December 21, 2021
Urticaria is an unpleasant and sometimes frightening disease of an allergic nature, accompanied by itchy skin rashes
Urticaria is an unpleasant and sometimes frightening disease of an allergic nature, accompanied by itchy skin rashes. The sensation is reminiscent of a nettle burn, hence the origin of the name of the diagnosis. Treatment of urticaria can never be done without the use of various antihistamines, because the bright and disturbing symptoms do not allow patients to delay therapy.
Fortunately, modern pharmacological agents are highly effective and act very quickly, so relief is almost instantaneous.
Urticaria: first aid
As soon as the first signs appear, immediate action must be taken. First you need to stop the allergen if its source is known, and also avoid taking NSAIDs, opioids, aspirin and calm down.
Pharmacotherapy for allergies is based on taking antihistamines. Only in cases of urticaria that are resistant to this treatment will other drugs be used. Everyone should have medications for allergic reactions, regardless of their medical history, because they are also used for insect bites, from which no one is immune.
A sudden rash does not appear the first time you encounter an allergen, but only the second time. To form a reaction, the presence of antigens to triggers is necessary. It could be anything, because few people know in detail the entire list of compounds to which they are hypersensitive.
Scheme for emergency care for urticaria
- Take an antihistamine orally and cutaneously: Fenistil, Loratadine, Dimetindene, Erius. The dosage form of remedies for urticaria can be different - tablets, sprays, drops, gels, ointments, injection solutions. Roller applicators are convenient for external use.
- Take a calcium gluconate tablet for faster relief of symptoms.
- If after taking the medicine there is no improvement, then after 15-20 minutes there is a reason to call an ambulance.
To prevent similar episodes of hives in the future, it is necessary to undergo allergy tests. Sometimes testing does not help clarify the cause, because each panel is designed for a specific set of allergens, which may not include the one you are interested in. But if the rash appears rarely and is easily eliminated with medications, then it is enough to simply have antihistamines for such a case.
A hypoallergenic diet is an important component in the prevention of urticaria, angioedema and other anaphylactic manifestations. What is allowed for allergy sufferers:
- Lean meat, steamed or boiled.
- The soup should be prepared only with the second broth (the first one must be drained).
- Oatmeal, buckwheat, rice.
- Low-fat dairy products, fruits, and vegetables are welcome.
You should not eat raisins, whole grain bread, brightly colored fruits, citrus fruits, eggs, chocolate, coffee, fish, seafood, store-bought sausages and baked goods - they often cause allergies. These recommendations are not for lifelong implementation, but only for the first time after the appearance of the rash. If you are aware of a specific allergen, you should avoid it as much as possible.
If it is difficult to establish, then the first suspicions of doctors fall on new care products, cosmetics, washing powder, or a product tried for the first time.
Treatment of urticaria, which is combined with other manifestations of allergies, must necessarily consult a doctor to prescribe a course of therapy.
Other drugs for urticaria
If antihistamines do not provide relief, a course of corticosteroids (injections or tablets) is prescribed. The selection of medications is made exclusively by doctors after a full examination and assessment of existing diseases. The prescribed dosage must be observed, since it is calculated based on the complexity of the disease and the patient’s body weight.
If the drug use regimen is violated, the desired therapeutic effect may not be achieved. How long does it take to clear up hives?
There are acute and chronic course of the disease. The first is when the rash lasts no more than 6 weeks. If it takes longer, we are talking about a protracted illness. When the period of exacerbation gives way to a short remission, and then blisters appear on the skin again, consult a therapist and allergist.
Without treatment, there is a risk of developing severe consequences, including autoimmune ones, which are even more difficult to correct.
Follow all medical advice to get better faster and not make your allergies worse. This will significantly improve your quality of life and give you greater freedom.
Treatment
Whatever the cause of urticaria, treatment is always selected by the doctor individually, taking into account the characteristics of the individual patient: his age, gender, lifestyle, professional activity, etc.
Allergic urticaria can be effectively treated with the use of antihistamines.
However, it is worth keeping in mind that taking these medications is a fight against the effect, and for a complete cure it is necessary to get rid of the cause, so special attention should be paid to the diet, excluding from it all products that can interfere with the release of the allergen from the body. Such products are: nuts, citrus fruits, honey, eggs, chocolate. If you are tired of hives, the itching of which is simply unbearable, you can speed up the removal of the allergen. To do this, you need to take enterosorbents and drink a lot of water. In hospital settings, droppers are sometimes used for this purpose.
Special ointments will help to quickly alleviate the condition at home. They not only relieve itching and reduce redness, but are also a preventive measure against the introduction of pathogenic microflora to the affected area of the skin.
Idiopathic urticaria is the most difficult to treat. In addition to detoxifying the body, it requires treatment of the underlying disease that caused a malfunction of the immune system. During the examination, special attention should be paid to the kidneys, liver, and the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and thyroid gland.
What else should you know about hives?
- If you've experienced a rash like this, know that you're not alone. About one in four people in the world have experienced something like this at least once.
- Women and children are most susceptible to such allergic reactions.
- 50% of cases of urticaria are accompanied by swelling of the face and larynx (Quincke's edema).
Non-food allergens that most often cause allergic rashes:
- insect bites;
- latex;
- mold;
- helminths and parasites;
- pollen of various plants;
- chemicals (detergents, pesticides);
- Sun rays;
- vibration;
- pet epithelium;
- dust;
- dust mite;
- feathers.
First, for diagnosis, an elimination diet is prescribed - a diet from which certain foods are alternately excluded. The person suffering from skin rashes is then sent for a blood test. If a lot of IgE to specific allergens is detected in it, this confirms the body’s increased reaction to them. But in a third of patients it is still not possible to determine the allergen even after several laboratory tests.
Treatment of urticaria with an unknown allergen is mainly symptomatic. Consultations with other specialized specialists are scheduled.
Diagnostics
As can be seen from the above, the causes of the disease are different. To prescribe effective treatment it is necessary to install it. That is why it is not recommended to self-medicate; it is better to immediately consult a doctor: a therapist, dermatologist or allergist. An appointment with a specialist always begins with an examination and interview of the patient.
During a conversation with the patient, the doctor finds out when urticaria appeared on the hands, whether there were similar symptoms before; the doctor may be interested in the living conditions and professional activities of the person seeking help, his diet, lifestyle, etc. An important point is to collect a history of previous illnesses, since the rash may be a consequence of them.
Acute urticaria, which has not been observed before, may be a reaction to an encounter with an allergen unfamiliar to the body. If you have recently taken long trips, tried new foods or cosmetics, you should also notify your doctor.
In some cases, laboratory tests may be required, especially when the rash on the hands may be the result of several causes at once, and it is difficult to determine the exact cause. Often, laboratory diagnosis comes down to identifying the allergen that caused the reaction in the form of itching and blisters.
Check yourself: classic symptoms of urticaria
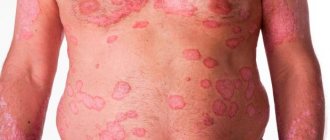
- First, pink or red itchy spots appear on the skin, which are covered with papules, vesicles, and blisters. Spots can migrate and change.
- These angioedema can be of any shape and size and are prone to coalescence and combing. Traumatization of the epidermis is accompanied by infection, the development of dermatitis, and the addition of various microflora (bacteria, fungi).
- Severe itching occurs, but with each touch of the affected area, the urticaria becomes more pronounced.
- Sometimes the body temperature rises, aches and headaches occur.
- The disease can be complicated by Quincke's edema: difficulty breathing, swallowing, nausea, vomiting, increased lip volume, swelling of the eyes, and then the entire face, which only increases. Mucous membranes are pasty, loose, swollen.
If anaphylaxis begins to develop, it is important to urgently call an ambulance.
Urticaria in children sometimes occurs without other symptoms other than changes in the skin, but more often develops after the onset of exudative diathesis. The likelihood of developing pathology is higher in children who receive artificial feeding and some foods that are not yet appropriate for them by age.
Where is it localized?
Urticaria, the symptoms of which are difficult to miss, can affect a variety of areas of the body, but is most often localized on the hands: on the fingers and the backs of the hands.
Blisters can also often be observed in the flexures of joints and fat folds. Sometimes the rash is localized on the legs, buttocks, back and abdomen. The most troublesome thing is hives on the face. The skin here is especially sensitive, so itching and burning are felt most acutely. Added to all the unpleasant sensations is the fact that the rash on the face significantly spoils the appearance, and, unlike other parts of the body, it is impossible to hide the face. The use of foundation, powder and other concealing agents is undesirable, since the rash may worsen from contact with certain cosmetic components.
Complications of urticaria
In addition to Quincke's edema, there is another threat - anaphylactic shock. This is a severe allergic reaction that can be fatal. There are several forms of anaphylaxis, and each of them has different symptoms (severe headache, abdominal complaints, and others).
If you have the slightest suspicion of an emergency, you should call a doctor as soon as possible. Treatment of mild forms of allergies does not cause difficulties: the patient is injected with adrenaline, a glucocorticosteroid, an IV is placed - and the critical situation passes.
If action is not taken quickly, the person may fall into a coma or even die.
What else can cause hives?
To avoid allergies more successfully, you need to think about every little thing that could cause reactions. For example, if you visit a restaurant and immediately or a few hours later your skin begins to itch, papules and blisters appear, then the first suspicions will fall on the food consumed in the establishment.
Allergens can be hidden in spices and seasonings, ready-made mixtures, complex cocktails, and store-bought semi-finished products. After the first episode of hypersensitivity, it is important for you to prevent new episodes, and also to always remember what and where you did, drank, ate, smelled, touched.
Our doctors
Orlova Tatyana Vladimirovna
Doctor - allergist-immunologist, pulmonologist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 38 years
Make an appointment
Shundeva Oksana Veniaminovna
Allergist, doctor of the highest category
Experience 39 years
Make an appointment
General information
The name of the disease is due to the fact that outwardly it looks like a nettle burn - the skin turns pink and swells, while small blisters can merge into large local spots (angioedema) of irregular shape.
Papules cause itching and discomfort; when scratched, the wound surface can become infected, and then dermatitis and other complications join the underlying disease. The disease is very common; every third person on the planet has suffered from urticaria in one form or another.