According to WHO, among viral infections, the ARVI group of viruses is in first place, and the herpes simplex virus, which can affect the genital area, is in second place. The uniqueness of this virus lies in its ability to invade various organs and systems, causing a wide variety of clinical manifestations and complications. For this reason, the formation of a unified approach to the diagnosis and treatment of patients with herpes is one of the most important tasks of modern healthcare.
- Causes of herpes
- Types
- Manifestations and symptoms in men and women
- Diagnostics
- How to treat during pregnancy
- Is it possible to resort to folk ones?
- Prevention
In total, 8 types of herpes viruses are known: HSV-1, HSV-2, varicella zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, HSV-6, HSV-7, HSV-8. The structure of virus particles of different types is practically no different from each other. The virus shell contains antireceptors, thanks to which it can attach to almost any tissue and affect the skin, mucous membranes, central and peripheral nervous systems, liver, blood vessels and blood cells. In addition, in some cases, HSV can lead to malignant transformation of cells.
Genital herpes is caused by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2), and less commonly by herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1). Previously, it was believed that HSV-1 manifested itself exclusively as rashes on the face, but it has now been established that each of these two types of viruses can also infect the genitals.
Causes of genital herpes
The genital form of the disease has tended to increase in incidence over the past decades. According to one version, in European countries this was facilitated by an increase in the number of sexual partners for the average person, as well as the widespread practice of oral sex. Also, this disease is more common in areas with high population density, in families with a low socio-economic standard of living and in cases of poor personal hygiene.
Read more
Primary infection with the herpes simplex virus in childhood occurs through airborne droplets - as statistics show, among children 6-7 years old, almost half are infected with herpes. Secondary infection most often occurs through genital, oral-genital and anal-genital contact. The virus that causes genital herpes enters the human body through intact mucous membranes or damaged areas of the skin during sexual intercourse. The highest incidence rate is observed among people aged 20-30 years. In many cases, the infected partner is unaware that he is infected, is an asymptomatic carrier of the virus, and transmits the virus to his sexual partners. A number of scientists believe that about 90% of adults are carriers of the herpes virus, but only 10-20% of them experience its clinical manifestations, including rashes on the genitals. This is due to a decrease in immune defense and the presence of other diseases that further weaken the body. It has been established that women suffer from genital herpes more often than men, which is due to their anatomical and physiological characteristics. Also, according to one version, the risk of HSV infection is increased by surgical termination of pregnancy and the use of intrauterine devices.
The virus is also transmitted vertically - from a sick mother to the fetus and through the use of household items together with an infected person. Also, if there are rashes on the lips and nose, there is a possibility of transferring the virus to the genitals. In addition, HSV is often detected in combination with ureaplasma, other STDs and cytomegalovirus.
Diagnosis of GG
Laboratory confirmation of herpes infection is extremely important. Asymptomatic isolation of HSV can be determined using a culture method or polymerase chain reaction, the sensitivity of which is 4–5 times higher than that when isolating HSV in culture, but does not always allow assessing the infectivity of the virus [18].
The specificity of the culture method reaches 100%, but its sensitivity is affected by the degree of virus isolation, the quality of sampling for research, storage and transportation.
Using indirect (serological) tests, it is possible to determine the presence of antibodies to viruses in a blood sample. Type-specific methods for determining antibodies to HSV-1 and HSV-2 will help in diagnosis. Antibodies to HSV-2 are detected 2–12 weeks after infection. These methods are based on the determination of antibodies to glycoprotein G2 for HSV-2 infection and G1 for HSV-1 infection. The sensitivity of the method varies from 96 to 100%, and the specificity is 97–98%. It is possible that patients newly infected with HSV will have negative serological tests because the average time to seroconversion is 22 days, with approximately 20% remaining seronegative within the first 3 months. Serological tests may also be negative if the patient is receiving antiviral therapy.
When studying skin biopsies using electron microscopy, a number of authors obtained data on the presence of a pathogen in the form of a provirus in places of traditional clinical manifestations during the period of remission of the disease. The study of the mechanisms of persistence and replication of HSV has shown that, perhaps, the full cycle of HSV reproduction and the release of full-fledged virions occur precisely in epithelial cells, i.e., during the formation of vesicles, when the pathogen exhibits its cytopathic effect.
Types of genital herpes
Primary genital herpes: symptoms and localization
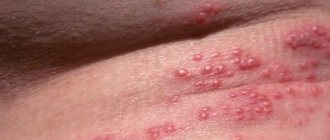
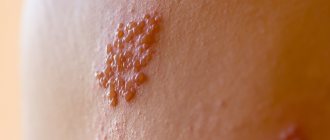
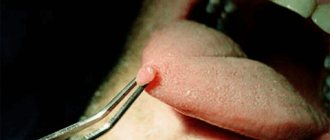
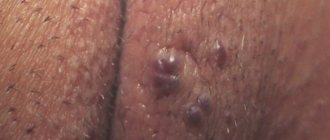
The first stage of the disease is manifested by the appearance of vesicular elements on the skin and mucous membranes. Initially, swelling, redness, itching and discomfort appear in the area where the virus has been introduced. Sometimes this is accompanied by weakness, lethargy, headaches, enlarged inguinal lymph nodes and increased body temperature. After a few days, rashes appear - small blisters filled with clear liquid, which soon burst open and form weeping erosions. Complete healing of the ulcers occurs in approximately 10-14 days.
The localization of rashes on the genitals is determined by the place where the virus enters the body. In women, clinical manifestations of herpes in the intimate area are observed on the labia majora and minora, in the vagina, in the cervix and perineum. In men, vesicles with transparent contents appear on the head and body of the penis, as well as on the scrotum.
The virus can also infect the urethra, bladder, anus, rectum, ovaries, cervical canal, fallopian tubes, uterus in women and prostate and seminal vesicles in men.
Recurrent genital herpes
50-70% of those infected with HSV experience a recurrent form. It makes itself felt by repeated blistering rashes that periodically appear in the same place. In the mild form, exacerbations occur no more than three times a year, the moderate form is characterized by exacerbations up to six times a year, and in the severe form, the patient suffers from monthly rashes and accompanying symptoms, which can significantly reduce the quality of life.
The arrhythmic course of HSV in the genital area is characterized by the presence of remissions, which can reach several months. According to observations, rare outbreaks of the disease are more intense in clinical manifestations than frequent ones. The monotonous course of the infectious disease most often manifests itself depending on the monthly cycle in women. And with HSV of the subsiding type, there is both a decrease in the intensity of symptoms and an increase in periods of remission.
Clinical forms
- Typical;
- Atypical;
- with macrosymptoms;
- with microsymptoms;
- Asymptomatic form;
It is very difficult to establish the real incidence of damage to the internal genital organs in both women and men, since in 25-40%, and according to some data, in 60% of patients, the disease occurs without subjective sensations. It can be assumed that this pathology occurs much more often than it is diagnosed.
With herpes of the internal genitalia there may be no complaints. Sometimes they note periodically appearing light mucous discharge from the urethra and vagina. During laboratory examination of smears of the cervical canal, vagina and urethra, an increased number of leukocytes is periodically noted (30-40 in the field of view of the urethral discharge, 200-250 or more in the field of view when examining smears from the vagina), indicating the presence of an inflammatory process.
The asymptomatic form of genital herpes of the internal genitalia (asymptomatic shedding of the virus) is characterized by the absence in patients of any complaints about the genital area, objective clinical data confirming inflammation. During a laboratory examination of the discharge of the urogenital tract, HSV is isolated, while in smears there are no signs of inflammation (leukocytosis). In 25-30% of men with idiopathic (when the cause of infertility is not clear) infertility, HSV is isolated from semen.
It is known that genital herpes, in 70-80% of cases, occurs in the form of a microbial association, in combination with chlamydia, urea-, mycoplasma, strepto-, staphylococci, fungal flora. It is possible that the genitals may be affected by HSV, gonococcus, treponema pallidum, and viral diseases transmitted through sexual contact, which indicates the need for a thorough examination of patients to exclude STIs and HIV infection.
Manifestations and symptoms of herpes in the intimate area in women and men
Herpetic cystitis of women
Herpetic cystitis is a pathology characterized by inflammatory processes in the bladder caused by the herpes virus. This disease manifests itself as discomfort when urinating and hyperemia of the skin and mucous membranes. Women are especially often bothered by the urge to urinate at night. If left untreated, herpetic cystitis can lead to complications, including herpetic salpingoophoritis. In this case, the inflammation affects the ovaries and fallopian tubes.
Herpes of the urethra and bladder
The disease makes itself felt by painful sensations and pain when urinating. There is a frequent urge to go to the toilet, there may be blood in the urine and discomfort in the bladder area. In men, detection of the herpes simplex virus in the urine may indicate inflammation of the prostate gland.
If you suspect herpetic prostatitis, which is characterized by frequent relapses, the patient must undergo a special examination for sexually transmitted infections of a viral nature.
Herpetic lesions of the anal area and rectum
The disease manifests itself with itching, burning and pain in the affected area. Bleeding may occur during bowel movements. As the disease develops, erosions and cracks form on the mucous membrane, which are often attempted to be treated only surgically, without the use of drug antiviral treatment.
Treatment of genital herpes during pregnancy
The greatest danger of this disease is that the virus can infect the nervous tissue of the fetus, which can lead to the development of intrauterine pathologies. It is especially dangerous if the disease develops in early pregnancy. It can interfere with the normal development of fetal organs and tissues and even lead to spontaneous miscarriage and premature birth. Herpes viruses occupy second place after the rubella virus in terms of teratogenicity - disruption of the process of embryogenesis, leading to developmental abnormalities. More than 60% of children infected with herpes develop encephalitis.
To prevent infection of the fetus as it passes through the birth canal, the expectant mother is most often recommended to have a cesarean section.
Serodiagnosis
Antibodies to the herpes virus appear in the blood serum by 4-7 days after the initial infection, reach a peak after 2-3 weeks and can persist throughout life. The diagnosis is made by the characteristic increase in antibodies and determination of their class. For example, the detection of a certain level of immunoglobulin M (antibodies) indicates a primary infection of a person or an exacerbation of herpes. The detection of a certain level of immunoglobulin G indicates that the human body has encountered the virus and has developed antibodies - the person is infected, but not infectious to others. The result is known the next day. The analysis can be repeated at intervals of several days.
Treatment of herpes in the intimate area with folk remedies: will traditional medicine help?
Traditional medicine existed in all periods of human history, and the experience of traditional healers multiplied over the millennia and was passed on from generation to generation. True, one cannot help but admit that today many of the recipes that our ancestors used have been lost and forgotten, and the assessment of traditional medicine by specialists is still ambiguous. What happens when treated with traditional medicine methods
Today, traditional medicine offers both rational methods, which, under certain conditions, can really help cope with various diseases, and irrational ones, which deserve critical evaluation by doctors. But this does not stop those who, instead of turning to a specialist, decided to help themselves on their own by testing the effectiveness of traditional medicine recipes. As a rule, such people will be disappointed - no decoctions, infusions, applications of medicinal herbs and other drugs prepared at home can help get rid of the manifestations of herpes in the intimate area. It must be remembered that refusal to see a doctor and lack of adequate treatment can lead to unpredictable consequences and the development of life-threatening complications.
Only antiviral drugs that not only relieve symptoms, but also fight the root cause of the disease can help reduce the severity and shorten the course of the disease.
Antiviral drug VIFERON for genital herpes
To combat herpes in the intimate area, it is recommended to use antiviral agents containing interferon. According to experts, interferon has a powerful antiviral effect, and its deficiency is one of the main causes of relapse of the disease. One of the drugs used to treat herpes is VIFERON - an antiviral and immunomodulatory drug with an indirect antibacterial effect, which has a number of unique pharmacological properties.
The drug contains interferon alpha-2b, which blocks the reproduction of viruses and also corrects the body’s own immunity. VIFERON is available in the form of suppositories, ointments and gels. To treat herpesvirus infections in children, suppositories are used in a dosage of 150,000 IU once every twelve hours, for adults - 1,000,000 IU, for pregnant women - 500,000 IU. Gel and ointment are also used to combat herpes in the intimate area. The gel has a hydrophobic base and is better absorbed on the skin, and the ointment has a hydrophilic base and is better absorbed on mucous membranes. The gel in the form of a strip no more than 0.5 cm is applied to the previously dried affected surface 3-5 times a day for 5-6 days. The ointment is applied to the affected surface 3-4 times a day for 5-7 days.
The drug VIFERON Suppositories (suppositories) suppresses the activity of viruses and increases the effectiveness of the body’s own immune response to pathogenic microorganisms. And VIFERON Gel and VIFERON Ointment, when applied to the skin and mucous membranes, form a thin protective layer, which allows you to fight viruses and also strengthens local immunity.
Immunomodulatory therapy
Another stage of complex treatment is immunomodulatory therapy aimed at strengthening the body's defenses. For this purpose, interferon preparations (Viferon, Genferon) are prescribed, as well as interferon inducers (Amiksin, Cycloferon), which have an antiviral effect and promote the production of interferon in the body.
A good effect is achieved by the use of vitamin therapy, in particular the prescription of calcium, zinc, vitamins B, C, E. In order to reduce the frequency of relapses, the patient may be prescribed subcutaneous administration of immunoglobulins. This treatment regimen helps restore the body's defenses and direct them to fight the viral infection.
Prevention of genital herpes virus infection
To prevent infection, you must remember to use a condom during casual sexual intercourse, as well as the use of antiseptics to treat areas of the skin where the virus can get. Relapses of the disease are observed with a decrease in immune defense, various diseases, stress, and even with frequent overheating and hypothermia. Therefore, in order for the clinical signs of herpes to make themselves felt as rarely as possible or not to appear at all, you must try to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat well and get enough rest, as well as regularly take vitamin supplements recommended by your doctor.
To prevent self-infection, in order to prevent the virus from being transferred from the face in the presence of rashes on the lips to the genital area, it is necessary to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and wash your hands more often. Each family member should have separate towels for different parts of the body.
After unprotected sexual intercourse, during sexual relations with a carrier of the herpes simplex virus, and when planning pregnancy, it is necessary to undergo regular examinations with a doctor.
Reference and information material
Author of the article
Belyaev Dmitry Alexandrovich
General doctor
Loading...
Take other surveys