The disease is treated by: Pediatric ophthalmologist
- Causes of blepharitis
- Types of blepharitis
- Blepharitis in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
- Diagnostics
- Treatment of blepharitis
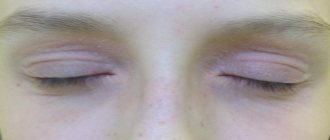
Blepharitis is a disease that occurs quite often in children. It is an inflammation of the edges of the eyelids, which is associated with very thin skin and fiber in this place, because the tissue is loose and there is no fat.
As the disease progresses, the eyes do not always change in appearance. This misleads parents, provokes inaction or, in some cases even worse, the use of folk remedies without consulting a doctor. You should know and always remember that blepharitis is a dangerous disease that can have a number of complications.
Causes of blepharitis:
- Staphylococcus aureus;
- the presence of parasites in the body;
- hypothermia;
- infectious diseases;
- psycho-physical fatigue;
- weak immunity;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract;
- Demodex is a mite that gets into the eyelash bulbs through contact with feathers, birds, diabetes, allergic diseases, etc.;
- helminths;
- constant eye strain;
- getting dirt, dust, smoke, etc. into the eyes;
- diabetes;
- avitaminosis;
- impaired metabolism;
- chronic tonsillitis;
- anemia.
Causes of peeling
Both external factors and internal causes can provoke peeling and redness of the skin around the visual apparatus. Increased dryness of the epidermis of adults and children is provoked by factors:
- hereditary predisposition;
- irritation;
- prolonged exposure to gadget monitors;
- sudden change in temperature;
- emotional stress;
- application of cosmetics;
- mosquito bites;
- allergic manifestations;
- ingress of dust microparticles;
- prolonged exposure to water;
- unbalanced diet;
- hormonal changes or disorders;
- dysbiosis.
To eliminate skin flaking, it is enough to reduce exposure to irritants and moisturize the dermis with emollients.
Blepharitis in children: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Signs of illness
Blepharitis is similar in symptoms to other diseases. Therefore, if any of the signs listed below are identified, parents should not draw independent conclusions, but immediately contact a specialist.
Symptoms of blepharitis:
- hyperemia (redness) of the conjunctiva;
- itching;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- eyelash loss;
- burning;
- narrowing of the eyes;
- irritation under the lower eyelid;
- crusts along the edges of the eyelashes, turning into bleeding ulcers;
- inflammation of the meibomian glands - leakage of a white-yellow mass from under the eyelids when pressed;
- peeling of the skin around the eyes, in the eyebrow area, on the head;
- vascular network on the face.
If you have several symptoms, you should never hesitate or self-medicate. The child needs to be shown to a specialist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
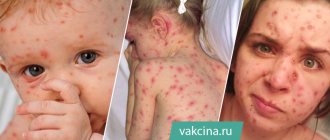
Blepharitis in children
Blepharitis in a child is an inflammation of the ciliary border of the eyelids. It is usually bilateral and tends to recur. There are many reasons for the development of the disease. These can be bacterial, viral, fungal or parasitic infections, allergic reactions, and other ophthalmological diseases. One of the most common causes of blepharitis is staphylococcus and demodex mites. Less commonly, the herpes virus. Untreated ophthalmological diseases, such as dry eye syndrome, can contribute to the development of infection.
Symptoms of blepharitis in a child
There are several clinical forms of blepharitis, and they all have their own characteristics. However, there are a number of common symptoms:
- Swelling and redness of the eyelids.
- Plaques and pathological discharge on the eyelids.
- Itching.
- Increased sensitivity to various irritants - smoke, dust, wind and even light.
Specific symptoms:
- Simple blepharitis - the edges of the eyelids become red and thickened. Whitish discharge accumulates in the corners of the eyes, and there may be redness of the conjunctiva.
- Scaly blepharitis. In addition to redness and thickening of the eyelids, scales accumulate on them, which are formed by clusters of skin cells. They are located not only on the eyelashes, but also on the eyebrows and scalp hair.
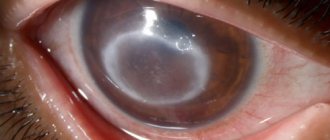
- Ulcerative blepharitis. Crusts form on the eyelids, and when removed, ulcers form. After healing, scars may form in their place, which impede the normal growth of eyelashes.
- Demodectic blepharitis is characterized by itching, in some cases patients talk about its unbearable nature. The sticky discharge dries and sticks to the eyelashes. During the daytime, there may be pain in the eyes.
- Allergic blepharitis occurs suddenly and is associated with the action of an allergic factor. This causes swelling of the eyelids, itching, photophobia and pain in the eyes, lacrimation. A so-called allergic bruise may also occur, in which the skin of the eyelids darkens.
Diagnosis and treatment of blepharitis in children
As part of the diagnosis of blepharitis, an examination by an ophthalmologist is performed. Eye biomicroscopy (examination of eye structures under magnification) is performed and visual acuity is determined. If demodicosis is suspected, eyelash microscopy is performed to identify mites. If a bacterial infection is suspected, a bacterial culture of the eye discharge is performed. For allergic blepharitis, it may be necessary to perform allergy tests. Treatment of blepharitis is long-term, complex and systemic. It requires an impact on the cause of the disease, so it is important to identify the etiological factor. In some cases, consultation with specialized specialists is necessary - allergists, ENT specialists, dentists, etc. It is important to ensure normal hygienic conditions at home and at work. If vision loss is detected, correction is necessary. When treating any form of blepharitis, it is important to regularly and correctly clean the eyelids of scales, crusts and discharge. When ulcers appear, medications that have a healing effect are prescribed. The key point in the treatment of blepharitis is etiotropic therapy. For bacterial infections, antibiotic therapy is carried out; for demodicosis, antiparasitic ointments are prescribed. In case of allergic etiology, contact with the allergen must be eliminated, and antihistamines are prescribed to relieve symptoms.
Diagnostics
A pediatric ophthalmologist examines the child, collects anamnesis and complaints. Concomitant diseases are also identified or rejected, and laboratory tests are carried out.
Biomicroscopy of the eye is used to determine visual acuity. The first technology makes it possible to assess the condition of the tear film, the edges of the eyelids, the eyeball, etc. Refraction and accommodation are examined, on the basis of which the following can be identified: myopia, astigmatism, etc.
To confirm or deny the presence of Demodex mites, eyelash microscopy is performed.
If there is a suspicion of the infectious nature of the disease, a BAC culture of a smear from the conjunctiva is performed.
To identify helminths, a stool test is prescribed, and in case of an allergic course of the disease, allergy tests are performed.
When blepharitis exists for a long time and causes hypertrophy of the eyelid margins, the doctor prescribes an examination to exclude various forms of cancer, carried out by biopsy followed by histological examination of the biomaterial.
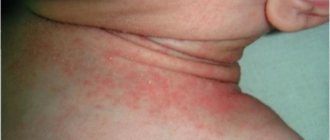
Redness and peeling under the eyes of a child
In childhood, dryness and redness are especially common, since the child’s skin has not yet fully formed. Predisposing factors to the appearance of dryness and redness are:
- excessive loss of moisture from the conjunctival membrane;
- instability of the conjunctiva to damage by infectious or bacterial microflora;
- watching TV for a long time;
- overstrain of the visual apparatus when working with small particles;
- frequent colds;
- foreign particles entering the membrane of the organs of vision.
It is important not to miss a symptom in infants, since the epidermis in this category is not fully formed. During early development, babies often develop allergic reactions, for example to foods.
Treatment of blepharitis
In case of an allergic form of the disease, complete exclusion of the identified allergen is recommended. Recommendations may also include, depending on the type of blepharitis:
- applying eye cream;
- special shampoo for seborrheic form;
- eyelid massage;
- strengthening the immune system;
- external treatment of eyelids and/or eyelashes;
- use of ointments;
- antimicrobial eye drops;
- diet adjustments;
- physiotherapy (electrophoresis, UHF, magnetic therapy, ultraviolet treatment, darsonval);
- removal of ulcer crusts in peptic ulcer disease.
If you delay treatment, ignore the doctor’s recommendations, or self-medicate, this can cost your baby his sight and also lead to other unpleasant consequences.
Prevention
For prevention purposes, the following restrictions must be observed:
- completely remove cosmetics from the epidermis before going to bed;
- It is recommended to use cotton pads rather than cotton wool for these purposes;
- in cosmetics, it is advisable to give preference to products without lanolin and neutral pH;
- complete rejection of cosmetics that have expired;
- a ban on the use of alcohol-containing preparations or cosmetics for the skin around the eyes;
- use clean brushes to apply makeup;
- It is prohibited to scrub or apply peeling to this area of the dermis;
- choose cosmetics according to the required skin type;
- Before any procedures, clean your hands with antiseptics.
With proper care for the skin around the eyes, excessive dryness can be completely eliminated.
"SM-Clinic" - taking care of your child
Our medical center employs some of the best pediatric doctors in various fields in St. Petersburg. Our professionalism is confirmed by an impeccable reputation. The clinic has advanced equipment that allows you to quickly and accurately diagnose various ophthalmological diseases, including blepharitis.
Make an appointment and come to us if you need truly competent help and effective therapy.
Ageev Vladimir Sergeevich Clinic
Author of the article
Ageev Vladimir Sergeevich
Candidate of Medical Sciences
Specialty: ophthalmologist
Experience: 16 years
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Pathological redness and peeling near the eyes
The presence of pathologically dry and hyperemic skin, which is provoked by pathologies, is indicated by additional symptoms:
- sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the organ of vision;
- active secretion of tear secretion;
- fear of bright radiation;
- purulent discharge;
- swelling of the area;
- intensely itchy areas;
- soreness;
- the appearance of crusts, ulcers or suppuration in the eyelash area.
In children, diseases of the visual system are accompanied by increased moodiness and deterioration of sleep. Among the pathologies that provoke the development of peeling in the area of the corners of the eyes, there are:
- improper functionality of the endocrine system;
- disturbances in liver function;
- myocardial pathology;
- diseases of the visual apparatus;
- decreased immune response.
Diseases of the visual organs can also lead to dryness:
Demodicosis
The development of the disease is caused by mites that live on the eyelash edge. The duration of the incubation period is unknown, but the development of the disease is long. Additional symptomatic manifestations of demodicosis are:
- purulent discharge;
- eyelash loss;
- feeling of tightness in the eyelids;
- peeling in the area of the affected organ of vision.
The diagnosis can only be determined after instrumental diagnostics.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Pathology develops against the background of active proliferation of a yeast-like fungus. Those areas where there is increased secretion of sebaceous secretions are susceptible to disease. Dermatitis is accompanied by peeling and the formation of flakes on the surface of damaged skin.
Acute blepharitis
Pathology develops against the background of damage to the eyelids by bacterial or viral microflora. Additional signs of blepharitis include burning, itching and swelling. To eliminate the disease, it is necessary to identify the pathogen.
Neurodermatitis
Atopic areas develop against the background of a decrease in the protective properties of the epidermis. Unfavorable environmental factors can provoke atopy. Young children are especially susceptible to peeling due to neurodermatitis.
To eliminate the symptom, it is necessary to use emollients. If additional symptoms appear, you should contact an ophthalmologist or dermatologist.
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is accompanied by redness and peeling around the eyes, which indicates the active proliferation of provoking microflora.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment (examination, consultation) with an ophthalmologist, primary, therapeutic and diagnostic, outpatient | 1950 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Prescription of treatment regimen (for a period of 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Biomicroscopy of the anterior segment of the eye | 500 rub. |
| Selection of glasses with plain lenses | 600 rub. |
| Subconjunctival injection (1 eye) | 500 rub. |
| Removal of a foreign body from the conjunctiva, from the eyelids | 800 rub. |
Traditional methods
In the absence of health-related problems, it is possible to use traditional methods to restore the water balance of the skin:
- Mask based on gelatin component. To obtain the mixture, dissolve 50 grams of gelatin in warm water until a homogeneous mass is obtained. The mask is applied for up to 20 minutes, after which it is washed off.
- Carrot mask. To prepare the mixture you need carrots, the yolk of 1 egg and potato flour. The ingredients are mixed and applied to the affected areas. The holding time of the mask is about 20 minutes. It is necessary to wash off with warm water.
- Parsley leaves. The ingredients are crushed until a homogeneous mass is obtained, which is applied to the pathological areas.
Traditional recipes can be used in combination with the main treatment, but the interval between medications should not be less than 2 hours.