Diathesis in children is not at all “reddened cheeks of a baby,” as many are accustomed to believe. This concept hides a number of pathologies. But the main thing you need to understand is that diathesis is not an independent disease. This term is used by doctors to describe a child’s tendency to certain diseases or reactions to specific stimuli. In fact, this is a hereditary feature of the body, which manifests itself at a very early age and, due to individual reasons, can develop into serious pathologies in the future.
Causes
Triggers for the development of diathesis are:
- Pathological conditions of the mother during the period of bearing a child, toxicosis, uncontrolled use of medications, infectious and somatic diseases, bad habits and poor nutrition during pregnancy.
- Fetal hypoxia, asphyxia during the birth process.
- Weak labor or rapid labor.
- Perinatal damage to the child's central nervous system.
- Metabolic and toxic-metabolic lesions.
- Low or high body weight of the baby at birth.
- Artificial feeding.
- Intestinal dysbiosis.
- Chronic infections of the child.
- Poor nutrition and disruption of daily routine, lack of water treatments and walks in the fresh air, unbalanced sleep and rest patterns.
- Negative influence of environmental factors: the environmental situation of the specific place in which the child lives, living conditions.
- Hereditary metabolic disorder.
- Frequent stress and negative psychological environment in the family.
- Excessive workload (for example, a busy school schedule combined with a large number of additional extracurricular activities).
How to help a child with atopic dermatitis: the best treatments
Damaged skin needs increased attention and careful care. To help a child with atopic dermatitis, clothing should only be made of cotton fabrics. Don't wrap up your child! Increased sweating increases itching and leads to an exacerbation of the process. Avoid using soaps and detergents that degrease your skin. When bathing a child, use herbal infusions (queen, celandine, chamomile). Wash clothes only with baby soap and rinse thoroughly. In many children, the manifestations of exudative diathesis increase when using disposable diapers. We'll have to give up on them and switch to gauze. But oilcloth placed under the sheet also exacerbates the process. In this case, use disposable cotton diapers with increased absorbency. They will protect the crib and upholstered furniture from “flooding”.
Staying in the gentle sun (do not overuse it!) and swimming in sea water (you can take a bath with the addition of sea salt) have a good healing effect.
For large wet areas, lotions with a 2% solution of tannin, 0.25% solution of zinc sulfate, 5% solution of Burov's liquid, decoctions of plantain, and chamomile are used. A very well proven treatment for atopic dermatitis in children is Calamine lotion, which has a drying, soothing, antipruritic, and anti-inflammatory effect. After you have dealt with the weeping, you can use ointments: naphthalan, intal, indomethacin.
Don't get carried away with hormonal ointments! Long-term use can cause degenerative changes in the skin. For severe itching, infusions of valerian, mint leaves, dill seeds, decoctions of string, nettle, and plantain (orally) are used.
To treat a secondary infection, use a 1-2% solution of brilliant green, a 0.5-1% solution of methylene blue, a solution of potassium permanganate 1:5000, and heliomycin ointment.
The best measure for the prevention and treatment of exudative diathesis is long-term breastfeeding and the creation of a hypoallergenic environment in the apartment.
Think about whether the presence of a four-legged (cat, dog), flying (parrot, canary) or swimming (fish) pet in the house is a provoking factor.
Types of diathesis
There are about a dozen different types of diathesis. Let's list the most common ones:
- Exudative-catarrhal. It is considered the most common species. The child has an increased reaction of the skin and mucous membranes to various irritants. Parents may first notice symptoms when their baby is 3–6 months old. Under favorable conditions and properly organized care, by 1–1.5 years the signs of diathesis may disappear. In some cases, they turn into a chronic form of allergy.
- Atopic . This is a child’s tendency to atopic diseases: neurodermatitis, allergies, bronchial asthma. From the first days of life, a baby may develop allergies to various foods, pollen, house dust, and at 2 or 3 years old, bronchial asthma may develop.
- Neuro-arthritic. It is characterized by increased nervous excitability, an unreasonable rise in body temperature, high levels of urea in the blood, and low appetite. In the first years of life, such children are thin, during adolescence they experience a sharp increase in body weight, and at an older age they may suffer from obesity. Such people are prone to developing type II diabetes mellitus, kidney inflammation (nephritis), atherosclerosis, gout and hypertension.
- Lymphatic-hypoplastic diathesis . This condition is characterized by hypoplasia of the adrenal glands, organs of the endocrine and reproductive systems, as well as increased susceptibility to stress, pathology of the lymph nodes and reduced function of the thymus gland.
Recommended regimen for using Enterosgel during exacerbation
- First of all, nursing mothers are recommended to take Enterosgel internally themselves to improve the quality of milk (1 tablespoon three times a day);
- A child under one year of age is given Enterosgel (paste) without the “sweet” label immediately before meals, before each feeding;
- For infants up to 6 months: add 2/3 of water or breast milk to 1/3 teaspoon of Enterosgel paste and give before each feeding;
- For children under one year of age Enterosgel: 1/2 teaspoon + ½ teaspoon of water, also before each feeding;
- After a year, Enterosgel is usually given simply 1-2 teaspoons three times a day, added to fruit puree;
- Locally, when it gets wet, periodically apply Enterosgel, diluted with 1/3 of the Tsindol mash, to the affected areas, and alternate this procedure with conventional local remedies.
Signs of diathesis
Depending on the type of diathesis, different symptoms of pathological conditions are distinguished.
of neuro-arthritic diathesis :
- The child has increased excitability, nervous tics and enuresis.
- He may complain of night terrors and “bad” dreams.
- Such children are often ahead of their peers in terms of mental and mental development. They grasp everything on the fly, learn easily, are active and want to know and try everything.
- At the same time, they experience sudden mood swings and tearfulness.
- Among other symptoms, they are very sensitive to odors.
- Tend to become thin at an early age.
- They may periodically complain of pain in the abdomen, joints and back.
- In the morning you may smell acetone from your mouth. This is what indicates an increased level of uric acid in the blood.
- Prone to allergic reactions.
- They may complain of headaches.
- These children often have poor appetite.
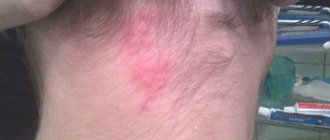
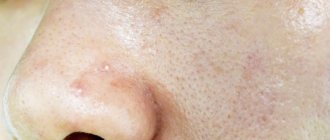
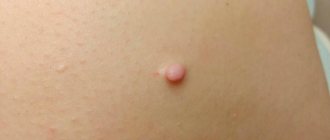
Exudative-catarrhal diathesis can manifest itself as follows:
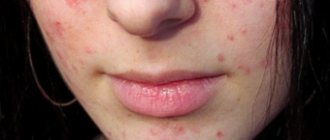
- Newborn babies have a blush on their cheeks. Itching prevents children from sleeping peacefully; children become nervous and irritable. Loose stools may appear.
- Gneiss can be seen on the scalp. This is flaking, reminiscent of dandruff in an adult.
- The skin is pale, the tongue is “geographical”.
- Diaper rash forms on the body.
- Later allergic rashes, crusts and papules appear.
- Children with this type of diathesis are prone to frequent bronchitis and sinusitis, and bronchial asthma.
Lymphatic-plastic diathesis can be determined by the following signs:
- Symptoms most often appear between 2 and 7 years of age.
- Babies are born with a lot of weight and gain significantly every month.
- The lymph nodes in the submandibular and peripharyngeal areas and the thymus may become enlarged.
- There is a decrease in T-lymphocytes in the blood.
- Children often suffer from colds and food allergies, which is why they are classified as frequently ill children.
- Adenoids appear, which make nasal breathing difficult, the brain chronically lacks oxygen, which can lead to a lag in mental and physical development.
- Such children often have abnormalities in the development of the heart and blood vessels.
Basic preventive measures
To avoid both diathesis in an infant and its progression into complications, you must follow simple rules:
- Continue breastfeeding for as long as possible;
- Carefully approach the choice of infant formula;
- Do not allow sudden changes in infant formula;
- Complementary feeding should begin no earlier than six months of age;
- Keep diapers clean, wash only with hypoallergenic products;
- Select toys from materials that do not cause allergies.
Treatment of diathesis
A pediatrician is involved in the diagnosis and treatment of pathologies associated with diathesis. It is he who collects anamnesis, prescribes studies and, based on their results, determines treatment tactics.
Exudative-catarrhal diathesis
- The doctor prescribes antihistamines to stop the allergic reaction.
- Prescribes sedatives for sound sleep, vitamins and medications that strengthen the body's defenses.
- Medicinal herbal baths are good for soothing, and for severe damage and itching - hormonal ointments.
- The most suitable climate for such children is southern, warm. Moderately abundant sun and air baths significantly alleviate the condition.
- The basis of therapy is proper balanced nutrition. Complementary feeding should be introduced by very carefully selecting and trying new foods. It's better to start with vegetables.
- It is important to follow the regime and exclude allergenic foods from the diet at the slightest suspicion of an allergy.
Neuro-arthritic diathesis
- Once or a couple of times a year, a pediatrician prescribes a course of treatment, which includes the use of anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs containing potassium and calcium, hepatoprotectors and other agents.
- If appetite decreases, he prescribes medications to increase it.
- The correct daily routine with long walks in the fresh air, sufficient sleep, hardening, and moderate physical activity is extremely important.
- The doctor recommends following a diet based on dairy products, cereals, vegetables and fruits, light meat dishes, and drinking plenty of fluids.
Lymphatic-plastic diathesis
- As part of therapy, the pediatrician prescribes a course of adaptogens, in some cases immunoglobulins and immunostimulants.
- Hardening and spa treatment are excellent for increasing immunity.
- An important point is to follow a diet. Its peculiarity is its high fiber content and balanced intake of proteins, liquids and salt.
- Doctors often recommend that children suffering from this form of diathesis refrain from visiting kindergartens. Frequent infections undermine already weakened immunity.
Let us repeat that diathesis in children is not a separate disease, but a pathological tendency to diseases and allergic reactions. A timely visit to the doctor and compliance with all his recommendations will help, if not get rid of the symptoms completely, then at least reduce the consequences for the child, which can manifest themselves in adulthood and result in serious illnesses.
FIND OUT PRICES
Diagnostics
If diathesis is not a diagnosis, then what do doctors diagnose and treat? The vast majority are allergic dermatitis.
- Helps identify an allergic reaction general clinical blood test
– its presence may be indicated by an increase in the number of eosinophils and an increase in ESR.
- It is of great importance to identify the allergen in order to further exclude the product from the diet or prevent household contact with substances/objects to which an allergic reaction has developed. If we are talking about food allergies, then when introducing complementary foods it is useful to keep a food diary and observe the child’s body’s reaction to new foods. You can identify an allergen not only using observations and exclusions of potential irritants
.
blood test for allergens
will give an accurate and unambiguous result .
Lymphatic-hypoplastic
Main symptoms:
- Enlargement of all groups of lymph nodes;
- Immune system dysfunction;
- Disturbances of the endocrine system;
- Enlargement of the thymus gland;
- Frequent diseases of infectious origin.
The child is lethargic, loses interest in everything around him, is absorbed in himself, and suffers from increased fatigue.
As a rule, this type of diathesis goes away on its own at six to seven years of age. It is necessary to protect the child from complications of infectious and viral diseases due to diathesis.
It is necessary to monitor the child's nutrition. The diet should include a sufficient amount of vitamins, amino acids, and microelements. Hardening and alternating cold and hot baths are recommended. Walking barefoot on grass and sand.
Important points when contacting a dermatologist if you have a hair disease.How to care for braces
- ADVANTAGES OF TREATMENT ABROAD
Prevention
It is necessary to monitor the child’s diet: a sufficient amount of plant foods, plenty of drinking regime with the addition of juices, dried fruit compotes, still alkaline mineral water, cranberry juice, rosehip decoction.
Treatment of chickenpox - symptoms and features of manifestation in children and adults. Why shouldn't you scratch chickenpox lesions?Vitiligo - causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis and treatment in the clinic and at home (video + 135 photos)
- Acoustic neuroma