Hiroshima, Nagasaki, Chernobyl are black pages in the history of mankind associated with atomic explosions. Negative radiation effects were observed among the affected population. The effect of ionizing radiation is acute, when the body is destroyed within a short time and death occurs, or chronic (irradiation with small doses). The third type of influence is long-term. It causes genetic effects of radiation.
The impact of ionizing particles varies. In small doses, radioactive radiation is used in medicine to combat cancer. But it almost always has a negative impact on health. Small doses of atomic particles are catalysts (accelerators) for the development of cancer and breakdown of genetic material. Large doses lead to partial or complete death of cells, tissues and the entire organism. The difficulty in monitoring and tracking pathological changes is that when receiving small doses of radiation, there are no symptoms. The consequences can take years or even decades to appear.
The radiation effects of human exposure have the following consequences:
- Mutations.
- Cancers of the thyroid gland, leukemia, breast, lung, stomach, intestines.
- Hereditary disorders and genetic code.
- Metabolic and hormonal imbalance.
- Damage to the organs of vision (cataracts), nerves, blood and lymph vessels.
- Accelerated aging of the body.
- Sterility of the ovaries in women.
- Dementia.
- Disorders of mental and mental development.
Features of injury
Radiation burns are caused by the following radiation:
- alpha;
- beta;
- gamma.
Alpha rays are easily blocked by air and clothing. They do not penetrate the epidermis. However, when exposed through cuts or wounds, it can provoke serious pathologies of internal organs.
Beta ray electrons have greater speed. Capable of passing through clothing deep into the fabric, causing burn injuries.
Gamma rays have powerful penetrating ability. These are high-energy particles on an electromagnetic basis. It is quite difficult to defend against it. Of all types of radiation, it poses the greatest danger. Causes irreversible pathologies of tissues and internal organs.
Burns after irradiation are divided into several types:
- Ultraviolet or solar. The most common method of defeat. Caused by prolonged exposure to the sun or after artificial tanning procedures. The risk group includes people with fair and sensitive skin, with weakened immunity, and people with diabetes;
- The most dangerous radioactive injuries are after a nuclear explosion, man-made disasters or contact with contaminated waste;
- Injuries as consequences of radiotherapy in the treatment of cancer.
Possible complications
Complications can be caused not only by the radiation burn, but by the radiation therapy itself. After a burn of this type, a person may feel a deterioration in their general condition, and the most dangerous consequences are infection of the injured areas and possible bleeding. If severe damage has been sustained, the condition of the entire human body deteriorates significantly, and the greatest amount of damage goes to the organ that was closest to the site of irradiation.
You should not self-medicate. As soon as you notice similar symptoms, contact a specialist. If the therapist makes the correct diagnosis and prescribes effective treatment, the recovery period will be much shorter than with self-medication, and the risk of complications will be significantly reduced.
Classifications of radiation burns
The lesion develops in four periods:
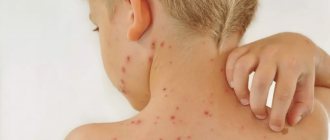
- Primary reaction. Appears within several hours after radiation exposure. Expressed in the form of slight swelling, burning and redness. Possible physiological changes in condition: weakness, headache, nausea;
- After the primary symptoms have subsided, the latent period begins. It is characterized by the absence of any signs of radiation. Depending on the causes of the lesion, this condition lasts from several hours to two to three weeks;
- Necrotic changes characteristic of this period are characterized by severe pain and swelling. Burn blisters and erosions appear. Severe injuries are accompanied by anemia, bleeding, and wound infection. Repeated suppuration is possible;
- The recovery period slows down significantly. It can last for many months and years. Ulcers and erosions do not heal well. An unstable, thin scar layer forms at the sites of healed injuries. Relapses of radiation sickness can occur after several years. Ulcers that do not heal for a long time can transform into malignant formations. This type of cancer cannot be cured.
The severity of burns is also divided into four groups:
- The mild form of the lesion is tolerated satisfactorily by patients. Curable even with weakened immunity;
- Moderate burns. The damage is characterized by swelling and changes in skin color. The initial period is asymptomatic. Complications appear after two weeks. Treatment and rehabilitation take about a month;
- Severe form of damage. Burns in this group are characterized by open wounds and ulcers. Tissues damaged by necrosis are not restored;
- Deadly form. The entire skin, muscles, bones and internal organs are affected. Possible deep charring of the flesh.
If you need developers, testers, designers or management in the IT field, then pay your attention to the IT recruitment agency HEAAD. The main part of their work is sourcing, as well as “selling” your vacancy.
Consequences and prognosis
The consequences of eye burns are determined by the depth of damage, the type of damaging factor, the severity of tissue damage and the timeliness of treatment.
Burn injuries to the eyes of II – IV degrees are accompanied by certain complications and do not go away without leaving a trace. In the tissues of the eye, scarring may occur, disruption of the lacrimal ducts, decreased transparency of the cornea, development of dry eye syndrome, cataracts or glaucoma. The outcome of burns can be damage to retinal cells in the macular area and the occurrence of irreversible blindness.
In the medical department, everyone can undergo examination using the most modern diagnostic equipment, and based on the results, receive advice from a highly qualified specialist. The clinic is open seven days a week and operates daily from 9 a.m. to 9 p.m. Our specialists will help identify the cause of vision loss and provide competent treatment for identified pathologies.
You can make an appointment at the Moscow Eye Clinic by calling 8 8 (499) 322-36-36 (daily from 9:00 to 21:00) or using the online registration form.
Causes
During the life cycle, a person is systematically exposed to radiation. Sources of natural, natural radiation can be considered:
- space;
- 60 radioactive substances that are contained in water, air, and soil.
Common artificial sources include:
- radionuclides that are used by agricultural and light industry;
- medical equipment;
- radiochemical production;
- man-made disasters, use of nuclear weapons, radiation waste and emissions.
Irradiation causes biological changes. Illness is the body's overall response to the volume and strength of energy absorbed. The reasons can be external and internal.
The first arises as a result of environmental contamination with isotopes emitting gamma rays. Every atom of air becomes a source of radiation. The consequence of this process can be both superficial lesions of the epidermis and death of a person.
This radiation negatively affects both the skin and organs. In severe cases, it causes detachment of the epidermis, the formation of ulcers, complete hair loss, and muscle atrophy. This depends on the dose of radiation and the time of exposure.
Radiation injuries can occur as a side effect of cancer therapy. External manifestations are similar to those of sunburn: erythema, itching, small blisters, peeling. The extent of damage depends on the susceptibility of the surface.
Internal radiation is caused by radioactive substances that enter through the air, skin, water and food. Causes pathology of the bronchi and gastrointestinal tract.
Prevention
Radiation burns during therapy are almost impossible to avoid, but there are several recommendations that will significantly reduce the chance of such damage:
- the doctor who is treating you must individually, regarding the nature of your skin and body, prescribe the dose and frequency of use of ionizing radiation;
- areas that are exposed to radiation must be lubricated from time to time with products that promote effective healing of body areas. It is recommended to perform such procedures at night.
Symptoms
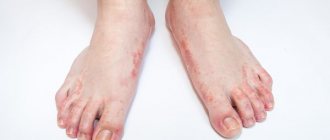
Signs, similar to the severity of the lesion, vary in degree:
- The mild form is characterized by burning, itching, peeling, slight swelling and pigmentary changes in the skin;
- Symptoms of the second degree are nausea, weakness, headaches, the appearance of erythema and burn blisters. The skin after regeneration is very thin;
- The condition is complicated by fever, severe painful erythema, and the appearance of abscesses under the blisters. Because the lesion causes the subcutaneous layer to die, scarring occurs slowly. Ulcerative relapses are possible. There is a risk of developing vein thrombosis;
- The condition is extremely serious due to deep charring of tissue over a large area.
Features of home therapy
After providing first aid for a 2nd degree burn, it is necessary to take a responsible approach to completing the course of treatment prescribed by the doctor. Rules that are recommended to be followed:
- eliminate heavy physical labor, since excessive stress provokes inflammatory processes in the body;
- avoid working in dusty and dirty objects to avoid infection of an open wound;
- Monitor the sterility of the dressings and follow the schedule for their replacement.
New tissues regenerate quickly if there are no complications due to external irritants. Recovery will take about 2 weeks, but may take up to 3 weeks for some. Healing slows down in older patients with chronic diseases. With successful therapy, recovery occurs without scars or scars.
Diagnostics
During a visual examination, the doctor pays special attention to erythema. Its condition, severity and time of appearance are important. Taking an anamnesis allows you to clarify when the injury occurred, symptoms, causes and circumstances of the injury.
If a burn is a side effect of therapy, then information about the intensity of radiation is taken from the patient's medical record. The consequences may be disturbances in the functioning of the heart and internal secretion organs. To determine pathologies, instrumental diagnostics are prescribed - MRI, ECG, ultrasound. If necessary, other specialists are involved.
Diagnosis
The doctor first of all pays attention to the occurrence of erythema, since at some stages it appears immediately and quickly passes. Next, the doctor asks about the symptoms. If radiation burns were caused by therapy, then medical records are collected to determine the radiation power, the frequency of its implementation and the state of health in general.
Such burns are often accompanied by problems with the endocrine and cardiovascular systems. To determine whether violations have arisen in these areas, detailed medical studies and consultations with specialists in this type of activity are carried out.
Treatment
Treatment of minor burns is carried out similarly to thermal injuries after the first signs appear. It is not recommended to use any means of assistance before consulting a specialist. This is especially true for fat-containing liquids and ointments. There is no need to treat wounds yourself, as lack of skills can increase pain.
What are the types of electrical burns?
Electrical burns can occur at home, at work, or even in the natural environment. Various types of damage are possible:
- Thermal ones manifest themselves in the form of a burn on the skin.
- Biological - muscles contract convulsively, problems with the functioning of the respiratory system, open wounds on the skin, and sometimes fractures occur.
- Electrolytic - damage to lymph and blood flow is dangerous due to disruption of organ functioning.
Based on the type of interaction, there are two types.
Current (contact)
This type occurs when a person comes into contact with an object or wire through which current passes. Current penetrates in the case of direct interaction. The formation of a current burn is a consequence of the conversion of electricity into heat.
The skin suffers because it has a greater degree of resistance compared to other tissues. More often, grade 1 or 2 is diagnosed. Stronger ones are less common.
Arc
This type of electrical burn is explained by the impact on the body of an electric arc with high temperature (more than 3500 degrees) and high energy.
You can get it when working with high-voltage lines and other high-voltage devices. The injuries are grade 3 and 4. The general condition depends not so much on the force of the blow, but on the area of the affected area.
Therapeutic method
All measures are aimed at stabilizing the patient’s condition. The victim is recommended to use local anesthesia for small localizations. Drugs with morphine and promidol are administered to a patient with severe burns.
The entire affected surface is treated with antiseptic substances. A protective bandage is applied. Infusion therapy is carried out to relieve the effects of shock and to restore fluid and protein levels. Cardiac activity and blood pressure readings are continuously monitored.
After stabilization of the patient's condition, infrared radiation therapy is prescribed. Antibiotics are used at the same time. Goal of treatment: relieve inflammation, prevent infection, remove intoxication.
Be sure to follow a salt-free diet high in calories and drink plenty of fluids.
Diagnostic measures
Before treating a 2nd degree burn, it is necessary to assess the extent and depth of tissue damage. You should definitely consult a doctor in the following situations:
- More than 5% of the skin surface is affected (in children - more than 2%).
- Localization - on the face or perineum, or the respiratory tract and esophagus are affected.
- The pain only gets worse over time.
- Swelling appears and foci of suppuration develop.
With a 2nd degree burn, bubbles with transparent contents usually appear. To determine the affected area, use the palm rule, the essence of which is that the area of the palm is counted as 1%. Based on this, they determine how much the affected area has spread and decide whether hospitalization is necessary. Even with a small degree of burn, but a significant area of damage, there is a risk of painful shock.
Medication method
If there are no blisters on the affected surface, the doctor prescribes ointments for treatment (Panthenol, Bepanten, etc.). Antihistamines relieve swelling and itching. Bubbles must be treated with antiseptics. Antibacterial creams are applied under a sterile dressing.
The patient is immediately prescribed antibiotics upon arrival at the medical facility to block possible infections. A tetanus vaccination is required. To prevent intoxication, the patient receives intravenous glucose, vitamins, and calcium gluconate.
To relieve pain from lesions of the mouth and throat, rinsing at least three times a day and painkillers are prescribed. If inflammation of the respiratory tract cannot be avoided, medications containing corticosteroids are prescribed. For pulmonary injuries, inhalations, magnetic therapy and electrophoresis are used.
Proper first aid
Further recovery depends on how competent first aid is provided for a 2nd degree burn. The procedure is as follows:
- Remove the source of damage.
- Rinse the damaged area under running cold water.
- Treat the skin with an alcohol-free antiseptic.
- Apply a sterile bandage.
- Give pain medication as needed.
But here is what you should absolutely not do in case of a 2nd degree burn:
- tear off clothing stuck to the wound;
- cool the burn with ice;
- bandage the wound tightly or use cotton wool in the dressing;
- Lubricate the damaged area with oil, sour cream or alcohol.
After providing first aid, you should consult a doctor. Only a specialist will determine how to treat a 2nd degree burn and give individual recommendations. As a rule, such lesions are treated at home. The exception is burns of the respiratory system and esophagus.
Traditional methods
Homemade recipes for treating burns are allowed for use only if the severity level is not higher than second. That is, there are no open wounds, and the integrity of the damaged area is not compromised. Herbal medicine can cope with injuries and completely restore tissue. This seriously relieves pain and significantly improves the condition:
- Sea buckthorn oil has powerful healing properties. There are many recipes for using it. Most often, a sterile napkin is soaked in it and placed on the burn. If the procedure is repeated every three hours, the pain quickly disappears and regeneration is significantly accelerated;
- If it is not possible to apply a bandage, the frequency of the procedure at the initial stage depends on the ease of absorption. Later, twice a week is enough;
- When treating esophageal cancer, sea buckthorn oil is taken orally. The course involves prophylactic administration during radiation therapy 3 times a day and then the regimen is continued for another three weeks;
- A product made from olive oil and wax has the same valuable qualities. The components mix well and apply to the affected areas. It is recommended to change the compress every two to four hours;
- Honey can serve as a preventative against blistering. In addition, it is an excellent antiseptic;
- Homemade ointment made from propolis and vegetable oil can stimulate regeneration and prevent infection. The ingredients are heated in a water bath and infused until a homogeneous consistency is obtained. After cooling, the product is applied to a napkin and applied to the burn;
- Freshly squeezed plantain juice has strong antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, healing and analgesic properties. They treat the affected surfaces several times a day. The product is well suited for lotions and compresses. Nettle has similar properties.
Prevention of burns when prescribing radiation therapy – what should the patient and specialists do?
Preventive measures include the following:
- Radiotherapy should be prescribed on an individual basis . For each patient, the dosage and frequency of isotope radio emission will be determined by the general state of his health.
- In order to protect the eyes from burns before and after radiation therapy, they are instilled with artificial tears : 1-2 drops in each eye. This will minimize the risk of developing photophobia and dry eyes in the future.
- After each course of radiotherapy, the immediate areas of exposure must be treated with wound healing agents . A similar procedure should be performed before going to bed.
Rate
—
The area is determined by several fairly simple and quick methods.
The "palm" rule - the surface of the victim's palm is approximately 1% of the surface of his body.
The rule of “nines” - the entire surface of the skin is conditionally divided into areas that are multiples of nine in area. Thus, the head and neck approximately make up 9% of the body area, the anterior surface of the torso - 18%, the posterior surface of the torso - 18%, the arm - 9%, the leg - 18%, the perineum - 1%.
There are also more accurate methods for determining area by measuring on graph paper with subsequent conversion to percentages, but they are not widely used and are used more for scientific purposes.
With burns of more than 15% of the body surface, burn disease develops - a severe violation of the general condition, accompanied by dehydration, shock, intoxication, the development of a septic condition, and failure of vital organs and systems. At the same time, burns of more than 40% of the body surface are considered very severe, and more than 80-90% of the body surface are often incompatible with life.
How to understand that a person has suffered from an electric shock
You can find out about an electrical burn by looking at the marks from the electric arc. The skin of the affected area changes color. It turns red or purple-gray. With severe injuries, blackening or even charring may occur. There is no clear location of the pain; it spreads throughout the body. Electric shock is indicated by muscle spasms and convulsions.
The main signs of electrical injuries include:
- Weak breathing, shallow. Sometimes asphyxia may occur.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Muscle cramps.
- Impaired consciousness, memory loss.
- Disorientation in space.
- Loss of sensation in a limb.
- Unstable vision, inability to focus.
- A clear outline of the burn on the skin.
- Unintelligible speech.
- The victim may complain of nausea and dizziness.
The victim needs to be attentive to the victim. If the current is exposed for a long time, then characteristic marks will remain on the skin. Possible swelling and numbness.
Rehabilitation after electric burns
At the stage of restoring the integrity of the skin, it is important to constantly disinfect the resulting wound. Very often, a blister with a clear liquid forms at the site of the electrical burn.
Attention! It is forbidden to burst the bubble yourself; it is best to entrust this to a specialist at the emergency room.
If you properly care for the affected area, then within a couple of weeks new skin will form under the fluid, and the blister will gradually dry out and fall off by this time. The new skin will be a little lighter and softer than the rest.
The process usually takes 1–2 weeks for grade 1, about 3–4 weeks for grade 2. For more serious injuries (grade 3–4), the recovery process is individual and depends on factors:
- general health;
- cell regeneration rate;
- presence of surgical intervention;
- individual attitude.
An unfavorable development of events is characterized by suppuration of the wound, which can only prolong the recovery period of the body. In this case, chills, weakness, and increased pain at the site of the injury may be felt.