale blisters and inflammation of the skin in places where sweat glands accumulate - on the face, neck, chest and armpits. These signs are accompanied by severe itching and pain in the affected area. Immunity pathologies, intense physical activity, frequent sauna visits, and wearing synthetic clothing can provoke an allergic reaction to sweat.
Allergy to tears.
Perhaps many people have noted the appearance of characteristic pink spots on the face, itching and burning of the mucous membranes of the eyes and inflammatory skin reactions while crying. If earlier doctors claimed that such a reaction occurs as a symptom of contact dermatitis, it has recently become clear that some components of tear fluid can actually provoke an increase in the concentration of IgE in the patient’s blood, and this indicates an allergy.
Allergy to hormones.
Just a few years ago, the vast majority of doctors argued that the molecules of hormonal substances are too small to cause the development of an allergic reaction. However, recent research has shown that this is not the case. Female sex hormones, in particular estrogen and progesterone, “work” especially actively in this regard. That is why officially confirmed cases of such an unusual allergy are observed only in women; the main symptoms are severe premenstrual syndrome and complicated menstruation.
Allergy to sperm.
One of the most unpleasant forms of biological allergies is the hypersensitivity of a woman or man’s body to sperm protein. If for a woman such a reaction can be explained by the protest of white blood cells against the introduction of foreign cells, then for men an allergy to their own sperm seems a strange phenomenon.
It is important to understand here that problems arise not when seminal fluid gets on the skin or mucous membranes, but when the patient’s blood mixes with sperm. The root cause of such rejection of one’s own germ cells is almost always trauma to the genital organs (testicles), and the consequences most often manifest themselves in the patient’s infertility.