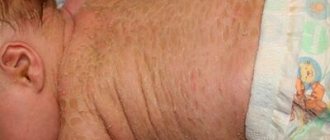
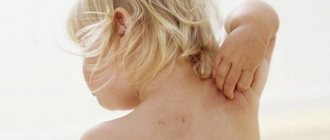
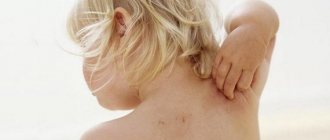
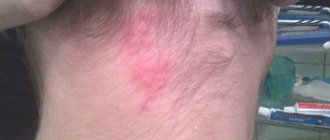
One of the most common problems related to both cosmetology and medicine is peeling skin on the nose.
Characteristic symptoms are:
- Skin hyperemia.
- Itching around the nose.
- Feeling of skin tightness and soreness.
Sometimes it’s enough just to properly care for your skin and properly protect it from drying out. If the problem remains a problem and peeling of the skin on and around the nose continues, you will need to consult a qualified specialist - a cosmetologist or dermatologist.
It is a mistake to think that peeling skin near the nose is the prerogative of those with dry skin. The skin begins to peel off due to the accelerated death of the epidermis, and the disease can be provoked by many reasons, including: vitamin deficiency, runny nose, allergies. The most unpleasant thing is that areas of flaky skin are difficult to hide even with the help of cosmetics and foundations, since they only highlight the existing problem.
Causes of manifestation
Allergic or cold runny nose
With rhinitis, the nasal mucosa becomes inflamed and due to frequent skin contact with the hands and handkerchief, severe irritation begins, which turns into peeling of the skin around the nose. In case of allergic peeling, it is necessary to exclude the patient’s contact with the allergen. After the runny nose ends, the peeling process ends on its own.
Avitaminosis
A pathological condition of the body associated with a lack of vitamins causes peeling of the skin on the nose. In addition to vitamins, the body may not receive enough microelements, mainly selenium, iodine and iron. With the timely use of vitamin complexes of groups A, B and E, the problem is quickly eliminated.
Abnormal air temperature
Very high, or vice versa, very low ambient temperature provokes peeling. Moisturizing the nasal mucosa and using rich face creams will help you quickly deal with the problem.
Cosmetical tools
Incorrectly selected cosmetics for facial care can dry out the skin, as a result of which it becomes dehydrated and degreased, and then dies.
Fungal diseases
The growth of the fungus Pityrosporum ovale, which causes facial seborrhea, is manifested by peeling of the skin around the nose and its redness. It is activated in case of weakened immunity, nervous overstrain, in case of gastrointestinal dysfunction, hormonal disorders. In this case, medical treatment cannot be avoided. The presence of fungus can be checked by a cosmetologist or dermatologist, who will take a skin scraping and send it to the laboratory to confirm the fungal disease.
Seborrheic psoriasis
Refers to a group of diseases in which the body's organs and tissues are destroyed under the influence of its own immune system. The “trigger” can be severe stress, nervous strain, poor diet, and alcoholism. Consultation and treatment with a dermatologist is required.
Dry nasal mucous membranes
Dryness of the nasal mucosa is a sign of certain pathologies, and if left untreated, this condition threatens atrophy. To help a person with such a problem, you can consult an otolaryngologist at a medical clinic and take the necessary tests. Timely treatment will help maintain mucosal balance and avoid loss of smell.
Causes
Both external and internal factors can lead to dry mucous membranes. In the first case, dryness is a response to the irritating influence of the environment, and in the second, it is a symptom of a certain pathology.
Dry nose can also be caused by:
- bad habits, smoking (active or passive, hookahs or electronic cigarettes);
- alcohol abuse (due to the effect of toxins on the body);
- living in industrial areas where there are emissions of harmful substances into the air;
- work in hazardous conditions, in dusty rooms;
- work in a hot room, in hot air conditions;
- abuse of air fresheners;
- monotonous diet, lack of vitamins and microelements.
Vasoconstrictor nasal drops can also cause dryness if used uncontrolled, for a long time and not as prescribed by a specialist. It is best to avoid drops and, if there is no nasal pathology, install a humidifier in the room, which will relieve dryness. This is especially true in autumn-winter, when the heating season is underway and the humidity in apartments is below normal.
Features of the course of the disease
Insufficient hydration of the nasal passages is accompanied by a feeling of burning, itching and dryness. At first, dryness can be dealt with by rinsing the nose with sea water and using moisturizing drops, but in the future the situation will not improve due to the progression of the pathology.
The first manifestations of nasal dryness should not be ignored and independent treatment should be started. This may lead to an imaginary improvement, but the mechanisms themselves and the cause of the pathology cannot be eliminated. If the condition has been haunting you for several days, contact an otolaryngologist and get examined.
The nasal passages and the tissues lining them are complex. They contain special glands that produce mucus in the required volume so that the nose does not dry out and performs its functions. The regulation of the glands is very delicate; they respond to changes in the external environment, harmful effects, etc. For example, in a dusty room, more mucus is released in order to delay microparticles in time and prevent them from entering the body. These particles are removed with mucus. But in a damp room, for example, in a swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse, the mucous membrane produces less secretion due to the already moist environment around. The main role of the mucous membrane and its variable reaction is to protect the body from pathogenic microbes and dust. Microscopic villi constantly work and expel foreign bodies, protecting the body. But with insufficient mucus secretion, dryness in the nose occurs, and the tissues themselves change their structure, lose elasticity, become inflamed and swollen, and microcracks and bleeding wounds form on the surface. All this provokes unpleasant sensations.
Excessive dryness in the nose appears at any age - both children and adults can suffer from it, but the mechanisms and causes of development differ. To determine exactly why your nose is dry, a visit to the clinic is necessary.
Symptoms
Symptoms of dry mucous membranes appear in combination with other manifestations, often significantly complicating a person’s life. Doctors name among the signs:
- itching in the nose, dryness and burning, which appear due to microtrauma due to loss of moisture from the cells of the nasal mucosa;
- dry mouth and nasal congestion, which especially often manifests itself in the morning, when the mucous membrane swells at night, and in the morning a person cannot breathe normally due to congestion;
- constant dryness, accompanied by crusts in the nose, which are difficult to remove with daily cleansing, and when the crusts are forcibly removed, minor bleeding appears;
- profuse hemorrhages from the nose, when the dry mucous membrane is often injured, and nearby large blood vessels begin to bleed;
- dryness of the border near the external opening of the nose, which is accompanied by cracks, peeling, the appearance of crusts and dried blood;
- loss of smell is one of the latest symptoms that appears in the absence of proper treatment for the pathology.
Complications
In addition to the fact that dry mucous membranes in themselves are a rather unpleasant symptom, they also lead to various complications. In patients with this pathology, doctors note:
- pharyngitis;
- bronchitis;
- sore throat;
- sinusitis;
- pneumonia;
- atrophic rhinitis;
- frequent cases of ARVI.
Complications associated with dry nasal mucosa appear as a result of disruption of natural processes, when the mucous membrane ceases to perform its functions, including protective ones. Warming the air, retaining allergens from the outside, dust and tiny particles, trapping pathogenic microorganisms - all these functions when the mucous membrane is dry cease to be fully performed, so the larynx, nasopharynx, and bronchi suffer. The development of complications may be delayed if the process lasts a long time.
Dry nose as a symptom of pathologies
A feeling of dryness in the nose should alert you, since this sign may be a symptom of another disease that needs treatment. Dry nose can be caused by:
- catarrhal rhinitis - a chronic form of pathology leads to atrophy of the mucous membrane;
- hypertrophic rhinitis - pathological growth of the lining membrane, due to which the passage of air is disrupted, swelling often appears;
- scleroma - the pathology is infectious in nature and can even lead to death;
- Sjögren's syndrome - inflammation of not only the nasal mucosa, but also the salivary glands;
- diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disorder, including at the micro level, when the nasal mucosa suffers;
- hormonal changes - usually occur in older people due to a decrease in the level of sex hormones, when dry skin manifests itself throughout the entire body, and not just in the nasal passages.
Treatment for dry nose
Therapy should be carried out by a specialist, as it is important to determine the cause. Methods for eliminating pathology include:
- isotonic salt solution for irrigation of the mucous membrane from the inside - such solutions are produced based on table salt. They have a very gentle effect on the mucous membrane, improve the rheological properties of the discharge, dilute its composition and increase the activity of the epithelial cilia. The chemical composition is more reminiscent of sea water. The drugs are effective at the early stage of pathology with minor dryness;
- oils for moisturizing when crusts form - doctors recommend using peach, sea buckthorn or flaxseed, which perfectly soften crusts and help cleanse the nose. After removing the crusts, if wounds appear, the area can be treated with Solcoseryl. It is better to use oil occasionally, as it disrupts the functioning of the eyelashes, making it difficult for them to move;
- ointments with an antiviral effect - oxolinic ointment or Grippferon is used to strengthen local immunity;
- drugs against nosebleeds - for weak walls of blood vessels, the drug “Ascorutin” is recommended, which also contains vitamin C to strengthen the immune system;
- inhalations - carried out both at home and in the clinic, special drugs (isotonic solutions) are added to the inhaler, which must be inhaled in sessions on the recommendation of a doctor;
- rinsing the nose - a procedure using a weak saline solution will help get rid of dust and small foreign particles, but it must be done strictly according to indications, so as not to upset the balance of the mucous membrane.
Treatment of dry nasal mucosa must be competent. The causes are not always obvious, so only a doctor, after an examination, will determine what caused the problem and prescribe remedies to eliminate the pathology.
Author
Yampolsky Sergey Zigfridovich
otorhinolaryngologist (ENT)
Candidate of Medical Sciences
40 years of experience
+7
Fight against peeling
In an attempt to hide traces of peeling, many scrape off the scales, thereby injuring the young skin underneath. The correct option would be: thoroughly steam the skin and clean it with a scrub, then apply a mask with a high fat content, and only then can you remove the soaked scales.
When contacting a dermatologist, you will need to study hormonal levels and blood tests, after which you will need to strictly adhere to a hypoallergenic diet, use a vitamin-mineral complex, Laennec therapy, antibacterial and antimicrobial drugs, and in difficult cases, you will need to use hormonal ointments.
Allergic rhinitis: how to get rid of symptoms
Allergic rhinitis (allergic runny nose)
is one of the most common diseases with which people turn to an allergist for help or seek salvation at the pharmacy.
The prevalence of pathology among the population of our country alone ranges from 11 to 24%. Allergic rhinitis (AR)
is an inflammatory lesion of the nasal mucosa that occurs as a result of an allergic reaction - immediate hypersensitivity.
After contact with the allergen, a complex of symptoms develops - this usually takes from a few seconds to 15-20 minutes.
Characteristic symptoms of AR include:
• itching and burning in the nose, frequent paroxysmal sneezing; • copious mucous discharge from a swollen nose; • difficulty in nasal breathing, decreased sense of smell; • swelling, itching and irritation of the eyes, lacrimation, a burning sensation, photophobia, a feeling of sand in the eyes.
There may be irritation, swelling, redness of the skin above the upper lip and at the wings of the nose; scratches in the nose area due to constant involuntary scratching of the tip of the nose; pain in the ears, throat, soreness; weakness, malaise, irritability, increased fatigue, impaired concentration and sleep.
There are two forms of the disease:
• seasonal AR (hay fever, hay fever), which is caused by contact with plant pollen; • year-round AR, its cause is allergens with which a person constantly comes into contact (house dust, dust mites, medications, food, yeast and mold allergens).
It is most often impossible to eliminate the presence of allergens, so AR requires adequate drug treatment. Therapy is selected taking into account the severity of clinical manifestations. Currently, a stepwise approach to the treatment of allergic rhinitis has been developed.
1st stage
In case of mild severity and short-term intermittent (characterized by periodic ups and downs) course of allergic rhinitis, it is recommended to take systemic (oral) antihistamines of the second generation.
Products with the active ingredient desloratadine have proven themselves to be effective in the treatment of AR: ESLONTIN ,
EZLOR , DEZLORATADINE VERTEX .
These are non-sedating long-acting antihistamines (up to 24 hours). Products based on desloratadine prevent the development and alleviate the course of allergic reactions, have antipruritic and antiexudative effects, reduce capillary permeability, and prevent the development of tissue edema and smooth muscle spasm. Desloratadine has no effect on the central nervous system, has virtually no sedative effect (does not cause drowsiness) and does not affect the speed of psychomotor reactions.
Topical (local) H1 antagonists may be the treatment of choice or used in addition to systemic antihistamines. In cases where nasal congestion is a severe symptom and needs correction, intranasal vasoconstrictors (decongestants) should be used in short courses.
FRINOZOL is recommended for pathogenetic and symptomatic treatment.
(cetirizine + phenylephrine), which has a vasoconstrictor and antiallergic effect. The drug contains an auxiliary humectant glycerol, which promotes moisture retention, which helps provide hydration for dry and irritated nasal mucosa. The recommended dose for adults is 1-2 injections into each nasal passage 2-3 times a day. The drug should not be used continuously for more than 7 days!
OXYFRINE) is also indicated as vasoconstrictors
,
IVILECT
,
Babyfrin
,
OTRIVIN EXPRESS
).
2nd stage
Used for mild and persistent (long-term) AR. In cases where ASIT (allergen-specific immunotherapy), courses of antihistamine therapy and short-term courses of decongestants are not effective enough in suppressing the symptoms of hay fever, treatment with mast cell membrane stabilizers (sodium cromoglycate, nedocromil sodium) in combination with the use of H1-antagonists is necessary.
3rd stage
Used for moderate severity, persistent (long-term) course. If the treatment described in the previous steps does not have an effect, the doctor may consider prescribing topical (local) corticosteroids. One of the points of comprehensive treatment of AR is reducing the patient’s contact with allergens. It is for this purpose (for rinsing and cleaning the nose) that saline nasal solutions (LINAQUA, AQUA MARIS) can be used on a regular basis. They are distinguished by ease of use, safety, and the possibility of use in complex pharmacotherapy.
THERE ARE CONTRAINDICATIONS, YOU MUST READ THE INSTRUCTIONS OR CONSULT WITH A SPECIALIST. BIOLOGICALLY ACTIVE SUPPLEMENT. NOT A MEDICINE.