Furunculosis is a disease of the epidermis caused by inflammation of the hair follicles and surrounding tissue. This disease causes severe discomfort, pain and itching.
In addition, after the disease, scars may remain on the skin, since it penetrates quite deeply.
In this article we will talk about the features of this disease, the causes and treatment of furunculosis.
Factors of occurrence
The causative agent of the infection is usually a pyogenic bacterium - Staphylococcus aureus. This bacterium is present on the skin of any healthy person, and causes infection only if it reaches the deep layer of the skin (for example, through microtrauma). The development of boils is also promoted by:
- dirty skin;
- increased sweating;
- overweight;
- poor nutrition;
- hot humid climate;
- hormonal imbalances in the body;
- poor metabolism.
People with diabetes mellitus, skin diseases, and those prone to stress and depression are often at risk of developing furunculosis because they have a weakened immune system.
General description of the disease
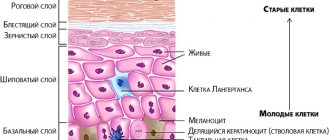
As mentioned above, furunculosis affects the deep layers of the epidermis. The causative agent in most cases is staphylococcus.
The disease can spread to large areas of the skin and often recurs in people with compromised immunity. This disease not only brings convenience, but also carries danger.
Therefore, everyone needs to know everything about chronic furunculosis.
The prognosis of the disease is usually good, but in the absence of proper treatment and control, furunculosis can lead to severe complications - the formation of blood clots, inflammation of the lymph nodes, and sepsis.All this is explained by the spread of bacterial infection in the body.
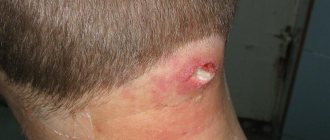
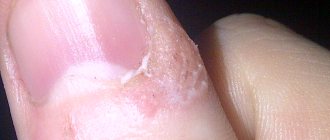
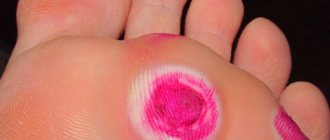
The most important symptom of furunculosis is the appearance of painful boils on the skin, in the center of which purulent discharge and dead epidermal tissue accumulate.
Once the pus and necrotic tissue are rejected, the wound closes and heals. Most often, rashes appear on the shoulders, back, neck, and abdomen. It is possible that boils may appear on the face, including in the nose and ears.
Stages of development
At the very beginning of development, a boil can easily be confused with an ordinary pimple. However, within 3-4 days the inflammation grows, covering the surrounding tissues. Upon palpation, you can feel the tension and density of these tissues.
After a few more days, a sac with a purulent formation forms in the center of the boil, a necrotic core appears and the tissue softens.
Over time, the boil, unable to withstand a large amount of pus, opens and the pus, rejecting the necrotic core, flows out. After which the swelling gradually subsides and redness passes, and a small scar forms in the center of the former boil.
The most dangerous boils are those that arise near the lips, ears and nose. You should not try to squeeze out boils yourself, even if they have arisen in other locations. This can lead to the spread of infection, which will entail serious complications leading to the development of regional lymphadenitis, lymphangitis, and thrombophlebitis.
Boil: symptoms
Boil has several stages of development. After infection of the hair follicle, increasing tissue infiltration occurs over several days (Fig. 8). At this time, there is still no pus inside the boil. Very often, in the center of the infiltrate (which looks like a red bump on the surface of the skin), you can see the mouth of the hair follicle with a hair shaft protruding from it.
When touched, you can feel that the tissues are tense and compacted, and the touch itself can be painful. After about 3-4 days, a cavity with pus begins to form inside the boil, and necrosis of the hair follicle also occurs, which leads to the formation of a necrotic core. At this stage, one or more white or black dots can be seen on the surface of the boil (Fig. 9-10).
Gradually, the amount of pus inside the boil increases, which can lead to its breakthrough (pus will begin to ooze through the formed hole). The necrotic core of the boil will gradually begin to move forward and be torn off. Outwardly, it looks like a horn is sticking out. If the rod does not fall out on its own, it must be removed by a surgeon.
General symptoms - usually there is a moderate body temperature, rarely high, sometimes it is completely absent (24stoma.ru). The pain is usually spontaneous and of low intensity. Severe pain can occur in cases where a boil forms in the nose (from the mucous membrane of the nasal passages) or a boil in the ear (when it forms in the ear canal itself).
Scheme of the gradual development of a boil from the stage of infiltration to the formation and rejection of the necrotic core, and recovery (Fig. 11) -
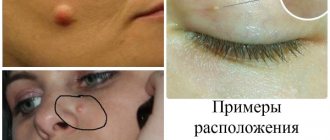
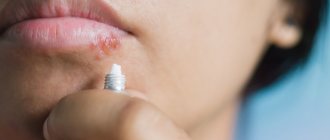
Boil on the face: features of the course of the disease
As a rule, such localization of inflammation leads to the development of significant swelling on the face. This is due to the characteristics of the blood supply to the face. It is especially dangerous when the boil occurs on the upper lip, on/in the nose or in the area of the nasolabial folds.
Such localization is fraught with the development of thrombophlebitis of the facial vein and the entry of infected blood clots into the vascular system of the brain, which can cause life-threatening conditions. Therefore, such chiries should only be treated by a doctor and under no circumstances should you try to squeeze them out.
Treatment at home
If the immune system is functioning well, the boil will heal itself in 7-8 days. But to make the process go faster, you can treat boils at home:
- at the initial stage of development, it is necessary to lubricate the abscess with a solution of fucorcin or brilliant green;
- at the stage of compaction and swelling of the connective tissue, it is good to sunbathe in the sun;
- To make the boil empty faster, you need to apply ichthyol ointment;
- It is better to treat an opened abscess with hydrogen peroxide, and also apply bandages with sodium chloride or honey;
- When the boil begins to heal, it is recommended to apply bandages using Vishnevsky ointment.
To prevent the development of purulent formations, you need to shower daily. Do not scratch the itchy area on the skin. Among other things, it is recommended to wear clothes made from natural fabric.
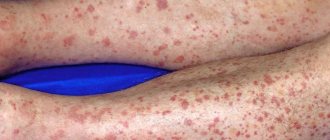
Photo of furunculosis
Read here! Laryngitis - first symptoms and tips on how to quickly cure the symptoms and cause of the disease (90 photos)
Please repost
0
2
When to contact a surgeon
Boils can be treated at home only for those who are not at risk (do not suffer from chronic diseases), and boils are small in size (up to 5 mm). You should not self-medicate in the following cases:
- if the appearance of a formation is accompanied by intense pain and fever;
- if the abscess has not opened within 2 weeks;
- if furunculosis has developed;
- if the abscess occurs in a small child;
- if the boil is near the nose, lips, in the ear canal;
- there was a relapse of the disease.
Disease detection
Diagnosis of the disease consists of conducting the following medical studies:
- Medical examination.
- Dermatoscopy.
- Examination of the boil contents for the presence of microorganisms.
Additional research methods include clinical tests of urine and blood, ultrasound, computed tomography, x-ray of the sinuses, and rhinoscopy.
Antibiotic treatment
In cases where the boil is large or located in sensitive areas, and its development is accompanied by intoxication, chills and severe inflammation, the surgeon prescribes antibiotics.
For a large boil and a slight increase in temperature, a weekly course is prescribed: the doctor prescribes clindamycin or doxycycline.
At high temperatures and severe inflammation, a two-week course of treatment is most often prescribed, which includes stronger antibiotic drugs: rifadin, rimactan or other analogues.
Don’t forget, Staphylococcus aureus easily adapts to a variety of antibacterial agents, and as soon as the body’s defenses are slightly reduced, they multiply and form new abscesses. Therefore, people with reduced immunity should immediately consult a doctor and not self-prescribe medications. Keep in mind that if you relapse, they will no longer help you!
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
How to treat boils -
It is possible to cure boils at home, but only in the cases listed below. In most cases, you should immediately consult a doctor (surgeon), especially if you have concomitant chronic diseases from the list below.
- You can treat it at home - if the size of the boil is no more than 5 mm and you do not have symptoms of intoxication or fever. You must also not have any of the diseases listed below. → if you have diseases: diabetes, oncology, reduced immunity, endocarditis or rheumatoid arthritis, obesity, taking prednisolone (in all these cases you need not only to be treated by a doctor, but also to use antibiotic therapy).
- You definitely need to see a doctor – → if the boil occurs in an infant, young child, → there are symptoms of intoxication, fever, → if a boil occurs on the upper lip, nose, nasolabial folds,
→ if there are symptoms of inflammation spreading: for example, the area of skin redness has increased or red stripes have appeared next to the boil, or another boil is forming nearby.→ if you have diseases from the list above.
What it is
A boil is a manifestation of pyoderma (streptoderma or staphyloderma - infection and reproduction of bacteria on the skin: streptococci or staphylococci).
A distinctive feature of a boil from other pustular skin lesions is the shape and size of the rash, the localization of inflammation around the hair follicle and a clear tracing of the stages of maturation and resolution of the infection.
Also, with this disease, the process of suppuration is very active and the volumes of pathological effusion are quite large, which is why boils on the body are popularly called boils or abscesses.
This is what a boil looks like
Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children in early or teenage years, as well as in elderly and elderly patients.
Statistical data indicate the detection of boils in 5-17% of people treated in dermatovenereal dispensaries. Dermatologists note a trend towards an increase in the incidence of boils in the facial area.
Prevention
Since treating boils is long and unpleasant, and complications pose a danger to health and life, it is recommended to take measures to prevent the occurrence of boils:
- keep your skin clean;
- avoid damage; in case of injury, immediately treat the wounds with bactericidal agents;
- If possible, wear loose clothing that does not chafe the skin;
- Eat a healthy diet with enough vitamins and minerals;
- strengthen the immune system - maintain normal activity, toughen up (but without fanaticism);
- in case of frequent interaction with contaminants, protect the epidermis with special clothing or film-forming sprays;
- be regularly checked for chronic and indolent diseases, and treat them in a timely manner;
- monitor normal hormone levels;
- minimize the use of pore-clogging cosmetics (especially for the fair sex).
It is also recommended to stop drinking alcohol and smoking, or at least not to abuse it.
How to distinguish a boil from a non-boil
Even knowing what a boil is, it is not always easy to differentiate it from other skin diseases. There are the following distinctive features characteristic of boils:
- increased temperature of the skin (with large ulcers - and the body), its redness;
- severe pain when palpated;
- the abscess is formed around the hair;
- inflammation goes quite deep into the dermis, swelling is present;
- a purulent core is observed.
Unlike acne, boils form at any age, often occur after a cold, and mature more slowly.