Home>Articles>Alcohol and allergic dermatitis
quick menu (hide)
- Alcohol and hives
- Alcoholic drinks and their consequences
- Drinks are allergens
The term “dermatitis” is commonly understood to mean many diseases. They can be of a physical, biological, chemical nature. The hereditary also plays an important role . One of the common forms of damage is allergic (urticaria is a separate area of it). It occurs along with seborrheic, contact, alcoholic, and atopic types. The article will discuss the possibility of simultaneous intake of alcohol and anti-dermatitis tablets.
Based on the nature of manifestation, etiology and pathogenesis, it is customary to distinguish itchy, fungal, dry, infectious, food, and red ailments. Regardless of the form of the pathology, the body reacts to a stimulating agent or a systemic difficulty (weakened immunity, gluttony, excessive amounts of alcohol consumed). Moreover, these factors themselves can act as causes of allergic processes and the formation of the first signs of skin ailments.
Possible causes of rashes after alcohol
Let's look at the three main causes of redness:
Allergy.
This is a question of individual intolerance to an alcoholic drink. Alcohol urticaria is the most common symptom of an allergic reaction. Do you want to avoid it in the future? Then you need to isolate the substance to which the reaction occurs. Usually these are food colorings and preservatives.
An allergic reaction occurs not only to “chemicals”. But also on the natural components of the drink. In this case, run to a specialist. It will help determine the active substance. And will give recommendations for treatment. And of course, you should refuse the drink that causes allergies.
The reaction occurs when taking alcohol and medications at the same time
Fact: combining alcohol with a number of drugs is prohibited. Most often we are talking about antibiotics. To avoid rashes, you should not combine medications with alcohol.
Chronic diseases of the liver, digestive and urinary systems.
Rashes on the face or body are the first sign of problems with these organs. Toxins that enter your body along with alcohol “settle” in tissues and organs, and some of them are “excreted” out - in the form of a rash.
Hives are a rash consisting of pink or red itchy blisters of varying sizes and shapes raised above the surface of the skin. Most often, this rash does not last long and is capable of migrating, that is, disappearing in one area of the skin and soon appearing in another.
Hives are acute if the rash lasts less than six weeks, and chronic if it lasts longer than six weeks or occurs frequently over several months or years. Acute and chronic forms of urticaria have different causes and course, and also require different approaches to treatment.
It is believed that every fifth person experiences acute urticaria at least once in his life. Children most often suffer from it. However, in most cases it is mild, passes quickly and does not entail any serious consequences.
Chronic urticaria occurs much less frequently - in one in a thousand people, more often among middle-aged women. Approximately a third of cases of chronic urticaria are accompanied by angioedema, that is, swelling of the lips, tongue, larynx, and joints. Swelling of the larynx can lead to difficulty breathing, which is seriously life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
Acute urticaria usually goes away very quickly, often even without the use of any drugs, and does not appear again. In the case of chronic urticaria, treatment is selected strictly individually and depends on the immediate cause of the disease. In this case, it is necessary to control the manifestations of the disease and, if possible, limit the impact of any factors that can enhance the pathological reaction, since there is a risk of developing respiratory complications.
Synonyms Russian
Urticarial rash, allergic rash, urticarial dermographism, acute urticaria, chronic urticaria, autoimmune urticaria, urticaria.
English synonyms
Urticaria, hives, acute hives, chronic hives, physical urticaria, welts, nettle rush, ordinary hives, pressure urticaria.
Symptoms
Urticaria is characterized by a certain appearance and dynamics of development, which helps the doctor during examination to distinguish it from other diseases and conditions.
Symptoms of urticaria:
- occurs abruptly, for no apparent reason, and goes away in most cases within a few hours or days;
- can migrate;
- presented by pink or red blisters, usually 1-2 cm in diameter, which rise above the surface of the skin and itch.
With chronic urticaria, the condition sharply worsens, breathing becomes difficult, joints swell; abdominal pain may indicate the addition of angioedema.
General information about the disease
The mechanism of urticaria is the effect of a pathological factor on mast cells (cells of the immune system that are located under the skin, around blood vessels and participate in inflammatory reactions). In case of urticaria, these cells secrete biologically active substances, in particular histamine, which increase the permeability of skin vessels and promote the release of fluid from them. This leads to the appearance of a characteristic rash.
The main causes of acute urticaria are:
- allergies - food, insect bites, medications (penicillin, aspirin, painkillers);
- contact with toxic and noxious substances, such as chemicals, poisonous plants, cosmetics, latex and others;
- physical impact - as a result, the so-called physical urticaria develops; the cause may be either a mechanical effect on the skin or heat, cold, or sun rays;
- viruses - a viral infection (ARVI, influenza) is apparently not the cause, but the trigger of urticaria, the immediate cause of which may be unknown;
- unknown causes – in many cases it remains unclear what caused the hives.
The cause of chronic urticaria is not fully understood. It is believed that it is based on a disruption of the immune system. Provoking factors may be solar radiation, heat, cold, or taking certain medications. Chronic urticaria can also be associated with other diseases, such as diseases of the thyroid gland, liver, and autoimmune pathology.
Who is at risk?
- Allergy sufferers.
- Children.
- In contact with chemicals, poisons, insects.
- People with chronic diseases.
- People with acute and chronic infectious diseases.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made by a doctor, as a rule, already during examination based on the characteristic appearance of the rash. In case of acute urticaria, additional research is usually not required, since most often it goes away on its own quite quickly and does not return. In case of chronic urticaria, to select treatment, it is necessary to identify the immediate cause of the rash. In this case, laboratory diagnostics is of great importance.
- Complete blood count (without leukocyte formula and ESR). Can detect an increased number of white blood cells if there is an infection in the body as a possible cause of the rash. There may also be an increased level of eosinophils, a type of white blood cell that is involved in allergic reactions, which indicates the allergic nature of the hives.
- ESR. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate, which is determined by their ability to stick to each other and depends on the ratio of proteins in the blood plasma. During infectious processes or pathologies of the immune system, the ESR changes, which can also help determine the cause of urticaria.
- General urine analysis. Allows you to evaluate the functioning of the kidneys and identify their possible pathology.
- Analysis of stool for protozoa and helminth eggs (worms). Allows you to identify the most common parasites that can cause urticaria.
- Antiperinuclear antibodies, antibodies to double-stranded DNA - studies aimed at detecting specific proteins (antibodies) involved in the destruction of the body's own cells, that is, in autoimmune diseases. Urticaria may be associated with these diseases.
- Immune status. Determination of the level of immune complexes circulating in the blood, that is, complexes of foreign substances (antigens) with antibodies. Their number can be increased due to inflammation, infection, or autoimmune process.
- , C4 complement components. Complement is a complex of proteins that is involved in the immune response to infection. Decreased levels of complement proteins, particularly C3 and C4, may indicate the presence of an autoimmune disease.
- Culture of the nasopharynx, examination of the intestinal microflora (microbial composition). They are used to identify the source of a chronic infection that may be causing hives. Additional bacteriological tests are prescribed during examination by a gynecologist and dentist.
- Liver tests (alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, total bilirubin, creatinine, urea). The level of liver enzymes, metabolic products in liver cells, is determined to identify possible liver pathology as the cause of the rash.
- Assessment of thyroid function (thyroxine, triiodothyronine, antibodies to thyroglobulin and thyroid peroxidase). The level of thyroid hormones and antibodies to them and to enzymes necessary for the synthesis of hormones are measured. A change in the level of these indicators may indicate an autoimmune lesion of the thyroid gland.
- Allergy tests, that is, determination of the total amount of immunoglobulins E and specific immunoglobulins E and G in the blood - proteins that are involved in allergic reactions. These tests are most often performed when acute urticaria is suspected of being allergic, to determine the substance that is causing the rash. In chronic urticaria, an allergic mechanism is unlikely.
Additional research methods
- Ultrasound of the abdominal organs and thyroid gland. Used to identify lesions of internal organs as a possible cause of urticaria.
- Skin biopsy. Taking a skin sample using a scalpel or a special thick needle after local anesthesia. The sample is examined under a microscope to exclude malignant skin diseases and bacterial lesions.
- Skin allergy tests. Used for allergic urticaria to identify the triggering factor of the rash. A small amount of allergen solution is applied to the skin of the inner forearm, and then a small injection is made to a depth of 1 mm (prick test) or a scratch (scarification test). The occurrence of skin redness and swelling in this area confirms the likelihood of an allergy to this substance.
- Provocative tests. Used for physical urticaria. The skin is affected mechanically - a piece of ice is briefly applied, rubbed with a spatula, exposed to sunlight - depending on the expected nature of the urticaria, and the skin's reaction to the irritant is observed.
In some cases, to identify the cause of urticaria, consultation with specialists such as an infectious disease specialist, gynecologist, dentist, or dermatovenerologist may be required.
Treatment
Acute urticaria usually goes away on its own within 24 hours and does not require treatment. Cold showers and taking antihistamines can reduce itching. Antihistamines block the effect of histamine, the main substance that causes the symptoms of hives. When the allergic nature of urticaria is established, the main importance is to eliminate the effect of the allergen on the body.
Treatment of chronic urticaria is more challenging. If the cause of chronic urticaria rash is known, it consists of treating the underlying disease. Often a positive effect is achieved by using an individually selected combination of drugs. For chronic urticaria, not only antihistamines can be used, but also certain types of antidepressants and steroids (synthetic analogues of adrenal hormones).
Prevention
- Elimination of exposure to established provoking factors on the body.
- Use medications in accordance with the instructions and strictly as prescribed by the doctor.
Recommended tests
- General blood analysis
- ESR
- Urine analysis with sediment microscopy
- Fecal analysis for helminth eggs
- Anti-double-stranded DNA antibodies (anti-dsDNA), screening
- Antiperinuclear factor
- Circulating immune complexes (CIC)
- Complement component C3
- Complement component C4
- Culture of flora with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics
- Intestinal dysbiosis with determination of sensitivity to antibiotics
- Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
- Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
- Total bilirubin
- Serum creatinine
- Urea in serum
- Free thyroxine (free T4)
- Total triiodothyronine (T3)
- Antithyroglobulin antibodies (antiTG)
- Antibodies to thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO)
- Total immunoglobulin E (IgE) in serum
Rash on face after drinking alcohol
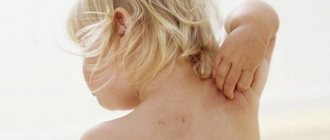
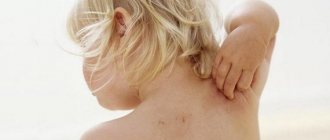
Most often, it is the skin of the face that becomes the “victim” of rashes. Reddish, similar to small eels - a disgusting thing. They are widespread and appear in large quantities. A similar rash is typical for people suffering from alcoholism, but it can also appear in an ordinary person who drinks alcohol quite rarely.
The rash may itch, become inflamed, gradually dry out and disappear. In many cases, spots on the face after drinking alcohol disappear by the evening of the next day or after a few days, in others they remain for a long time.
Curious…
...that most often it is not women who go to the doctor with a rash on their face, but men: the former often associate the rashes with an allergic reaction to cosmetics or mistake them for ordinary acne.
There is no point in fighting spots on your face with the usual methods, as you do with acne. Of course, regular hygiene procedures (washing with soap, soda) will not hurt, but they will not solve the problem. It is best to visit a doctor - a dermatologist, allergist and therapist - and identify the cause. Very often, this reason is not an allergy, but problems with the liver and gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention and treatment of urticaria
Treatment of allergic urticaria is carried out using a set of methods:
- following a hypoallergenic diet or eliminating a product or medication that provokes an attack of the disease;
- use of hypoallergenic detergents and cosmetics in everyday life, caution when taking antibiotics and vitamins;
- to quickly relieve an episode of rash, use antihistamines internally (in the form of tablets) and externally (in the form of gels and ointments that relieve itching);
- for more severe manifestations, the administration of glucocorticoids and the use of hormonal ointments is indicated;
- During treatment, it is recommended to consume large amounts of fluid and intestinal sorbents to help remove the allergen from the gastrointestinal tract;
- Additionally, you can take sedatives.
It is better to entrust the correct choice of therapy and prescribe modern, effective and safe medications to a doctor - a dermatologist or allergist.
To prevent the recurrence of urticaria, it is necessary to avoid the action of the provoking factor. It is also not recommended to wear thick synthetic clothing or stay in damp places.
Rash on the body after drinking alcohol
The face is the first area where a rash appears due to allergies or liver problems. And if you notice rashes or redness, it is better to consult a doctor immediately. Subsequently, the problem can “spread” to the body. However, sometimes rashes immediately appear on the body without affecting the face.
The appearance practically does not deteriorate, but constant itching causes significant discomfort. The so-called “alcoholic urticaria” can significantly complicate life.
If “urticaria” appears on the body - red blisters accompanied by itching, you should not try to treat it with anti-allergy medications or sedatives. It is likely that this “urticaria” is only a symptom of a more serious disease of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, and urinary system.
Contact a specialist immediately. He will conduct a diagnosis and prescribe the necessary medications.
Treatment of the disease at the Mama Papa Ya clinic
Clinic "Mama Papa Ya" is located in Lyubertsy. Here we see qualified doctors of various specialties who will provide assistance to patients with urticaria:
- in the clinic you can do the necessary tests and undergo the necessary examination;
- can be treated for both adults and children;
- consultations with specialists in various fields provide the most complete treatment for urticaria;
- We offer affordable prices for medical services and convenient work hours.
To make an appointment, call the phone number listed on the website or through the form provided.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga
{loadmodule formrec}
What do the rashes indicate?
If you notice a rash on your body after drinking alcohol, it's time to see a doctor. This may be a symptom of a disease or disorder in the body. We have already discussed the causes of the rash. And if you can completely rule out an alcohol-drug reaction, you may be suffering from an individual intolerance to a particular component of the alcohol. Well, or we are talking about diseases of the liver or other organs of the body.
Curious…
Alcoholism rash is often called eczema or “alcohol urticaria.” Excessive alcohol consumption affects liver function. Kidney and gastrointestinal diseases occur. This leads to rashes. Eczema is considered practically incurable, but getting rid of it is quite simple: just give up alcohol and put your body in order.
You should definitely check with a doctor. But you can limit yourself to checking yourself if you are confident in your own health. In particular, you can try other alcohol. If no rashes occur after drinking another alcoholic drink, it is likely an allergic reaction.
What about our liver?
You should definitely check with a doctor the condition of the liver, bladder and gall bladder, stomach and intestines and other organs. This is not as difficult to do as it seems: simple tests will help identify violations, and therefore begin treatment.
However, it is not necessary to run to the doctor after the appearance of a rash. Perhaps its appearance is not related to alcohol. It is also possible that you are allergic to any food product or cosmetic product. But we do not recommend trying to find out for yourself what you are allergic to. Anything can happen.
Photos of rash
A rash after drinking alcohol, on the face or body, takes various forms. Much depends on the individual characteristics of the body. See the photo for more details.