Price
Allergology-immunology
| Name of service | Price |
| Consultation with an allergist-immunologist, primary | 3 500 ₽ |
Advantages
- The latest, constantly updated equipment
- Interest-free installments for all services
- Online consultations with an ENT doctor
- Visit of an ENT doctor to your home
- Friendly and qualified staff
- 24/7 ENT assistance
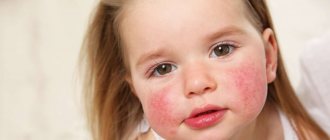
Hives are a condition characterized by a reddish, itchy rash on the skin that is caused by an allergic reaction. It is not contagious and is most often caused by a specific allergen, but in some cases the cause is unknown.
An allergic reaction to hives is fraught with serious complications that require urgent medical attention and are life-threatening. Therefore, you should not endure unpleasant attacks, but contact an allergist and find out how to treat urticaria in your particular case.
Causes of urticaria
The cause of allergic urticaria is a malfunction of the immune system. In allergic urticaria, the body reacts to an objectively neutral substance (allergen) as if it were harmful and releases a protein called histamine. When histamine is released, the tiny blood vessels on the surface of the skin (capillaries) become inflamed. Fluid accumulates underneath them, causing blisters.
Why allergies occur with urticaria (substances and provoking conditions):
- medications, including some antibiotics and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (including aspirin);
- foods that are known to cause histamine production (spinach, fish, yogurt, tomatoes, meat, chocolate, nuts, shellfish, eggs, strawberries);
- alcohol abuse;
- infections including influenza, colds, mononucleosis and hepatitis;
- intestinal parasites;
- sudden change in air temperature;
- high body temperature;
- pet hair;
- dust mites;
- insects;
- latex;
- pollen;
- some chemicals;
- thyroid diseases;
- lupus;
- exposure to sunlight;
- severe stress.
In some cases, doctors do not find the exact cause of the allergy in the form of hives.
Allergic urticaria in children
Children are very susceptible to skin rashes, and this is the most common reaction in the case of allergies. Children under 3 years of age most often suffer from manifestations of nettle fever. But older children can also experience trouble in the form of itchy rashes.
The location of blisters is similar to adults - on the extremities (most often in folds and places of close contact with clothing), around the mouth or eyes.
The mechanism of manifestation of the rash is the formation of a large amount of histamine due to the penetration of an allergen substance into the body. The surface of the skin becomes swollen and blisters form. The skin lesion disappears quite quickly and without a trace if the child does not scratch the sore spot. But then it can appear again, in another part of the body.
The doctor can quickly diagnose the cause that provoked the hives if the parents determine the time and place of the first appearance of the spots. Accurate diagnosis involves taking the following samples: skin scraping and blood test.
Symptoms of urticaria
With hives, itchy blisters appear on the body - pink or red, oval or round in shape. They can vary from a few millimeters to several centimeters in size. Hives blisters usually appear in batches, often on the face and extremities (urticaria on the arms and legs). Allergic urticaria may appear on only one part of the body, or the rash may cover most of the body.
The blisters usually disappear on their own within 24 hours, but new ones may form afterwards. In some cases, hives may remain on the skin for several days. For people with chronic urticaria, symptoms of allergic urticaria may last for months or years.
In some cases, it is recommended to call an ambulance, as serious complications of allergies due to urticaria are possible - anaphylaxis, Quincke's edema, myocarditis.
Dangerous symptoms, in addition to allergy manifestations of urticaria on the body:
- chills,
- elevated temperature,
- abdominal pain,
- nausea, vomiting,
- cardiopalmus,
- swelling of the mucous membrane of the mouth, tongue, lips,
- weakness and dizziness.
Types of allergic urticaria
Hives can be acute or chronic.
Acute allergy with urticaria is the most common type. Symptoms last less than 6 weeks and usually occur in allergic urticaria on the face and neck, fingers and toes. In the acute type, the allergen is usually immediately clear.
Chronic urticaria in adults lasts more than 6 weeks. Most often, it is an idiopathic form of urticaria of unknown origin that can last for months or years. On the skin, allergies with this type of urticaria occur in completely different places.
Allergic urticaria in adults
The disease has a number of features when it occurs in an adult. Fever may present as follows:
- Spicy. Rashes appear on the body and limbs, they are accompanied by itching, which increases in warmth. Redness occurs 15-20 minutes after contact with the allergen substance. The blisters disappear quickly and leave no marks or scars.
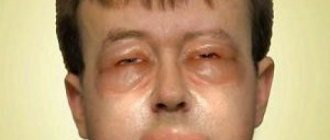
- Quincke's edema. It is characterized by swelling and larger rashes, appearing on the face near the eyes or mouth. A rash appears on the nasal mucosa and on the conjunctiva of the eyes. In exceptional cases, it is accompanied by swelling of the genitals and limbs. It often causes difficulty breathing and can even be life-threatening.
- Persistent papular. It develops due to long-term treatment of any type of disease and is characterized by the formation of papular blisters (nodules that are located above the skin level). The blisters are noticeably raised above the skin. The patient has to fight the disease for a long time – up to several months. The entire period is accompanied by itching.
- Chronic. It is characterized by wave-like increases and decreases in the level of severity of symptoms. Periods of recovery are followed by exacerbations with severe itching. The time period of the disease is calculated in decades. In rare cases, skin lesions become papular. This form of urticaria is characterized by the manifestation of Quincke's edema. When scratching itchy areas, the disease may be accompanied by an infection, which significantly complicates the course of the disease.
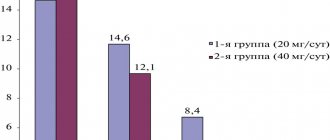
- Solar. The main cause is UV radiation, but the development of allergies is also associated with chronic diseases (for example, chronic liver disease). The appearance of urticaria lesions varies among patients. The rash can be mild or severe; the size of the lesion and blisters, color saturation, shape and location will differ. The severity of the disease is determined by the severity of itching. The most severe form is accompanied by the development of neurotic disorder and insomnia6,7.
Treatment of urticaria
Acute allergic urticaria is treated mainly with antihistamines (cetirizine, fexofenadine). They need to be taken regularly over several weeks. The principle of their action is to block the action of histamines, due to which the rash is reduced and the itching of allergies in urticaria stops. Some antihistamines cause drowsiness. Some of them are not suitable during pregnancy unless prescribed by a doctor. Such drugs should not be self-prescribed for allergic urticaria in any case.
The chronic form causes long-term discomfort, and in this case, the symptoms of urticaria are treated. Antibiotics may be prescribed to reduce redness, swelling and other symptoms if the cause is identified.
Physiotherapy provides good help for allergic urticaria.
At the Ear, Nose and Throat Clinic we provide effective treatment for urticaria in adults and children - identifying the root cause and prescribing effective therapy, including physiotherapeutic methods.
What does allergic urticaria look like?
The main symptom of an allergy type of urticaria is an urticarial rash. These are blisters that look like nettle burns. They are of different sizes, more often have a rounded shape, less often - irregularly elongated, convex, can merge with each other, are surrounded by a fuzzy pink border along the periphery, and turn pale when pressed. The rash is painless and accompanied by severe itching. The rash can be located anywhere, including on the scalp, palms and soles. In the head and neck area, rashes and itching are characterized by greater intensity. The appearance of blisters is preceded by itching and redness of the skin.
In the generalized form of allergic urticaria (a large area of rashes merging with each other), general symptoms appear - weakness, fever, chills, gastrointestinal upset. Source: Characteristics of patients with chronic urticaria at the stage of outpatient examination. Skorokhodkina O.V., Klyucharova A.R. Practical medicine No. 4, 2015. p. 131-135.
Quincke's edema is characterized by the sudden development of limited swelling of the skin, mucous membranes, and subcutaneous fat. The skin at the site of swelling is pale and cold. Edema can occur in the mucous membranes of different organs and systems - respiratory, digestive, urinary, nervous, with symptoms corresponding to damage to each of them. Laryngeal edema is especially dangerous, as it can lead to stenosis and asphyxia. The onset of laryngeal edema is characterized by hoarseness and difficulty breathing.
Allergic urticaria: recommendations to avoid
If the allergy trigger for hives is known, patients should avoid exposure to it as much as possible.
If you know that you are susceptible to spontaneous allergy symptoms due to hives, follow these guidelines:
- abstain from alcohol or reduce its consumption;
- do not prescribe any medications for yourself;
- avoid stress as much as possible;
- use anti-allergenic soaps, skin creams and cleansers;
- Avoid foods that trigger the production of histamine (they are listed in the “Causes of urticaria” section).
Seeing a doctor in a timely manner will help maintain your health.
Don't delay treatment, call right now. We work around the clock. tel. (24 hours a day)
Treatment of allergic urticaria
Diagnosis of the disease is carried out in 4 stages:
- a specialist conducts an initial examination;
- anamnesis, possible causes, etc. are collected;
- after this, diagnostic samples are taken;
- tests are prescribed.
The treatment procedure occurs step by step:
- eliminating the influence of a provocateur (allergen) and cleansing the body;
- pharmacotherapy (course of taking medications);
- diet prescription.
The drugs used in specific cases will be different. In the case of the endogenous nature of fever, the main task is to eliminate the root cause and prescribe effective treatment.
Often, a severe form of the disease requires the prescription of corticosteroids (Prednisolone) and antihistamines (Cetrin®). The drug Cetrin® copes with all symptomatic manifestations of allergic reactions. The effect of taking it is noticeable already 20 minutes after taking the tablet. The product is non-addictive and suitable for long-term use.
Cetrin® belongs to the second generation antihistamines, which eliminates the manifestation of a number of negative symptoms8.
Self-medication for both adults and children can be hazardous to health. A timely visit to a specialist will help you quickly cope with hives and identify the causes of its occurrence.
Bibliography
- Federal clinical guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of urticaria / Russian Association of Allergists and Clinical Immunologists: approved by the President of the RAACI on December 23, 2013 - Moscow, 2013. - 9 p.
- Mukhin, N. A. Gout: Faces of the disease / N. A. Mukhin // Modern rheumatology. – 2007. – No. 1. – 5 s.
- Ivashkin, V.T. Gastroenterology. National leadership / V. T. Ivashkin, T. L. Lapina. – M.: Iz-vo GEOTAR-Media, 2008. – 754 p.
- Vasilyeva, A.A. Acute urticaria and angioedema in the practice of a family doctor / A. A. Vasilyeva, R. F. Khakimova // Bulletin of modern clinical medicine, vol. 4 – 2011. – No. 4. – 54-58 s.
- Revyakina V. A. Urticaria in pediatric practice / V. A. Revyakina // Emergency Medicine - 2007. - No. 4. – 93-96 p.
- Hives. Atopic dermatitis: guidelines for students of medical, pediatric and dental faculties / Ed. ed. V. M. Chervenets. – M.: Alquist Publishing House, 2012. – 22 p.