Types of urticaria
Urticaria can be acute or chronic. The first is more common in preschool and teenage children. Lasts up to one and a half months. Skin rashes can be in the form of spots or blisters (their diameter often exceeds 1 cm).
Chronic urticaria lasts more than one and a half months. It is usually diagnosed in people aged 20-40 years. Periods of remission are periodically replaced by exacerbations, which affects the size and number of spots on the body.
Depending on the cause of the disease, urticaria is classified into:
- Contact/allergic.
- Urticarial vasculitis (the walls of small vessels and skin capillaries become inflamed).
- Medicinal.
- Physical: - cholinergic; - dermographic; - cold; - caused by physical activity; — slowed down by pressure; - solar; - aquagenic (skin reaction to contact with liquids (pure water does not cause a reaction); - vibration.
- Idiopathic (the cause of the problem remains unclear).
Causes of urticaria
Blisters on the skin and mucous membranes with urticaria are formed due to the release of histamine into the blood. Under the influence of allergic components, the capillary walls become more permeable, so fluid from the vessels freely enters the dermis, and blisters form.
Hives can be caused by:
- Medicines (NSAIDs, antibiotics).
- Food products (considered allergenic: seafood, eggs, nuts, fish, milk, citrus fruits, cocoa, etc.).
- Contact with latex, household chemicals.
- Fungal skin diseases.
- Tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sinusitis.
- Serum sickness.
- Hypo- and hyperthyroidism and other thyroid diseases.
- Streptococcus, Yersinia, Staphylococcus.
- Insect bites (hornets, wasps, bees, less commonly mosquitoes).
- Parasites.
- Stress.
The risk of developing hives increases significantly if:
- In addition to a tendency to allergic reactions, the patient has bronchial asthma and rhinitis.
- The patient has an upper or lower respiratory tract infection.
- There are gastrointestinal diseases and tumors.
- Climatic conditions have changed (when changing place of residence).
- The patient spent a long time in the cold, in direct sunlight.
Causes of urticaria
Acute, new-onset or chronic induced urticaria may be a reaction to a viral infection, medication, food, exercise, intense sunlight, contact with animals, cosmetics, chemicals (such as latex or nickel), or may be caused by other causes.
Acute urticaria may be one of the manifestations of a parasitic infection. But since, according to WHO, parasite infections are not widespread in our region, when deciding whether to schedule an examination, it is necessary to take into account risk factors and other manifestations of infection (visiting regions with a high risk of becoming infected, eating raw fish or meat, the presence of gastrointestinal complaints). -intestinal tract, blood eosinophilia and others).
Most cases of chronic urticaria have no external causes.
Under the influence of external factors or without external causes, histamine and other substances are released from mast cells, swelling and itching of the skin begins, and rashes appear. Isolation can be caused by different types of immunological reactions. These may be allergic reactions, reactions caused by the influence of complement or immune complexes. Chronic urticaria is usually associated with autoimmune reactions, but there is no reliable test to accurately determine this.
Symptoms of urticaria
Among the main symptoms of urticaria:
- skin redness;
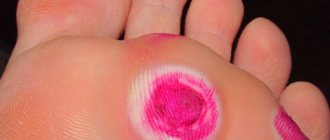
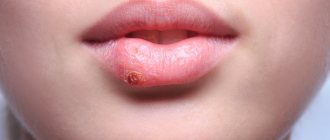
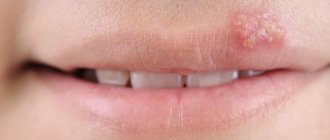
- the appearance of red spots on any part of the body (as if from contact with nettles);
- formation of blisters (they can be seen by looking at a photo of hives);
- itching, burning of the skin;
- disappearance of rashes within one day.
If we talk in more detail about the unique signs of different types of urticaria, then:
- With the dermographic form, blisters form as the scratching progresses.
- In the nervous form, the rash occupies large areas of the body and goes away within half an hour. Fainting, dizziness, and increased sweating may occur.
- With cold urticaria, blisters occur precisely during exposure to the cold. After warming up, they very quickly disappear without a trace. There is a risk of developing Quincke's edema.
- With the sun form, the skin becomes covered with spots in the first minutes of exposure to direct sunlight. Possible fainting, obstructive pulmonary disease, hypotension.
- With the contact form, blisters appear only in those areas that came into contact with the allergen.
Dangerous symptoms of urticaria
Anaphylactic shock is the most dangerous symptom of urticaria and can be fatal. You can suspect its development based on the following signs:
- swelling of the neck, tongue;
- a sharp decrease in blood pressure;
- severe abdominal pain;
- fainting;
- feeling of lack of air, hoarseness of voice.
If you experience similar symptoms, consult your doctor
. It is easier to prevent a disease than to deal with the consequences.
Urticaria - first symptoms, causes
24.05.2021
Urticaria is a disease characterized by rashes in the form of nodules and blisters on the skin that look like a nettle burn. They can occur randomly, gradually erupting and disappearing in different parts of the body. It can be acute or chronic, and can occur as an allergic reaction . Most often, urticaria is an allergic reaction or, in rare cases, a symptom of infection with worms.
Forms of urticaria
Acute form. It appears abruptly, symptoms last 1-2 weeks. Itching appears in the area of the rash, the surface of the skin is hot. If urticaria appears due to an allergic reaction , then when you get rid of the affecting allergen, the symptoms quickly disappear.
Chronic form. The rash spreads more slowly, but lasts longer - more than 2 weeks or a month. Appetite is lost, headache, weakness, nausea , and sometimes neurotic disorders occur. Especially in children who scratch the papules, and as a result, dermatitis due to bacteria entering the scratched wounds. The chronic course is influenced by external factors (sun, cold, etc.).
Types of urticaria
- Easy. External signs are almost invisible, the person feels normal.
- Average. The rash is noticeable, body temperature rises, itching, nausea and headache appear. edema may appear .
- Heavy. Quincke's edema develops . In severe cases, medical .
Symptoms of urticaria
- Convex red skin lesions
- Itching in the area of the rash
- Temperature increase
- Weakness, joint pain and headache
- Difficulty breathing
- Difficulty swallowing
- Abnormal stool
- Moderate or painful itching
Allergic urticaria causes cold symptoms: runny nose , watery eyes and high fever. In a complicated form, Quincke's edema , which can appear on the mucous membrane, lips, cheeks, eyelids or in the nasopharynx.
Cause of hives
Hives can appear for more than just one specific reason. It can appear at different ages for different reasons. The most common are:
- certain foods;
- chemical additives, sulfides or salicylates;
- fluff, dust, cigarette smoke, pollen of certain plants, various detergents and cosmetics and other household allergens ;
- antibiotics and other drugs;
- reaction to vaccinations, insect bites;
- donated blood or drugs based on it;
- exercise, chills, skin contact with the sun (solar urticaria ), sweating or overheating;
- infections;
- psychogenic reaction, stress;
- chronic infection or helminthiasis;
- hormonal disruptions during pregnancy , puberty, lactation and menopause .
Most cases of hives have an unknown cause. There is a high probability that it may suddenly disappear. But you shouldn’t fully count on this.
Treatment of urticaria
Self-medication is not recommended. At the first symptoms you should consult a dermatologist . A specialist can tell you exactly what to do. But general recommendations will not hurt, and may even help get rid of hives . Especially when it comes to acute symptoms.
- Carefully review your medical history, from which you can determine the allergen or take allergy tests to identify the allergen . If there is a suspicion that urticaria appeared due to external factors (cold, pressure, heat, etc.), you need to conduct a physical provocative test and eliminate the allergen ;
- try to eliminate contact with the allergen or at least minimize it;
- improve your immunity , start leading a healthy lifestyle;
- When washing, use a soft washcloth so as not to injure the skin;
- treat skin hygiene with maximum care so as not to get pustular diseases.
Drugs for the treatment of urticaria
When self-medicating (which is strictly prohibited), it is necessary to take into account contraindications and side effects of drugs.
- Sedatives. Reduce itching.
- Antiallergenic and antihistamine drugs. Reduces sensitivity to the allergen , relieves burning and itching;
- Steroids. Anti-inflammatory.
- Ointment or cream. Eliminate the rash.
- Drugs that enhance immunity .
- Hormonal drugs. For severe autoimmune forms.
Published in Allergology Premium Clinic
Diagnosis of urticaria
The doctor can make a preliminary diagnosis immediately after examining the patient’s skin. The spots that appear on the body due to urticaria are difficult to confuse with another skin pathology. But in order to eliminate error, establish the cause of the disease and prescribe the most effective treatment, the patient is additionally prescribed tests:
- General blood analysis. This is done in order to understand whether there is anemia, whether the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is increased and, thus, exclude/confirm the presence of immune or inflammatory processes.
- Stool analysis. Indicated for the detection of parasites as a cause of allergic urticaria.
- Functional liver tests. They determine the functioning of the organ and exclude its diseases.
Also during diagnosis, a study of thyroid function is usually carried out to find out whether the disease is caused by hyper- or hypothyroidism.
To identify the allergen that is responsible for hives, the patient is recommended to do skin allergy tests or donate blood from a vein.
Types of urticaria
Depending on the time of existence of the rash, the disease occurs in two forms:
- acute urticaria, which resolves spontaneously in less than 8 weeks, and under the influence of medications - within a few hours;
- chronic urticaria, which can be a symptom of a serious illness and exists without changes for more than 8 weeks; in this case, a generalized rash on the body is possible.
Depending on the predominant mechanism of development of the pathology, several types of urticaria can be distinguished:
- Allergic urticaria appears in response to an allergen entering the body (not necessarily on the skin, most often inside), for example, a food product (strawberries, citrus fruits, seafood and many others) or medications.
- Cholinergic urticaria occurs under the influence not of histamine, but of acetylcholine, secreted by skin cells in response to high temperature, load, stress, and mechanical factors.
- Cold urticaria occurs when the skin is exposed to cold air, dampness, or wind.
- Solar urticaria is associated with an abnormal reaction of the skin to ultraviolet radiation and usually occurs on exposed areas of the skin.
- Urticaria pigmentosa is a special form of the disease that most often occurs in young children and is accompanied not only by rashes, but also by darkening of areas of the epidermis as a result of the accumulation of melanin in them. Another name for the disease is cutaneous mastocytosis.
In approximately half of the cases, patients with any type of pathology experience autoimmune urticaria, which is associated with the appearance of antibodies to the cells of the immune system in the body. When exposed to an allergic factor, these antibodies quickly interact with receptors on the membranes of these cells, leading to the release of histamine. This condition is usually genetically determined. In other cases of the disease, the autoimmune component cannot be determined. Thus, there is currently no treatment method aimed at the cause of the disease, and therapy is carried out mainly symptomatically.
Treatment of urticaria
Urticaria is not considered a dangerous disease unless it is associated with angioedema and suffocation. Experts recommend immediately contacting an allergist.
seek qualified medical help if:
- the patient begins to choke;
- he has swelling of his tongue/pharynx;
- hives cannot be treated at home.
In order for the treatment of urticaria to be as effective as possible, it is necessary to stop the negative impact of the allergen on the body. It all depends on the cause of the disease. So, if we are talking about the solar form, you need to get out of the scorching sun, if you are talking about the cold form, you need to get out of the cold air into a warm room. If the rash is caused by a drug, you need to stop taking it and drink some enterosorbent. It is also important to take an antihistamine right away. It could be:
- "Zodak", Zyrtek";
- "Loratadine";
- "Allergozan", "Suprastin";
- "Parlazin";
- "Ebastine" and others.
If antihistamines do not provide improvement in the patient’s condition within 24 hours, you should take hormonal tablets - Prednisolone or Dexamethasone.
Locally, urticaria can be treated with ointments:
- Non-hormonal (Soventol, Fenistil gel, Psilo-balm).
- Hormonal (Sinaflan, Flucinar, Laticort, Hydrocortisone, Fluorocort, Advantan, Afloderm, Cloveit, Lokoid, Dermovate).
Immunosuppressants (for example, Cyclosporine) are indicated for patients with severe forms of autoimmune urticaria and when antihistamines are ineffective. You should first consult an allergist-immunologist.
.
Traditional treatment for urticaria
The following decoctions help eliminate the symptoms of acute urticaria:
- Pour 50 g of nettle leaves into 2 cups of boiling water. Leave for 1 hour. Strain. Soak the cloth in the broth and apply to the inflamed skin.
- Pour 50 g of raspberry roots with 2 glasses of water. Boil for 15 minutes. Leave for 1 hour. Take the decoction orally, 100 ml 5-6 times a day.
For chronic urticaria, the following recipe helps:
- Mix celandine, string, sage, chamomile, and valerian in equal proportions. 5 tbsp. collection, pour a liter of boiling water and keep on low heat for 5 minutes. Add the resulting broth to the bath. The duration of the water procedure is 15 minutes. You need to repeat it every day for a week.
For allergic urticaria, you should grind the roots of the marsh calamus and take 1/2 tsp. once a day with water. St. John's wort oil also helps. They are recommended to wipe the inflamed areas of the skin.
You can fight nervous urticaria with a mixture of valerian and hawthorn. Add 30 drops of these compositions to water and drink before bed. Mint infusion is also effective. It can be prepared until acute symptoms are eliminated instead of regular black tea.
If urticaria often recurs, you can resort to the help of hop cones, valerian roots and lemon balm. To do this you need to mix 1 tbsp. each of the named types of plant materials, pour a glass of boiling water over the mixture and leave. After an hour, strain. Take half a glass three times a day.
Treatment of urticaria in adults and children
The main group of drugs for the treatment of both acute and chronic urticaria are histamine type I receptor blockers (antihistamines). In accordance with the international recommendations of GA2LEN, it is possible to combine different drugs or increase the dose of an antihistamine (in our country, an increased dose of antihistamines is not officially registered).
For severe exacerbations, short-term use of corticosteroid hormones is possible. This treatment does not affect the prognosis of the disease, but can quickly reduce severe and pronounced symptoms.
If the effect of antihistamines (at the maximum dose) is insufficient in the treatment of chronic urticaria, it is possible to prescribe antileukotriene drugs and type II histamine receptor blockers. And in severe cases - biological therapy with the drug omalizumab or immunosuppressive therapy with cyclosporine.
Features of the treatment method for urticaria
Even with significant itching, a large area of rash and a long (sometimes many years) course, chronic urticaria does not lead to changes in the internal organs. In most cases, it gradually (sometimes over several years or even decades) stops.
The main task of the doctor here is to maintain a comfortable quality of life for the patient, determine the possible causes of the disease and monitor to identify other diseases with similar rashes.
Drugs for the treatment of severe forms of urticaria
Omalizumab is an antibody to immunoglobulin E and is used for severe chronic idiopathic urticaria and bronchial asthma. Before prescribing the drug, the doctor will conduct an examination and make sure that simpler methods of treatment were ineffective. The drug is administered subcutaneously once every 4 weeks. Treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis, but always under the supervision of a doctor. The drug is generally well tolerated and side effects are rare. The downside is the high cost of treatment.
Cyclosporine is another drug that is prescribed for severe chronic idiopathic urticaria. Belongs to a group of drugs that reduce the body's immunological reactions and therefore have an anti-inflammatory effect. In addition to the treatment of chronic urticaria, it is used in dermatology to treat severe forms of atopic dermatitis, psoriasis and some other diseases. Before starting treatment and during treatment, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the body; the doctor will conduct an examination and make sure that simpler methods of treatment were ineffective.
How is urticaria treated at the Rassvet clinic?
In order to prescribe the necessary treatment, your dermatologist will examine your skin and ask questions about your condition.
It is important to tell your doctor what factors you feel are causing your condition to worsen; what treatment did you receive before, was it effective; which medications worked best and which had no effect.
The diagnosis of urticaria is established based on a doctor’s examination; there are no specific laboratory diagnostic tests. Additional research may be required to clarify the form of the disease. If your doctor has doubts about whether your condition fits the diagnosis of urticaria, a diagnostic skin biopsy (taking a piece of skin) and histological examination (examining the resulting material under a microscope) may be necessary.
Finding medications to control the disease may take some time. First, small doses of drugs are prescribed, then they are gradually increased. After achieving stable improvement, treatment should be continued; in the future, the dose of prescribed medications can be gradually reduced until completely discontinued.
Recommendations of a dermatologist for patients with urticaria
Advice for patients:
- Seek immediate medical help if you experience rapid or difficult breathing, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, or loss of consciousness;
- exclude trigger factors (factors that cause deterioration) that you are reliably aware of, foods to which you have a proven allergy.
The prescription of a diet for chronic urticaria is controversial. The benefit of a diet avoiding pseudoallergens or histamine-containing foods in the treatment of chronic urticaria has not been proven by research. Following such diets poses significant challenges and is not supported by most current clinical guidelines.
Author:
Voronina Vera Removna dermatologist
Diet for urticaria
During the treatment of urticaria caused by food intolerance, it is necessary to avoid eating foods that stimulate the release of histamine. These include:
- coffee, chocolate, honey;
- citrus fruits, nuts;
- products containing dyes, emulsifiers, preservatives;
- milk, chicken eggs;
- baking, mayonnaise, mushrooms, peas;
- chicken, spices, vinegar;
- soybeans, beans, pineapples and some others.
Strong tea, coffee and alcohol should also be avoided. Procedures such as freezing, cooking, and peeling help to slightly reduce the allergenicity of products.
The basis of the diet for allergic urticaria should be porridge cooked in water, vegetarian and cereal soups, baked apples, olive oil, compotes, kefir.
If the patient does not know what foods he has an allergic reaction to in the form of urticaria, he can act as follows:
- After eliminating the symptoms of the disease, do not eat anything for one day.
- From the second day, start eating one product at a time. At the same time, keep a food diary and monitor your condition.
When treating urticaria, it is important to drink a lot - at least two to three liters of water per day. This helps remove allergens from the body faster.
Why is urticaria dangerous?
Hives can lead to very severe allergic reactions - swelling of the tongue and throat, breathing problems and even anaphylactic shock. If these symptoms occur, it is important to immediately call an ambulance, otherwise the patient may suffocate.
In 1/3 of patients, urticaria becomes chronic, that is, even after treatment, from time to time it reminds itself of relapses. In 15% of patients it contributes to the development of depressive disorders.
It is important to know that urticaria can be a symptom of another, more serious disease - oncology.
Myths and truth about urticaria
Urticaria is a skin disease. It is characterized by rashes similar to nettle burns and itching of varying severity, often severe. If the rash lasts less than 6 weeks, it is acute urticaria. More than 6 weeks - chronic.
Myth .
Urticaria may be accompanied by poor health, fever, cough, headache, rashes in the mouth, swelling, joint pain, diarrhea, and vomiting. Is it true . Such symptoms may be a manifestation of a systemic allergic reaction (this may also include urticaria) or individual diseases.
Myth . Hives are an allergy.
Is it true . The disease is associated with the release of biologically active substances (transmitting signals from cell to cell) by immune (mast) cells of the skin under the influence of various reasons. One of the reasons may be allergies. In most cases, the manifestation of chronic urticaria occurs without an understandable external cause as a result of the action of autoantibodies (antibodies to the body's own proteins) on cell receptors.
Myth . Urticaria occurs due to the presence of chronic infection and bacterial allergies, worms, disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, and the circulation of toxins in the body.
Is it true . The most common cause of acute urticaria is viral infections (ARVI).
Urticaria can occur when infected with worms, but there is no need to look for worms in all patients. Our region, according to WHO, is not endemic (infection with worms in central Russia occurs infrequently). Therefore, when urticaria manifests itself, it is logical to conduct an examination for worms after staying in regions with a high prevalence of helminthic infestations (Asia, Africa), in the presence of other symptoms and characteristic changes in a routine blood test.
It is assumed that infection of the gastrointestinal tract with H. pylori (a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers and erosions) may be important. The connection between urticaria and other diseases or functional disorders of the gastrointestinal tract has not been confirmed. Moreover, it makes no sense to search for and treat certain elusive and unmanifested conditions. The circulation of toxins in the body is a myth (there is no evidence), and accordingly, urticaria cannot occur for this reason. Chronic urticaria or so-called urticaria-like rashes (similar to hives) may indicate the occurrence of some serious common diseases.
Myth . If the patient has a high sensitivity of the body to allergens, then he may experience chronic recurrent urticaria. High sensitivity markers can be antibodies to Epstein-Barr viruses and cytomegalovirus.
Is it true . Allergic urticaria occurs acutely upon contact with a specific allergen. There are usually few such allergens for one patient. These can be foods (usually fish, nuts, eggs), insect bites. The detection of antibodies to viruses in the blood indicates that a person has had contact with the virus and has developed a protective reaction of the immune system. Antibodies to viruses are not related to allergies and do not affect the release of biologically active substances in urticaria.
Myth . If you have urticaria, it is necessary to conduct a comprehensive examination.
Is it true . In most cases, acute urticaria does not require examination. For chronic urticaria, specific studies are indicated, but not a complete examination of the body.
Myth . In acute cases of urticaria, it is necessary to go to the hospital, otherwise recovery will be delayed and complications will arise.
Is it true . Indications for hospitalization are severe urticaria, combination with edema, bronchospasm or other manifestations of anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction), or a violation of the general condition.
Myth . If you have urticaria, you must follow a special hypoallergenic diet. In case of acute urticaria, it is forbidden to eat even food that was previously well accepted by the body. During an exacerbation, a person’s reaction to food is difficult to predict, so a gentle menu or even complete fasting is necessary.
Is it true . It is necessary to exclude only those foods to which a person has a proven allergy. The prescription of a diet for chronic urticaria is controversial. The benefit of a diet avoiding pseudoallergens or histamine-containing foods in the treatment of chronic urticaria has not been proven by research. Following such diets poses significant challenges and is not supported by most current clinical guidelines.
Myth . For urticaria, it is necessary to prescribe corticosteroid hormones in tablets or droppers.
Is it true . Indications for the use of corticosteroid hormones include severe urticaria, edema, bronchospasm, or other signs of anaphylaxis. This treatment will help relieve severe or life-threatening symptoms, but will not affect the further course of the hives.
Myth . It is necessary to cleanse the body with laxatives, enemas, sorbents, diuretics, hepatoprotectors and choleretic agents, use hyposensitizing drugs such as sodium thiosulfate and calcium gluconate, restore the microflora with probiotics and drink vitamins.
Is it true . All these drugs have no proven effectiveness; their effect is assumed to be through their influence on non-existent mechanisms. In accordance with modern recommendations, treatment should be aimed at reducing the release of biologically active substances, primarily histamine. The main group of drugs for the treatment of both acute and chronic urticaria are type I histamine receptor blockers (antihistamines), a combination of different drugs or an increase in dose is possible. If the effect of using antihistamines is insufficient, antileukotriene drugs and type II histamine receptor blockers are added to treatment. And in severe cases, antibodies to immunoglobulin E (omalizumab) or immunosuppressive therapy with cyclosporine.
All myths are quoted from the Russian-language Internet, although they are quoted from the international consensus document EAACI/GA2LEN/EDF/WAO and the Federal Clinical Guidelines of RODVK.
Author:
Vera Removna Voronina , dermatologist
Prevention of urticaria
There are no special measures to prevent hives from occurring. Help minimize the risk of developing the disease:
- Keeping a food diary (you need to write down everything that was eaten during the day and how you feel).
- Avoiding contact with potentially dangerous allergic compounds (foods, medications, low/high temperatures, etc.).
- Pre-purchase antihistamines for urticaria. Allergists recommend that all people who have at least once had an allergy keep tablets such as Suprastin, Zyrtek, Parlazin, etc. on hand. If you take them at the first symptoms of the pathology, you can avoid complications.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing made from natural fabrics (provides high-quality air exchange and avoids additional irritation of the skin).
- Avoiding stressful situations.
- Elimination of allergenic foods from the diet.
- Competent and timely treatment of chronic diseases.
This article is posted for educational purposes only and does not constitute scientific material or professional medical advice.