More than 70% of Russians are infected with the herpes virus, but in most cases it does not pose any threat to health. The virus is relatively safe and becomes active only against a background of weakened immunity, especially in the autumn-winter period. It manifests itself in the form of a rash on the lips, genitals and other areas. As a rule, neoplasms go away on their own, but in some cases you may need to get help from a doctor.
Causes of the disease
Herpes is an infectious disease. This is a virus that enters the body in different ways:
- sexual;
- contact (household);
- airborne (sneezing, coughing);
- placental (from a pregnant woman to a child).
In this case, herpes is most often transmitted by contact. The virus lives in saliva, so a person can become infected through a kiss, toys, underwear, dishes and other objects.
There are several factors that provoke the activation of the virus:
- constant stress;
- depressive states;
- prolonged hypothermia of the body, including one-time hypothermia;
- ARVI with and without complications;
- diseases that suppress the human immune system;
- bad habits, especially alcoholism, unhealthy diet;
- severe intoxication;
- Alzheimer's disease.
Herpes is present in the body of almost every person, but most of the time it is in an inactive state. Usually the virus “wakes up” against a background of weakened immunity. This can happen for various reasons, including against the background of severe stress, lack of sleep and other unfavorable factors.
Stomatitis: causes
A variety of factors and diseases contribute to the development of stomatitis in adults. For ease of diagnosis, doctors combined the causes of stomatitis into four groups, highlighting the main problem conditions:
- Mechanical injury. Ulcers appear as a result of some irritating factor. Damage can be caused by eating hard foods, poorly installed dentures, tartar buildup, and sharp edges of chipped crowns. Pathogenic microflora enters the damaged area, causing inflammation and active formation of ulcers.
- Chemical or thermal burn. Aggressive chemical agents can be food (citrus fruits), medications, nicotine, incorrectly selected toothpastes or mouth rinses. Thermal burn occurs when consuming excessively hot food or drinks.
- Poor oral hygiene. Failure to comply with regular hygiene procedures, tartar, and plaque provoke the active proliferation of bacterial microflora, which leads to inflammation of the oral mucosa.
- Chronic diseases. In adults, stomatitis develops as a reaction to problems of the gastrointestinal tract, cardiovascular system, due to anemia, endocrine pathologies, and HIV infections.
In addition to the listed categories, the causes of stomatitis can also be internal problems:
- vitamin deficiency, micronutrient deficiency - unbalanced diet, metabolic disorders in the body;
- allergies - of any origin;
- heredity - the individual reaction of the immune system to deteriorating health;
- a general decline in immunity - as a result of serious illnesses.
Unfavorable factors become catalysts for the development of pathology, and external circumstances aggravate the course of the disease.
The variety of causes points to an important point: there is no obvious causative agent of stomatitis. In order for an ulcer to localize, several circumstances must coincide - decreased immunity for any reason, an abundance of pathogenic microflora in the oral cavity, a traumatic agent.
How does herpes on the lips manifest itself: symptoms
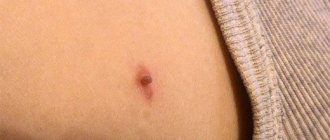
After activation in the first period, which lasts from 2 to 10 days (depending on the individual characteristics of the body), the herpes virus does not manifest itself in any way. After this, characteristic white bubbles (growths) appear on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes of the face (including on the lips), which merge with each other. Often the symptoms are accompanied by itching and a slight, barely noticeable tingling sensation.
In some cases, other symptoms are possible, for example:
- headache;
- general weakness;
- fatigue;
- elevated body temperature.
Very rarely, the development of the virus can lead to herpetic meningitis. This is a dangerous condition accompanied by inflammation of the brain. In such cases, it is necessary to seek medical help as soon as possible.
Symptoms of stomatitis and its classification
If a child has a white sore on the inside of his lip, it is better to take him to a dentist for an examination to prevent negative consequences. Most often, the disease is diagnosed in children from one to 3 years of age; it is slightly less common in infants. Preschoolers and schoolchildren encounter the disease extremely rarely. The peak incidence usually occurs in the spring, when everyone feels their immunity weakens.
Experts distinguish 4 types of stomatitis: traumatic, infectious, allergic and chronic. First, small ulcers appear on the child’s lips, and then swelling of the mouth and lips becomes noticeable. The mucous membrane takes on a bright red color. Then the marks begin to spread to the tongue, palate and cheeks. Often they are the result of tissue injury from braces, a plate or a damaged tooth.
The appearance of bubbles indicates the infectious nature of the disease. Formations can make themselves felt on the face (on the nose, cheeks and lips). Such manifestations linger for several days, and then turn into traces of erosion, bringing with them headache, joint or muscle pain, as well as enlarged lymph nodes. Additional symptoms of stomatitis are dryness and burning in the mouth. Pain occurs when eating food. In extreme cases, the papillae located on the tongue may lose sensitivity.
Diagnosis: which doctor to contact
You should consult a doctor in case of complications (for example, headaches), as well as in cases where the rash becomes more and more numerous and does not go away for a long time. For herpes, contact the following specialists:
- gynecologist (for women);
- urologist (for men);
- therapist (if the rash does not appear in intimate areas);
- pediatrician (for treating children).
The doctor examines the patient, asks questions, analyzes complaints. If necessary, several laboratory tests are carried out to study:
- blood;
- sperm;
- urine;
- vaginal discharge;
- urethral discharge;
- biological material from ulcers or other skin lesions.
Along with the cause of the rash, it is equally important to determine the type of virus. To do this, a common PCR analysis is performed, which stands for polymerase chain reaction.
Herpes on the lips: treatment
If the immune system is strong enough, rashes on the lips and other places will go away even without treatment in just a few days or weeks. In some cases, special therapy will be required. The course depends on what specific cause led to the development of herpes.
As a rule, treatment is complex and includes the following measures:
- taking antiviral drugs;
- taking anti-inflammatory drugs;
- vitamin complexes;
- special diet (increasing the proportion of protein foods, greens, fresh vegetables and fruits, as well as fermented milk products);
- drink: plenty of it.
Why does lip inflammation develop?
There are many reasons for the occurrence of cheilitis. Different reasons cause different types of lip inflammation. However, there are some common catalysts, for example, deficiency of vitamins, iron, calcium, excessive use of various medications (for example, antibiotics), constant exposure to drafts or living in a city with very low air temperatures in winter, strong and regular ultraviolet radiation, poor immunity.
The causative agents of allergic cheilitis are, of course, allergic reactions to cosmetics or food, infectious - various diseases (viruses, fungi), glandular - dermatological diseases, meteorological - frequent chapped lips and being outside without hygienic lipstick, and candidal - stomatitis and simply poor care behind the oral cavity.
Exfoliative cheilitis occurs in those who often bite off pieces of skin from their lips or simply constantly lick them (observed only in women). These actions can be triggered by frequent anxiety and stress. Manganotti cheilitis occurs only in adult men and is provoked by various injuries to the oral cavity, stomach diseases, frequent and long exposure to the sun or in a solarium, as well as clear signs of aging, which are caused by the fact that the mucous membrane is now regenerating more slowly. Hypovitaminosis occurs due to a lack of vitamins B2, B2 and other B vitamins.
What to do first if herpes appears
First of all, you need to carefully monitor your personal hygiene - constantly wash your hands with soap or other means. Also, do not put your hands near your eyes, much less touch the cornea. Insert lenses only after first washing your hands or wearing sterile medical gloves. The fact is that the virus can spread to the mucous membrane of the eyes.
Also, you should not touch the swellings themselves or touch them with your fingers. You can use lipstick and other products, but only without sharing them with other people. You should not remove blisters or crusts yourself - then the virus can spread to other areas of the skin. During the period of illness, you should avoid oral sex.
Important! If a young mother has herpes, she should take care of the safety of the child. Before picking him up or feeding him, you must wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
Types of stomatitis in adults
Effective treatment of stomatitis in adults begins with the diagnosis of pathology. Identifying the provoking factor is one of the main tasks of the dentist. The situation is aggravated by the fact that many reasons are similar - they overlap each other, distorting the clinical picture. For this reason, only experienced doctors treat stomatitis in adult patients.
There are a variety of classifications of stomatitis:
- according to the course - acute periodic, chronic, recurrent;
- by external manifestation - redness, aphthae, erosion;
- by localization - on the lip, on the tongue, on the palate, in the throat.
When diagnosing and selecting a treatment plan, dentists try to take into account the versatility of the disease - the form, causes, degree of damage to the mucous membranes, stage of the disease, and other classification parameters. Based on these factors, it is customary to identify the most popular types of stomatitis in adults:
- aphthous;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- candida;
- prosthetic;
- allergic;
- ray.
Aphthous stomatitis
Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by the appearance of round ulcerative formations covered with necrotic plaque. This is the most common variant of the disease - it occurs in 65-70% of dental patients.
The causes of aphthae formation are viral and bacterial diseases. Localization of ulcers is on almost any mucous tissue of the oral cavity.
Initially, the patient is faced with the fibrinous form, when local blood circulation is disrupted. If left untreated, the disease turns into a necrotic form, accompanied by tissue death, or into a scarring form - the mucosal tissue changes structure.
Ulcerative stomatitis
Ulcerative stomatitis is characterized by the formation of deep, painful ulcers in the mouth. They usually arise due to:
- poor hygiene - a large amount of plaque on the teeth, tartar;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - metabolic disorders;
- chemical burns - abuse of especially spicy foods.
Lesions affect the deep layers of tissue, so treatment of ulcerative viral or bacterial stomatitis in adults is carried out only by a dentist according to a carefully developed plan.
A separate type of ulcerative stomatitis is ulcerative-necrotizing gingivitis, Vincent's stomatitis. The cause of the disease is the active proliferation of pathogenic microflora, the influence of spindle bacillus and Vincent's spirochete. The disease is observed against the background of a sharp decrease in immunity and is characterized by reactive development. Patients complain of swelling of the gums, suppuration, pain, putrid breath, and loss of appetite. Without treatment, tissue necrosis progresses and tooth roots are exposed.
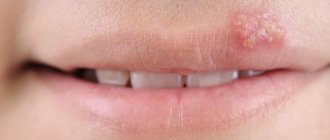
Herpes (herpetic) stomatitis
Viral herpetic stomatitis is a contagious variant of the disease provoked by the herpes virus. Transmitted through hygiene items, through negligence, by airborne droplets.
Externally it differs from other types, since the lesions look like fluid-filled blisters before turning into ulcers.
During treatment, the doctor conducts complex therapy, including taking medications.
Candidal stomatitis
The cause of candidal stomatitis is a fungus that causes the appearance of a cheesy coating on the oral mucosa. Underneath the plaque is a swollen, inflamed area. When the formations are removed, the tissue surfaces begin to bleed.
The causes of the disease are decreased immunity and poor hygiene. Treatment requires careful selection of drugs so as not to aggravate the situation.
Prosthetic stomatitis
The pathology is typical only for adult patients, as it is a consequence of improper prosthetics, individual intolerance to the crown material, and poor quality of care for the orthopedic product.
The disease manifests itself as inflammation of the soft tissues around the prosthetic structure, turning into ulcers and erosion.
Allergic stomatitis
A distinctive feature of the disease is dryness and itching in the mouth. This is how increased sensitivity to allergens manifests itself. At the site of the inflamed areas, aphthae and ulcers quickly form. In severe cases, an ulcerative-necrotic form may develop.
Pathology happens:
- acute - single manifestation;
- chronic - with constant relapses and complications.
Treatment requires an integrated approach.
Radiation stomatitis
The reason for the appearance is the patient undergoing radiation therapy or chemotherapy and, as a result, a decrease in immunity. It occurs acutely - with inflammation and ulcers. Requires careful attention from the doctor during treatment to avoid worsening the situation.