What is a polyp in the uterus
A uterine polyp is a benign space-occupying formation that forms in the uterine cavity against the background of local hyperplasia of cells in the growth layer of the endometrium. The pathology can affect patients of different age groups. Detectability is approximately 6-20%.
The sizes of endometrial polyps range from 1-2 millimeters to several centimeters.
The formation is attached to the uterine wall through a thin stalk or a wide base. Nutrition is provided by a vessel in the center of the polyp. Pathological structures can be either single or multiple. When several formations are detected, they speak of polyposis. Polyps can cause intermenstrual bleeding, abdominal pain, and problems with conception. Usually pathology is diagnosed during ultrasound. In gynecology, polyps are considered potentially malignant formations that need to be removed surgically.
Polyps by type of attachment
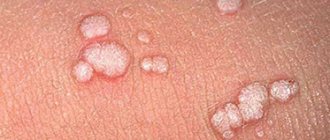
What causes papillomas on the neck
The main factors influencing the appearance of defects on the body of a patient infected with HPV include:
- reduced immunity;
- mechanical damage to the skin;
- violation of blood microcirculation;
- hormonal disorders (women are especially at risk during pregnancy and menopause;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- nervous tension and stress;
- eating disorders (abuse of spicy, fatty foods);
- bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- presence of skin allergies.
People with fair skin who have a large number of freckles, birthmarks or moles on their bodies are at particular risk. Also at risk include people who:
- take antibiotics for a long time;
- suffer from diabetes;
- are obese;
- abuse natural or artificial tanning.
Do not miss
- Do not miss
Do papillomas need to be removed? Dermatologist advice
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of polypous growths are still being studied, but an important role in etiopathogenesis is played by:
- hormonal imbalance;
- injuries, including medical procedures (curettage);
- infectious, inflammatory diseases of the genital organs;
- uncontrolled use of oral contraceptives, etc.
Diagnosis of polyps is difficult; often they do not manifest themselves at all, and the disease is asymptomatic. Reasons for examination include excessive discharge (leucorrhoea) and intermenstrual bleeding. The diagnosis is made by ultrasound examination of the uterus. Hysteroscopy is used to identify small polypous growths. If a polyp is detected, treatment is required. Sometimes reverse development of the tumor is observed after conservative therapy. Removal is resorted to if there is no result.
Hysteroscopy is usually used for diagnostic examination and resection of a mass in the uterus. It can also be removed with a laser, but the prices for such a service are higher due to the high cost of the equipment.
There are several theories for the development of cervical and uterine polyps. Most often, a polyp in the uterus appears as a result of hormonal imbalance - this is the most common version of the causes of the pathology. Under the influence of high levels of estrogen, the endometrium of the uterus (inner layer) grows. The endometrium can grow evenly, then hyperplasia appears. In case of uneven growth of the endometrial layer, polyps form in the uterus and cervix. Progesterone deficiency ensures the active growth of benign formations.
The following factors contribute to the appearance and growth of polyps in the cervix and uterus:
- Fibroids and myomas.
- Ovarian dysfunction.
- Polycystic ovary syndrome.
- Endometrial hyperplasia.
- Chronic infection in the genitourinary organs, including sexually transmitted infections and human papillomavirus. During inflammation, there is a sharp increase in the number of leukocytes (immune cells), which, along with the destruction of pathogenic microorganisms, promotes the growth of cells of the inner uterine layer.
- Cervical polyps most often appear after unsuccessful curettage.
- Chronic stress leads to an increase or decrease in hormone levels.
- Vascular obstruction - epithelium grows around a blocked vessel.
- Hereditary factor - polyps of the uterus and cervix are more often formed in those patients whose relatives suffered from polyposis. This category of women should be especially attentive to their health and undergo regular preventive examinations.
- An inactive lifestyle contributes to the appearance of congestion in the pelvic organs, as a result of which the uterus and appendages experience a lack of oxygen, which leads to hormonal imbalance and cell proliferation.
- The drug Tamoxifen is used in the treatment of cancer; it causes hormonal disorders. In some patients, a polyp may form in the cervical canal of the cervix or in the uterus.
Diseases of the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, obesity) contribute to the development of polyposis. The endocrine glands function in close connection, so disturbances in one gland lead to a malfunction of the other, in particular in the ovaries, which begin to produce sex hormones at an accelerated pace. In diabetes mellitus, microcirculation is disrupted, cell hypoxia occurs, which contributes to their proliferation and atypical changes. With excess weight, adipose tissue produces estrogens, which provoke an increase in cervical polyps. When ovarian function is disrupted, a large amount of estrogen is synthesized, which is released into the blood constantly (normally, the hormone is produced in the first 14 days of the cycle).
As a result, during menstruation, individual fragments of the endometrium remain in the uterine cavity, rather than exfoliating and coming out. Gradually, connective fibers and vessels grow into these areas. This is how a uterine polyp appears.
Cervical polyp: why does it appear and what to do with it?
A woman is most often warned that there is something wrong with her reproductive system by symptoms such as menstrual irregularities, pain in the lower abdomen, and vaginal discharge with an unpleasant odor. But a cervical polyp is a disease that can occur without visible external signs. We talked about it, as well as the benefits of regular preventive examinations, with Lana Taimurazovna Andieva, an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic Vladikavkaz.
— Lana Taimurazovna, tell us about cervical polyps: what are they?
— A cervical polyp is a benign formation that grows from the wall of the cervical canal. May have a stalk or a wide base. Depending on the morphological characteristics and the predominance of one or another type of tissue, polyps are glandular, fibrous and glandular-fibrous.
— Why do polyps appear on the cervix?
— The causes of the development of polyps can be inflammation, hormonal disorders, trauma to the cervix due to childbirth or surgery, including abortion.
70% of patients with cervical polyps are patients with chronic inflammatory processes of the female genital organs: endometritis, salpingo-oophoritis, cervicitis, colpitis, etc. Cervical polyps, which are formed due to hormonal disorders, accompany cervical fibroids or endometrial hyperplastic processes . The disease occurs in women who have given birth many times, as well as those who have had numerous abortions in history or any operations on the cervix that led to injury to the cervical canal.
Read material on the topic:
Fear has big eyes. Is fibroids really that dangerous?
— What are the symptoms of cervical polyps?
— The disease can be asymptomatic and discovered accidentally during a vaginal examination, ultrasound or colposcopy. The patient may also be brought to us by bloody discharge from the genital tract after sexual intercourse; menstrual irregularities, which are expressed in an increase in the intensity of blood discharge; the appearance of intermenstrual spotting, nagging pain in the lower abdomen, serous or serous-purulent discharge.
Hysteroscopy
— What diagnostics may be required to confirm the diagnosis?
- Hysteroscopy helps to fully describe the formation, see where it comes from, its size. Ultrasound and colposcopy can detect a cervical polyp, but they may not notice it if the polyp does not protrude into the vagina, but remains in the canal. And examination with a hysteroscope gives us the opportunity to examine the cervical canal from the inside.
Read more about gynecological ultrasound in our article
— Is it necessary to remove a polyp on the cervix? Is it possible to get rid of this formation without surgery?
“It definitely needs to be removed.” It is impossible to cure a cervical polyp with conservative therapy, without surgery. Removal of a polyp in the cervix is a surgical procedure, after which a histological examination of the removed material is required.
— What methods exist for removing cervical polyps?
— The most optimal, I think, is the radio wave method. In our clinic we have a Fotek device, which can perfectly remove polyps of the cervical canal. It has many advantages. Among them are the accuracy of the section, the thinness of the incision, minimal trauma to the tissue in the surgical area, a significant reduction in pain during operations, as well as a smoother course of the postoperative period. Plus, the procedure is almost bloodless, since coagulation (“sealing”) of the vessels is carried out at the same time.
There is also a method when this operation is performed under the control of a hysteroresectoscope, and a method when the cervical canal is curetted to remove polyps. But with the Fotek device, in my opinion, this can be done much better - both in terms of rehabilitation and the operation itself.
— Is anesthesia used when removing a cervical polyp?
— If separate diagnostic curettage is performed, or the polyp is removed in a hospital setting, then a short-term anesthesia is given. But, as a rule, it is enough to locally anesthetize the neck, and the operation will be easy. It will not cause any discomfort to the patient.
— Why is a polyp on the cervix dangerous? What will happen if it is not treated?
— A polyp on the cervix does not often become malignant. Maximum up to 10% of cases. However, if such a risk exists, the polyp must be removed and subjected to histological examination.
— Is it possible to prevent the disease?
- Here we will return again to the reasons that cause the development of cervical polyps. It is necessary to visit a gynecologist in a timely manner, monitor the cleanliness of the vagina, be sure to get tested for sexually transmitted infections, treat inflammatory diseases of the pelvic organs in a timely manner, and pay attention to hormonal abnormalities. During surgical interventions, perform manipulations in the cervical canal as carefully as possible, without injuring the cervix. But the last point no longer depends on the patient, but only on the doctor.
You can make an appointment with an obstetrician-gynecologist here. ATTENTION: the service is not available in all cities
Interviewed by Marina Volovik
The editors recommend:
Myths and truth about cervical erosion Endometriosis: symptoms, diagnosis and treatment What does a pelvic MRI show in women? Precancer: to be afraid or not to pay attention?
For reference:
Andieva Lana Taimurazovna
Graduate of the North Ossetian State Medical Academy in 1999.
In 2002 she completed her residency. She specialized in colposcopy at the Rostov Oncology Research Institute, and in radio wave surgery at the Center for Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology in Krasnodar.
Currently, he is an obstetrician-gynecologist at the Expert Clinic Vladikavkaz.
Receives at the address: st. Barbashova, 64a.
Symptoms of polyps in the uterus
The main signs of polypous growths are:
- spotting at the end of sexual intercourse of varying intensity;
- bleeding;
- nagging pain in the lower abdomen, above the pubis;
- intense menstruation, and, as a result, signs of anemia - pale skin, general weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness.
Often, polyps occur without any external signs and are an accidental “find” during a routine examination.
Signs of polyp formation
Transmission routes
HPV is transmitted through contact of an infected person with a healthy person, through mucous membranes or damaged areas of the skin.
The following routes of transmission of infection exist:
- from mother to child, in utero, or vertical transmission, which is rare but has serious consequences;
- through household appliances - if hygiene rules are not followed, the same utensils or personal hygiene products are used for several people;
- sexually, which is the most significant factor in the statistics of the spread of HPV.
Since the virus is highly contagious (infection occurs easily, with a minimum number of copies of the pathogen) and is tropic to the upper layers of the skin - the epidermis, papillomas on the eyelids can appear through any route of infection. The triggering factor can be a genetic predisposition, immunological or hormonal disorders, as well as stress factors for the body - smoking, alcohol consumption, vitamin deficiency, chronic fatigue syndrome.
Treatment of uterine and cervical polyps with conservative methods
There are conservative and surgical methods of therapy. Symptoms and treatment of a polyp in the uterus are two interrelated factors. The brighter the clinical picture, the more important the treatment measures. If there is a small formation caused by excess estrogen, hormonal drugs are prescribed, with the help of which it is possible to reduce their size or completely disappear. Treatment of uterine polyp without surgery (removal of the polyp) with the help of medications is recommended for adolescent patients who have not given birth.
If the disease is of infectious-inflammatory origin, a course of anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is necessary. Treatment of uterine polyps with drugs is carried out for women of any age category. When conservative therapy is ineffective, the polyp is removed.
Prevention of stomach polyps
The goal of prevention is to identify gastric formations in the early stages of development. It is recommended to perform an endoscopic examination for persons over 45 years of age as a screening test, even in the absence of clinical symptoms, since the disease manifests itself only at a late stage, when surgical treatment is already required. Following the principles of oncological vigilance, patients with a burdened hereditary history, that is, in the presence of oncological diseases of the gastrointestinal tract in close relatives, require an immediate preventive examination of the stomach and colon.
How to get a service at the Clinic
Our Clinic conducts all types of endoscopic examinations using high-quality equipment, both under local anesthesia and general anesthesia. All identified pathological formations are subject to histological verification. Material is also taken to check for the presence of H. pylori infection and to determine the stage and severity of inflammatory and atrophic changes in the gastric mucosa (OLGA class), which indicates, as mentioned earlier, the risk of developing an oncological process.
As for surgical endoscopic treatment, the clinic can perform it on an outpatient and inpatient basis. The decision is made by the attending physician, based on the size of the pathological lesions, their number, histology results and concomitant pathology.
How much does it cost to treat polyps in the uterus?
The cost of treatment differs in different clinics. It primarily depends on the type of formation and the choice of treatment method. Thus, with conservative therapy, it may include control examinations to monitor the effectiveness of therapy. If the patient’s condition does not improve during therapy, surgical removal of the polyp may be required. Different surgical treatment methods also have an impact on cost. The use of expensive equipment increases the price. In fact, it is possible to find out how much it will cost to remove a polyp only after a complete examination of the patient. In addition, prices are influenced by the clinic’s pricing policy and the level of qualifications of doctors.
Endometrial polyp: how dangerous the disease is and how best to remove it
Gynecologist-surgeon Bulat Ilyasovich Nuriev about hysteroresectoscopy and other methods of surgical treatment of polyps.
Endometrial polyp is one of the most common gynecological pathologies. As soon as the disease becomes known, every woman has many questions. How dangerous is this? Can a polyp turn into cancer? Is it possible to get pregnant with a polyp? Will removing a polyp lead to infertility? The questions are important, and I will try to answer them in this article.
Cancer risk
The endometrium is the mucous tissue that covers the inside of the uterus and serves as the place where the embryo attaches. A polyp is an overgrown area of the endometrium. Most often this is a benign formation. However, there is a risk of malignancy. About 1 in 40 polyps become cancer. The risk increases with the onset of menopause, when 1 polyp in 20 turns into a malignant formation. The only way to avoid this is to remove the polyp.
Danger to pregnancy
Endometrial polyp prevents you from getting pregnant and carrying a pregnancy to term. Even if you succeed in conceiving a child, there is still a possibility of miscarriage with a polyp, since the polyp prevents the embryo from gaining a foothold in the uterine cavity. It is no coincidence that when conception is carried out using IVF, removal of polyps is a mandatory procedure, since embryos are obtained at the cost of great effort and expensive procedures.
Will surgery itself lead to infertility? This depends on the method used for removal, and we will talk about this later.
Ultrasound diagnostics is not 100% accurate
Symptoms of a polyp include: heavy and painful periods, bleeding before and after periods. But this doesn't always happen. In most cases, the disease is asymptomatic and is discovered by chance at a gynecologist's appointment or if a woman encounters difficulties in conceiving.
The main method for diagnosing polyps is ultrasound of the pelvic organs. It is better to do an ultrasound examination in the first half of the cycle, that is, in the first week after menstruation. This is the optimal time when the endometrium is thin and the polyp is clearly visible. But ultrasound diagnostics does not give a 100% guarantee. Therefore, patients are faced with the fact that one doctor found a polyp, but another did not. The reasons for the different results may well be that you were examined on a bad day of your cycle or the location of the polyp is inconvenient for visualization.
No other imaging modalities (MRI, CT, HSG) are advantageous for diagnosing polyps. The only study that will reliably determine whether there is a polyp or not is hysteroscopy.
Why should you refuse hysteroscopy with curettage?
Hysteroscopy is an examination of the uterine cavity using a thin tube with optics that is inserted into the uterus through the vagina. Hysteroscopy can be diagnostic (went in and looked) and operative (went in, looked and removed).
In the case of endometrial polyps, classical diagnostic hysteroscopy is not an effective method. The doctor finds the polyp using a camera. Then he takes out the camera, inserts a curette into the uterine cavity and begins to scrape out the tumor. At the same time, he does not see the polyp itself, but determines its location from memory. This method is very common in domestic gynecology, but has two significant drawbacks:
1. The method is very rough. Scraping with a curette injures the endometrium and uterine cavity, which can lead to infertility. To prevent this from happening, the high skill of a gynecologist-surgeon is required, which no one can guarantee.
2. The method is unreliable. Working blindly, the doctor cannot be 100% sure that he has removed the polyp. In approximately 50% of cases, relapses occur after curettage, since the stalk of the polyp remains intact.
How to remove a polyp without injury and risk of relapse
An alternative to diagnostic hysteroscopy with curettage is hysteroresectoscopy. The difference is that during hysteroresectoscopy there is a special loop on the tube with the camera. Entering the uterine cavity, the doctor, under camera control, immediately cuts off the polyp along with the stalk using this loop.
At the Nuriev Clinic we use a bipolar hysteroresectoscope, which, compared to other models, is more gentle on the endometrium and safe for reproductive health. This instrument cuts away polyps with a thin strip of plasma.
There are other methods:
• The hysteroscope can be equipped with microscissors or microforceps, but this option is only suitable for small polyps. • There is a method of removal using a morcellator: the polyp is sucked into a tube, where it is cut off by a surgical knife. The advantage of this method is that the procedure does not cause heating of the endometrium. However, the method is significantly more expensive than hysteroresectoscopy. • It is also significantly more expensive to remove a polyp using a laser, although this method does not provide any advantages.
Any of these methods can be a good alternative to traumatic and ineffective curettage. The most optimal of them in terms of price and gentle effect on the uterine cavity is hysteroresectoscopy.
Conclusions:
So, what to do if you are diagnosed with an endometrial polyp? There are two most basic tips:
First, talk to your doctor about your pregnancy plans and your risk of developing cancer.
Secondly, if you have been prescribed a hysteroscopy, ask how exactly the procedure will be performed. Often, the term “hysteroscopy” refers to all methods: from primitive curettage to expensive laser.
At the Nuriev Clinic, we prescribe hysteroresectoscopy for most cases.
Causes of papillomas on the eyelids
Infection with papillomavirus occurs through household, sexual, contact (even through microscopic damage to the dermis). Most strains are characterized by a very long latent period: the virus may not detect its presence in the host body for years.
The unfavorable conditions and conditions mentioned above include, first of all, weakened immunity; in turn, this is facilitated by situations of chronic stress, lack of healthy sleep, serious illnesses or large-scale surgical interventions, and also, as statistical studies show, hyperinsolation (excess natural or artificial ultraviolet radiation).
It has long been noted that warts occur more often in children and the elderly - this fully applies to papilloma of the eyelid and is explained, again, by the instability and insufficiency of immune defense during the stages of rapid development or aging of the body.
Surgical removal of papillomas
“Outpatient procedures” - this term implies a wide range of modern hardware methods for removing papillomas; the choice belongs to the doctor and will be determined by the clinical situation and the technological capabilities of a particular clinic (excimer laser, liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulator, polished alloy steel scalpel).
The duration of the rehabilitation period is approximately equal to the duration of healing of a small cutaneous wound and is, on average, several days. “Several” – depends on age, immune status and individual regenerative capabilities. Vitamin and antioxidant complexes are shown. When scar defects form (usually noticeable only to the patient himself when looking closely in the mirror), the problem is easily solved by cosmetic laser resurfacing.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of papilloma on the eyelids is carried out by a doctor, who also prescribes treatment . Often the first person to make a diagnosis is an ophthalmologist. As a rule, a visual examination is sufficient for initial diagnosis. The ophthalmological arsenal also includes special examination techniques:
- biomicroscopy using a slit lamp;
- biopsy of the formation;
- optical coherence tomography (to identify possible additional papillomatous growths).
It is also necessary to consult a dermatologist to, together with an ophthalmologist, select the optimal treatment method, taking into account individual characteristics.
Treatment prices
At the time of publication, the cost of safe elimination of eyelid papilloma in our ophthalmology center is approximately 5-6 thousand rubles; to this should be added the cost of histological examination (approximately 2.5 thousand). The variation is due to the choice of specific intervention method; the criteria for such a choice, in turn, are localization, size, dynamics, age and other numerous nuances, which are the responsibility of the doctor whom you trust and whom you have contacted.