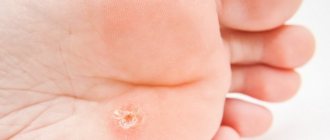
Calluses
occur in places where the skin experiences constant friction or pressure. By forming a callus, the body tries to protect itself from this adverse effect.
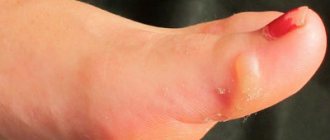
First there is a wet callus
- a bladder filled with liquid - lymph. Lymph is needed for the speedy healing of damaged tissues. If the mechanical irritation stops, new skin forms under the blister and the callus disappears.
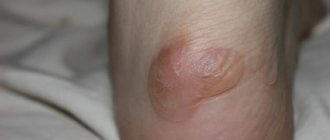
If the external influence continues, the body begins to build up a protective layer of dead, horny cells. Dry callus appears
, looking like a white-yellow compaction, usually with round outlines.
Calluses form on the hands (during physical work) and on the feet (on the heels or toes). As a rule, it is foot calluses that worry us.
What is a callus
A callus is a conical thickening of the skin that occurs in areas of constant friction or pressure. Most often, calluses appear on the feet (heel, big toe, side of the foot) and on the hands. In men, a callus may appear on the penis due to frequent wearing of too tight underwear.
The main symptom of the appearance of callous formations is the formation of tubercles of rough skin. Depending on the location and appearance, there are several types of calluses:
- dry;
- wet;
- bone.
A dry callus is a small area of thickened, dead skin that is yellowish in color. A wet callus has a thinner surface and is often filled with lymphatic fluid. Callus occurs during the process of bone regeneration after fractures. Separately, bloody calluses, core calluses, and calluses are also distinguished.
Core (root) callus is a type of dry callus and is distinguished by the presence of a thickened keratin core. The external manifestation of a root callus is similar to that of a plantar wart, so a dermatologist can make an accurate diagnosis after performing a dermatoscopy.
Calluses (corns) are wide, flat thickenings of the skin that do not have a hard center. Corns on the feet and hands rarely cause pain when pressed.
A callus with blood is a type of wet callus filled not only with lymph, but also with blood. A callus occurs when blood vessels are too close to the surface of the skin that has been subjected to friction.
Corns
| Removal of complicated corns when pain occurs (1 unit) | – | 500 |
| Removal of uncomplicated corns (1 unit) | – | 350 |
| Application of unloading material when removing corns - level I (1 unit) | – | 350 |
| Application of unloading material when removing corns - level II (1 unit) | – | 550 |
| Recommendations and instructions for foot care | – | 500 |
| Unloading dressing (1 unit) | – | 350 |
| Applying an antibacterial and antiseptic bandage to the problem area - level I (1 unit) | – | 550 |
| Applying an antibacterial and antiseptic bandage to the problem area - level II (1 unit) | – | 550 |
| Bandaging the problem area (1 unit) | – | 500 |
Causes of calluses
In response to constant friction and pressure, cells begin to synthesize increased amounts of keratin, the skin's protective protein. With calluses, keratin can form a plug in the deep layers of the skin. The main reasons for the formation of calluses on the feet and hands are:
- wearing shoes of the wrong size;
- foot deformities (hammer toes, bunions, bone spurs);
- chafing of the skin due to professional activities (musicians, weightlifters, artisans);
In tight shoes, the skin of the foot is strongly compressed, and in too loose shoes, it slips and rubs, which can cause internal (core) calluses to develop. Calluses on the foot due to toe deformities occur due to improper weight distribution. Due to frequent rubbing of the skin of the hands with professional instruments (strings, bars), calluses appear on the hands.
Treatment depending on location
The easiest way to treat a callus on the foot. In this case, there are practically no restrictions when choosing methods.
If the callus is located on the little finger, there are certain difficulties, since it is more difficult to fix the patch on it, and not all surgical methods of removal are allowed.
If the subcutaneous callus is located between the fingers, then it is especially difficult to deal with it. In this case, surgical removal in a clinic or the use of improvised means in the form of various phytotherapeutic recipes is indicated.
In the first case, we are talking about cryodestruction, that is, the formation on the toe is destroyed by exposure to liquid nitrogen. Under its influence, after several sessions, the rod and ingrown cap fall off on their own. The whole procedure takes little time, after which you can immediately return to your normal rhythm of life. You cannot try to cut it off yourself. This will only injure the callus.
There are home methods that are suitable for treating both interdigital formation and similar problems on the foot. In addition to classic baths, compresses based on aloe leaves are used. It is more convenient to fix them between the fingers, where they act as a plaster. A hard-to-reach place can be lubricated with a mixture of propolis in alcohol and various essential oils, covering it with a bandage.
Dry and wet calluses
Dry calluses are keratinized areas of skin that form in places where bone presses on the skin of the feet (tops of the toes). If you frequently wear tight shoes, dry subungual callus may form.
Wet (water) calluses are whitish-gray in color and have a softer texture because they form in areas of increased sweating on the feet and hands. Water calluses often form between the fingers and toes. If a wet callus on the foot is damaged, an infection can enter the wound, so it is important to treat the damaged area of skin with antiseptic agents.
Contraindications for cryodestruction of calluses
Contraindications to the use of liquid nitrogen for the destruction of calluses are:
- Cold intolerance - manifested by the formation of an itchy rash on the skin when exposed to low temperatures (in the cold, when exposed to cold water, when applying an ice cube).
- The presence of allergic rashes, pustular elements or a violation of the integrity of the skin in the area of expected exposure. To use cryodestruction in this case, preliminary treatment of existing rashes is required.
- Insufficiency of arterial circulation in the feet against the background of obliterating atherosclerosis, complications of diabetes mellitus.
- The presence of cryoglobulinemia is a rare disease in which special proteins are formed in the blood (cryoglobulins) at temperatures below 37°C. This condition accompanies various vasculitis - vascular inflammation, Raynaud's syndrome, viral hepatitis C, etc.
Callus
Callus formation is an important step in the process of bone tissue repair after injury because it helps connect the parts of the damaged bone. After a fracture, the callus is enriched with calcium and gradually turns into normal bone tissue.
Due to insufficient immobilization or poor circulation at the fracture site, callus may form too slowly (delayed fracture consolidation). Its slow formation can cause the bone to heal incorrectly and cause pain.
Features of treatment in a child
A callus can also appear in a child. In this case, the methods for removing it will be different. The fact is that children have more delicate skin. Even if a corn or callus has formed on it, it will still be more sensitive than that of an adult. For children under 10 years of age, not only salicylic acid in solution form is not used, but also its preparations, including patches like Salipod.
Home remedies can be widely used, for example, the warm soap and soda baths described above, lotions made from aloe juice (to obtain it, take a plant older than 3 years) or apple cider vinegar solution. Such compresses can be left overnight so that they have time to take effect.
It is recommended to visit a doctor. The pediatrician will refer the child to a surgeon or podiatrist if the callus has developed a deep root, and it cannot be removed with compresses and pumice. A doctor is consulted when the area of the formation is large or it becomes especially painful.
How to get rid of calluses?
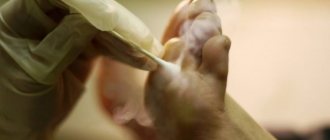
To get rid of calluses, it is enough to temporarily eliminate activities that cause chafing of the skin. You can remove dry calluses manually: you need to steam the skin of your hands and remove rough areas using pumice. In addition, the surgeon may recommend the use of keratolytic agents, which soften the skin. You cannot remove calluses on your own with the help of keratolytics if you have diabetes or pathologies of the immune system, since after removal a wound may form through which an infection can enter the body
You should see a doctor if the callus is painful to step on or touch, as this symptom may indicate the presence of a heel spur, a calcified growth on the surface of the bone. Removal of the callus core is performed by a doctor because removing the callus at home is ineffective and unsafe.
To quickly cure a water callus and avoid its damage, it is necessary to reduce the contact of the inflamed skin with the shoes: you can put a foam insert or a cotton ball between your toes. If the water callus bursts, the doctor prescribes the use of wound healing agents with an antiseptic effect.
Callus removal is performed surgically using local anesthesia. First, the surgeon cuts off the keratin growth on the skin, and then pulls out the rod. To speed up the healing process and prevent the wound from becoming infected, it is recommended to wear a sterile dressing for several days after the callus removal procedure. The surgeon also prescribes local use of antiseptics for two to three weeks after removal of the callus.
How to prevent skin problems in the future
A patch for calluses on the heel and other areas will help speed up recovery and relieve discomfort. But it is easier to prevent the formation of calluses than to treat the consequences. Preventive measures include the following:
- regular pedicure, daily foot hygiene;
- moderate skin hydration;
- wearing comfortable shoes of your size with a hard back and wide toe;
- changing and cleaning shoes several times a season;
- therapeutic exercises, foot massage;
- preventing the risk of microtrauma;
- refusal to wear wet socks and gloves.
The listed preventive measures will reduce the risk of callus formation (wet, dry, core). If trouble cannot be avoided, it is advisable to immediately begin treating the calluses and should not cut them off.
Callus or wart?
A wart is a small growth that is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Calluses and warts may be similar in appearance. A wart can be distinguished by its more granular structure and location (warts can appear on any part of the body). To accurately make a diagnosis (callus or wart) and select treatment, the surgeon can conduct a dermoscopic examination and additionally prescribe a test for human papillomavirus (HPV).
Balm Karavaev for eliminating formations
Another popular remedy is Karavaev’s balm. Medicines are sold under several brand names, but only one has been officially registered - Vitaon.
Balsam Karavaev is a plant-based preparation. It contains essential oils of pine, cumin, rose hips, extracts of yarrow and St. John's wort, as well as celandine, which is considered an excellent remedy for warts and calluses. Vitaon also contains calendula extract. The balm has anti-inflammatory properties and helps heal wounds. But its effectiveness is lower than that of keratolytic agents.
What recommendations are important for a patient to follow after cryodestruction of a callus?
After removing the callus with nitrogen, it is important to:
- limit the pressure on the site of destruction by reducing the load (walking, playing sports, wearing high heels, tight shoes, etc.);
- do not injure, rub or scratch the frozen area;
- Maintain foot skin hygiene: wash your feet daily with soap, then dry them with a clean towel, change your socks.
To prevent recurrence of callus formation, it is necessary to eliminate possible causative factors:
- wearing tight or narrow shoes;
- use of shoes with or without high heels.
It is also important to promptly treat lesions of the osteoarticular system to prevent further joint deformation, and for overweight patients to reduce it. Doctors recommend using orthopedic pads to reduce the likelihood of relapses of calluses, and timely pedicures to eliminate local thickening of the skin of the sole.