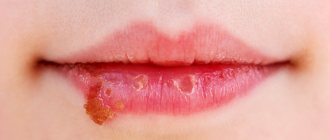
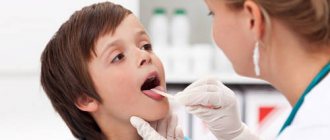
Herpetic infection is quite insidious, doctors note. At the same time, traditionally people are accustomed to the fact that it manifests itself in the form of rashes on the face - in the area of the lips and nose. Another option is genital herpes. But when faced with the appearance and manifestation of herpes in the ear, many are perplexed. Although, as experts note, this is not so rare.
Vladimir Zaitsev, Ph.D., otolaryngologist of the highest category, told AiF.ru about how to recognize herpes in the ear and what it means for a person .
Briefly about the origin
A blister in the ear can appear for various reasons :
- strong skin friction;
- contact of the surface with substances that cause an allergic reaction;
- taking contraindicated medications;
- fungal disease or viral infection (lichen);
- poor nutrition.
It is possible that a blister may appear after removing a wart with liquid nitrogen and even during frostbite.
All reasons are characterized by one word - irritation . It occurs in the area of origin or the entire organism as a whole.
REFERENCE : The common belief that the formation resulting from a burn is a blister is wrong .
Distinctive features
As the ENT doctor notes, all options should not be compared with a herpes infection that manifests itself on the lips. For example, herpes in the ear leads to otitis media.
“We know that there are three types of otitis in humans - external, that is, the one that forms near the ear canal of the ears, otitis media and internal otitis, when a person suffers from serious health problems and dizziness. If we are talking about a herpetic infection, then most often we are talking about damage to the outer ear and skin here. It happens less often that herpes affects the area deeper or behind the membrane,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
A herpetic infection is much stronger than a viral or even bacterial one. This is due to the fact that such infections take longer and are more difficult to treat. One of the reasons is the difficulty of diagnosis, since not all doctors immediately suspect that the causative agent is herpes.
“There are often situations when a person has already had otitis media before and even without the development of purulent processes. Accordingly, everything went easily and quickly for him, he remembered that there were no problems. And so the situation repeats itself, but let’s say the pain is worse, even after a few years, he again starts treatment according to a similar scheme, but it doesn’t work. The infection here is different, and it requires a special approach,” explains Zaitsev.
My ear is blocked. How to distinguish otitis media from wax plug Read more
What to do if it itches?
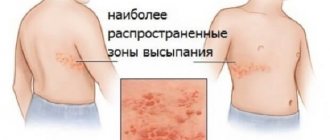
What is this blister behind the ear that is constantly itching , what should I do? If you want to scratch the blister, you should keep in mind that after the blister ruptures, there is a high probability of leaving a scar that will remain for a very long time.
Scratching the blisters itself does not pose any real health hazard, excluding the potential for the process of rotting and infection to begin. The smart choice is obvious - endure .
In case of severe scabies, it is also necessary to use anti-itch medications in order to curb the desire to get rid of itching with your own hands.
Symptoms of the problem
Of course, many are concerned with the question: how can one recognize that it was herpes that attacked? A person has a certain set of complaints in such a situation, says the ENT doctor:
- pain in the ear is aching and shooting, radiating behind the ear;
- hearing loss;
- increased body temperature;
- the formation looks like a boil;
- ear red, tense;
- the skin is hot, the area hurts.
If both the doctor and the patient suspect a boil, they try to get rid of it in the usual ways, the otorhinolaryngologist notes. Thus, the person himself feels pain when pressing on the damaged area; he tries to squeeze out the “boil,” believing that pus has accumulated there. The doctor, for his part, can use a scalpel to remove the pus that he thinks is in the damaged area.
“But such measures do not help, it only gets worse. Because the area is already inflamed and irritated, and such actions cause tissue crushing, the skin is even more injured even from a careful cut with a scalpel,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Diagnosis of the condition is required. The doctor must evaluate which parts of the ear are affected, at what stage of the process, examine the ear canal from the outside, whether the eardrum is involved in the process and what happens to the middle ear, how complex the situation behind it is.
Rinse before otitis media. How not to treat ARVI Read more
First aid
To reduce the pain from a blister, you need to do the following:
- Wash the affected area with warm water and soap.
- Wipe the area with alcohol or iodine.
- Open the formation with a sterilized needle, make pricks along the edges.
- Allow the liquid to drain completely from the ruptured bladder.
- Lubricate with an antibacterial agent , then bandage the wound with a bandage.
IMPORTANT : If signs of rotting, redness or increased temperature of the surface of the skin appear, you should consult a qualified physician . A dermatologist deals with these types of diseases . There are also clinics specializing in skin diseases - cosmetology and dermatology.
Causes
Acute purulent inflammation of the middle ear is a consequence of the penetration of pathogenic microflora into it and its activation against the background of a decrease in the body’s own defenses.
Often the infection enters the middle part of the hearing organ through the inflamed auditory tube connecting the nasopharynx to the ear. With sinusitis, sinusitis, proliferation of adenoid vegetations, tonsillitis and other ENT diagnoses, pathogenic microflora enters the auditory tube (for example, with sharp blowing of the nose), it becomes inflamed - eustachitis develops. If treatment was ignored or was ineffective, pathogenic organisms enter the ear through the auditory tube. This is the first variant of infection.
The second way is through a rupture in the eardrum or damage in the mastoid process (the area of the temporal bone associated with the middle ear). Otitis of this etiology is called traumatic.
A rarer route is through the blood, when during infectious diseases, for example, scarlet fever or measles, pathogenic flora spreads through the bloodstream and enters the hearing organ.
The disease develops due to decreased immunity. Factors provoking this may be:
- problems with the endocrine system;
- lack of vitamins;
- bad habits;
- diseases of the ENT organs;
- diabetes;
- frequent entry of water into the ear (local immunity decreases).
Treatment of the disease
It can be carried out in two different ways: pharmacy and folk . Which one is better to use depends on the specific situation.
For the purpose of improving literacy, it would be a good idea to consider each of them.
Pharmacy method
Penicillin, sodium salt and other similar drugs are used In modern realities, bacteria (more precisely, staphylococci) have become more resistant to antibiotics, so it is necessary to use only modern types, for example, ceftriaxone.
Ointments recommended for the skin surface : gentamicin, 10% ichthyol, Vishnevsky ointment. Physiotherapeutic procedures also bring good results.
ethnoscience
If you have blisters on your ear, traditional medicine will help get rid of them.
A great variety of different remedies: from lavender tea to tea tree juice.
Aloe vera has a soothing and anti-inflammatory effect. To use it, you need to rub the plant leaf on the affected area.
Apple cider vinegar is an excellent antibacterial home remedy. Before use, dilute it halfway with water and apply to a cotton swab.
Wetting your skin with green tea will also provide anti-inflammatory benefits.
Treatment
Naturally, therapy must be started - no self-medication, no options to let things go by themselves. “Antibiotics are prescribed preventively for herpes in the ear, because against the background of a herpes infection, immunity is greatly reduced, and a bacterial infection can quickly appear. These can be systemic drugs that are taken orally, and various antibacterial ointments. Antiviral drugs are also offered, which can also be taken orally or externally. They also use symptomatic therapy - we relieve swelling, remove congestion in the ear, bring the temperature in order,” says Vladimir Zaitsev.
Herpetic otitis is treated like regular otitis. But, the otorhinolaryngologist notes, the optimal solution would be if a person has already had a herpes infection in the ears before, and he knows both the symptoms and treatment. In other cases, it is necessary to exercise special caution and clearly monitor the progress of treatment in order to adjust it quickly if necessary.
Stages of otitis media
There are three stages of acute otitis: pre-perforative, perforative and reparative. But this does not mean that a person will necessarily go through all these stages. With good immunity and timely visits to an otolaryngologist, it is possible to stop inflammation in the initial phase.
The first stage is the so-called acute catarrhal otitis media (acute non-purulent otitis media). Catarrhal otitis in children and adults occurs with intense pain in the ear, which increases towards night. At this moment, it’s as if something is pulsating or shooting in the ear; the pain can radiate to the teeth or the temporal part of the head. This condition is very difficult to tolerate. The ear tissues swell, the eardrum and auditory ossicles become less mobile, which certainly affects hearing acuity. During this same period, noise in the ear appears. Temperatures may rise to fairly high levels. The patient feels lethargic, tired, and loses his appetite. Further development of catarrhal otitis in a child and an adult patient can be prevented if in time, when the first signs of inflammation are detected, you consult an otolaryngologist. If treatment of acute otitis in children and adults was not carried out on time, the second stage occurs.
The perforated stage is when the pus accumulated in the tympanic cavity breaks through the eardrum, forming a hole in it - a perforation. It is at this stage that suppuration from the ear canal is observed. At the same time, the patient feels noticeable relief: the pain subsides, the body temperature drops, and the patient’s general condition improves. Suppuration can last up to five to seven days. If a natural rupture of the eardrum does not occur, the otolaryngologist will do it forcibly.
By the way, it is not pus that may accumulate in the tympanic cavity, but serous fluid. In this case, a person is faced with acute serous otitis. But this is a topic for a separate article.
The reparative stage is the final stage in the development of the disease. This is the so-called healing stage. The suppuration stops, the restoration of the eardrum begins, and hearing gradually returns to normal.
Typically, the disease, provided that all three stages are completed, lasts two to three weeks.
Treatment of acute purulent otitis
Treatment of otitis media in adults, and especially children, should be carried out under the supervision of an ENT doctor. It should be borne in mind that the treatment regimen will vary depending on the current phase of the disease.
So at the initial stage, until the eardrum ruptures, the doctor prescribes ear drops (Otinum, Otipax, etc.), which have an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect. There is no point in using local antibiotics in this case, since the problem is behind the membrane, and if there is no hole in it, the medicine will not reach its target. Therefore, the patient is prescribed general antibacterial drugs.
As soon as the eardrum ruptures, the above drops cannot be used, as they can harm the labyrinth of the inner ear. In this case, antibacterial ear drops, such as Otofa or Normax, are prescribed.
To relieve tissue swelling, you can use antihistamines (Zodak, Zyrtec, etc.) and vasoconstrictor nasal drops (relieves swelling of the auditory tube).
When the temperature rises, it is recommended to use antipyretic drugs (for example, Nurofen or Paracetamol).
Any drug, especially an antibacterial one, should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor and taken strictly taking into account the dosage and frequency of administration.
Don't forget about physical therapy. Physiotherapy helps relieve inflammation and speed up recovery.
As therapeutic procedures, the otorhinolaryngologist performs toileting of the middle and outer ear, placing medicinal micro-compresses, and rinsing the tympanic cavity with medicinal solutions.
If the purulent masses were unable to rupture the eardrum on their own, the otolaryngologist “helps” by making an incision in it and releasing the purulent accumulations outward.
Treatment of otitis media
If you have otitis media, treatment can only be prescribed by an otolaryngologist. Treatment of otitis media depends on the stage of the disease and the patient’s condition.
In acute eustachitis, treatment of otitis media is aimed at restoring the functions of the auditory tube. Sanitation of the paranasal sinuses, nose and nasopharynx is carried out in order to eliminate infection - rhinitis, sinuitis, etc.).
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (otrivin, nazivin, etc.) are prescribed; in case of excessive mucous discharge from the nose, drugs with an astringent effect (collargol, protargol) are prescribed. Catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out using aqueous solutions of corticosteroids, and pneumomassage of the eardrums.
In the stage of acute catarrhal otitis media, catheterization of the auditory tube is carried out with the introduction of aqueous solutions of corticosteroids and antibiotics (penicillins, cephalosporins) into the cavity of the middle ear. Local anesthesia is prescribed (otipax drops, Anauran, Otinum). An intra-ear endaural microcompress according to Tsytovich is carried out: a cotton or gauze turunda soaked in a drug with an analgesic and dehydrating effect is inserted into the external auditory canal. Painkillers with an antipyretic effect (nurofen, solpadeine, etc.) are also prescribed. If there is no effect from symptomatic therapy, antibiotic therapy is prescribed within 48-72 hours.
Purulent otitis in the pre-perforated acute stage requires the same set of procedures as in the second stage, but supplemented with the following measures:
- prescription of penicillin antibiotics (amoxicillin, etc.), cephalosporins or macrolides;
- paracentesis (incision of the eardrum) when the eardrum appears to bulge.
It is important to prevent complications of the disease at this stage. After spontaneous opening of the eardrum or paracentesis, the disease progresses to the next stage.
The post-perforation stage of acute purulent otitis media involves the following treatment regimen:
- started antibacterial therapy continues;
- catheterization of the auditory tube is performed with the introduction of corticosteroids and antibiotics;
- a thorough toilet of the external auditory canal is carried out daily - cleaning it from purulent contents;
- transtympanic infusion of drops with an antibacterial and anti-edematous effect is prescribed (alcohol-based drops (otipax, 3% boric acid solution) are not used in this case).
In the scarring stage of AOM, spontaneous restoration of the integrity of the membrane occurs, and all functions of the ear are completely restored. However, this period requires mandatory observation by an otolaryngologist: there is a danger of chronic inflammation in the middle ear, its transition to a purulent form, or the development of an adhesive scar process in the tympanic cavity. It is also possible to develop mastoiditis.
1 Audiometry in MedicCity
2 Audiometry in MedicCity
3 Audiometry in MedicCity
In case of acute otitis media, timely contact with an otorhinolaryngologist is very important. The only measure to prevent complications is correct and timely diagnostic and treatment measures for otitis media. Sometimes the consequences of acute otitis media are adhesions in the tympanic cavity (adhesive otitis media), dry perforation in the eardrum (dry perforated otitis media), purulent perforation (chronic suppurative otitis media), etc. In addition, AOM can lead to such complications as such as mastoiditis, labyrinthitis, petrositis, meningitis, sepsis, venous sinus thrombosis, brain abscess and other life-threatening diseases of the patient.
Types of otitis
Depending on the direction of the pain, it is customary to distinguish 3 types of otitis: external, middle and internal otitis.
Otitis externa most often appears as a result of mechanical damage to the auricle or external auditory canal. The following symptoms are characteristic of external otitis of the ear: aching, dull pain, swelling of the ear, and a slight increase in temperature.
Otitis of the middle ear is an inflammatory disease of the air cavities of the middle ear: the tympanic cavity, the auditory tube and the mastoid process.
Internal otitis is untreated otitis media of the middle ear. With internal otitis, inflammation of the inner ear occurs and the entire vestibular apparatus is damaged.
Prevention
There are no specific preventive measures to avoid suppurative otitis media. To reduce your risk of getting sick, strengthen your immune system and promptly treat any ENT infection you encounter. An important point: treatment should not only be timely, but of high quality: no self-medication, only competent assistance from an otolaryngologist. There is no need to start the disease. At an early stage, any disease is much easier to treat: in many cases, the accumulation of purulent masses in the middle ear could be easily avoided by contacting an ENT doctor in time.
If you or your loved ones are faced with hearing problems, do not waste time: make an appointment by calling +7 (495) 642-45-25 and come.
We will definitely help you!
Diagnostics
For an experienced otolaryngologist, diagnosing the disease is not difficult. When making a diagnosis, the ENT doctor relies on the patient’s complaints and the results of otoscopy (examination of the hearing organ). The patient may be referred for a number of laboratory tests that will confirm or refute the presence of inflammation. To assess the degree of hearing impairment, audiometry or tuning fork testing is performed. To assess the condition of the components of the middle ear, tympanometry is performed. In severe cases, the patient is sent for X-ray, CT, MRI.
Complications of acute purulent otitis
If the disease is treated late or incorrectly, acute inflammation can become chronic.
Chronic purulent otitis is the most common complication of the acute form. There are two forms of chronic suppurative otitis media – mesotympanitis and epitympanitis. The disease can also lead to:
- labyrinthitis - inflammation of the inner ear;
- to the spread of purulent inflammation to the membranes of the brain (meningitis, brain abscess);
- sepsis;
- paresis of the facial nerve, when the face becomes asymmetrical and the affected side loses its mobility;
- mastoiditis – inflammation of the mastoid process of the temporal bone;
- hearing loss or complete hearing loss.
Physiotherapy for acute purulent otitis media
An important stage in the treatment of the disease, which enhances the effect of drug therapy and accelerates the recovery process, are physiotherapeutic procedures.
For acute purulent otitis, the following types of physiotherapy are effective:
- infrared laser therapy (reduces inflammation and relieves swelling of tissues);
- vibroacoustic therapy (improves blood and lymph flow, providing a good therapeutic effect for inflammation of the middle ear);
- ultraviolet irradiation (has a bactericidal effect);
- ultrasonic medicinal irrigation (has an anti-inflammatory effect);
- photodynamic therapy (helps relieve inflammation);
- ultrasound therapy (promotes deeper penetration of medicinal ointment, relieving inflammation and swelling of tissues);
- infrared laser exposure (stops the inflammatory process).
Which procedures should be used and how many sessions will be needed is determined by the ENT doctor, based on the patient’s condition.
Treatment of otitis media during pregnancy
If you experience ear pain during pregnancy, you should urgently see an ENT doctor. Remember that in this case you cannot apply heating pads or warm compresses to the sore spot! This can be very dangerous if purulent inflammation begins in the ear.
If the pain increases and greatly bothers a pregnant woman, and there is no way to see a doctor in the near future, you can take several independent steps. For example, you should put vasoconstrictor drops into your nose.
What is prohibited for otitis media
- Under no circumstances should foreign bodies be introduced into the ear (geranium leaves, ear phyto-candles). This will make diagnosis difficult and may lead to a worsening of the condition (for example, leaves that have not been removed begin to rot and become a source of infection).
- If the pain is severe, do not apply a heating pad to your ear or apply warm compresses. This is dangerous if purulent inflammation has begun in the ear. Compresses can only help at stages 1-2 of the disease.
- You should not put melted oil in your ear: if there is a perforation, the oil will end up in the tympanic cavity.
- You should not put camphor oil or camphor alcohol into your ear - it can burn the walls of the ear canal and irritate the eardrum, which will increase ear pain.
At MedicCity you will be denied professional help for otitis media and other ENT diseases. Our otolaryngologists will conduct a comprehensive examination of the patient and prescribe a treatment regimen, depending on the cause and stage of the disease. However, the success of treatment depends no less on the patient himself: the sooner he consults a doctor, the more effective the result will be and the lower the likelihood of complications. It is also important to follow preventive measures. So, in the cold season, to prevent otitis media, it is important to wear a hat, protect your ears from drafts, and of course, boost your immunity!