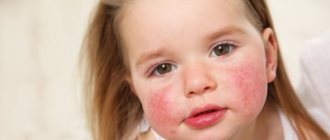
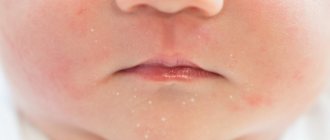
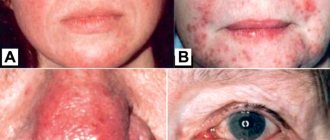
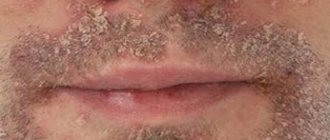
Diathesis is a constitutional feature of the body that reflects its predisposition to pathological reactions to external stimuli and the diseases that cause them. Despite the fact that diathesis is considered a childhood problem, adults encounter it no less often. They also consider it not a disease, but a manifestation of a hereditary predisposition to immune and infectious diseases. Treatment of diathesis in adults is carried out according to the same principles as in children.
What is diathesis?
Diathesis is a constitutional anomaly, and now this term is used more as a tribute to the domestic tradition in pediatrics. A similar concept is “hereditary predisposition.” Such signs are not described in foreign literature. There is no separate section for them in the International Classification of Diseases.
Diathesis in children is not a disease, but only a combination of various functional changes that do not always contribute to the development of any diseases. To prevent such a reaction from developing into pathology, it is necessary to monitor the child with an experienced pediatrician and comprehensive treatment of diathesis.
Uric acid diathesis - is it always a manifestation of impaired purine metabolism?
Uric acid diathesis is often considered as a synonym for neuro-arthritic diathesis, which is one of the variants of constitutional abnormality. The concept of “constitution” characterizes the totality of morphofunctional properties of the child’s body, which determine the individual characteristics of its reactivity [1–3]. Diathesis, or otherwise a constitutional anomaly, characterizes the characteristics of one or another type of metabolism, which under certain conditions can be realized in pathology. Neuro-arthritic diathesis is characterized by an increased intensity of purine metabolism, the end product of which is uric acid (UA). Like other types of diathesis, uric acid diathesis is not considered a pathology, but is a borderline condition characterized by an increased risk of a number of diseases. With this type of diathesis, there is a tendency to dyskinesia of the gastrointestinal tract with the occurrence of acetonemic vomiting; cardiovascular pathology, diseases of the nervous system, arthritis, urolithiasis and cholelithiasis, diabetes mellitus, etc. are more common. The mere fact of a violation of UA metabolism, from the point of view of Prof.'s point of view N.P. Shabalova, is an important, but not the only marker of this type of diathesis, which can predispose to certain types of pathology. In this regard, within the framework of this publication, I would like to raise the question of whether uric acid crystalluric diathesis should always be considered as uric acid diathesis due to a violation of purine metabolism. First of all, it is necessary to determine what characterizes uric acid crystalluric diathesis and does it differ from uric acid diathesis in the generally accepted sense? The main and defining sign of this type of diathesis is the frequently occurring crystals of uric acid or its salts in the urine sediment. But this phenomenon is precisely one of the signs characterizing uric acid diathesis, which is based on excessive formation of uric acid as a manifestation of the tension of purine metabolism. Therefore, one should consider uric acid crystalluric diathesis (UCD) as a synonym for uric acid diathesis, and therefore neuro-arthritic diathesis. The reasons for the formation of crystals of magnesium and its salts are different (Fig. 1). In clinical practice, we often encounter children in whose urine sediment crystals of uric acid and its salts are often found in the absence of any signs of neuro-arthritic diathesis. In other words, there is no increased nervous excitability both in infancy and in subsequent age periods. They also lack accelerated mental development, no emotional lability, no tendency to acetosis, and therefore they do not have increased levels of ketone bodies, ammonia, and sUA in the blood, i.e., an acetonemic crisis does not develop. Noteworthy is the fact that these children do not have hyperuricosuria, and uric acid crystalluria is observed even in the absence of increased urine osmolality, i.e. crystalluria occurs in non-concentrated urine. This allows us to distinguish this type of diathesis as a special type of uric acid diathesis and, in any case, not to consider it as a manifestation of neuro-arthritic diathesis. If there is no disorder of purine metabolism, what then underlies this type of diathesis? The development of uric acid crystalluric diathesis is based on the reduced ability of urine to prevent the formation of crystals of released uric acid and its salts. It is known that urine has an increased dissolving ability compared to water. This is due to the fact that urine is a complex multicomponent solution containing various ionized elements of crystalline substances and large-molecular organic colloidal substances. The interaction between them ensures increased solubility of salts per unit volume [4]. Therefore, even at a high concentration of crystal-forming salts (in this case, LA and its salts, urates), no crystal formation occurs. LA and its salts are known to be poorly soluble in acidic urine, and the lower the pH of the urine, the worse it is. Moreover, their concentration in the urine may be insignificant, and vice versa, if the urine reaction becomes neutral or alkaline, crystal loss does not occur even under conditions of hyperuricosuria. Therefore, it is advisable to consider uric acid crystalluric diathesis, in contrast to uric acid diathesis, not as a manifestation of impaired purine metabolism, but as a consequence of the limited ability of the distal tubule to alkalize urine. This ability is known to be associated with the function of ammoniogenesis. Ammoniogenesis is always associated with the oldest function of the tubular epithelium - acidogenesis, in which hydrogen ions (H+) are synthesized under the action of the enzyme carbonic anhydrase present in the tubular epithelium. The resulting H+ is secreted into the lumen of the tubule and thereby acidifies the urine. Their increased formation and secretion occurs when acidic valences accumulate in the process of metabolism, which helps maintain the acid-base state of the body. Normally, increased acidogenesis is always accompanied by increased formation of ammonia under the influence of the enzyme glutaminase, which splits ammonia from glutamine. Ammonia diffuses into the lumen of the tubule and, combining with H+, forms ammonium ion (NH4+), which alkalinizes the urine. Insufficient ammoniogenesis function is manifested by aciduria, when the urine pH is stably low and does not exceed 6.0, which contributes to the loss of UA crystals. Violation of this function may be hereditary and run in families. Until recently, this variant of uric acid diathesis was considered idiopathic. Impaired ammoniogenesis function can occur secondary to any renal pathology with the development of tubulointerstitial syndrome.
| Rice. 1. Causes of uric acid crystalluria |
Thus, considering uric acid diathesis from the standpoint of today, one should distinguish diathesis caused by the peculiarities of purine metabolism from diathesis caused by impaired function of ammoniagenesis. At the same time, it is important to identify the primary form of impaired ammoniagenesis, which, most likely, is familial in nature, and it is this form that should characterize this type of uric acid diathesis, which, in contrast to neuro-arthritic diathesis, it is advisable to call MCD. Identification of this type of diathesis will make it possible to more rationally prevent the possible transition of this type of diathesis into uric acid nephropathy, and then into interstitial nephritis of dysmetabolic origin or urolithiasis (Fig. 2). With this diathesis, there is no need, unlike neuro-arthritic diathesis, to strictly adhere to a diet with restriction of foods rich in purines, because there is no disorder of purine metabolism, and therefore there is no hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria. It is only necessary to maintain sufficient diuresis and promote alkalinization of urine by periodically administering citrates, appropriate mineral waters and a number of other drugs, trying to maintain urine pH in the range of 6.4–6.8.
| Rice. 2. Evolution of uric acid crystalluric diathesis |
Uric acid nephropathy, unlike MCD, is already a pathology, and its occurrence is still associated with the presence of a neuro-arthritic diathesis in such children, i.e., with a disorder of purine metabolism [5–7]. However, urate nephropathy occurs not only as a result of a violation of purine metabolism, when there is increased endogenous synthesis of UA, but also as a consequence of a violation of its transport in the kidneys, as well as due to the low inhibitory ability of urine, realized by a violation of ammonia formation in the distal nephron.
The term “uric acid (uricosuric) or urate nephropathy” is often used to define various diseases associated in one way or another with impaired uric acid metabolism and manifested either by damage to the kidneys or only to the urinary tract. In the first case, when crystallization occurs in the parenchyma (interstitium) of the kidneys and in response to this, an abacterial inflammatory process occurs, we should speak of interstitial nephritis. In the second case, when crystalluria occurs only in the lumen of the tubules, this may be the norm, or characterize the presence of uric acid crystalluric diathesis, or be a manifestation of urate nephropathy.
The main symptom of MCD is the occurrence of increased crystal formation. If crystals of uric acid or its salts form en masse in the lumen of the tubules and the kidney parenchyma is not affected, and only crystalluria is present in the urine sediment, then this is not nephropathy. This may be the norm when, with an excess of exogenous purines, the release of small crystals of urate salts increases and conditions for the formation of microliths from them do not arise. When the same is observed in the absence of an excess of exogenous purines and there is no increased endogenous formation of them (no hyperuricosuria), then the presence of MCD should be assumed.
In the practical work of a pediatrician, as well as a pediatric nephrologist, a diagnosis of “uric acid or urate nephropathy” is often made if crystals of uric acid or its salts are found in the urine sediment. The mere fact of the presence of salt crystals is not a basis for making this diagnosis. Dysmetabolic nephropathy should be discussed only with frequently observed crystalluria, accompanied periodically by microhematuria, abacterial leukocyturia, and dysuria. In this case, there is no impairment of renal function, since crystal formation and the pathological process caused by it occur only in the lumen of the urinary tract, without affecting the interstitial tissue of the kidneys by the inflammatory process. However, increased formation of crystals during metabolic nephropathy can also be observed in the interstitium of the kidneys, which often causes the appearance of echo-positive signals during ultrasound examination, which disappear with sufficient drinking regimen. In this case, there is no inflammatory process in the interstitium, the occurrence of which will characterize the transition of metabolic nephropathy to interstitial nephritis of dysmetabolic origin. In this case, renal dysfunction can be detected due to damage to the tubulointerstitium in the form of a decrease in the concentrating ability of the kidneys, acidogenesis and ammoniagenesis, which can be detected in the early stages during stress tests.
What should the doctor do if, when examining children with uric acid crystalluria, hyperuricemia and hyperuricosuria are not detected? If increased crystalluria is detected, it is necessary, first of all, to exclude the presence of aciduria. To do this, the pH should be determined in urine samples collected at different times. If persistently low pH values (< 6.0) are detected, ammonia function must be assessed to determine the cause. This can be done by performing a stress test with ammonium chloride (Rong-Davis test) [8]. In this case, a compensated metabolic acidosis should occur, in response to which the formation and release of hydrogen ions by the distal tubules and the formation of ammonia from glutamine by activating the enzyme glutaminase are enhanced. Since this test is labor-intensive, requires the use of complex and expensive equipment and is poorly tolerated by patients, a stress test with Lasix was developed and proposed [8, 9], which, without causing acidosis, enhances acidogenesis and ammoniagenesis. The absence or insufficient production of ammonia in response to exercise indicates that the cause of aciduria is reduced ammoniaogenesis. This so-called idiopathic form of uric acid nephropathy is actually a distal tubulopathy leading to aciduria.
In this regard, it is necessary to distinguish between two types of uric acid diathesis - diathesis caused by the intensity of purine metabolism, which occurs with increased excretion of uric acid and its salts in the urine, and diathesis caused by a reduced ability of the distal nephron to alkalize the urine. This contributes to aciduria and loss of uric acid crystals and its salts in the absence of hyperuricosuria. The second type of uric acid diathesis, in contrast to the neuro-arthritic version of uric acid diathesis, should be designated by the term “uric acid crystalluric or aciduric diathesis”, which is often familial in nature and is caused by a reduced ability of the kidneys to alkalinize urine, thereby emphasizing that its main symptom is aciduria. Thus, a differentiated approach to patients who have urate crystalluria is required. When aciduric diathesis is detected, there is no need to limit the child, as well as the adult, in taking foods rich in purines. Treatment and prevention in such individuals should be aimed at increased fluid intake and alkalinization of urine. As for herbal medicine, it should be controlled not only by the amount of diuresis, but also by the urine reaction
Literature
- Maslov M. S. Constitutional anomalies (diathesis) in childhood / Multi-volume guide to pediatrics. Ed. prof. Tour A.F.M., 1960, vol. 1, p. 471–524.
- Sergeev Yu. S. Human constitution, constitutional types, constitutional anomalies and diathesis in children // Pediatrics. 2005, No. 5, p. 67–71.
- Shabalov N.P. Diathesis and constitutional anomalies as a pediatric problem // Pediatrics. 2005, No. 5, p. 72–76.
- Tomakh Yu. F., Klepikov F. A. Crystalluric diathesis. Kharkov, 1992. pp. 24–49.
- Yuryeva E. A., Dlin V. V. Metabolic nephropathies in children. In the book: Dysmetabolic nephropathies, urolithiasis and nephrocalcinosis in children. M., 2005. pp. 9–72.
- Korovina N. A., Zakharova I. N., Gavryushova L. P. et al. Dysmetabolic nephropathies in children: diagnosis and treatment (a guide for doctors). M., 2007. pp. 12–16.
- Malkoch A.V. Dysmetabolic nephropathies and urolithiasis. In the book: Practical guide to childhood diseases. T. 6: Nephrology of childhood. Ed. Tabolina V. A., Belmera S. B., Osmanova I. M. M., 2005. pp. 472–516.
- Rivkin A. M., Papayan A. V. Laboratory diagnostics: urine examination and clinical assessment of results. In the book: Clinical nephrology of childhood. Ed. prof. Papayana A.V. St. Petersburg, 1997. pp. 60–80.
- Arkhipov V.V., Rivkin A.M. Diagnosis of the functional state of the kidneys using furosemide. Guidelines. Ed. prof. Papayana A.V. St. Petersburg, 1996. 13 p.
A. M. Rivkin, Candidate of Medical Sciences, Associate Professor
SPbGPMA, St. Petersburg
Contact information about the author for correspondence
Causes of diathesis
Risk factors for the development of constitutional anomalies:
- chronic diseases in parents, for example, allergies;
- poor nutrition of a pregnant woman, her medication intake, illnesses during pregnancy;
- complicated course of pregnancy and childbirth;
- frequent infectious diseases in a child, taking a large number of medications;
- incorrect, unbalanced feeding.
The main causes of diathesis:
- unsynchronized maturation of the liver, kidneys, blood elements, and nervous system in the child’s body;
- disruption of the immune system;
- insufficient hormonal activity of the adrenal cortex (hypocortisolism).
How is the disease diagnosed?
Typically, your doctor will order blood and urine tests to measure your creatinine and uric acid levels. Blood is taken from a vein. If the results are abnormal, a 24-hour urine test is performed. Typically, it also shows elevated uric acid levels. The patient is then prescribed a purine-restricted diet, followed by a repeat urine test. This approach helps determine whether uric acid diathesis is caused by:
- consuming large amounts of purines in food;
- hyperproduction of uric acid in the body;
- insufficiently effective removal of purine metabolic products from the body.
If you have symptoms of gout, your doctor will recommend testing your intra-articular fluid. A sample is taken using a thin needle. If uric acid crystals are found in the fluid, a diagnosis of gout is made.
Symptoms of diathesis in children
In total there are more than 20 types of diathesis. They may be asymptomatic or accompanied by a variety of symptoms. All constitutional anomalies are characterized by common symptoms:
- fatigue, inability to adapt to changing environmental conditions;
- difficulties in learning, communicating with peers, social maladjustment;
- frequent colds;
- broncho-obstructive syndrome;
- skin rash;
- enlarged tonsils, adenoids;
- impaired metabolism, low weight, short stature.
How to treat uric acid diathesis
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of the disease. If it is asymptomatic, treatment is not required, since the benefit of drugs that reduce uric acid levels has not been proven. In all other cases, the underlying disease is treated.
To reduce the severity of gout symptoms, the following are prescribed:
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Colchicine;
- Allopurinol.
For kidney stones smaller than 5 mm, your doctor may advise drinking plenty of water and taking over-the-counter pain relievers until the stones pass on their own. Sometimes drugs are also prescribed that normalize purine metabolism and facilitate the removal of kidney stones from the body, such as Restructa Pro Injection S and Urolesan.
For larger stones, extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy or surgery is prescribed.
Types of diathesis
The most common types of constitutional anomalies in children:
- Exudative-catarrhal diathesis
There is a tendency to swelling, inflammation, diaper rash, peeling of the skin, and damage to the mucous membranes. Frequent infections, skin rashes on the cheeks and buttocks, and unstable weight gain occur. This is a common diathesis in newborns and children in the first 3 months of life, which is detected in half of infants, but usually goes away by 3 years of age. Its variety is allergic diathesis, which can later transform into chronic atopic diseases (rhinitis, asthma, dermatitis).
- Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis
There is an enlargement of the lymph nodes and the thymus gland with simultaneous suppression of protective forces, and the functioning of the endocrine glands is disrupted. This is a common diathesis in infants and children under 3 years of age. As a result, the child often suffers from infectious diseases, and severe lesions can develop - sepsis, pneumonia.
- Neuro-arthritic diathesis
The child has high levels of uric acid in his blood. There is increased nervous excitability, joint pain, bouts of vomiting, and smooth muscle spasms. The age of manifestation of pathology is about 6 years.
Causes of the disease
Uric acid is a substance that is formed when purines are broken down. Most of it dissolves in the blood, passes through the kidneys and is excreted from the body along with urine. An increase in uric acid levels can occur for the following reasons:
- the kidneys stop effectively filtering and removing uric acid from the blood;
- a person consumes a lot of foods high in purines (red meat, legumes, liver, seafood, alcoholic beverages, especially beer);
- the body produces too much uric acid.
In the latter case, the cause of increased levels of purine metabolic products is most often genetic disorders.
Diathesis in adults
Diathesis in adults is a misnomer, since this condition occurs only in children. In the future, it can cause the development of various diseases:
- exudative diathesis: bronchial asthma, cholecystitis, duodenitis;
- lymphatic diathesis: bronchial asthma, nephropathy, myocardial dystrophy;
- uric acid diathesis: hypertension, urolithiasis and cholelithiasis, gout, peptic ulcer, colitis, bronchial asthma.
A separate form of pathology, not related to constitutional anomalies and occurring in children and adults, is hemorrhagic diathesis. This is a large group of diseases that are united by a tendency to bleeding and hemorrhage. They occur when there is damage to blood vessels, platelets, or disruption of the plasma component of hemostasis. Such diseases, unlike ordinary diathesis, are treated by a hematologist.
Frequently asked questions about uric acid diathesis
What to do if you have uric acid diathesis?
First of all, consult a doctor. Now there are medications that effectively cope with the consequences of uric acid diathesis, such as gout and kidney stones.
What may be the primary symptoms?
It all depends on where in the body the uric acid crystals have settled. If the joints are affected, we are talking about gout. The first signs of this disease are pain, swelling and stiffness of the joint (usually the big toe). If the crystals have settled in the kidneys, there may be no symptoms for a long time, since kidney stones form gradually. This can be suspected by such signs as sharp pain in the lumbar region, frequent urge to urinate, and blood in the urine.
What are the most effective drugs?
Treatment should be prescribed by a doctor, since uric acid diathesis can lead to the development of diseases, the treatment methods for which differ significantly.
Treatment of diathesis
To find out how to treat diathesis in a child and how to prevent its consequences, you need to consult a pediatrician. If necessary, additional tests are prescribed and
consultations (ENT doctor, allergist, dermatologist, neurologist and others).
The basis of treatment is a hypoallergenic diet for the pregnant woman, and in the future for the child, limiting hot, spicy, fatty foods. The child is vaccinated according to an individual schedule. It requires constant careful care and attention. For lymphatic diathesis, home education up to 5–6 years of age may be recommended.
All medications are prescribed individually. These can be enzymes, antihistamines, vitamins, calcium supplements, adaptogens. For skin lesions, a non-hormonal ointment for diathesis, for example, naphthalan, can be used. Baths with infusions of chamomile, string, and bran are useful.
Prevention of diathesis
Prevention of the development of constitutional anomalies should begin during pregnancy and continue at least during the first year of life. Main events:
- regular monitoring during pregnancy;
- prevention and treatment of gestosis, other anomalies of pregnancy and childbirth;
- proper diet and emotional peace of the expectant mother;
- early attachment of the newborn to the breast;
- breastfeeding with the correct, gradual introduction of new products;
- hypoallergenic diet of the child and mother feeding breast milk;
- use only cotton linen, wash with baby soap or special powder;
- gymnastics, massage, hardening procedures, starting from a very early age;
- compliance with all vaccination instructions;
- upon admission to kindergarten or school - a course of adaptogenic drugs as prescribed by a doctor.
Atopic dermatitis and diathesis - symptoms and treatment
Treatment tactics depend on the severity and duration of the disease:
- with a mild course of the disease without sensitivity to allergens and complications, outpatient treatment is possible;
- in severe cases and the body’s reaction to atopenes, hospitalization is required.
Basic therapy includes taking anti-inflammatory, antipruritic and hyposensitizing agents that suppress the allergic reaction [10] [12].
First of all, you need to get rid of the itching. Since it is associated with inflammation, antihistamines and sedatives, topical corticosteroids or calcineurin inhibitors (Tacrolimus and Pimecrolimus) can be used to eliminate it [13].
With the development of moderate and severe forms of the disease, if topical medications do not help, the patient is administered Dupilumab (contraindicated in patients under 18 years of age).
The second goal of treatment is the correction of dry skin (xerosis), vascular and metabolic disorders. To do this, you need to eliminate provoking factors, avoid constipation and diarrhea, take antihistamines, sedatives and immunocorrective drugs. Reflexology, ultraviolet skin irradiation, selective phototherapy and photochemotherapy are also indicated. Antiseptic wet-dry dressings, hot poultices and paraffin applications are applied to the skin, and corticosteroid ointments are applied.
Diet therapy is carried out in three stages:
- Stage I - diagnostic diet. It is aimed at eliminating from the diet a product that is believed to have become an allergen. If the patient’s condition improves during this diet, then an allergy to the product is confirmed.
- Stage II - therapeutic diet. Aimed at eliminating not only all food allergens, but also provoking factors;
- Stage III - expansion of the diet during remission[14].
In the infant form of the disease, special attention should be paid to complementary foods: it should be hypoallergenic. To do this, you need to exclude foods and substances such as milk, gluten, sugar, salt, broth, preservatives, artificial colors and flavors. If a child has gastrointestinal disorders, then the first complementary food should be industrially produced dairy-free cereals that do not contain sugar or gluten (for example, buckwheat, rice and corn). In case of constipation or excess body weight of the baby, complementary feeding begins with pureed zucchini, squash, cabbage and other vegetables. The protein part of the diet includes puree from rabbit, turkey, horse meat and lamb. Fruit complementary foods consist of green and white apples. It is recommended to give juices only towards the end of the first year of life.
For general treatment, it is recommended to use “Desloratadine”: in the form of syrup it can be given to children from one year old, in the form of tablets - starting from 12-13 years. A short course of glucocorticosteroids in tablet form is indicated only in cases of severe exacerbation. Ointments, gels and creams with glucocorticosteroids are also recommended for exacerbations and severe forms of the disease [15]. These include hydrocortisone, fluticasone and others. Activated zinc pyrithione in the form of 0.2% aerosol, cream and 1% shampoo is used taking into account its ability to provoke an exacerbation of viral diseases and enhance the effects of the sun [14].
During hospitalization, infusion therapy is performed - intravenous administration of a Cyclosporine solution with an initial dose of 2.5 mg/kg per day. In severe cases, the dose can be increased to 5 mg/kg per day. If a positive result is achieved, the dosage is gradually reduced until completely discontinued. It is recommended to use moisturizing and softening creams “Locobase Ripea”, “Likoid Lipokrem”, “Lipikar” and milk “Dardia” in combination.
Stable remission is facilitated by living for 2-3 years in an area with a warm climate (Mediterranean, desert climate, highlands)[10].
Why should you contact the Mama Papa Ya clinic?
When a child has diathesis, it is important to pay attention to the little things - organizing nutrition, care, drawing up an individual vaccination calendar, a regime of hardening procedures, and so on. Often an examination by specialized specialists is required. The network of family clinics “Mama Papa Ya” offers medical services for the prevention and treatment of diathesis. By contacting one of our clinic branches located in Moscow or other cities, you will receive:
- consultation with a qualified pediatrician on all issues of interest;
- necessary diagnostic and treatment procedures;
- visiting all the necessary doctors in one clinic;
- possibility of observing children of different ages.
Make an appointment with a doctor by phone or on our website.
Reviews
Good clinic, good doctor!
Raisa Vasilievna can clearly and clearly explain what the problem is. If something is wrong, she speaks about everything directly, not in a veiled way, as other doctors sometimes do. I don’t regret that I ended up with her. Anna
I would like to express my gratitude to the staff of the clinic: Mom, Dad, and me. The clinic has a very friendly atmosphere, a very friendly and cheerful team and highly qualified specialists. Thank you very much! I wish your clinic prosperity.
Anonymous user
Today I had a mole removed on my face from dermatologist I.A. Kodareva. The doctor is very neat! Correct! Thanks a lot! Administrator Yulia Borshchevskaya is friendly and accurately fulfills her duties.
Belova E.M.
Today I was treated at the clinic, I was satisfied with the staff, as well as the gynecologist. Everyone treats patients with respect and attention. Many thanks to them and continued prosperity.
Anonymous user
The Mama Papa Ya clinic in Lyubertsy is very good. The team is friendly and responsive. I recommend this clinic to all my friends. Thanks to all doctors and administrators. I wish the clinic prosperity and many adequate clients.
Iratyev V.V.
We visited the “Mama Papa Ya” Clinic with our child. A consultation with a pediatric cardiologist was needed. I liked the clinic. Good service, doctors. There was no queue, everything was the same price.
Evgeniya
I liked the first visit. They examined me carefully, prescribed additional examinations, and gave me good recommendations. I will continue treatment further; I liked the conditions at the clinic.
Christina
The doctor carefully examined my husband, prescribed an ECG and made a preliminary diagnosis. She gave recommendations on our situation and ordered additional examination. No comments so far. Financial agreements have been met.
Marina Petrovna
I really liked the clinic. Helpful staff. I had an appointment with gynecologist E.A. Mikhailova. I was satisfied, there are more such doctors. Thank you!!!
Olga