A skin growth on a cylindrical pedicle, sometimes almost invisible, is called papilloma. It often appears out of nowhere and does not appear for a long time. But with any “jump” of immunity or in the heat, it suddenly appears to your eyes, first as a single person: one papilloma “mother” can “pop out” in the armpit or on the eyelid (her favorite places, for example, on the bends of the elbows and in the popliteal fossae), and then “let in” the “babies”, that is, literally “sprinkle” all sorts of places on our body. For some, this phenomenon will only be a temporary disorder - well, they say, it gets in the way, clings to clothes, and if it’s “stuck” on the face, it’s ugly, a cosmetic defect, but you don’t have to notice! But is this small growth so harmless, especially when it forms a whole colony around itself? Should I delete it, or leave it and forget it?
Is human papillomavirus (HPV) a sexually transmitted disease?
HPV - in more detail stands for “a virus that causes a benign tumor of epithelial origin in the form of a papilla” - papilloma (papilloma: Latin papilla - nipple and Greek -oma - tumor). It is classified as a sexually transmitted disease (STD). The concept today has, unfortunately, become much broader, and if earlier we heard about several “terrible”, as it seemed to us, classical diseases of Venus, which are actually treated simply and are detected quickly (syphilis, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, chancroid), then The list of “new” STDs - insidious, difficult to diagnose, and sometimes difficult to treat and completely incurable (HIV) - is constantly growing.
So, we include the following “new” STDs: chlamydia, mycoplasmosis, ureaplasmosis, gardnerellosis, genital herpes, candidiasis, and human papillomavirus. If growths from papillomavirus have formed in the areas of the genital or perianal organs, then they are called “pointed candylomas,” but in fact they are the same virus, only its different strains (types).
Prevention of papillomas
It is not easy to get rid of a virus that causes formations on the human body. But there is a small set of measures to help protect yourself from infection or eliminate the possibility of relapse:
- Work to improve your immunity: sports, hardening, good sleep, healthy eating, giving up bad habits.
- The use of immunostimulating drugs is allowed, as agreed with the attending physician.
- Follow the rules of personal hygiene.
- Vaccination against several strains of the virus is possible. However, in our country this vaccination has not yet been fully studied, and therefore it is not included in the preventive vaccination calendar. You can do it either under the direction of a specialist, or at your own request.
- Be attentive to your sexual partners, and also, if possible, avoid being in large crowds of people in saunas, baths, swimming pools - in places with a warm and humid environment that is favorable for the spread of the virus. You also need to be careful with other people's personal hygiene products.
- Regularly see a proctologist to monitor the condition of the rectum.
Are papilloma and condyloma the same thing?
Genital condylomas in the perineal area are sometimes single, and sometimes look like growths that resemble cauliflower in appearance. Sometimes these formations cause itching, irritation when touched, and sometimes they bleed. SM-Clinic doctors are often approached by patients who, having seen enough advertising, have been treated for years with “one pill” for supposed “exacerbations” of candidiasis (thrush). Upon examination, it turns out that the smear in such patients is normal, and the often recurring itching is actually caused by condylomas.
Difference between condylomas and papillomas
Condylomas and papillomas that occur on the human body have a common nature - a viral type pathogen. In addition, the signs of the presence of these pathologies in the rectum are also similar. But there are also differences between them:
| Appearance | Infection method | Treatment | |
| Condylomas | “hang”, protrude forward, are formations of the papillary type. | appear as a result of sexual contact with an infected partner. | must be excised. |
| Papillomas | similar to warts - pathologies that have grown into the mucous membrane or skin. | may occur even after contact with the patient’s personal belongings. | sometimes it is not necessary to remove them, since they do not always cause pain, discomfort and are not so dangerous. |
Papillomatosis in the throat
There is also papillomatosis of the respiratory tract, when the tissue lining the nasopharynx begins to grow from the nose to the lungs, also often affecting the larynx. This is also one of the types of disease caused by the papilloma virus; the formations in this case are considered benign. SM-Clinic doctors are good at diagnosing this type of HPV and successfully treating it, while the disease is not always recognized by local or ENT doctors, who at best shrug their shoulders and prescribe rinses.
Symptoms of polyps in the intestines
Polyps rarely cause clinical symptoms. This is bad. Judge for yourself: an invisible harmless neoplasm turns into an invisible dangerous disease and appears when it is already too late. Even in the case of clinical manifestations, symptoms are nonspecific.
For example, a polyp is characterized by:
- Rectal bleeding
. Bleeding from the rectum is caused by many other diseases: hemorrhoids, anal fissures, rectal cancer. No one can tell with the naked eye what is behind the bleeding, but the symptom requires attention in any case. - Change in stool color
. Blood sometimes appears as red drops in the stool, sometimes it changes the color of the stool to crimson. Foods, medications, and dietary supplements can also change the color of your stool. So this sign is also non-specific, but worthy of attention. - Changes in bowel function
. The list of diseases that cause constipation or diarrhea is even more extensive. If bowel movements continue for more than a week, we may be dealing with a large polyp. Mucus discharge from the rectum is also a noticeable sign. - Pain
. Colon polyps also periodically manifest as pain. The formation partially compresses the intestines and causes cramping pain in the lower abdomen. It is clear that the polyp is not the only cause of this symptom. - Iron-deficiency anemia
. The list of causes of anemia is also quite extensive. Anemia is indicated by general weakness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and diarrhea. What is the connection between polyps and anemia? When a polyp causes bleeding, iron deficiency anemia is expected.
Rectal bleeding
Chronic bleeding leads to iron deficiency, which over time leads to a lack of red blood cells and hemoglobin, so in case of anemia, the patient should be examined for hidden bleeding, which in turn may indicate the presence of polyps.
Thus, abdominal pain, bloody stools, and changes in bowel movements indicate the need to see a doctor, however, as we have already said, these symptoms do not always appear, so you cannot count on them.
Who is at risk of getting the papilloma virus?
Papillomas and condylomas can appear, disappear and appear again, because they are manifestations of a viral infection, and their presence depends on the state of the body’s defenses at the moment, that is, immunity. Infection is most likely among smokers and alcoholics, and among those who are indiscriminate in sexual relations.
Women who use oral contraceptives (COCs) for a long time are also at risk of contracting the virus. The carrier of the virus can be both old and young. It is enough for your body to experience internal stress of various origins: you have had the flu or ARVI, gastrointestinal problems have worsened, your body cannot cope with long-term medication use - and here you have a weakened immune system, and with it the papillomavirus.
It is enough to be in close contact or live next to a person carrying the virus, take a swim in a “dirty” pool or shower in a public bath, or just walk along the beach - and if your immune system fails, the virus will invade your life. The papillomavirus “loves” heat and high humidity, when your skin is not protected by clothing. He immediately finds refuge on your heated skin.
Why are polyps dangerous?
Colorectal polyps (those found in the large intestine) can lead to cancer. The main danger is adenomatous polyps. Colon polyps are diagnosed using colonoscopy. This procedure involves inserting a probe into the anus and examining the inside of the large intestine.
It is recommended that every person undergo a colonoscopy at age 55 as a screening measure for colon cancer, then repeat every five years. By this age, half the population will have an adenoma in the intestine.
The risk would be a lesion greater than 1 cm in diameter. If there is a history of colorectal cancer (the disease was diagnosed in one of the parents or a brother/sister), examination is necessary 10 years earlier than the age at which the tumor was detected in a relative.
Colon cancer, if detected early, can be treated well. If you eliminate the focus at the level of the polyp, then you can forget about this trouble for five years, and then repeat the colonoscopy. People are afraid of the procedure, which makes early diagnosis difficult.
Pregnancy with papilloma virus
Infection from mother to fetus during childbirth occurs in almost 98% of cases. For a baby who passes through the birth canal, literally strewn with condylomas, the virus enters the mouth and eyes, so all women planning a pregnancy should be tested in advance and, if necessary, treated for HPV and all types of STDs. Only after completion of treatment can you plan to conceive.
If the disease was in a latent form and was first discovered during pregnancy, and this happens often (immunity weakens during pregnancy), then it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor: treatment of papilloma during pregnancy is possible.
Treatment methods for polyps and papillomas of the anus
Treatment of polyps and condylomas usually involves their removal.
Removal of polyps and condylomas of the rectum
Removal of condylomas in the “Family Doctor” is carried out using a laser or a radio wave device “Surgitron”. Removal of rectal polyps can be done during endoscopy if the location and size of the polyp allows it. In difficult cases, planned hospitalization in a surgical hospital is performed to remove the polyp.
Make an appointment Do not self-medicate. Contact our specialists who will correctly diagnose and prescribe treatment.
Rate how useful the material was
thank you for rating
We treat papilloma
Scientists have discovered more than 100 varieties of the HPV virus, but some types of genital candyloma can lead to cervical cancer, especially HPV subtypes 16, 18, 31. And the reason for this is that often, due to an asymptomatic course, a person goes nowhere for a long time appeals! Dispensary examinations have disappeared from our lives, which is why diagnosis can be quite late.
To avoid this, you need to visit an obstetrician-gynecologist twice a year, and once a year have a cytology smear (also called a Papanicolaou test or “atypia smear”) to detect precancerous changes in the cervix. It is also necessary to undergo a blood test to determine the DNA of the virus using PCR. SM-Clinic's own laboratories use high-quality reagents to more accurately determine test results. After going through them, it will become clear what types of HPV are present or absent in your body, and whether treatment is worthwhile.
- Non-oncogenic papillomaviruses - HPV 1, 2, 3, 5.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of low oncogenic risk - HPV 6, 11, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 70, 72, 81.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of intermediate oncogenic risk - HPV 26, 53, 66.
- Oncogenic papillomaviruses of high oncogenic risk - HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59 and 68.
Do not forget that the appearance of papillomas indicates trouble in your body: these small unpleasant skin protrusions, which are easy to get rid of, signal that you have not seen a doctor for a long time, and may have developed gynecological diseases, kidney disease, gastritis or colitis.
Under no circumstances should papillomas be torn off, tied with threads, or combed out - this provokes the virus to aggressively “seize” new territories - it will simply move to an unaffected organ.
Removal without traces or complications is carried out at SM-Clinic using painless methods that do not leave marks or scars. Immunity-boosting treatment is also carried out in parallel.
What is a polyp?
How is a polyp different from a papilloma? A polyp is the result of uncontrolled cell division of the mucous membrane, which led to the appearance of a tumor. Polyps are found only on internal organs.
This is also a benign formation, however, the risk of some types of polyps degenerating into cancer is much higher than that of papillomas. The causes of polyps are not fully understood. This disease can be inherited.
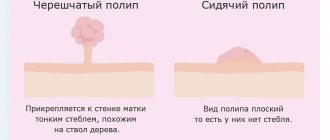
Polyps may differ depending on the way they are attached to healthy tissue (pedunculated polyps and sessile polyps), as well as depending on the location.
A polyp may appear:
- In the nose. Even one polyp can cause an allergic rhinitis.
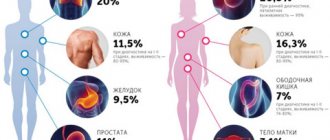
- In the cervix or body of the uterus. Low risk of developing into cancer. Favorable prognosis 95%.
- On the surface of the bladder. 5-10% of such tumors may have a tendency to degenerate.
- Inside or outside the gallbladder. The main reason is parasites.
- In the colon.
Diagnosis of intestinal polyps
The main means of diagnosing the underlying disease is screening. This is the gold standard for diagnosing the disease and the most effective strategy - screening allows us to detect a problem before it develops into a malignant disease. Screening can also detect cancer at an early stage, and starting treatment at this stage is much safer and more effective.
Since a colorectal polyp is considered a precancerous condition, special attention is paid to identifying this pathology during screening.
During screening, two tests are performed. The stool is first examined for occult bleeding. This method detects even small amounts of blood in the stool that is not visible during gastric emptying. However, a positive test result does not mean the presence of a polyp, especially cancer. This only indicates that there is hidden bleeding in the body. Colonoscopy helps determine its cause.
Colonoscopy is the most sensitive method for detecting polyps and cancer. During the examination, a thin tube with a camera is inserted into the back of the body. The doctor sees the intestinal mucosa with his own eyes. The examination also allows you to do a biopsy - take a sample of polyp tissue for histological examination. A wire loop is also placed over the colonoscope to remove polyps painlessly.
Colonoscopy
If the result of a stool test is within the normal range, a repeat test is prescribed after two years, but if prescribed by a doctor, it can be done earlier.
Polyps can be detected using a virtual colonoscope (CT colonography), a moving sigmoidoscope, and other methods, but you will still need a colonoscopy to biopsy or remove the polyp.
Treatment of polyps - polypectomy
“No polyp - no risk” - this is the main principle of polyp treatment. Most polyps are not cancerous, however, unfortunately, no one can say for sure which polyp will turn into cancer and which will remain harmless, so the approach is simple: all polyps should be removed, and the sooner this happens, the better.
There are several ways to do a polypectomy:
- Removal with tweezers or a wire loop - in this case, the polypectomy is performed during a colonoscopy. If the polyp is longer than one centimeter, fluid is injected under it. The formation rises high, which allows it to be isolated from surrounding tissues and facilitate its removal.
- Minimally invasive surgery - Polyps that are excessively large or that cannot be removed safely should be removed laparoscopically during a colonoscopy. This is a minimally invasive procedure.
- Complete proctocolectomy - in case of congenital pathologies, due to the large number of polyps, it is impossible to remove them one by one, so the doctor completely excises the large intestine and rectum.
Treatment and observation do not end with the removal of polyps, especially if the polyp is neoplastic and large. According to statistics, in thirty cases out of a hundred, tendon regeneration occurs, so observation after polypectomy is necessary.
Colonoscopy is recommended after polyp resection:
- 5-10 years later if you only had one or two small polyps;
- After 3 years, if you had more than two or at least 1 cm of adenoma polyp;
- 3 years if you had more than ten adenomas;
- 6 months if you had a very large adenoma or an adenoma that needed to be removed piece by piece.
By the way, it is believed that aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs reduce the risk of polyp recurrence, but they can only be taken with a doctor’s prescription and in no case arbitrarily.