Chancroid in women (photo attached) is a very dangerous sexually transmitted disease, being one of the stages of syphilis. Even in the early stages, syphilitic infection is very dangerous for sexual partners, and in an advanced stage it becomes a life-threatening pathology for the sick woman herself. Chancroid in women must be identified as early as possible, and only in this case can treatment give a positive result.
Incubation period and pathogenesis of the disease
The entry points for syphilis pathogens are damaged mucous membranes and skin. The period of illness from the moment pathogens enter the patient’s body until the appearance of primary changes (chancroid) is called incubation. During the incubation period, bacteria multiply intensively in lymphatic vessels and nodes. Reproduction of pale treponema occurs by division at a rate of one division in 30 - 32 hours. There are no clinical manifestations of the disease during this period, serological tests remain negative. The incubation period averages 3 to 4 weeks. Sometimes the incubation period is shortened to 8 - 15 days, or extended to 190 days. In case of simultaneous infection of 2 sources, a shortening of the incubation period is recorded. When taking antibiotics after infection, its lengthening is noted.
At the end of the incubation period, primary syphiloma appears at the site of introduction of pale treponema - chancre (hard ulcer), erosive or ulcerative chancre, an increase in regional lymph nodes (regional lymphadenitis) is noted, and later the entire lymphatic system begins to respond to the infection (syphilitic lymphadenitis or polyscleradenitis). With maximum accumulation in the lymphatic system, bacteria penetrate through the thoracic lymphatic duct into the subclavian vein. Syphilitic septicemia develops. In some patients, this period is manifested by an increase in body temperature, severe headaches and muscle-joint pain, weakness, and general malaise.
Serological reactions become positive 3 to 4 weeks after infection.
The spread of pale treponema with blood throughout the body marks the development of the next stage of the disease - secondary syphilis.
- Primary affect (primary syphiloma) forms 3 to 4 weeks after the initial infection.
- Within 1 - 2 weeks, the chancre increases in size, and then after 6 - 8 weeks the ulcer scars even without treatment, erosion epithelializes after 4 - 5 weeks.
- On the 5th - 6th day after the appearance of primary syphiloma, regional lymph nodes enlarge.
- After 5 - 6 weeks, polyscleradenitis develops, which indicates the generalization of a specific process.
- Serological reactions become positive 3 to 4 weeks after infection.
- The primary period lasts about 7 weeks.
- The end of the primary period is marked from the moment of occurrence of secondary syphilides.
Rice. 2. The appearance of hard chancre in the anus and oral cavity is associated with sexual perversions.
What should I do if I'm pregnant?
If you think you are or may become pregnant, it is important to get tested for syphilis. If the mother has syphilis, the baby may be born with congenital syphilis. It can cause stillbirth and birth defects, but you can avoid this by getting tested for syphilis during the first and third trimester of pregnancy.
Is there a cure for syphilis?
Yes, syphilis is highly treatable, especially in the initial stages. As a rule, syphilis is treated with penicillin, but if you are allergic, a similar medicine will be found for you.
How do I know if I have syphilis?
Syphilis is diagnosed only through a blood test; according to the law on medical care for the population of Russia, you can take a syphilis test for free, anonymously at any speed center.
Chancre is the first symptom of syphilis
After 3 - 4 weeks from the moment of infection, the patient develops primary syphiloma - an ulcer or erosion - at the site of introduction of the pathogens.
An ulcer in syphilis has a hard infiltrate at the base, which is why it is called a “hard” ulcer or chancre. With a deep ulcer, the infiltrate at the base is powerful and has a cartilaginous structure.
With erosion, the infiltrate at the base is weakly expressed and hardly noticeable upon examination.
Primary syphilomas in syphilis are painless and even without treatment, after 6 - 8 weeks the ulcers scar, after 4 - 5 weeks erosions become epithelialized, which is why patients often do not go to doctors and miss the favorable period for effective treatment. The appearance of hard chancre, the development of regional lymphadenitis and lymphangitis, positive specific serological reactions are the main signs of the primary period of syphilis. Treatment of the disease during this period always ends with a complete cure.
Chancre is the most important sign of primary syphilis.
Rice. 3. Primary syphilis - hard chancre on the penis.
What does chancre look like?
Hard chancre in the form of erosion has clear boundaries, a smooth bottom and gently sloping edges, bright red color, raised above the skin level, there is no hyperemia of the surrounding tissue, a dense infiltrate is located at the base. There is no pain on palpation. In closed areas of the body (genital mucosa, oral cavity), the surface of primary syphilomas is smooth and shiny, bright red in color, moist with exudate, round or oval in shape. The surface of syphilomas located on open areas of the body, including the red border of the lips, shrinks into a crust, but all the signs of a hard ulcer remain.
Erosive hard chancre occurs in 80% of cases. In recent years, hard chancres that lack a clearly defined compaction at the base have become increasingly common.
Hard ulcerative chancre is a deeper defect. Develops in people with reduced immunity. The bottom of such an ulcer is dirty yellow, often with small hemorrhages and copious discharge. The infiltrate at the base often has a nodular shape. Such ulcers heal with a smooth scar with a hypochromic (colorless) rim along the periphery. In recent years, ulcerative chancres, including those complicated by pyogenic infection, have been increasingly detected.
The duration of healing of the primary defect directly depends on the severity of the infiltrate at the base. If the infiltrate at the base is weakly expressed (erosive defects), then healing occurs in 1 - 2 weeks, no trace remains. Large chancres, which have a strong infiltrate at the base, persist for up to 2 - 3 months and often persist even in the secondary period of syphilis. They heal with a scar.
Rice. 4. An ulcer with syphilis has a hard infiltrate at the base, which is why it is called a “hard” ulcer.
The size of chancre
- The size of chancre in diameter is 1 - 2 cm.
- Less common are dwarf hard ulcers. Their size is 2 - 3 mm in diameter.
- There are giant hard ulcers that have pronounced compaction at the base. They are localized on the scrotum, pubis, abdomen, chin, forearms and inner thighs - in places where fatty tissue is abundant.
- There are hard ulcers that tend to grow peripherally (burn chancre). They represent erosion with blurred, irregularly shaped edges, a granular bottom, and a dark red color.
Rice. 5. Primary syphilis is a giant chancre of the anterior abdominal wall.
Number of hard chancres
In 60 - 90% of cases, single primary syphilomas occur. Multiple syphilomas are less common. They are formed during the simultaneous penetration of pathogens in different places or during repeated infections during the first 10 - 14 days. Their number can reach 50 or more.
Rice. 6. Multiple hard chancre in men and women.
Rice. 7. Multiple hard chancres on the sides of the frenulum of the penis.
Rice. 8. Multiple hard chancre on the penis.
Varieties of chancre
- Diphtheria chancre is covered with a gray necrotic crust.
- Chancroid herpetiformis resembles genital herpes.
- Cortical chancre. Located in open areas, primary syphilomas quickly dry out and become crusty, resembling pyodermic elements.
- Slit-like chancres resemble cracks; they are located in the corners of the mouth, folds of skin and interdigital spaces.
- Folman's balanitis is a rare type of primary syphiloma. It is characterized by the presence of many small erosions on the head of the penis, partially merging in places, with sharply demarcated edges; the seal at the base is absent or barely noticeable.
- The frenulum of the penis, the external opening of the urethra, the folds of the anus, and the tonsils are the main locations of painful chancre.
Localization of chancre
The localization of hard chancres can be divided into genital, extragenital and perigenital. Primary syphiloma is most often located on the genitals. The penis, scrotum, less commonly the pubic skin, and inner thighs are their main locations in men. The labia majora and minora, clitoris, frenulum, cervix and rarely the inner wall of the vagina are the main locations of primary syphilomas in women.
The appearance of chancre in the anus and oral cavity is associated with sexual perversions. Chancres of the oral cavity and around the nipple are more often recorded in women. Primary defects in the anal area are more often recorded in men.
Extragenital chancres are recorded on the lips, tonsils, tongue, gums, facial skin, including eyelids, fingers, abdominal skin, thighs and other parts of the body.
In 12% of cases, the localization of primary syphilomas cannot be detected.
Rice. 9. Primary syphilomas on the face and upper eyelid.
Treatment methods
To prevent infection and the formation of syphil, you need to use condoms and not give your personal hygiene items to other people. If contact with an infected person does occur, then start taking sulfonamides within the first hours.
With timely treatment, chancre disappears after a week, heals completely in 1-2 months - often before secondary syphilis develops, but then appears again. The cause is an infection, so therapy is primarily aimed at eliminating it and preventing its spread, preventing subsequent complications.
However, for this it is necessary to differentiate syphilis from:
- other sexually transmitted diseases;
- acute tonsillitis;
- fungal infections;
- herpes;
- traumatic ulcers and erosions;
- tuberculosis.
To do this, blood tests are performed using nonspecific tests (for example, PRP, Wasserman reaction). If a positive result is obtained, then specific diagnostics are additionally carried out, with the help of which the presence of antibodies to certain pathogenic microorganisms is detected.
Drug treatment
The therapeutic regimen includes drugs for external and internal use. The causative agents of the disease are highly sensitive to penicillin, tetracycline and macrolide antibiotics.
During treatment, blood is regularly drawn for testing. This is used to evaluate the effectiveness of therapy. Antibiotic treatment is supplemented with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory external agents.
| Drugs | Effect of drugs, treatment regimen |
| Azithromycin, Ceftriaxone, Doxycycline | Prescribed if the patient is allergic to penicillin drugs. |
| "Bicillin" | Contains only one antibiotic. Available in powders, it works for a long time. Causes the death of Treponema pallidum. The drug is administered 2 times a day, 3 million units. with an interval of 5 days, or 5 million units. once at the same interval. |
| "Erythromycin" | One of the safest antibiotics that can be given even to children. Adults are prescribed 3-4 tablets (0.5 mg) per day on an empty stomach, 30 minutes before meals. If after it, then after 1.5 hours. The dosage is calculated based on body weight. |
| "Extencillin" | The main drug for the treatment of primary syphilis. Prescribed to eliminate an infection that causes the formation of chancres. The drug is administered intramuscularly, twice a day. Before this, Extencillin is mixed with novocaine - 2.4 million units/0.5% (at the rate of 100,000 units/ml). If syphilis is primary, then the drug is administered once, into the buttocks. |
| Disinfectants | If there are chancres and ulcers, they are disinfected with benzylpenicillin and dimexide - in the form of lotions and baths. Such compresses help the active substances penetrate deep into the tissues. Applications with mercury or heparin ointment may be prescribed. They are changed daily. To speed up the healing of hard chancre, from which a yellowish substance comes out, the affected areas are lubricated with products containing erythromycin. Mercury-bismuth and syntomycin ointments are highly effective. |
| For washing, rinsing | When syphilitic chancre appears on the mucous membranes of the mouth, it should be rinsed with a solution of furatsilin mixed with boric acid and gramicidin. Their proportions are prescribed by a venereologist. |
| When a fungal infection occurs | If a fungal infection occurs during antibiotic treatment, then Tinidazole (1.5-2 g once a day, for up to 10 days), Metronidazole (250 mg twice a day, for 10 days) are additionally prescribed. . |
| Probiotics | These drugs are given after the end of antibacterial therapy. Antibiotics destroy not only pathogenic, but also beneficial microflora. Therefore, after them it is necessary to take probiotics, which restore the microflora of the digestive system. For example, “Bifiform”, “Linex” (2-3 capsules per day, course from 10 to 21 days). |
| Multivitamins | They are necessary as an additional means to improve the general condition and strengthen the immune system (for example, “Duovit”, “Alphabet”, “Vitrum”). Give one tablet once a day, the course of treatment is a month. |
| Antihistamines | They are prescribed only when allergic reactions occur (Suprastin, Tavegil). They are given 1-2 tablets per day, with meals. |
Azithromycin
All drugs are selected individually, depending on contraindications and concomitant diseases. Treatment is required for anyone who has had sexual contact with someone who is sick, especially if condoms were not used.
During therapy, these people need to temporarily abstain from sexual intercourse. Especially if hard chancre appears on the genitals. When they are localized on the fingers or in the oral cavity, you need to use only individual cutlery and personal hygiene items.
Traditional methods of treatment
Chancres and erosions can be lubricated with antiseptic and anti-inflammatory folk remedies. For example, fresh burdock root oil. It is crushed, filled with vegetable oil and left for 24 hours. Then cook over low heat for 15 minutes, cool and filter. The product is used to lubricate chancre, erosions and ulcers several times a day.
Applications are made with propolis infusion. The tincture (10%) is diluted in boiled water in a ratio of 1:3. You can also tie fresh plantain and burdock leaves to chancre and ulcers (you need to mash them first). Additionally, baths with iodine are given.
Chancres and erosions are smeared with an infusion of yarrow, onion, and resin from coniferous trees. They are taken in equal proportions and mixed with natural wax or pork fat to the consistency of an ointment. Then apply the product to the affected area.
After completion of therapy, the patient should be observed by a venereologist, first every three months for a year. Then - at intervals of 6 months, then - once a year. The duration of control examinations is determined by the venereologist.
Signs and symptoms of syphilis in men during the primary period of the disease
Hard chancre in men has its own characteristics, which depend on their location:
- small erosive chancres are often located on the head of the penis;
- ulcerative chancres are located in the head groove, they are large in size, and have a powerful infiltrate at the base;
- primary syphilomas, located on the frenulum of the penis, have an elongated shape, are easily injured and bleed during erection;
- in primary syphilomas located on the sides of the frenulum, there is no compaction at the base;
- in the region of the edge of the foreskin there are linear chancres;
- the seal at the base of the chancre, located in the area of the inner layer of the foreskin, looks like a visor;
- the hard chancre located on the crown of the glans penis resembles a swallow's nest;
- when located in the urethra, chancres have a dense consistency, are painful on palpation, always bleed, urination is also painful, scanty serous-bloody discharge is noted, in some cases, when cured, a cicatricial narrowing of the organ occurs;
- when the lymphatic capillaries are damaged and the outflow of lymph is impaired in the area of the scrotum and penis, indurative edema occurs, characterized by a sharp increase in the organ, which becomes dense; after pressing, no hole remains. There is no pain. The swelling subsides slowly even with treatment.
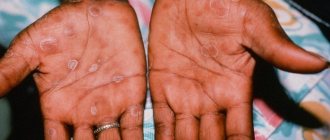
Rice. 10. Primary syphilomas in men - localization on the head of the penis (photo on the left) and in the area of the inner layer of the foreskin (photo on the right).
Rice. 11. Ulcerative chancre, located in the head groove, is large in size, has a powerful infiltrate at the base and is linear in direction.
Prices for services
Initial appointment with a urologist FOR MEN + ultrasound of the prostate gland (assessment of complaints, medical history, if necessary, rectal digital examination, ultrasound of the prostate gland in men)
Primary appointment – visiting a doctor of a specific specialty for the first time. Includes a conversation with the patient, an initial examination, anamnesis, if necessary, a digital rectal examination, and an ultrasound of the prostate gland. The price is valid from 02/01/2021 The price is not valid for appointments at the branches of Bolshevikov Ave. and Prosveshcheniya Ave. Make an appointment
700 ₽ 900 ₽
Repeated appointment with the urologist
Make an appointment
550 ₽ 700 ₽
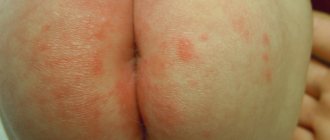
Signs and symptoms of syphilis in women during the primary period of the disease
Chancroid in women has its own characteristics, which depend on their location:
- erosive chancres are more often located in the area of the labia majora, indurative edema is less often recorded;
- chancre located in the area of the urethra always has a dense base;
- in chancre located in the area of the vulvovaginal fold, the compaction at the base is not pronounced;
- primary syphilomas, located on the cervix, are erosions of round shapes, with a flat bottom, clearly defined boundaries, intense red color, scanty serous discharge;
- when lymphatic capillaries are damaged and lymph outflow in the area of the clitoris and labia is impaired, unilateral indurative edema occurs, characterized by a significant increase in the organ, which becomes dense, dark red in color, often with a bluish tint. After pressing, there is no hole left. There is no pain. The swelling subsides slowly even with treatment.
- Primary vaginal syphiloma is extremely rare;
- in the area of the nipple in women, chancre is recorded in the form of erosions, usually single, with pronounced compaction at the base, covered with a crust;
- The crescent-shaped crack has a primary defect localized at the base of the nipple.
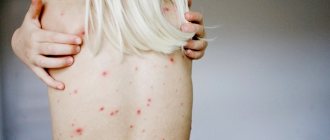
Rice. 12. Primary syphilis in women on the labia majora (photo on the left) and cervix (photo on the right).
Rice. 13. The first signs of syphilis in women are primary ulcers on the genitals.
Rice. 14. The photo shows an atypical form of chancre in a woman - indurative edema (photo on the left) and a primary defect in the nipple area (photo on the right).
The appearance of an erosive ulcer on the genitals or inducing swelling of the labia majora is the first sign of syphilis in women.
Pathogen
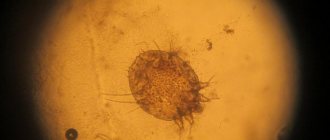
Finding the pathogen in a fully developed chancre is significantly hampered by the fact that its secretion contains a mass of foreign cocci and bacilli, which interfere with both microscopic examination and cultivation. Ducret managed to eliminate this obstacle by the fact that he received chancre while strictly observing asepsis, re-inoculating pus from the graft chancre that had not yet opened. In this way he was able to gradually eliminate all foreign microbes and, in the 5th or 6th generation, obtain graft pustules that contained only one single microorganism - Haemophilus ducreyi. The latter was found exclusively and constantly in all subsequent generations, on the basis of which Ducret correctly concluded that it should be recognized as the causative agent of chancroid.
The bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi is 1.5-2 µm long and 0.5-1 µm wide, with rounded ends and a slight constriction in the middle. The microorganism is found in several copies in the protoplasm of purulent bodies or between them.
The causative agent of chancroid does not lose its harmfulness from the addition of water, urine, vaginal mucus, saliva, and semen. Alkalis, acids, alcohol, sublimate, carbolic acid destroy it. The shank compartment, collected in glass tubes, loses its virulence very quickly when heated above 40°C.
The causative agent of chancre does not penetrate through intact epithelium, but it is inoculated at the mouths of the follicles (follicular chancre). Due to the difference in anatomical structure, different places on the skin react somewhat differently to the same pathogen. Thus, chancre obtained by inoculating a branch of the same ulcer occurs most on the inner surface of the thighs, less on the stomach and least on the outer surfaces of the shoulders; ulcers on the mucous membranes are also mostly small.
Other types of chancre
In primary syphilis, 75% are chancre located in the oral cavity, on the face, and very rarely on the scalp. The remaining 25% are primary syphilomas of the upper extremities, anus, mammary glands, thighs and abdomen. Bipolar chancre is the name given to primary syphilomas that appear simultaneously on the genitals and other parts of the body. They are rare.
Hard chancre of the oral cavity
Among the primary defects of extragenital localization, the most common are hard chancre on the lips, tonsils and tongue. The gums, pharynx, hard and soft palate are rare localizations.
Hard chancre on the lips is almost always single, located on the red border of the lips, has the appearance of an ulcer or erosion, covered with a dense crust, less often with a grayish coating. Sometimes the ulcerative defect hypertrophies with the appearance of painful cracks. Primary syphiloma contains many pale treponema. There is an increase in the mental and submandibular lymph nodes.
The hard chancre in the corners of the mouth looks like a crack. When the mouth is wide open, its oval shape and compaction at the base are visible.
Hard chancre on the tongue is often single, erosive or ulcerative in nature, sometimes has a slit-like shape and is located along the tongue.
Chancres of the tonsils can have ulcerative, sore throat-like (chancre-amygdalitis) or combined forms. On an enlarged and dense tonsil with an ulcerative form, an oval-shaped meat-colored ulcer with flat edges appears. The mucous membrane around the ulcer is hyperemic.
With chancre-amygdalitis, the tonsil enlarges and thickens, acquires a copper-red color, there are no acute inflammatory phenomena, there is no primary defect in the form of an ulcer or erosion and there is no inflammation of the surrounding tissues, and there are many pale treponemas on the surface of the organ.
Eye damage due to syphilis.
Chancres of the conjunctiva, skin of the eyelid and ciliary margin are isolated.
Rice. 15. Primary syphilomas on the lips.
Rice. 16. Syphilis of the tongue in the primary period - chancre. It is an erosion or ulcer with a dense infiltrate at the base.
Rice. 17. In the photo there is chancre-amygdalitis.
Primary syphilomas of the rectum
Around the anus, primary syphilomas have a “gathered” or fissured appearance. There is pain on palpation, and chancre often bleeds during defecation. With primary syphilomas of the rectum, there is pain before and after defecation, and the stool is glassy in nature.
Chancre felon
Primary syphilomas of the hands are more common in men, mainly on the terminal phalanges of the thumb, index or middle fingers of the right hand. Due to swelling and inflammation, the finger becomes club-shaped and bluish-red in color, “shooting” pains appear, the edges of the ulcer are uneven, overhanging, corroded, the bottom of the ulcer is covered with necrotic-purulent discharge.
Fungal chancroid is characterized by fleshy growths in the form of cauliflower.
Rice. 18. Chancre felon.
Basics of pathology
Oral syphilis is a type of sexually transmitted sexually transmitted disease. The pathology is caused by a pale spirochete localized on the oral mucosa. The first signs are visualized in this part of the body.
According to the International Classification of Diseases according to etiology, syphilis is classified into:
- Congenital
- Acquired
Important! Syphilis in the mouth can be treated only at the initial stage of pathology development. If left untreated, the infection quickly spreads through the flow of blood and lymph to all organs and tissues.
Complications of primary syphilis
When a secondary infection occurs, the clinical manifestations of chancroid may change. Inflammation of the glans penis (balanitis) and the inner layer of the foreskin (posthitis) may develop. Balanoposthitis causes the development of complications such as narrowing of the foreskin (phimosis) and pinching of the head of the penis by the ring of the foreskin (paraphimosis). In weakened individuals, gangrenization and phagedenism develop. Decreased immunity and poor hygiene contribute to the development of complications.
Complications in men develop when hard chancre is localized in the coronary sulcus or on the inner sheet of the foreskin.
- When a trichomonas or bacterial infection is attached, acute inflammation develops around primary syphilomas, which is complicated by narrowing of the foreskin, which makes it impossible to open the head of the penis. The penis enlarges, turns red and becomes painful. Forcible opening of the glans penis can lead to paraphimosis. Failure to provide medical care in a timely manner can lead to necrosis of the foreskin and tissues of the glans penis.
- When infected with B. fusiformis, gangrenization of chancre develops. A black scab forms on the surface of a hard ulcer, which, when sloughed off, reveals a deep ulcer. There is severe swelling and hyperemia of the surrounding tissues. The patient's general condition deteriorates sharply.
- The surrounding tissues are swollen and hyperemic. It's getting worse.
- As the disease progresses, the process spreads beyond the chancre. Bleeding occurs. As a result of necrosis, the head of the penis may be torn away, causing perforation and destruction of the urethra (phagedenism).
Rice. 19. In the photo, urethral chancre complicated by balanoposthitis.
Rice. 20. Complications of chancroid in men - phimosis.
Rice. 21. Complications of chancroid in men - paraphimosis.
Rice. 22. Complicated course of primary syphilomas in men.
Rice. 23. Development of gangrenous inflammation of primary syphiloma.
Risks of getting sick
If you are confident that your body is ready to withstand any challenge, know: after the first contact with a patient, the chances of being photographed showing syphilis on the face are 80%. The remaining 20% is not due to the presence of immunity to treponema, but to too little of it to cause a big problem.
Regional lymphadenitis, lymphangitis and polyscleradenitis
Regional lymphadenitis
Regional lymphadenitis (scleradenitis) is, after chancre, the second most important symptom of primary syphilis. Scleradenitis develops 6 - 7 days after the initial manifestation of syphilis - chancre and often on the affected side (unilateral localization).
The lymph nodes are painless, woody in density, mobile, and not fused with the surrounding tissues. Sometimes lymph nodes appear simultaneously with primary syphiloma. Several lymph nodes may enlarge at the same time, the largest of which is located closer to the chancroid. When a secondary infection occurs, the lymph nodes become fused into conglomerates, the phenomena of periadenitis are pronounced, and sometimes fistulas are formed. Syphilitic lymphadenitis resolves slowly.
Inguinal lymphadenitis is often bilateral, it develops when hard chancre is localized on the external genitalia, ulnar and axillary lymph nodes increase when syphilomas are localized on the hands, cervical and submandibular - when localized on the lower lip, preauricular and submandibular - when localized on the upper lip, submandibular , cervical and preauricular - when localized on the tonsils, sublingual - on the tongue, preauricular - on the skin of the eyelids, axillary - when primary syphiloma is localized on the skin of the mammary gland, when chancre is localized in the rectum and on the cervix, the lymph nodes located in the small pelvis.
Rice. 24. Regional lymphadenitis is, after chancre, the second most important symptom of primary syphilis. The photo shows inguinal lymphadenitis.
Syphilitic lymphangitis
Inflammation of the lymphatic vessels (lymphangitis) is the third main symptom of primary syphilis. The causative agents of syphilis multiply in the lymphatic system and the lymphatic vessels are the first to be affected in this process. Lymphangitis begins from the site of primary syphiloma and reaches nearby lymph nodes. The inflamed vessels thicken and become like a dense elastic painful cord. Lymphangiitis, like lymphadenitis, resolves slowly.
Rice. 25. The photo shows sclerosing lymphangitis.
Causes
Treponema pallidum enters the body during unprotected sexual intercourse, kissing, or using other people's personal hygiene products. Infection can occur through secretions from chancres if they get on mucous membranes or wounds. In rare cases, infection occurs after the use of unsterile instruments during surgery or in beauty salons.
Sometimes infection begins through a blood transfusion. Chancres rarely form on the eyelids, near the eyelashes. They mainly appear in people who prefer to contact their genitals with their tongue. Then, during the process, infection occurs, and treponema pallidum attaches to the mucous membranes.
Several syphilomas at once are often provoked by scabies, injuries, and coal rash. If a person has chronic diseases or severely reduced immunity, then the likelihood of chancre formation is very high.
Pathological anatomy
In the initial inflammatory nodule, equipped with a pustule at the apex, between the stratum corneum and the Malpighian reticulum, a small accumulation of purulent cells densely lying next to each other is noticed, which extends deep into the papillary layer. The adjacent part of the Malpighian reticulum is densely permeated with leukocytes; in the papillary layer beneath it, an abundant accumulation of plasma cells is noticeable; the blood and lymphatic vessels are greatly dilated and surrounded by plasma cells. The bottom of the ulcer is formed by a thick infiltrate of plasma cells, the upper layer of which has lost the ability to stain. At the periphery, the strands of the epidermis are thickened and end with a pointed edge. In slightly older ulcers, numerous ray-shaped slits are seen at the bottom, which are separated from one another by columnar remains of preserved tissue and filled with necrotic tissue containing many chains of bacteria. As the virulence of bacteria decreases, the cracks close, the protrusions lying between them are connected to each other, the necrotic belt is limited to the surface and decreases in width. If epithelial coverage slows down, granulation tissue may mushroom over the edges of the ulcer, but for the most part such growth does not occur, and after complete cleaning of the bottom of the ulcer, a slightly deepened scar is formed.
The pus of a chancroid ulcer contains mainly multinucleated leukocytes, often with a pale or disintegrated nucleus; epithelial cells with a pale nucleus and vacuolated protoplasm containing bacteria are also often found. In addition, pale hyaline balls, large mononuclear basophilic cells, red blood cells, and rarely plasma cells are found.
Lymphatic vessels in the infiltrate reach almost to the bottom of the ulcer and even open freely in it; this explains the ease with which bacteria penetrate the lymphatic system.
Diagnostics
To carry out successful treatment, it is important to detect syphilis chancre in time and begin treatment of the disease. Before prescribing drug therapy, it is necessary to verify the correctness of the diagnosis, since the possibility of false suspicions cannot be excluded.
The following types of studies can be used for diagnosis:
- ELISA;
- Wasserman reaction;
- microprecipitation reaction;
- RIBT;
- REEF;
- passive hemagglutination reaction;
- serological tests.
Syphilis is confirmed by the presence of treponema pallidum in tissue scrapings, as well as antibodies to it in blood samples. Based on the results of tests and physical examination, one can judge the extent of the infection.
It is also necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis of the following diseases (depending on the location of the chancre and the presence of accompanying symptoms):
- angina;
- herpes;
- candidiasis;
- tuberculosis;
- traumatic erosions.