The liver is the body's filter. It cleanses the blood of toxins, poisons, heavy metal salts, toxic bile pigments, breakdown products of alcoholic beverages and much more.
The patient’s skin condition directly depends on the detoxification function of the liver. If the gland works intermittently, the condition of the skin deteriorates greatly. Rashes, spider veins, areas of hyperemia, urticaria and much more may appear on it.
In addition, jaundice syndrome often develops against the background of liver and gallbladder pathologies. With it, the skin, eye sclera and mucous membranes change their color. Let's take a closer look at what symptoms can be used to recognize diseases of the hepatobiliary system and how the condition of the skin changes with them.
How is the liver connected to the skin?
The liver is the filter of our body. All substances that enter the body with food, water, air, etc., pass through the liver, are purified and only then removed from the body naturally. When the functioning of this organ is disrupted for any reason, it can no longer perform its filtering function and intoxication occurs. First of all, its symptoms are visible on the skin. The body tries to get rid of accumulated toxins using the largest organ of the body - the skin.
What happens to the skin if there are liver problems? It is necessary to pay attention to its general condition:
- Change in skin color,
change in color - redness (see photo), yellowness, blueness, excessive pallor are alarm bells; - dry skin and flaking, as well as excessive oiliness and sweating, can also indicate liver pathologies;
- the appearance of marks on different parts of the body;
- rash elements - multiple formations on the skin of unknown origin that cause itching.
The liver is perhaps the organ whose disease you should think about first if your skin is not the same as before.
What liver pathologies are manifested by rashes?
The liver suffers for various reasons. Some of them cause a reaction on the skin in the form of rashes. This is for example:
- Rash due to hepatitis C
viral hepatitis A, B, C (see photo), D, E, G and their consequences - cirrhosis, cancer; - poisoning by toxins - medicinal, food, chemical, alcoholic and narcotic;
- helminthiases - amoebas, lamblia, schistosomes, echinococci, roundworms - all of them can cause abscesses;
- non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) - develops due to poor diet;
- vascular disorders - hepatic vascular thrombosis, hepatic artery occlusion, ischemia;
- hereditary diseases - hemochromatosis, Gilbert's syndrome, Wilson-Konovalov disease;
- autoimmune pathologies - primary biliary cirrhosis, autoimmune hepatitis, primary sclerosing cholangitis, autoimmune cholangitis;
- oncological diseases;
- organ injuries can have long-term consequences.
It is quite difficult to determine on your own what exactly from this list provokes your rash, especially if the disease is in the initial stage. However, timely diagnosis is very important for successful treatment. Therefore, if a rash appears, it would be better to seek advice from a doctor.
Diagnostics
One of the most informative and at the same time accessible methods for diagnosing liver condition is a biochemical blood test. It allows you to detect various components of bile in blood serum, as well as fragments of destroyed hepatocyte membranes.
In case of liver disease, the following changes are observed in the biochemical blood test:
- increased levels of bile acids;
- increased bilirubin content;
- increased cholesterol levels;
- the presence of alkaline phosphatase, leucine aminopeptidase and 5'-nucleotidase in the blood serum;
- increased transaminase concentration.
If any of these markers are detected in the patient’s blood, the doctor will refer him for additional studies to determine the cause of these disorders. So, an ultrasound examination of the liver may be required. With an ultrasound examination, you can not only obtain an image of the liver and determine its size, but also visualize the bile ducts: with cholestasis, they will be expanded above the blockage site.
If the doctor suspects the presence of viral hepatitis, you will have to undergo additional testing. A blood test for markers of viral hepatitis is a search in the blood serum for immunoglobulins characteristic of these diseases. These are specific protective proteins that are released when an infection enters the body to neutralize it. Each type of infection has its own type of antibody.
If an abscess or cancer is suspected, an x-ray examination is performed. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging make it possible to obtain truly high-quality layer-by-layer visualization of any organ, therefore this diagnostic method is also actively used in the diagnosis of liver diseases. However, the main disadvantage of this study is its high cost, which somewhat narrows the range of patients.
If it is necessary to clarify the diagnosis, a liver tissue biopsy may be prescribed. Patients are very wary of diagnostic procedures of this kind, because a biopsy is an invasive method that involves taking a small sample of tissue using a special needle. However, this approach is fully justified if other diagnostic methods turn out to be uninformative, and a person’s health and life are at risk.
Types of rashes in liver diseases
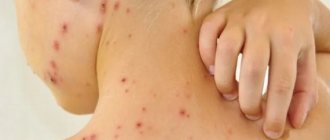
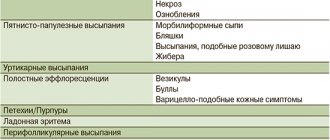
The appearance of the elements of the rash can tell a lot about its causes. When the liver is unhealthy, the following signs of disease appear on the skin:
- Pustules. Elements of the rash are inflammatory in nature, with purulent contents. They can be superficial, but sometimes develop into furunculosis. In liver diseases, they appear regularly throughout the body. This may indicate that the function of immunoglobulin synthesis and the general state of immunity are reduced in the liver.
- Hemorrhages. Single spots and their clusters are red, seemingly located under the skin. They are called petechiae and appear due to hemorrhages in small vessels. The reason is that the production of blood protein is disrupted, which causes hemorrhagic syndrome. Petechiae are often found in humans along with large bruises.
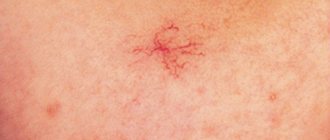
- Spider veins are clusters of small vessels that are visible through the skin. If there are many such accumulations and new ones constantly appear, the matter is probably a change in the structures of the liver. Such rashes are localized on the face, neck, back, and tend to increase in size.
- Liver plaques on the eyelids
Liver plaques. These are flat lumps on the skin that look like yellowish subcutaneous granules. They are located on the eyelids (see photo), in the armpits, legs and arms. - Erythema is redness on the skin in the form of round spots. They disappear when pressed.
- Allergic dermatitis. A small red rash may be the first sign of a liver reaction to toxins or allergens.
- Eczema. Itchy rashes, including blisters with purulent or liquid contents. Bursting one by one, the bubbles become covered with crusts.
- Hives. A rash in the form of large spots of different shapes merging with each other, with a swollen surface, which is accompanied by itching. Feels hotter than healthy tissue. Occurs due to a reaction to allergens.
Almost all types of rash are accompanied by itching of varying severity. Of course, they may indicate other diseases not directly related to the liver. Therefore, you must always look at the big picture. Associated symptoms will help differentiate liver pathologies from other diseases.
What explains the skin manifestations?
If the liver for some reason can no longer cope with its functions, the skin suffers first. At the same time, itching of the skin in liver diseases is one of the earliest and most characteristic symptoms of the disease. Later, spots on the skin and a rash appear, and only after some time (from a month to several years) other symptoms appear (darkening of the urine, disruption of the intestines, pain in the right hypochondrium, etc.). Why do liver disorders so quickly affect the condition of the skin?
The main reason is an increased amount of toxic substances that circulate in the blood. A healthy liver has time to filter out toxic substances that enter the body. However, with inflammation, proliferation of connective tissue and partial replacement of liver tissue with fat, the ability to neutralize harmful substances is significantly reduced. The body is not only unable to effectively deal with toxins, but also begins to poison itself - with liver diseases, the digestion and assimilation of food significantly deteriorates, which begins to ferment in the intestines, causing putrefactive processes.
It is not difficult to guess that sooner or later the products of decay and fermentation in the intestines will end up in the blood and lymph, which will immediately affect not only the condition of the skin, but also the nervous system. It is the large amount of toxins in the blood that explains poor sleep, fatigue, irritability and lack of focus.
As we found out, with general intoxication of the body due to liver disease, symptoms such as spots on the skin occur. However, itching often occurs. It can occur on any part of the body, but is most often noted on the patient's palms and soles. This symptom is not an independent disease, as many may initially think.
With stagnation of bile, caused by spastic conditions of the sphincters of the bile ducts, the blood is saturated with its salts, which cause a feeling of itching.
Other symptoms of liver disease other than rash
In addition to skin manifestations, the liver signals its ill health with many other abnormalities. The patient may be concerned about:
- nausea;
- heartburn;
- belching;
- dizziness;
- feeling of increased appetite;
- loss of appetite;
- pungent odor of sweat;
- pain in the hypochondrium - acute or diffuse, nagging;
- abdominal enlargement;
- swelling of the body;
- low-grade fever;
- weight gain or loss;
- bitterness in the mouth;
- bad breath;
- white or brown coating on the surface of the tongue;
- increased vascular pattern on the abdomen;
- changes in the color, shape or texture of stool;
- general weakness, inability to perform mental and physical work.
None of this is normal. If one or more signs from this list appear, you need to undergo a comprehensive examination at the clinic.
What to do
Having discovered manifestations that are atypical for a healthy person, many people are wary, but do not rush to see a doctor. Meanwhile, delay can be fatal.
Prolonged discomfort in combination with skin disorders is a reason to consult a therapist. He will prescribe blood, urine and stool tests, liver tests, ultrasound of internal organs and decide what to do next. In case of serious pathologies, the therapist refers patients to a hepatologist - a specialist in liver diseases.
Possible treatments
There are quite a few diseases that affect the liver. The choice of treatment options is just as great. Not just any method will be suitable - this decision is within the competence of the doctor. What can be offered? These are the following drugs:
- Hepaprotectors. This is a group of medications with herbal or synthetic ingredients that are aimed at restoring damaged organ cells. These include Karsil, Gepabene, Ursosan, Essentiale, Bonjigar, Gepadif.
- Antihistamines. If the rash is caused by a liver reaction to allergens, these drugs help stop the acute immune response. Well-known drugs are Suprastin, Loradatin.
- Sorbents. Since a diseased liver is unable to cope with the flow of toxins, its function must be taken over by sorbents - substances capable of absorbing (sucking in) components that poison the body. You need to use Enterosgel, White Coal, Polysorb, Polyphepan.
- Antiviral agents. Prescribed for hepatitis - each type has its own medicine.
- Antihelminthic drugs. If one type of worm is diagnosed, treatment is prescribed by a parasitologist. Popular methods of expelling worms on your own are fraught with the formation of abscesses in the liver.
- Immunomodulators. Prescribed to support the immune system during periods of weakness due to illness (Likopid, Amiksin and others).
- Vitamins. Due to liver dysfunction, the body does not receive enough nutrients, so their deficiency needs to be replenished.
A large number of medications can completely destroy the liver, so it is extremely important that they are prescribed by a specialist. Skin manifestations usually disappear after the diseased organ is put in order, so only products aimed at reducing discomfort are used externally. Hormonal-based creams and ointments will help relieve itching and swelling. Preparations containing dexpanthenol promote healing and softening of tissues.
Is folk treatment possible?
At home, treatment is possible only in combination with therapy prescribed by a doctor and with his permission. To get rid of a disturbing rash, you can use infusions:
- chamomile;
- oak bark;
- sequences;
- sage;
- calendula;
- celandine.
These infusions will help reduce the discomfort that the rash brings - itching, swelling, hyperthermia.
In order to help the diseased organ, you can take herbal infusions orally. Very useful:
- corn silk;
- tansy;
- dandelion;
- birch leaves;
- milk thistle;
- St. John's wort;
- rose hip;
- mint;
- yarrow;
- motherwort;
- horsetail;
- oregano;
- hop;
- dill;
- fennel.
The list goes on. These herbs can be taken either separately or as part of a mixture. And remember that under no circumstances should they replace the main treatment.
It is very useful for liver diseases to take freshly squeezed juices from pumpkin and carrots. However, if you have sallow skin, these vegetables can make it even worse.
What is needed besides treatment
Any disease requires not only taking medications, but also introducing some changes into your life, such as diet. The liver is an important link between food and its benefits to the body. Therefore, nutrition must be correct. It is not recommended for a person with a diseased liver to consume fatty, fried, salty, spicy, and sweet foods. It is better to eat more vegetables and fruits, whole grains. It is acceptable to consume low-fat milk and meat.
You should give up bad habits. This may be difficult, but remember: the liver is a self-healing organ, so by removing the source of negative influence on it, you will increase the likelihood of recovery many times over. A healthy liver will provide smooth, beautiful skin without breakouts.
Safety precautions: how to avoid relapse
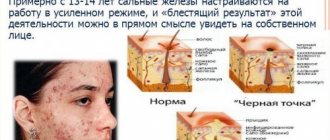
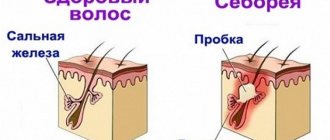
Cleansing the liver and facial skin are connected, and the opposite effect in the form of the return of acne at the slightest problem with filtering toxins occurs constantly. How to prevent acne from returning after cleansing? There are several ways:
- once and for all formulate a diet that excludes foods harmful to the liver;
- give up alcohol - all organs will be grateful, not just the liver;
- give up strict diets that provoke fatty hepatosis;
- monitor your immunity, promptly treat all colds and infectious diseases;
- take hepatoprotectors in preventive courses as needed;
- drink more clean water;
- regularly breathe fresh and clean air in parks or gardens, preferably outside the city.
Quite simple tips that, unlike the strict prohibitions of a chronic patient, can be violated occasionally - one fried pie every couple of months will most likely not cause acne. And the best part: the rules can be supplemented with your own observations, because each organism is unique.
It is important to remember that acne resistant to cosmetic procedures and the liver have a very direct connection. Therefore, if suddenly acne and oily skin become a problem, you need to make an appointment with a hepatologist. Just in case.