Causes
Hyperhidrosis is increased sweating associated with excessive activity of the sweat glands. Sweating can be generalized or localized. In the first case, the whole body sweats, in the second - only certain areas where there are especially many sweat glands - usually the palms, feet, and armpits.
Excessive sweating is not always a sign of illness. It is completely normal to sweat when doing physical work or being in a hot room. Strong emotional stress can also cause this reaction.
But if a person constantly sweats with any load or without it at all, regardless of the air temperature around him, it is worth looking for the cause of this phenomenon. Generalized hyperhidrosis can occur with fever, tuberculosis, fainting, or while taking certain medications (for example, antidepressants or migraine medications).
Focal, local hyperhidrosis is usually associated with improper functioning of the autonomic nervous system: due to incorrect receptor activity, the sweat glands are commanded to work at full capacity. In turn, autonomic disorders can occur as a result of hormonal imbalances, diseases of the cardiovascular or endocrine systems.
Predisposition to hyperhidrosis is often genetic. The disease usually appears in adolescence and reaches its peak at 25-35 years of age.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
Patients with general hyperhidrosis should seek medical help to determine the cause of the disease and select an adequate treatment regimen. Before the diagnosis is verified, frequent hygienic showers and treatment of areas of the skin that are subject to friction with clothing, talcum powder or special powders help reduce unpleasant symptoms. Clothing and underwear should be chosen from natural materials. To eliminate the unpleasant odor of sweat in the armpits, you can use strong antiperspirants.
Hygiene measures for sweating
Conservative therapy
Medications that eliminate excessive sweating are not effective enough. To reliably relieve sweating disorders, it is necessary to carry out etiotropic therapy aimed at eliminating the cause of hyperhidrosis. Medicines are combined with local antiperspirants and physiotherapy methods (laser exposure, iontophoresis). Psychotherapy is used according to indications. The treatment regimen for general sweating includes the following medications:
- Anticholinergics
. To reduce sweat production, atropine and its derivatives are prescribed, which reduce nervous stimulation of the sweat glands. For better effect, medications are combined with herbal sedatives. - Anti-inflammatory drugs.
Medicines from the NSAID group quickly reduce the amount of inflammatory mediators in the blood and speed up recovery. They also have a powerful antipyretic effect. - Antibacterial agents
. For bacterial infections, specific etiotropic therapy with medications that selectively act on isolated pathogens is indicated. The course lasts at least 14 days. - Anti-tuberculosis drugs
. To eradicate Koch's bacillus from the body, several groups of antibacterial drugs that are active against Mycobacterium tuberculosis are combined. Medicines are taken for a long time. - Detoxification therapy
. In case of poisoning with exogenous poisons or neoplastic syndrome, intravenous infusion of glucose-salt and colloid solutions is necessary. Diuretics are additionally prescribed to remove toxins.
Surgery
To eliminate generalized hyperhidrosis, a remote surgical method can be used - sympathectomy (intersection of the nerve trunk at a certain level, which reduces the work of the sweat glands). The optimal method is endoscopic sympathectomy, which is characterized by minimal trauma and a short rehabilitation period. Percutaneous and open methods are also used. If general sweating is caused by oncological causes (various types of lymph node tumors), lymphoid tissue is removed, which is combined with radiation and chemotherapy.
How to live with hyperhidrosis?
Increased sweating can cause a lot of trouble. People develop complexes due to sweat stains on clothes, unpleasant odor, and constantly wet palms. All this does not contribute to successful social contacts, and in severe cases people begin to avoid communication.
Psychological complexes are not so bad. Due to constant exposure to sweat, the skin softens and swells, its structure changes, and it becomes vulnerable to fungal infections. Irritations and ulcers appear.
In a word, hyperhidrosis is not fatal, but very unpleasant.
Depending on the severity of symptoms, there are 4 degrees of severity:
- First degree - unexpressed sweating, almost does not bother you;
- Second degree – the problem causes some inconvenience, but has little effect on the quality of life;
- Third degree – the quality of life noticeably deteriorates, complexes appear, communicating with people becomes more difficult;
- Fourth degree – sweating is significantly increased, and a change in the smell of sweat may occur (bromhidrosis).
In most cases, diagnosis is not difficult. In doubtful cases, doctors resort to a special test (Minor's test), which allows them to visualize the hyperactivity of the glands.
How to help yourself?
The first thing to do is to abandon the factors that provoke sweating. You should give preference to loose clothing made from natural materials and well-ventilated shoes. It is advisable to avoid hot dishes with a lot of spices, chocolate and coffee. You need to dress for the weather and avoid stress. And, of course, shower more often and use special antiperspirants with a high concentration of aluminum salts.
Unfortunately, even careful adherence to these recommendations helps to cope with increased sweating only in the mildest cases, with the first degree of hyperhidrosis.
If increased sweating causes significant inconvenience, then neither giving up pepper and ginger, nor wearing cotton clothes, nor all kinds of foot baths or physiotherapeutic procedures will help - more effective and modern means are required.
Previously, patients who did not respond to traditional treatments had only one option - surgery to remove the sweat glands or resection of the nerves that regulate their function. Nowadays such interventions are rarely used because they are traumatic and the risk of complications is too high.
One of the most common and unpleasant complications after nerve removal is compensatory hyperhidrosis, in which all sweat glands begin to work more actively than before. It turns out that the palms remain dry after the intervention, but the whole body constantly sweats. It is unlikely that anyone will like this effect, so operations are prescribed only in the most severe cases, when no other types of treatment help or cannot be used due to contraindications.
What remains in such a situation? Botulinum toxin injections! Yes, the same Botox that is used to prevent and eliminate facial wrinkles. You can use Botox and Dysport, Relatox, Xeomin.
What examinations are needed for excessive sweating and how to deal with it
Murzaeva Irina Yurievna
Endocrinologist, Preventive Medicine Doctor
July 10, 2014
The long-awaited summer and warmth has arrived. There was a need to raise this topic. Excessive sweating (or hyperhidrosis) comes in varying degrees of severity. This is a problem that causes discomfort to a huge number of people every day, limiting their usual life and wardrobe choices.
A little classification:
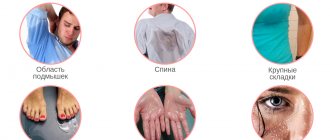
- there is sweating in certain areas of the body, local hyperhidrosis: only the palms, or only the feet, or only the armpits, or other areas of the body (areas under the breasts, inguinal folds, scalp, face);
- there is sweating widespread throughout the body, diffuse hyperhidrosis.
In any case, before starting treatment, it is worth finding out the possible causes of sweating.
More often there are 2 forms of local hyperhidrosis: palmar-plantar, axillary, in these 2 cases, as a rule, there is no need to look for the cause, such sweating is constitutionally caused: it is either a lot of sweat glands in these areas of the body, or they respond much more actively to stimulation by stress and etc., or there is double autonomic innervation (activity associated with the supply of nerves to the organ) of the sweat glands.
But increased sweating in other areas may depend on specific reasons:
sweating of the head - as a manifestation of VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia), menopause, arterial hypertension;
sweating of skin folds – fungal infection, carbohydrate metabolism disorders, obesity, etc.;
sweating of the face - as a condition after infectious damage to the salivary glands, damage to the facial nerve, etc.
There may be areas of hyperhidrosis around psoriatic plaques, areas of vitiligo (skin pigmentation disorders).
There may be even more reasons for widespread hyperhidrosis; they are divided into groups.
- Endocrine: DTG (diffuse toxic goiter), diabetes mellitus, pheochromocytoma, hypoglycemia, acromegaly, carcinoid syndrome.
- Infectious (acute and chronic): tonsillitis, tuberculosis, malaria and many others.
- Neurological: parkinsonism, condition after a stroke, diencephalic syndrome, VSD (or NCD), just stress (psychogenic hyperhidrosis), anxiety disorder, etc.
- Oncological: lymphomas, erythremia, etc.
- Genetic syndromes: cystic fibrosis, etc.
- Prem medications: Aspirin, insulin, Promedol, some painkillers, etc.
Tremors, agitation, and excessive sweating may be characteristic symptoms of acute alcohol and opiate withdrawal reactions.
Naturally, all these pathologies have additional symptoms, which only a doctor can deal with by prescribing the appropriate examination, including hormonal examination.
Now the main question is how to deal with this?
When clarifying a specific pathology, for example, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, etc. - treatment of the underlying disease. In the absence of causes of hyperhidrosis (constitutional, idiopathic), the following can be used as auxiliary local therapy:
- if we are talking about common hyperhidrosis, this is hardening (take a contrast shower twice a day, 30 seconds with cold and 30 seconds with hot water. Shower for 15 minutes, after waking up in the morning and evening), use of a cryosauna, IRT (acupuncture), sunny - air baths.
- if it is local hyperhidrosis, there are also several methods of treatment. You can solve the problem radically (especially if hyperhidrosis interferes with professional activities) - with the help of injections of Dysport, Botox in the palms, feet or axillary areas. There are attempts to treat hyperhidrosis with other surgical methods - surgical curettage ("husking") of the sweat glands, liposuction of the armpits, endoscopic sympathectomy - removal of nerve fibers approaching the sweat glands (more often with sweaty palms).
A new treatment method has emerged - removal of sweat glands using a neodymium laser.
Locally, you can use antiperspirant-type products (blocking sweat glands), the most effective of which are: for feet - Dry-Dry foot antiperspirant, Oriflaim antiperspirant spray "Active Care", for palms - Dry-Dry, Odaban hand lotion, for the axillary areas - MAXIM, Dry-Dry, Odaban, Lavilin from HLAVIN (used once every 3-5 days), BIOTHERM deo pure, Clinic Dry Form (every other day), Rexona “Long-term protection”, Clarins (daily). Among deodorants that eliminate only odor: LUSH TEO, Weleda (citrus deodorant), etc.
Antiperspirants do not need to be used daily!, unlike deodorants. This is not very favorable, especially if you are prone to swelling; blocking the sweat glands can increase this swelling!
You can also resort to traditional methods of treatment, but this is for ardent opponents of “chemistry” 8):
For hyperhidrosis of the palms: hot hand baths with salt water. For a liter of water, take 3 tablespoons of salt - table or sea. Place your hands in the water and hold until it cools down. Remove and pat dry with a napkin without rinsing. Do baths twice a day
For foot hyperhidrosis. Baths with potassium permanganate (the water should be pink) give good results. If the sweating of the feet is moderate, you can wipe the feet (the skin of the feet and the spaces between the toes) after washing with a solution of salicylic or boric alcohol, and then treat with a mixture of powder and boric acid (1:20).
Teymurov's pasta. Before using the paste, wash your feet thoroughly with soap and water and dry thoroughly. The paste is rubbed into the skin of the feet for 1-3 minutes. The course of treatment with Teymurov paste usually lasts 3-4 days, a second course of treatment can be carried out after a week.
The champion in popularity among folk remedies for treating hyperhidrosis is considered to be oak bark tincture . To prepare the tincture, you need to pour one spoon of oak bark with boiled water, one liter is enough. You can additionally boil the resulting mixture for 5 minutes and leave it to brew for half an hour. Then we lower our arms or legs there. It is worth carrying out at least 10 such procedures, once a day. Oak bark baths can also be made with milk; you only need one glass. The mixture will need to be kept on low heat for about half an hour after it boils. You can prepare a bath: pour 0.5 kg of oak bark into 4 liters of water and boil for 30 minutes, strain and add the decoction to the bath water.
Folk remedies for hyperhidrosis should be used with the same caution as medications. It is important that folk wisdom be used wisely, so involve a specialist in resolving this issue.
In order to strengthen the nervous system in case of excessive sweating, sedatives are used: infusion or tincture of valerian, belladonna preparations - Bellataminal, infusion or tincture of motherwort. Water infusions are taken 1 tablespoon 3 times a day for 2-3 weeks.
The Drionik physiotherapeutic device gives good results.
In addition, it is necessary to exclude spicy, salty and spicy foods from the diet. They promote profuse sweating; alcohol and coffee also increase sweating.
You should not wear synthetic clothes if you sweat excessively; they do not allow air to pass through and promote even more sweat. In addition, synthetic clothing retains the pungent odor of sweat for a long time.
B vitamins, calcium, iron, vitamin D are often added to treatment - their lack can also cause sweating, especially vitamin D deficiency.
I hope my advice will be useful to you. Good luck!
How does botulinum toxin work?
Botulinum toxin is a toxic substance that affects the nervous system. Eating it is extremely dangerous, but in the form of injections the toxin is successfully used in medicine. The toxin is well purified and not hazardous to health. Microdoses of botulinum toxin help relax not only muscles, in order to remove constipation and wrinkles, but are also used to treat migraines and eliminate excessive sweating. Botulinum toxin blocks the transmission of nerve impulses to the sweat glands, as a result, sweat production stops (effectiveness of treatment with botulinum toxin).
The effect lasts for a long time, and then the functions of the sweat glands are gradually restored. In this case, repeated injections are required.
Advantages
- Painless. Injections are performed with a thin needle; an anesthetic is first applied to the skin;
- Safety. Only proven certified drugs are used - “Botox” and “Dysport”, “Relatox”, “Xeomin”;
- Versatility. The technique is suitable for the treatment of hyperhidrosis, regardless of the cause that caused it;
- A quick solution to the problem of hyperfunction of the sweat glands. One session is enough to forget about wet palms, feet, and armpits;
- Long lasting effect. On average, the result lasts for a period of 6 months to a year. In the future, injections can be repeated.
Important: if hyperactivity of the sweat glands is caused by some disease, it is recommended to undergo a course of therapy and consult with your doctor regarding the optimal time for injections.
Drugs for hyperhidrosis - general and local drugs
Drugs used in the topical treatment of hyperhidrosis include:
- aluminum-zirconium salts;
- aluminum sulfate;
- 20% aluminum chloride in anhydrous ethanol.
In general treatment, oxybutynin is most often considered. There is also a combination drug containing wolfberry alkaloids, ergotamine tartrate and phenobarbital recommended for the treatment of migraine pain and nervous hyperactivity. In some cases, this formula is also used in the treatment of hyperhidrosis, as it has an anticholinergic effect.
Preparation
Depending on the processing location, the following types of preparation are required:
- Armpits. The day before the procedure, you need to shave your hair;
- Feet. If there are calluses or hyperkeratosis, excess hardened skin should be removed a few days before your visit to the clinic.
A week before the procedure, it is recommended to stop using special antiperspirants with aluminum salts. You should refrain from drinking alcohol for 2-3 days.
Important! Regardless of the treatment area, at least a week (or preferably two) before the procedure, you should not take medications that affect blood clotting.
Minor's sample
Injections should only be performed by a cosmetologist in a clinic setting. This is a general rule for all injection procedures.
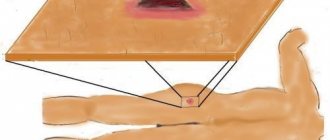
First, the doctor will conduct an examination and collect anamnesis to identify contraindications. After this, the Minor test is performed. This is a completely painless test. The skin is first treated with an iodine solution, and after it dries, it is powdered with starch to stimulate sweat production. Areas with hyperfunction of the sweat glands turn dark purple or black. It is in this area that the injections are performed.
The sample is used if necessary and to assess the effectiveness of treatment. The stained areas are not visible after the test for several months. Then, as the glands restore their function, colored areas appear, and they gradually become more numerous - unless, of course, the cause of hyperhidrosis has not been eliminated.
Diagnostics
The cause of general hyperhidrosis is determined by a general practitioner or family doctor. The diagnostic search is aimed at identifying primary disorders of the body, which can be manifested by profuse sweating. For examination, modern laboratory tests and various instrumental visualization methods are used. The most informative ones are:
- Specific tests
. To assess the amount of sweating, there are quantitative diagnostic methods - gravimetry and evapometry. Hyperhidrosis is established when secretion exceeds 20 mg/minute. Qualitative methods are suitable for assessing the area of pathological sweating; the Minor test and the ninhydrin test are used. - Blood tests
. Tests for the main hormones are required: thyroid, corticosteroids, tropic substances of the anterior pituitary gland. In women, the levels of estrogen and progesterone are examined. To identify the cause of the inflammatory process, clinical and biochemical blood tests and a proteinogram should be studied. - Bacteriological analysis
. To confirm the presence of infectious pathogens, culture of blood, throat swabs or sputum is performed on selective nutrient media. Serological tests are effective for detecting antibodies to pathogenic microorganisms in plasma. To detect brucellosis, the Burnet allergy test is informative. - X-ray examination
. X-ray of the chest is necessary to exclude tuberculous or oncological processes. X-rays are used to look for suspicious space-occupying formations and changes in the vascular pattern. For a more detailed study of the lungs and mediastinum, a CT scan of the chest cavity and MRI are recommended. - Invasive methods
. In case of detection of formations in the chest cavity, transthoracic biopsy (TTB) and subsequent cytomorphological examination are indicated to exclude malignant processes. If the lymph nodes are enlarged, a biopsy of the pathological formation is performed.
How is the procedure done?
The doctor marks the injection points of the drug, applies an anesthetic to the skin, and then, when it takes effect, disinfects the epidermis. After such preparation, you can begin injections. Their quantity, as well as the dosage and type of drug are selected individually.
After the administration of Botox or Dysport, the skin is again treated with an antiseptic. This completes the procedure and the patient can leave the clinic.
Approximate consumption of the drug, effectiveness, duration of action.
| A drug | Approximate consumption, units. | Efficiency, % | Duration of effect, months |
| "Dysport" | 200 — 300 | 90 — 100 | 8 — 12 |
| "Xeomin" | 50 — 100 | 70 — 80 | 5 — 8 |
| "Relatox" | 50 — 100 | 90 — 100 | 8 — 12 |
| "Botox" | 50 — 100 | 90 — 100 | 8 — 12 |
Effect
The result appears within 1-2 days after the procedure and increases over the course of several more days. Sweating noticeably decreases, the unpleasant odor disappears, redness and irritation of the skin disappear.
Important! If hyperhidrosis of the feet was accompanied by a fungal infection, then reducing sweating is only the first step towards recovery. It is also necessary to undergo a full course of treatment for the fungus.
When treating hyperhidrosis, higher doses of botulinum toxin are used than when correcting facial wrinkles, so the results last longer. The duration of the effect depends on the individual characteristics of the body and on how carefully the doctor’s recommendations are followed.