From birth, every person is endowed with a special color of skin, hair and eyes. This is due to genetics and is determined by race. Special cells are responsible for color - melanocytes, which produce the pigment melanin. The shade of the epidermis depends on its quantity. The more dye present in the epidermis, the darker the person’s color type.
However, throughout life, skin pigmentation disorders may occur, which are caused by various pathological processes. In some cases, the spots that appear go away without treatment, in other situations they remain for the rest of life and can only be removed surgically. It all depends on what causes the pigmentation of the skin. Darkening is caused by an excess of melanin, lightening by a lack.
Types of pigmentation disorders
The classification of disorders that cause skin color changes is based on the amount of melanin and the factors that contribute to its production. In this regard, they share:
- Congenital, these include juvenile lentigo, pigmented nevi (moles).
- Hereditary, caused by the appearance of freckles, melanism, Peutz-Jeghers-Touraine syndrome, lentiginosis.
- Acquired, developing during life.
- Limited in nature - senile lentigo, linear pigmentation, chloasma, melasma.
- Diffuse, caused by exposure to toxins, cachetic melasma, Addison's disease.
- Medicinal, in which the appearance of spots is caused by taking a number of pharmacological drugs over a long period. These include toxic Hofmann-Habermann melasma, Riehl melanosis, and poikiloderma reticularis pigmentosa.
Changes in skin color can also be caused by fungal infections and other external factors.
Secondary pigmentation disorders include post-traumatic and post-inflammatory changes in skin color.
Let's look at common types of pathologies.
Cutaneous-ocular albinism. This is a heterogeneous disease that forms at the stage of intrauterine development and is determined by modern diagnostic methods. In this case, the skin color acquires a light milky tint, pigmentation affects the iris of the eyes and hair. Most often, with albinism, patients experience deafness, the development of epilepsy is possible, and there is a high probability of skin cancer.
Treatment is ineffective; it consists of using sunscreens and vitamin A. Patients are advised to avoid exposure to ultraviolet rays.
Another type of primary pigment disorder is hyperchromia, which is characterized by the formation of macules and chloasma (freckles). The spots are round or oval in shape and miniature in size. They are most often localized on the face, however, they can be distributed throughout the body.
Hyperchromia is caused by a hereditary factor and does not pose a threat to health. It appears in infancy. The formation of freckles is promoted by exposure to sunlight, so they become more noticeable in the warm season. The size of the macules can vary from 1 to 10 mm.
The appearance of chloasma is associated with hormonal imbalance, so pregnant women are more often affected by pathology. The spots usually go away after childbirth and require treatment. Skin color is restored on its own when hormonal levels return to normal. However, if the cause of the appearance of age spots is due to the presence of photosensitivity, then drug therapy is prescribed.
Another skin pigmentation disorder is vitiligo. The etiology of this disorder has not been determined. However, it has been revealed that the development of light spots is due to a lack of the enzyme responsible for the formation of pigment. The cause of the development of the disease is malfunction of the thyroid gland, adrenal glands, and pituitary gland.
The first signs of pathology are observed in childhood. Depigmented spots are located symmetrically, localized on the face and other parts of the body, and have a tendency to grow together. At the same time, the skin of the affected areas does not die and does not cause discomfort to patients.
Among the diseases transmitted by inheritance, the following are common:
- Tuberculous sclerosis.
Pathology manifests itself in the form of depigmented spots. Patients present with characteristic seizures, sebaceous adenoma, and mental retardation.
- Neurofibromatosis.
The disease manifests itself at 3 years of age in the form of light brown spots that are located in the armpits. By the age of 10, soft, brownish tumors covered with normal skin appear on the body.
- Mainihan's disease or leopard syndrome is a pigmentation disorder in which, in addition to external manifestations in the form of fused freckles, there is deformation and disturbance of pigmentation of the eyes, deafness, growth retardation, genital pathologies, and pulmonary stenosis.
There are a number of other disorders that arise against the background of external factors.
Stages of skin photoaging
Age-related changes in the skin of the face are enhanced by photoaging - fading under the influence of regular contact with the sun's rays. Photoaging should not be confused with natural aging caused by hormonal changes. Its symptoms can also appear at a young age.
There are four stages:
- No wrinkles. At this stage, people aged 20-35 years have noticeable light pigmentation, there are no deep wrinkles or keratosis.
- Medium type photoaging – facial wrinkles. They appear in people aged 35-50 years.
- Pronounced photoaging. There are many wrinkles on the face, they are noticeable even at rest, there are spider veins, dyschromia, and other types of defects. Such signs are typical for people over 50 years of age.
- Extreme degree of photoaging. At the age of 60-75, the skin acquires a yellow-gray tint, wrinkles are very pronounced and localized over the entire surface, and sometimes precancerous changes begin to appear.
Women are most susceptible to photoaging during the period of hormonal changes - during menopause.
Causes of changes in skin pigmentation and symptoms
Changes in skin color in certain areas - in the décolleté, arms, legs or face - are associated with disorders in the reproduction of melanocytes. This mechanism has not yet been fully studied. However, it is known that there are factors that contribute to the appearance of age spots. These include:
- Hormonal imbalances associated with puberty, pregnancy, menopause.
- Exposure to sunlight, which includes photoaging.
- Lack of vitamins in the body or, on the contrary, their excess.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Improper lifestyle, alcohol abuse and smoking.
- An age factor that is associated with a natural decrease in melanin production.
- Diseases of internal organs, for example, the gallbladder and liver, in which yellowing of the skin and sclera of the eyeballs is observed.
In addition, changes in skin color can be caused by the use of certain types of medications, in particular tetracycline, antihistamines and sulfonamides.
What causes age-related changes in the skin on the face in women?
The beautiful half of humanity suffers over the years for the following reasons:
- During perimenopause, the amount of collagen decreases. Because of this, the fat layer decreases - the skin loses its elasticity and “deflates”.
- Due to collagen deficiency and hormonal changes, skin elasticity decreases. It sags in the neck, chin and cheeks, and lines and wrinkles appear in the forehead and above the lip.
- Expression wrinkles become more pronounced - the corners of the lips droop, the face takes on a tired expression.
- The same hormonal disorders lead to age-related pigmentation on the face, arms and chest.
Diagnostics
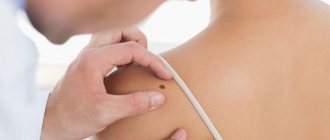
Basically, pigmentation disorders do not pose a particular danger to the health and life of patients and only cause psychological discomfort from a cosmetic defect. However, if the affected areas are injured or exposed to ultraviolet radiation, melanomas can develop into malignant tumors.
Therefore, when age spots appear, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination and determine the cause of their occurrence.
Diagnostics consists of:
- In external visual examination of the skin.
- In collecting anamnesis, which is often not limited to interviewing the patient, but also concerns his immediate family.
- In a dermoscopic examination, in which a device is used to repeatedly magnify and detail the pathological area of the skin.
- In computer diagnostics, which provides the study of affected areas and their comparison with reference samples.
- In histological analysis of tissue sections.
Based on the data obtained, treatment tactics are selected and internal medications are prescribed, as well as external means, for example, the use of photoprotective ointments, peelings, laser resurfacing and other methods of hardware therapy.
Other methods to combat age-related skin changes
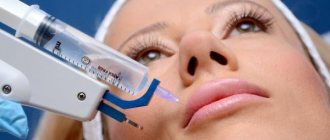
Cosmetology clinics also use effective injection techniques:
- Mesotherapy. Cosmetologists know well which components fight age-related skin changes, so they offer optimal formulations for subcutaneous administration. They contain vitamins, amino acids, enzymes, peptides, hyaluronic acid, etc.
- Biorevitalization. Hyaluronic acid is injected subcutaneously or intradermally and moisturizes the deep layers.
- Botulinum therapy. Botulinum toxin temporarily blocks the nerve endings associated with the facial muscles, which helps smooth out facial wrinkles.
How is ultrasonic facial cleansing performed?
Before the ultrasound procedure, the facial skin is thoroughly cleansed of makeup, dirt and dust, then the skin must be steamed. A special gel is applied to clean, steamed skin and only then can the metal paddle of the device be smoothly moved over the surface of the skin.
When treating the skin with a scrub apparatus, a slight tingling sensation may occur. The entire cleaning procedure can last from 40 minutes to an hour and a half.
The procedure for ultrasonic skin cleansing should be carried out by an experienced cosmetologist who can professionally assess the quality of the procedure and give recommendations for further facial skin care.
Rosacea
This sign of aging is characterized by facial flushing, telangiectasias, rough skin, and inflammatory papulopustular changes.
The exact pathogenesis of the disease has not been studied: the role of heredity, skin microbiome, dysregulation of the immune system, and abnormal signal transmission to nerves and blood vessels has been suggested. An important aspect of rosacea are triggers - provoking factors, which are individual for each person and are determined experimentally.
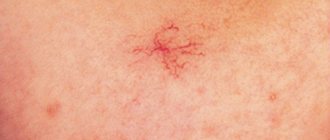
During attacks of rosacea, a person experiences erythema on the face, sometimes with telangiectasia. Over time, inflammatory papules and pustules appear in the area of the nose, forehead and cheeks ( Fig. 6 ); rhinophyma, conjunctival vascular injection, chalazion and episcleritis may appear. Learn more about rosacea and its treatment options here.
Rice. 6. Rosacea with inflammatory elements on the cheeks (Danish national service on dermato-venereology)
1.Human skin
The skin is a thin outer shell that protects the body from the adverse effects of external factors. It is an independent organ that performs many functions and is a kind of mirror reflecting the state of human health.
Due to the close physiological relationship of the skin with various systems and organs, on the skin we can see the result of many internal pathological processes and diseases. Correct assessment of the condition of the skin is an indispensable aid in diagnosing health problems.
A must read! Help with treatment and hospitalization!
Who is recommended for ultrasonic peeling?
Almost everyone who wants to improve the condition of their facial skin can use ultrasonic peeling.
Ultrasonic peeling is an alternative to other methods of skin cleansing. Such, for example, as:
- Chemical peeling, which penetrates deeply into the dermis and can cause a chemical burn.
- Mechanical facial cleansing. It is recommended to first perform ultrasound peeling, that is, in this case the skin is cleansed using a combined method.
- If you need to hold an event and look good, then ultrasonic peeling will help you.
- Ultrasound peeling procedures can improve the appearance of aging skin in older women.
The effect of ultrasonic skin cleansing is noticeable immediately, but it will become more obvious after three days:
- the skin becomes smooth and elastic;
- through the cleansed pores of the skin she can breathe;
- after removing the upper keratinized layer of skin, a layer of young cells appears;
- fine wrinkles are smoothed out due to the acceleration of cellular metabolism;
- the process of cell restoration is activated.
Skin micromassage, which occurs at the cellular level, accelerates metabolism and improves the supply of blood and lymph to cells. After removing the stratum corneum of the skin, the active components of creams and face masks penetrate into it better.
Ultrasound peeling can be performed at any age and on any skin type. Under the influence of ultrasonic waves, the structure of cells is reformed, which begin to actively produce collagen and elastin - components that improve the condition of facial skin.
Etiology and pathogenesis
There are many etiological factors for uneven skin color, and below we will give only a few of them.
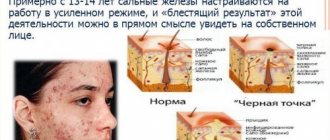
One of the most common causes is ultraviolet radiation - prolonged exposure to the sun or regular visits to solariums. Under the influence of UVB, melanocytes begin to intensively produce pigment, which can be deposited in different amounts in different parts of the body (for example, due to greater insolation of some areas and less of others) - as a result, this forms an uneven skin color.
Recent research suggests that HEV rays of 400–500 nm (High-energy visible light, blue light) emitted by modern gadgets contribute to the appearance of uneven skin color. An important feature of HEV radiation is its deeper penetration into the skin compared to UVB and UVA ( Fig. 1 ).
Rice. 1. Comparison of penetration depth of UVB, UVA and HEV radiation
Please note: ultraviolet B ( UVB ) reaches a maximum of the papillary layer of the dermis, ultraviolet A ( UVA ) reaches the reticular layer, while blue light ( HEV ) from electronic gadgets penetrates even the upper layers of subcutaneous fat.
Uneven skin color can occur as a result of environmental pollution ( pollution ). This problem is extremely relevant today for Asian countries with high urbanization and a significant density of inhabitants per square kilometer. However, the pollution factor should be taken into account by all people living in large cities. Studies have shown that under the influence of particulate matter with a diameter of 2.5–10 microns (PM2.5–10), a receptor protein (Aryl hydrocarbon receptor, AhR) is activated in human epidermal keratinocytes, which triggers genes responsible for the formation of age spots and premature skin aging . Thus, protection against pollution using cosmetics with Pollution Protection Factor (PPF) becomes very important.
Uneven color may be caused by hormonal changes (aging, menopause) or taking certain medications ( contraceptives, doxycycline).
Any inflammation acne sufferers .
Vitiligo contributes to the formation of depigmented areas of varying sizes on the skin, which overall creates a picture of uneven tone.
Vitamin B3 (niacin) deficiency causes pellagra, which causes uneven skin color, dryness, and increased sensitivity to the sun. More serious symptoms include diarrhea and dementia.
Uneven tone can also occur due to diseases of internal organs, vascular pathologies, disturbances in the microbial composition of the skin, etc.